This is an old revision of this page, as edited by InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) at 08:34, 19 November 2024 (Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5) (Whoop whoop pull up - 21816). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 08:34, 19 November 2024 by InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) (Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5) (Whoop whoop pull up - 21816)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Not to be confused with Conkeror or conqueror. Web browser and file manager Konqueror 20.12.2 on Arch Linux Konqueror 20.12.2 on Arch Linux | |
| Developer(s) | KDE |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 23 October 2000; 24 years ago (2000-10-23) |
| Stable release | 24.11.90 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ (Qt) |
| Engines | WebKit, KHTML, Qt WebEngine (Chromium) |
| Operating system | Unix-like |
| Type | Web browser, file browser |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | apps |
Konqueror is a free and open-source web browser and file manager that provides web access and file-viewer functionality for file systems (such as local files, files on a remote FTP server and files in a disk image). It forms a core part of the KDE Software Compilation. Developed by volunteers, Konqueror can run on most Unix-like operating systems. The KDE community licenses and distributes Konqueror under GNU GPL-2.0-or-later.
The name "Konqueror" references the two primary competitors at the time of the browser's first release: "first comes the Navigator, then Explorer, and then the Konqueror". It also follows the KDE naming convention: the names of most KDE programs begin with the letter K.
Konqueror first appeared with version 2 of KDE on October 23, 2000. It replaced its predecessor, KFM (KDE file manager). With the release of KDE 4 in 2008, the functionalities of web browser and file manager were separated: Dolphin replaced Konqueror as the default KDE file manager, while the KDE community continues to maintain Konqueror as the default KDE web browser.
Major supported protocols
Konqueror can utilize all KIOslaves installed on the user's system. Some examples include:
- FTP and SFTP/SSH browser
- Samba (Microsoft file-sharing) browser
- HTTP browser
- IMAP mail client
- ISO (CD image) viewer
- VNC viewer
A complete list is available in the KDE Info Center's Protocols section.
User interface
Konqueror supports tabbed document interface and Split views, wherein a window can contain multiple documents in tabs. Multiple document interfaces are not supported, however it is possible to recursively divide a window to view multiple documents simultaneously, or simply open another window.
Konqueror's user interface is somewhat reminiscent of Microsoft's Internet Explorer, though it is more customizable. It works extensively with "panels", which can be rearranged or added. For example, one could have an Internet bookmarks panel on the left side of the browser window, and by clicking a bookmark, the respective web page would be viewed in the larger panel to the right. Alternatively, one could display a hierarchical list of folders in one panel and the content of the selected folder in another. Panels are quite flexible and can even include, among other KParts (components), a console window, a text editor, and a media player. Panel configurations can be saved, and there are some default configurations. (For example, "Midnight Commander" displays a screen split into two panels, where each one contains a folder, Web site, or file view.)
Navigation functions (back, forward, history, etc.) are available during all operations. Most keyboard shortcuts can be remapped using a graphical configuration, and navigation can be conducted through an assignment of letters to nodes on the active file by pressing the control key. The address bar has extensive autocompletion support for local directories, past URLs, and past search terms.
Web browser
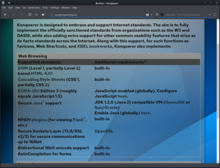
Konqueror has been developed as an autonomous web browser project. It uses KHTML as its browser engine, which is compliant with HTML and supports JavaScript, Java applets, CSS, SSL, and other relevant open standards. An alternative layout engine, kwebkitpart, is available from the Extragear.
While KHTML is the default web-rendering engine, Konqueror is a modular application and other rendering engines are available. In particular, the WebKitPart component using the KHTML-derived WebKit engine has seen a lot of support in the KDE 4 series. However, the KHTML rendering backend contains unique features, such as the ability to save a full archive of any given webpage into a single file with the ".war" extension.
Konqueror integrates several customizable search services which can be accessed by entering the service's abbreviation code (for example, gg: for Google, or wp: for Misplaced Pages) followed by the search term(s). One can add their own search service; for instance, to retrieve English Misplaced Pages articles, a shortcut may be added with the URL http://en.wikipedia.org/Special:Search?search=\{@}&go=Go.
KHTML's rendering speed is on par with that of competing browsers, but sites with customized JavaScript are often problematic due to KHTML's much smaller mind- and market-share, resulting in fewer JavaScript features built into the JS engine.
KJS is Konqueror's JavaScript engine that was originally developed by Harri Porten in 2000. On June 13, 2002, Maciej Stachowiak announced on a mailing list that Apple was releasing JavaScriptCore, a framework for Mac OS X that was based on KJS.
Kubuntu's 10.10 Maverick Meerkat release switched the default browser from Konqueror to rekonq, as well as a Firefox installer being added. Kubuntu subsequently switched from rekonq to Firefox, with the release of 14.04 Trusty Tahr.
File manager
Konqueror also allows browsing the local directory hierarchy—either by entering locations in the address bar, or by selecting items in the file browser window. It allows browsing in different views, which differ in their usage of icons and layout. Files can also be executed, viewed, copied, moved, and deleted.
The user can also open an embedded version of Konsole, via KDE's KParts technology, in which they can directly execute shell commands. In addition to the Konsole KPart, Konqueror can also use a Filelight KPart, to view a radial diagram of the user's filesystem.
Although this functionality has not been removed from Konqueror, as of KDE 4, Dolphin has replaced Konqueror as the default file manager. Dolphin can – like Konqueror – divide each window or tab into multiple panes. Konqueror makes more powerful use of this feature, allowing as many vertically and horizontally divided panes as desired. Each can link to different content or even remote locations, so that Konqueror becomes a powerful graphical tool to manage content on multiple servers all in one window, "dragging and dropping" files between locations.
-
 Konqueror's file manager
Konqueror's file manager
-
 A screenshot of Konqueror 20.12.2 showing the default homepage
A screenshot of Konqueror 20.12.2 showing the default homepage
-
 Konqueror displaying the contents of an audio CD
Konqueror displaying the contents of an audio CD
File viewer
Using the KParts object model, Konqueror executes components that are capable of viewing (and sometimes editing) specific filetypes and embeds their client area directly into the Konqueror panel in which the respective files have been opened. This makes it possible to, for example, view an OpenDocument (via Calligra) or PDF document directly within Konqueror. Any application that implements the KParts model correctly can be embedded in this fashion.
KParts can also be used to embed certain types of multimedia content into HTML pages; for example, the KMPlayer KPart enables Konqueror to show embedded video on web pages.
KIO
Further information: KIOIn addition to browsing files and websites, Konqueror utilizes KIO plugins to extend its capabilities well beyond those of other browsers and file managers. It uses components of KIO, the KDE I/O plugin system, to access different protocols such as HTTP and FTP (support for these is built-in), WebDAV, SMB (Windows shares), SFTP and FISH (a handy replacement to the latter when the SFTP subsystem is disabled on the remote host).
Similarly, Konqueror can use KIO plugins (called IOslaves) to access ZIP files and other archives, to process ed2k links (edonkey/emule), or even to browse audio CDs, ("audiocd:/") and rip them via drag-and-drop. Likewise, the "man:" and "info:" IOslaves can be used to fetch man and info formatted documentation.
Konqueror Embedded

An embedded systems version, Konqueror Embedded was previously available. Unlike the full version of Konqueror, Embedded Konqueror is purely a web browser. It does not require KDE or even the X window system. A single static library, it is designed to be as small as possible, while providing all necessary functions of a web browser, such as support for HTML 4, CSS, JavaScript, cookies, and SSL.
As of June 2019, this project's page on the KDE website has been taken down.
Download manager
 KGet on KDE Plasma 5.10.5, showing an ongoing download KGet on KDE Plasma 5.10.5, showing an ongoing download | |
| Initial release | May 26, 2002; 22 years ago (2002-05-26) |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 22.12.0 |
| Repository | invent |
| Engine |
|
| Type | Download manager |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | apps |
KGet is a free download manager for KDE and is the default download manager for Konqueror. It is part of the KDE Network package. By default, it is the download manager used for Konqueror, but can also be used with Mozilla Firefox and Chromium-based web browsers as well as rekonq. KGet was featured by Tux Magazine and Free Software Magazine.
History
On KDE 3, KGet 0.8.x, 1 supported HTTP/FTP download. On KDE Software Compilation 4, KGet 2 was released; it supported bandwidth throttling segmentation, multi-threading, and the BitTorrent protocol.
Features
- Downloading files from FTP, HTTP(S) and BitTorrent sources.
- Pausing and resuming of downloading files, as well as the ability to restart a download.
- Gives of information about current and pending downloads.
- Embedding into system tray of the host system.
- Integration with the KDE Konqueror and Rekonq web browsers.
- Metalink support which contain multiple URLs for downloads, along with checksums and other information.
- Automatically tags downloaded files with download information (such as the download URL) using Nepomuk.
- Download from multiple servers to speed up download time (segmented file transfer).
See also
- Comparison of file managers
- Comparison of web browsers
- Comparison of download managers
- KHTML
- KJS
- KSVG
- List of web browsers
- KIO
References
- "v24.11.90". Retrieved 11 December 2024.
-
Compare:
"Konqueror FAQ". konqueror.org. Retrieved 2017-08-23.
Where does the name Konqueror come from? It's a word play on the other browsers' names. After the Navigator and the Explorer comes the Conqueror; it's spelled with a K to show that it's part of KDE. The name change also moves away from "kfm" (the KDE file manager, Konqueror's predecessor) which represented only file management.
- K Desktop Environment (KDE) Archived 2007-06-09 at the Wayback Machine
- K Desktop Environment - KDE 2.0 Release Announcement
- "Konqueror - Konqueror FAQ". Archived from the original on 2008-07-23. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- "Projects/WebKit/Part - KDE TechBase". KDE TechBase. Retrieved 2010-03-30.
- Stachowiak, Maciej (2002-06-13). "[KDE-Darwin] JavaScriptCore, Apple's JavaScript framework based on KJS". opendarwin.org. Archived from the original on 2007-03-10. Retrieved 2015-05-13.
- Laishram, Ricky. "Rekonq To Be The Default Web Browser In Kubuntu 10.10". Techie Buzz. Retrieved 7 May 2011.
- "Kubuntu 14.04 LTS". Kubuntu.org. Archived from the original on 11 November 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- Hausmann, Simon (2001-09-01). "Konqueror/Embedded: An Open-Source Web Browser For EmbeddedLinux Systems". Linux Journal. Slashdot Media. Retrieved 2024-04-09.
- "Konqueror - Konqueror Embedded". Archived from the original on 2019-06-19. Retrieved 2013-11-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - "KGET Advanced Download Manage". SourceForge. Retrieved 2012-12-14.
- "Releases 22.12.0 2022-12-08". Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- Upfold, Peter (July 23, 2008). "Using KGet Download Manager with Firefox". FOSSwire. Archived from the original on February 11, 2009. Retrieved September 26, 2018.
- Guilloux, Nicolas (2020-01-26). "KGet-Integrator". GitHub. Retrieved 2021-12-29.
- "Simplify Downloads With Kget". TUX Magazine. 2005-03-29. Archived from the original on 2008-09-07. Retrieved 2012-12-14.
- ^ Richmond, Gary (2007-10-08). "Managing and configuring downloads with KGet". Free Software Magazine. Archived from the original on 2012-11-12. Retrieved 2012-12-14.
- Marinof, Mihai (9 October 2006). "KGet Review". Softpedia. Retrieved 2012-12-14.
- "'Multi segment KIO' is available by default in KGet".
- "Question: I want to download 1 file, but open, let's say, 8 connections for that file to a faster download".
External links
| KDE | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software compilation |  | ||||||||||||||||||
| Applications by KDE |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Platform |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Community | |||||||||||||||||||
| People | |||||||||||||||||||
| Web browsers | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| File managers (comparison) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-platform | |||||
| Unix-like | |||||
| DOS | |||||
| OS/2 etc. | |||||
| Windows |
| ||||
| Macintosh OSs |
| ||||
| BeOS etc. | |||||
| Download managers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client software for downloading computer files | |||||||
| Microsoft Windows |
| ||||||
| Unix-like | |||||||
| Multi-platform | |||||||
| Related articles | |||||||