This is the current revision of this page, as edited by M97uzivatel (talk | contribs) at 12:05, 15 October 2024 (multispace). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 12:05, 15 October 2024 by M97uzivatel (talk | contribs) (multispace)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Heterocyclic organic compound (C4H4N2)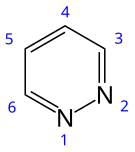
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Pyridazine | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name 1,2-Diazabenzene | |||
| Other names
1,2-Diazine Orthodiazine Oizine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 103906 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.478 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 49310 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C4H4N2 | ||
| Molar mass | 80.090 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.107 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 208 °C (406 °F; 481 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | miscible | ||
| Solubility | miscible in dioxane, ethanol soluble in benzene, diethyl ether negligible in cyclohexane, ligroin | ||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.52311 (23.5 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
224.9 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms | 
| ||
| Signal word | Warning | ||
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H319, H335 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, P501 | ||
| Flash point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Pyridazine is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4N2. It contains a six-membered ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C. It is isomeric with two other diazine (C4H4N2) rings, pyrimidine and pyrazine.
Occurrence
Pyridazines are rare in nature, possibly reflecting the scarcity of naturally occurring hydrazines, common building blocks for the synthesis of these heterocycles. The pyridazine structure is a popular pharmacophore which is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found within the structure of several drugs such as cefozopran, cadralazine, minaprine, pipofezine, and hydralazine.
Synthesis
In the course of his classic investigation on the Fischer indole synthesis, Emil Fischer prepared the first pyridazine via the condensation of phenylhydrazine and levulinic acid. The parent heterocycle was first prepared by oxidation of benzocinnoline to the pyridazinetetracarboxylic acid followed by decarboxylation. A better route to this otherwise esoteric compound starts with the maleic hydrazide. These heterocycles are often prepared via condensation of 1,4-diketones or 4-ketoacids with hydrazines.
References
- "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 141. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- "Pyridazine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Gumus, S. (2011). "A computational study on substituted diazabenzenes" (PDF). Turk J Chem. 35: 803–808. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- Fischer, E. (1886). "Indole aus Phenylhydrazin". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 236 (1–2): 126–151. doi:10.1002/jlac.18862360107.
- Tišler, M.; Stanovnik, B. (1968). "Pyridazines". Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry Volume 9. Vol. 9. pp. 211–320. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60374-8. ISBN 9780120206094.
| Simple aromatic rings | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ring |
| ||||||||||||
| 2 rings |
| ||||||||||||