This is the current revision of this page, as edited by AnomieBOT (talk | contribs) at 12:29, 26 November 2024 (Dating maintenance tags: {{Onesource}}). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 12:29, 26 November 2024 by AnomieBOT (talk | contribs) (Dating maintenance tags: {{Onesource}})(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Uramustine" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2024) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 5% |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.574 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
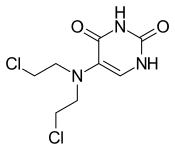
| Formula | C8H11Cl2N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 252.10 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Uramustine (INN) or uracil mustard is a chemotherapy drug which belongs to the class of alkylating agents. It is used in lymphatic malignancies such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It works by damaging DNA, primarily in cancer cells that preferentially take up the uracil due to their need to make nucleic acids during their rapid cycles of cell division. The DNA damage leads to apoptosis of the affected cells. Bone marrow suppression and nausea are the main side effects.
Chemically it is a derivative of nitrogen mustard and uracil.
References
- Ghorani-Azam A, Balali-Mood M (2015). "Clinical pharmacology and toxicology of mustard compounds.". In Balali-Mood M, Abdollahi M (eds.). Basic and clinical toxicology of mustard compounds. Cham: Springer. p. 74. ISBN 978-3-319-23874-6.
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |