This is the current revision of this page, as edited by 5.178.188.143 (talk) at 16:02, 12 October 2024 (→References). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 16:02, 12 October 2024 by 5.178.188.143 (talk) (→References)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)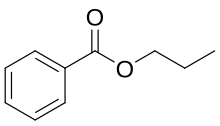
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Propyl benzoate | |
| Other names n-propyl benzoate, benzoic acid propyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.292 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 164.201 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless oily liquid, nutty odor |
| Density | 1.0230 g/cm at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −51.6 °C (−60.9 °F; 221.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) |
| Solubility in water | insoluble |
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -105.00·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Methyl benzoate Ethyl benzoate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Propyl benzoate is an organic chemical compound used as a food additive. It is an ester.
Uses
Propyl benzoate has a nutty odor and sweet fruity or nut-like taste, and as such, it is used as a synthetic flavoring agent in foods. It also has antimicrobial properties and is used as a preservative in cosmetics. It occurs naturally in the sweet cherry and in clove stems, as well as in butter.
Reactions
Propyl benzoate can be synthesized by the transesterification of methyl benzoate with propanol. Propyl benzoate can also be synthesized by means of Fischer esterification of benzoic acid with propanol.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 3–484. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ Ash, Michael; Ash, Irene (2004). Handbook of Preservatives. Synapse Information Resources. p. 508. ISBN 1-890595-66-7. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ Burdock, George A. (1997). Encyclopedia of Food and Color Additives. CRC Press. p. 2340. ISBN 978-0-8493-9416-4.
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
| Esters | |
|---|---|
| Methyl esters | |
| Ethyl esters | |
| Propyl esters | |
| Butyl esters | |
| Amyl esters | |
| Hexyl esters | |
| Phenyl esters | |
| Heptyl esters | |
| Benzyl esters | |