This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Citation bot (talk | contribs) at 05:50, 9 December 2024 (Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Prodrugs | #UCB_Category 151/338). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 05:50, 9 December 2024 by Citation bot (talk | contribs) (Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Prodrugs | #UCB_Category 151/338)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | aminopenicillin |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Rapidly hydrolyzed to ampicillin |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H27N3O7S |
| Molar mass | 465.52 g·mol |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Bacampicillin (INN) is a penicillin antibiotic. It is a prodrug of ampicillin with improved oral bioavailability.
It was sold under the brand names Spectrobid (Pfizer) and Penglobe (AstraZeneca).In 2015, Pfizer discontinued Spectrobid, and no generic manufacturer has taken over production. Bacampicillin is thus unavailable in the United States, and is no longer FDA approved.
Synthesis
Semi-synthetic antibiotic related to penicillin.
The relatively small chemical difference between ampicillin and benzylpenicillin not only allows for substantial oral activity but also results in a substantial broadening of antimicrobial spectrum so as to allow for use against many Gram-negative bacteria. Many devices have been employed in order to enhance still further the oral absorption of ampicillin. Bacampicillin is a prodrug of ampicillin designed for this purpose.
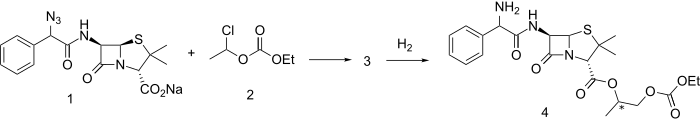
An azidopenicillin sodium salt (1) is reacted with mixed carbonate ester 2 (itself prepared from acetaldehyde and ethyl chloroformate) to give ester 3. Reduction of the azido linkage with hydrogen and a suitable catalyst produces bacampillin (4). Both enantiomers are active. The drug is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is quickly cleaved by serum esterases to bioactive ampicillin, acetaldehyde, CO2 and ethanol.
References
- Bodin NO, Ekström B, Forsgren U, Jalar LP, Magni L, Ramsay CH, Sjöberg B (November 1975). "Bacampicillin: a new orally well-absorbed derivative of ampicillin". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 8 (5): 518–25. doi:10.1128/aac.8.5.518. PMC 429411. PMID 1211909.
- "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs , BACAMPICILLIN HYDROCHLORIDE". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- "Organon USA Inc. et al.; Withdrawal of Approval of 67 New Drug Applications and 128 Abbreviated New Drug Applications". unblock.federalregister.gov. 13 October 2015. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- DE 2311328, Ekström, Bertil; Kovacs, Ödön Kalman Jozsef & Sjöberg, Berndt Olof Harald, "Penicilline und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung ", published 1973-10-18, assigned to Astra Läkemedel AB
- Ekstrom BA, Kovacs OK, and Sjoberg BO, (1973). Chem. Abstr., 80, 14921q(1974).
- DE 2144457, Ekström, Bertil Ake & Sjöberg, Berndt Olof Harald, "α-Aminopenicilline und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung ", published 1972-03-30, assigned to Astra Läkemedel AB
- Ekstrom BA, Sjoberg BO, U.S. patent 3,873,521 and U.S. patent 3,939,270 (1975 and 1976 both to Astra).
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |