This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Franconkuls (talk | contribs) at 12:07, 24 October 2024 (Fixing misquoted value for bandgap (IOFFE suggests 2.17eV rather than 2.12eV).). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 12:07, 24 October 2024 by Franconkuls (talk | contribs) (Fixing misquoted value for bandgap (IOFFE suggests 2.17eV rather than 2.12eV).)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)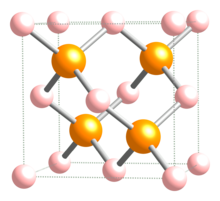
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.126 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | AlAs |
| Molar mass | 101.9031 g/mol |
| Appearance | orange crystals |
| Density | 3.72 g/cm |
| Melting point | 1,740 °C (3,160 °F; 2,010 K) |
| Solubility in water | reacts |
| Solubility | reacts in ethanol |
| Band gap | 2.17 eV (indirect) |
| Electron mobility | 200 cm/(V·s) (300 K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.9 W/(cm·K) (300 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 3 (infrared) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Zinc Blende |
| Space group | Td-F-43m |
| Lattice constant | a = 566.0 pm |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
60.3 J/mol K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-116.3 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | TWA 0.010 mg/m |
| REL (Recommended) | Ca C 0.002 mg/m |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Ca |
| Related compounds | |
| Related semiconductor materials | Aluminium gallium arsenide, Aluminium indium arsenide, Aluminium antimonide, Boron arsenide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Aluminium arsenide (AlAs) is a semiconductor material with almost the same lattice constant as gallium arsenide and aluminium gallium arsenide and wider band gap than gallium arsenide. (AlAs) can form a superlattice with gallium arsenide (GaAs) which results in its semiconductor properties. Because GaAs and AlAs have almost the same lattice constant, the layers have very little induced strain, which allows them to be grown almost arbitrarily thick. This allows for extremely high performance high electron mobility, HEMT transistors, and other quantum well devices.
Properties
It has the following properties:
- Thermal expansion coefficient 5 μm/(°C*m)
- Debye temperature 417 K
- Microhardness 5.0 GPa (50 g load)
- Number of atoms in 1 cm: (4.42-0.17x)·10
- Bulk modulus (7.55+0.26x)·10 dyn cm
- Hardness on the Mohs scale: ~ 5
- Insolubility in H2O
Uses
Aluminium arsenide is a III-V compound semiconductor material and is an advantageous material for the manufacture of optoelectronic devices, such as light emitting diodes.
Aluminium arsenide can be prepared using well-known methods, such as liquid and vapor-phase epitaxy techniques or melt-growth techniques. However, aluminium arsenide crystals prepared by these methods are generally unstable and generate arsine (AsH3) when exposed to moist air.
Synthesis
Little work has been reported on the preparation of aluminium arsenide, mainly because of the practical difficulties involved. Preparation from the melt is difficult because of the high melting point of the compound (about 1,700 °C) and of the extreme reactivity of aluminium at this temperature. A few workers have prepared small crystals from the melt, and polycrystalline ingots have also been produced. The best of this material has an impurity carrier density of the order of 10/cm and is p-type.
Reactivity
Aluminium arsenide is a stable compound; however, acid, acid fumes and moisture should be avoided. Hazardous polymerization will not occur. Decomposition of aluminium arsenide produces hazardous arsine gas and arsenic fumes.
Toxicity
The chemical, physical and toxicological properties of aluminium arsenide have not been thoroughly investigated and recorded.
Aluminium compounds have many commercial uses and are commonly found in industry. Many of these materials are active chemically and thus exhibit dangerous toxic and reactive properties.
Effects of exposure
Aluminium compounds have many commercial uses and are commonly found in industry. Many of these materials are active chemically and thus exhibit dangerous toxic and reactive properties. The chemical, physical and toxicological properties of aluminium arsenide have not been thoroughly investigated and recorded; however, there are some known chronic and acute symptoms based on chemical delivery.
Inhalation of aluminium arsenide may cause acute irritation to the respiratory system. It may also cause chronic arsenic poisoning, ulceration of the nasal septum, liver damage and cancer/diseases of the blood, kidneys and nervous system. Aluminium arsenide is poisonous if ingested and may cause gastrointestinal and skin effects and acute arsenic poisoning. Chronic implications from ingestion include arsenic poisoning, gastrointestinal disturbances, liver damage, and cancer/disease of the blood, kidneys and nervous system. If applied to the skin, aluminium arsenide may cause acute irritation, but there are no chronic health effects recorded.
Special precautions
Precautions to be taken in handling and storage: Store in a cool, dry place in tightly sealed containers. Ensure there is good ventilation. Open and handle container with care. AlAs reacts on contact with acids or moisture to give a host of volatile, highly toxic arsenic compounds such as Arsine.
References
- "AlxGa1−xAs". Ioffe Database. Sankt-Peterburg: FTI im. A. F. Ioffe, RAN.
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0038". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Guo, L. "Structural, Energetic, and Electronic Properties of Hydrogenated Aluminum Arsenide Clusters". Journal of Nanoparticle Research. Vol. 13 Issue 5 p. 2029-2039. 2011.
- S. Adachi, GaAs and Related Materials: Bulk Semiconducting and Superlattice Properties. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1994)
- Berger, L. I. (1996). Semiconductor Materials. CRC Press. p. 125. ISBN 978-0-8493-8912-2.
- ^ Dierks, S. "Aluminum Arsenide - Material Safety Data" Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine. The Fitzgerald Group, MIT, 1994.
- Willardson, R., and Goering, H. (eds.), Compound Semiconductors, pp. 1, 184 (Reinhold Pub. Corp., New York, 1962).
- Sax. Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. Eighth edition. 2005.
External links
| Aluminium compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al(I) |
| ||||
| Al(II) | |||||
| Al(III) |
| ||||
| Arsenic compounds | |
|---|---|
| Arsenides | |
| As(III) | |
| As(III,V) | |
| As(V) | |
| Arsenides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary arsenides |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ternary arsenides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quaternary arsenides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quinary arsenides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||