This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Arthurfragoso (talk | contribs) at 23:15, 16 December 2024 (Fixes images on dark mode). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 23:15, 16 December 2024 by Arthurfragoso (talk | contribs) (Fixes images on dark mode)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)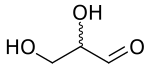 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Glyceraldehyde | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 2,3-Dihydroxypropanal | |
| Other names
Glyceraldehyde Glyceric aldehyde Glyceral | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.264 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H6O3 |
| Molar mass | 90.078 g·mol |
| Density | 1.455 g/cm |
| Melting point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) |
| Boiling point | 140 to 150 °C (284 to 302 °F; 413 to 423 K) at 0.8 mmHg |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Glyceraldehyde (glyceral) is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3H6O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colorless, crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word comes from combining glycerol and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is glycerol with one alcohol group oxidized to an aldehyde.
Structure
Glyceraldehyde has one chiral center and therefore exists as two different enantiomers with opposite optical rotation:
- In the D/L nomenclature, either D from Latin Dexter meaning "right", or L from Latin Laevo meaning "left"
- In the R/S nomenclature, either R from Latin Rectus meaning "right", or S from Latin Sinister meaning "left"
| D-glyceraldehyde (R)-glyceraldehyde (+)-glyceraldehyde |
L-glyceraldehyde (S)-glyceraldehyde (−)-glyceraldehyde | |
| Fischer projection | 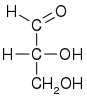
|

|
| Skeletal formula | 
|

|
| Ball-and-stick model | 
|
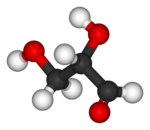
|
While the optical rotation of glyceraldehyde is (+) for R and (−) for S, this is not true for all monosaccharides. The stereochemical configuration can only be determined from the chemical structure, whereas the optical rotation can only be determined empirically (by experiment).
It was by a lucky guess that the molecular D- geometry was assigned to (+)-glyceraldehyde in the late 19th century, as confirmed by X-ray crystallography in 1951.
Nomenclature
In the D/L system, glyceraldehyde is used as the configurational standard for carbohydrates. Monosaccharides with an absolute configuration identical to (R)-glyceraldehyde at the last stereocentre, for example C5 in glucose, are assigned the stereo-descriptor D-. Those similar to (S)-glyceraldehyde are assigned an L-.
Chemical synthesis
Glyceraldehyde can be prepared, along with dihydroxyacetone, by the mild oxidation of glycerol, for example with hydrogen peroxide and a ferrous salt as catalyst.
Its cyclohexylidene acetal can also be produced by oxidative cleavage of the bis(acetal) of mannitol.
Biochemistry
The enzyme glycerol dehydrogenase (NADP) has two substrates, glycerol and NADP, and 3 products, D-glyceraldehyde, NADPH and H+.
The interconversion of the phosphates of glyceraldehyde (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) and dihydroxyacetone (dihydroxyacetone phosphate), catalyzed by the enzyme triosephosphate isomerase, is an intermediate step in glycolysis.
See also
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4376
- Bijvoet, J. M.; Peerdeman, A. F.; Van Bommel, A. J. (1951). "Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Optically Active Compounds by Means of X-Rays". Nature. 168 (4268): 271–272. Bibcode:1951Natur.168..271B. doi:10.1038/168271a0.
- "22.03: The D and L Notation". Chemistry LibreTexts. 2015-03-19. Retrieved 2022-01-09.
- Wu, Gongde; Wang, Xiaoli; Jiang, Taineng; Lin, Qibo (2015-11-27). "Selective Oxidation of Glycerol with 3% H2O2 Catalyzed by LDH-Hosted Cr(III) Complex". Catalysts. 5 (4): 2039–2051. doi:10.3390/catal5042039. ISSN 2073-4344.
- Dhatrak, N. R.; Jagtap, T. N.; Shinde, A. B. (2022). "Preparation of 1,2:5,6-Di-O-cyclohexylidene-D-mannitol and 2,3-Cyclohexylidene-D-glyceraldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 99: 363–380. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.099.0363. S2CID 254320929.
- Kormann, Alfred W.; Hurst, Robert O.; Flynn, T.G. (1972). "Purification and properties of an NADP+-dependent glycerol dehydrogenase from rabbit skeletal muscle". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Enzymology. 258 (1): 40–55. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(72)90965-5. PMID 4400494.
| Types of carbohydrates | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||||||||
| Geometry | |||||||||||||||
| Monosaccharides |
| ||||||||||||||
| Multiple |
| ||||||||||||||
| Fructose and galactose metabolic intermediates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fructose | |||||||
| Galactose | |||||||
| Mannose | |||||||