This is the current revision of this page, as edited by John B123 (talk | contribs) at 08:33, 21 December 2024 (Restored revision 1256832623 by Citation bot (talk): Unexplained removal of content). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 08:33, 21 December 2024 by John B123 (talk | contribs) (Restored revision 1256832623 by Citation bot (talk): Unexplained removal of content)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Travel to engage in sexual activityThis article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Sex tourism is the practice of traveling to foreign countries, often on a different continent, with the intention of engaging in sexual activity or relationships, in exchange providing money or lifestyle support. This practice predominantly operates in countries where sex work is legal. The World Tourism Organization of the United Nations has acknowledged that this industry is organized both within and outside the structured laws and networks created by them.
Sex tourism is commonly regarded as a transnational challenge, as it can be seen to target marginalised demographics in developing nations, such as countries in the Americas or Southeast Asia. The chief ethical concerns arise from: the economic gap between tourists and residents, the sexual trafficking of children and women and the parties taking advantage of the ability to engage with minors. These groups and individuals are subject to the foreign prostitution laws of the destination's jurisdiction, often resulting in exploitation and abuse. Prostitution activities that involve minors are universally non-consensual and illegal.
Sex tourism is known as a multibillion-dollar industry that globally supports a workforce estimated in the millions, with service industries such as the airline, taxi, restaurant and hotel industries profiting. The bulk of sex tourism involves males traveling from countries in the Global North to countries in the Global South, such as in East and Southeast Asia and Latin America. Although much rarer, female sex tourism also exists.

Legal issues
This particular industry of sex work is a predominant reason for world travel and is extremely profitable. The market can become exceedingly exploitative and unethically abused as tourists are motivated to engage in sexual conduct due to the untraceable nature and lack of law enforcement control, especially with accessibility to minors.
Ethical issues arise due to the situations of participating parties; many sex workers are from low-income backgrounds usually located in underdeveloped societies whose only means for providing basic needs is to engage in sexual services. While sex workers can engage voluntarily in the industry, there is a distinct difference between the coercion found in international sex trafficking and sex tourism which exploits the limited work options for low socioeconomic local residents.
Government and law enforcement often do not place priority on policing prostitution and sex trafficking. For example, in Cambodia, the Cambodian government has previously overlooked tourists having sex with Cambodian adolescents.
Individuals are not exempt from prosecution. Sex tourism as recognised by the CDC supports human trafficking and slavery. Even if prostitution is legal in a country or region, human trafficking, sexual encounters with a minor, and child pornography are almost universally criminal in nature and individuals caught breaking these laws can be prosecuted. Citizens of any foreign country must abide by the laws of the country in which they hold citizenship in addition to the local laws of the country they are visiting, including laws regarding consent.
Demographics
Demographics include: female sex tourism (women seeking men), men seeking men, adults seeking children, and men seeking women. Sex tourists generally come from Western world countries but they may also come from other countries as well. The most common destinations for these sex tourists is to visit less economically developed nations in Asia, such as: Thailand, the Philippines, Vietnam, Cambodia, Nepal, as well as countries in Central and South America like Mexico or Brazil.
A study conducted by the non-profit public charity ProCon, revealed the percentage of men who had paid for sex at least once in their lives between 1994 and 2010. It found the highest rates were located in Cambodia, where 59–80% of men had paid for sex at least once. Thailand was a close second with an estimated 75% of men, followed by Italy at 16.7–45%, Spain at 27–39%, Japan at 37%, the Netherlands at 13.5–21.6%, and the United States 15.0–20.0%.
Challenges in gathering data has made it hard to find out the exact number of people who work in the sex tourism industry. Estimates show 24.9 million victims that are trapped in modern-day slavery, 4.8 million (about 19%) were sexually exploited. It is estimated that about 21% of the total victims of commercial sexual exploitation are children, with the US Department of State estimating that over one million children are trafficked for sex throughout the world. The sex tourism industry often preys on those that are the most vulnerable, potentially explaining why children and women are more likely to be forced into the industry.
Cultural attitudes
Globally, cultural attitudes towards sex tourism can be seen to be different. In less developed countries for example, families in poor rural areas may sell their children to human traffickers, who will take the children to major cities to work in the sex industry. In Thailand for example, women will support their husbands by becoming sex workers. To work in the sex industry, particularly in less developed countries, can often be seen as a viable source of income available to struggling families from low socioeconomic backgrounds.
The cultural attitudes of sex tourism in highly developed countries such as Australia however where sex trafficking is illegal and highly policed can offer a different perspective to those of lesser backgrounds. Brothels are still vivid within states such as Tasmania and New South Wales where people can exchange money for sex. Recent studies suggest that sex slavery is still happening in Australia, exploiting the vulnerability of individuals and families from poor backgrounds.
Male tourists, sometimes known as sexpats (expatriate + sex tourist), join online communities in which they share advice on destinations and, although it is not among the most common cases, there is the category of "girlfriend experience" which, in some cases, evolves into an emotional relationship.
General attitudes towards sex work are complex and often regarded as controversial. Many countries where tourists come from, can have harsher attitudes towards sexual services. Often the men who travel seeking to pay for sex may do so because it is much harder to engage in sex work in their home countries. Furthermore, in some countries, such as Cambodia and Thailand, this practice is considered commonplace, and men who do not engage in commercial sex may be considered unusual by their peers.
Sociologists from the University of Leicester conducted a research study for the Economic and Social Research Council and End Child Prostitution and Trafficking campaign, which interviewed over 250 Caribbean sex tourists. Amongst their findings were:
- Preconceptions about race and gender influenced the tourist's opinions.
- Underdeveloped countries are considered culturally different, so in Western tourist's understanding, the exploitation or male domination of women is without consequence or stigma of that found in their home countries.
Despite a great deal of interest in sexual tourism amongst theorists, detailed studies of cultural attitude are rare, regardless of the increasing accessibility of group studies in the past three decades.
Economic and policy implications
Sex tourism has implications for all nations involved. Economically, sex tourism is encouraged by the tourist sectors of destination countries. It draws wealthy individuals with the allure of cheap, unstigmatised sexual activities, and stimulates the economy of poorer nations. This line of sex work ensures a consistent flow of income into developing countries' economies.
In an article published by the University of Chicago, it is argued that the promotion of sex tourism caters to tourists by enticing racial and ethnic stereotypes. This in turn creates ethical and policy implications, as colonial and traditional attitudes reinforce inequality between the groups. The state plays a vital part in this interaction, as governments create financially motivated barriers when asked to formulate more progressive and ethical policy.
Sex work may yield higher wages than work in the formal sector, and can encourage engagement with the industry for those seeking to achieve a much higher quality of life. This economic temptation can often lead to sexual exploitation of children. Young girls and adolescent women are some of the most common to be sold into slavery or transported across national borders to work in the commercial sex industry.
Gay sex tourism
The sex tourism industry offers a market for gay, bisexual and bi-curious tourists. Studies suggest that gay sex tourism has similar motivations to non-gay sex tourism. These studies suggest, "leisure activities and holidays have a particular significance for gay men, as they provide an opportunity for constructing, confirming and/or changing their sexual identity."
Popular gay sex tourism markets can be found in Gran Canaria, Ibiza, Sardinia, Sicily and Fire Island. Similar to heterosexual sex tourism markets, some arrangements may be monetary and others may not. Different places have different ways of identifying their interest in such arrangements. For example, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, gay sex tourism has become a popular niche hosting a racially diverse market. The workers there are called "Michês" and stand out by wearing bright blue towels and often work in saunas.
Adult-only resorts
Over recent years, adult-only sex resorts have become a popular alternative for travellers wanting to experience consensual sex abroad whilst avoiding the ethical issues of paid sexual activity. Those resorts can be characterised as safe, consensual spaces, and sexually positive nature, where all expressions of gender, orientation, and relationships are free of any pressure. These resorts largely occur in Mexico and the Caribbean. Certain establishments will be clothing-optional resorts, where travellers can meet and make use of "playrooms".
Child sex tourism
Main article: Child sex tourismSome sex tourists travel in order to engage in sex with children. While it is criminal in most countries, this industry is believed to involve as many as 2 million children around the world. Thailand is considered to have the worst child sex trafficking record, followed closely by Brazil.
"Child sex tourists may not have a specific preference for children as sexual partners but take advantage of a situation in which children are made available to them for sexual exploitation. It is often the case that these people have travelled from a wealthier country (or a richer town or region within a country) to a less-developed destination, where poorer economic conditions, favourable exchange rates for the traveller and relative anonymity are key factors conditioning their behaviour and sex tourism."
In an effort to eradicate the practice, many countries have enacted laws that allow the prosecution of their citizens for child abuse that occurs outside their home country, even if it is not against the law in the country where the incident took place. This is evident in America, under the United States Protect Act. In the United Kingdom, the Sexual Offences Act 2003 allows for prosecution in British criminal courts of British citizens who commit sexual offences against children while traveling abroad; this legislation was used to prosecute Richard Huckle in 2016. In Ireland, the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences) Act 2017 gives worldwide jurisdiction to prosecutors for sexual offences committed against children outside the state, and was used to prosecute Kieran Creaven for sexual acts with a child and producing child pornography in The Philippines in 2021. The Code of Conduct for the Sexual Exploitation of Children in Travel and Tourism is an international organisation composed of members of the tourism industry and children's rights experts with the purpose to eradicate the practice of child sex tourism.
UNICEF notes that sexual activity is often seen as a private matter, making communities reluctant to act and intervene in cases of sexual exploitation. These attitudes make children far more vulnerable to sexual exploitation. Most exploitation of children takes place as a result of their absorption into the adult sex trade where they are exploited by local people and sex tourists. The Internet provides an efficient global networking tool for individuals to share information on destinations and procurement.
In cases involving children, the U.S. has relatively strict domestic laws that hold accountable any American citizen or permanent resident of the U.S. who travels abroad for the purpose of engaging in illicit conduct with a minor. As of 2009, sex tourism and human trafficking remain fast-growing industries.
Regulation

Regulations and government involvement can be seen to have a positive impact on the community. It is argued that, by decriminalising prostitution, a government can protect sex workers under labor laws accessible by workers in other fields. For example, in the Netherlands, sex workers have access to unlimited free STI testing.
The criminalisation of sex-related jobs may be seen to increase workers' vulnerability to HIV by escalating stigma and discernment. It is suggested that judgement towards sex workers within the healthcare community acts as a barrier to accessing regular and informed care.
Opposition

One of the primary sources of opposition to sex tourism is child sex tourism. This act is internationally defined as travel to have sex with a person under 18 years of age. An example of this would be when tourists from wealthy countries take advantage of legal prostitution, lower consent ages, and the lack of extradition laws in order to engage in sex with minors in foreign countries. Developed nations with more conservative views of sexuality can provide a steady stream of tourists who feed the sex tourism industry. Human rights organisations and governments argue that this pattern creates an incentive for trafficking of children and violation of children's human rights.
Oppositions to sex tourism also stem from concerns around the trafficking of women. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime targets the trafficking of women and children as a central concern in their approach to transnational crime. The United Nations Global Report on Trafficking in Persons states that women "comprise the vast majority" of human trafficking victims for sexual exploitation across the world. They also note that women make up a relatively large portion of human trafficking offenders—about 30% of convicted human traffickers are women. It can be seen that women who become involved in human trafficking were once victims of sex trafficking and sexual exploitation themselves.
These factors can all contribute to the debate on human rights and their relations with sex tourism. The sex tourism industry showcases a global view in sexual exploitation, and a lack of concern for the rights and dignity of sex workers. It can be argued that through the growing international porn industry, indicate a normalisation of prostitution and an increase in the exploitation of women.
Prostitution by country
Main article: Prostitution by countryThe legality of prostitution and enforcement of such laws varies considerably around the world.
-
 Prostitution in North America
Prostitution in North America
-
 Prostitution in Central America and the Caribbean
Prostitution in Central America and the Caribbean
-
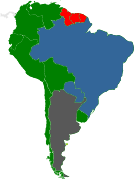 Prostitution in South America
Prostitution in South America
-
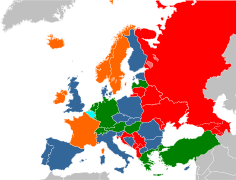 Prostitution in Europe
Prostitution in Europe
-
 Prostitution in Africa
Prostitution in Africa
-
 Prostitution in Asia
Prostitution in Asia
-
 Prostitution in Oceania
Prostitution in Oceania
- Decriminalization - No criminal penalties for prostitution
- Legalization - prostitution legal and regulated
- Abolitionism - prostitution is legal, but organized activities such as brothels and pimping are illegal; prostitution is not regulated
- Neo-abolitionism - illegal to buy sex and for 3rd party involvement, legal to sell sex
- Prohibitionism - prostitution illegal
- Legality varies with local laws
See also
- Cuban jineterismo
- Female sex tourism
- Gigolo
- Male prostitution
- Male prostitution in the arts
- Prostitution by country
- Prostitution in India
- Prostitution in Germany
- Prostitution in the United Kingdom
- Prostitution in Ukraine
- Prostitution in Russia
- Prostitution law
- Sex trafficking
References
- Williams, Erica L. (2012). "Sex Tourism". The Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Globalization. doi:10.1002/9780470670590.wbeog516. ISBN 978-1-4051-8824-1.
- Marina Diotallevi, ed. (October 1995). WTO Statement on the Prevention of Organized Sex Tourism. Cairo (Egypt): World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 14 August 2003. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
Adopted by the General Assembly of the World Tourism Organization at its eleventh session - Cairo (Egypt), 17–22 October 1995 (Resolution A/RES/338 (XI))
- Lu, Timothy Siliang; Holmes, Andrea; Noone, Chris; Flaherty, Gerard Thomas (2020). "Sun, sea and sex: a review of the sex tourism literature". Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines. 6 (1): 24. doi:10.1186/s40794-020-00124-0. PMC 7691961. PMID 33292661.
- Hannum, Ann Barger (2002). "Sex Tourism in Latin America". ReVista: Harvard Review of Latin America (Winter). Archived from the original on 4 September 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- "La explotación sexual de menores en Kenia alcanza una dimensión horrible" [The sexual exploitation of children in Kenya reaches a horrible dimension] (PDF) (in French). Spain: Unicef España. 17 January 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- Kachipande, Sitinga (2023). "Sun, Sand, Sex, and Safari: The Interplay of Sex Tourism and Global Inequalities in Africa's Tourism Industry". Journal of Global South Studies. 40 (1). Project MUSE: 1–37. doi:10.1353/gss.2023.0007. ISSN 2476-1419.
- ^ Lovelock, Brent; Lovelock, Kirsten M. (2013). The Ethics of Tourism: Critical and Applied Perspectives. Routledge.
- ^ United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime and the Protocols Thereto. Vienna: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2004.
- ^ McPhee, Duncan. Sex Offending and Sex Tourism: Problems, Policy, and Challenges. Palgrave Studies in Risk, Crime and Society.
- "'The women who sold their daughters into sex slavery".
- "Sex Tourism | Travelers' Health | CDC". wwwnc.cdc.gov. Retrieved 5 May 2021.
- Andrews, Sara K. (2004). "U.S. Domestic Prosecution of the American International Sex Tourist: Efforts to Protect Children from Sexual Exploitation". The Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology. 94 (2): 415–454. doi:10.2307/3491375. ISSN 0091-4169. JSTOR 3491375.
- ^ Global Report on Trafficking in Persons. Vienna: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2014.
- ^ "Percentage of Men (by Country) Who Paid for Sex at Least Once: The Johns Chart". ProCon. Archived from the original on 5 March 2022. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- "Human Trafficking by the Numbers". Human Rights First. Archived from the original on 7 May 2019. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- "Trafficking in Persons". United Nations : Office on Drugs and Crime. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- "Paradigms of sex tourism", Sex Tourism, Routledge, pp. 65–86, 8 July 2005, doi:10.4324/9780203991763-7, ISBN 978-0-203-99176-3, retrieved 11 May 2021
- ^ Samarasinghe, Vidyamali (2008). Female Sex Trafficking in Asia: The Resilience of Patriarchy in a Changing World. New York and London: Routledge.
- The Conversation, Human trafficking and slavery still happen in Australia. This comic explains how, June 12, 2019
- ^ Monge-Nájera, J. (2016). Male sexual tourism in Costa Rica: team spirit, peer dialogue and gender roles in a large sample of Internet forum posts. Cuadernos de Investigación UNED, 8(2), 207-216.
- Blevins KR and Holt TJ. (2009). Examining the Virtual Subculture of Johns. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography, 38 (5), 619-648
- Milrod C and Weitzer R. (2012). The Intimacy Prism: Emotion Management among the Clients of Escorts. Men and Masculinities, 00 (0), 1-21.
- Taylor, Jacqueline Sánchez (May 2000). "Chapter 3: Tourism and 'embodied' commodities: sex tourism in the Caribbean". In Clift, Stephen; Carter, Simon (eds.). Tourism and Sex: Culture, Commerce and Coercion. Tourism, Leisure and Recreation. Continuum International Publishing Group. pp. 41–53. ISBN 978-1-85567-549-0. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- Bender, Kimberly (June 2004). "The Implications of Sex Tourism on Men's Social, Psychological, and Physical Health" (PDF). The Qualitative Report. 9 (2): 176–191.
- "BangkokPod Interviews Kaewmala of Thai Sex Talk". 13 February 2011. Archived from the original on 11 December 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- "Open-Ended Prostitution as a Skillful Game of Luck: Opportunity, Risk and Security among Tourist-Oriented Prostitutes in Bangkok". Erik Cohen Department of Sociology and Social-Anthropology Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Archived from the original on 19 February 2013.
- ^ Mahler, Karen (1997). "Global Concern for Children's Rights: The World Congress Against Sexual Exploitation". International Family Planning Perspectives. 23 (2): 79–84. doi:10.2307/2950828. JSTOR 2950828. S2CID 58440462.
- ^ Patil, Vrushali (2011). "Reproducing-Resisting Race and Gender Difference: Examining India's Online Tourism Campaign from a Transnational Feminist Perspective". Signs. 37 (1): 185–210. doi:10.1086/660181. S2CID 146310057.
- Monterrubio, J. Carlos (7 December 2008). "Identity and Sex: Concurrent Aspects of Gay Tourism". mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- Hughes, Howard (February 1997). "Holidays and homosexual identity". Tourism Management. 18 (1): 3–7. doi:10.1016/s0261-5177(96)00093-3. ISSN 0261-5177.
- Hughes, H. L. (2006), Pink tourism: Holidays of gay men and lesbians, CABI, pp. 1–14, doi:10.1079/9781845930769.0001, ISBN 9781845930769
- MITCHELL, GREGORY (2011). "TurboConsumers in paradise: Tourism, civil rights, and Brazil's gay sex industry". American Ethnologist. 38 (4): 666–682. doi:10.1111/j.1548-1425.2011.01329.x. ISSN 0094-0496. JSTOR 41410425.
- ^ "Sex tourism is changing. Can Asia keep up?". South China Morning Post. 16 October 2019. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- Janet Bagnall (2007). "Sex trade blights the lives of 2 million children; Canada is not doing enough to fight the international scourge of sex tourism". Montreal Gazette.
- "The Crisis of Child Sexual Exploitation in Brazil: Between 250,000 and 2 million children forced into prostitution in Brazil". Libertad Latina. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- "Child Sex Tourism". ECPAT International. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
- Chaninat & Leeds (3 September 2009). "US Sex Laws Abroad: The Long Arm of Uncle Sam". Sex Laws in Thailand, Part 1. Thailand Law Forum. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- "Richard Huckle given 22 life sentences for abuse of Malaysian children". TheGuardian.com. 6 June 2016.
- Ireland, Government of Ireland (16 November 2017). "Criminal Law (Sexual Offences) Act 2017". Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- "Former RTÉ Sport producer Kieran Creaven jailed for 10 years". RTE.ie. 3 December 2021.
- ^ Guzder, Deena (30 August 2009). "Local Thai NGOs discuss efforts to end commercial sexual exploitation". Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting. Archived from the original on 16 April 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2022.
- ^ Godwin, John (October 2012). "Sex Work and the Law in Asia and the Pacific" (PDF). UNDP Reports. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ^ Bang, Brandy; Baker, Paige L.; Carpinteri, Alexis; Van Hasselt, Vincent B. (2014). Commercial Sexual Exploitation of Children. Springer.
- ^ Barry, Kathleen (1994). The Prostitution of Sexuality. New York: NYU Press. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- Overs, Cheryl (2 August 2017). "Sex work and the law – it's complicated". The Conversation. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- "Prostitution laws around the world - National | Globalnews.ca". Global News. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- "Countries and Their Prostitution Policies - Prostitution - ProCon.org". Prostitution. Retrieved 11 October 2021.