This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Citation bot (talk | contribs) at 03:08, 24 December 2024 (Added bibcode. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Whoop whoop pull up | Category:O-methylated anthocyanidins | #UCB_Category 3/8). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 03:08, 24 December 2024 by Citation bot (talk | contribs) (Added bibcode. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Whoop whoop pull up | Category:O-methylated anthocyanidins | #UCB_Category 3/8)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Not to be confused with Malvidine.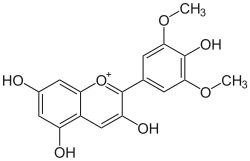
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 3,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxy-3′,5′-dimethoxyflavylium | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy)-1λ-benzopyran-1-ylium | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C17H15O7+ |
| Molar mass | 331.2968 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, the 3',5'-methoxy derivative of delphinidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature.
Natural occurrences
Malvidin is responsible for the blue color found in petals of the Primula plants of the polyanthus group. Blue flowers of the blue pimpernel (Anagallis monelli) have also a higher concentration of malvidin.
It is responsible primarily for the color of red wine, Vitis vinifera being one of its sources. It is also present in other berries, such as blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum) or the saskatoon berries (Amelanchier alnifolia).
Chemistry
Slightly acidic and neutral solutions of malvidin are characteristically of a red color, while basic solutions of malvidin yield a blue color.
The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid.
Use as a marker in archaeology
The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid as revealed in the examination of jars containing shedeh, a drink of Ancient Egypt. Malvidin is also present in the site of the Areni-1 winery, a 6,100-year-old winery discovered in 2007 in the Areni-1 cave complex in the village of Areni in the Vayots Dzor province of Armenia.
Glycosides
- Malvin is a malvidin diglucoside.
- Oenin is the malvidin-3-glucoside.
- Primulin is the 3-O-galactoside of malvidin.
- Malvidin 3-rutinoside is a pigment responsible for bract color in Curcuma alismatifolia (the Siam tulip). Acylated malvidin 3-rutinosides are responsible for the violet color of Petunia integrifolia subsp. inflata.
- Malvidin-3-O-glucoside-5-O-(6-acetylglucoside) is a pigment responsible for the blue color in 'Johnson's Blue' and other 'blue' geraniums
See also
References
- "Phytochemicals: Malvidin". Top Cultures. Archived from the original on April 1, 2010. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- Mazza G (2005). "Compositional and functional properties of saskatoon berry and blueberry". International Journal of Fruit Science. 5 (3): 99–118. doi:10.1300/J492v05n03_10.
- Bakowska-barczak; Marianchuk, M; Kolodziejczyk, P (2007). "Survey of bioactive components in Western Canadian berries". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 85 (11): 1139–52. doi:10.1139/y07-102. PMID 18066116.
- Nakayama, M; Roh, MS; Uchida, K; Yamaguchi, Y; Takano, K; Koshioka, M (2000). "Malvidin 3-rutinoside as the pigment responsible for bract color in Curcuma alismatifolia". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 64 (5): 1093–5. doi:10.1271/bbb.64.1093. PMID 10879491.
- Tatsuzawa, F (1999). "Acylated malvidin 3-rutinosides in dusky violet flowers of Petunia integrifolia subsp. Inflata". Phytochemistry. 52 (2): 351–355. Bibcode:1999PChem..52..351T. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00095-3.
- Markham, Kenneth R.; Mitchell, Kevin A.; Boase, Murray R. (1997). "Malvidin-3-O-glucoside-5-O-(6-acetylglucoside) and its colour manifestation in 'Johnson's Blue' and other 'Blue' geraniums". Phytochemistry. 45 (2): 417–423. Bibcode:1997PChem..45..417M. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00831-X.