This is the current revision of this page, as edited by OAbot (talk | contribs) at 06:04, 30 December 2024 (Open access bot: doi updated in citation with #oabot.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 06:04, 30 December 2024 by OAbot (talk | contribs) (Open access bot: doi updated in citation with #oabot.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol | |
| Other names 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.009 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H10O |
| Molar mass | 86.132 g/mol |
| Density | 0.853 g/cm |
| Boiling point | 130 to 132 °C (266 to 270 °F; 403 to 405 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.433 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| Flash point | 36 °C (97 °F; 309 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Prenol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Isoprenol, also known as 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol, is a hemiterpene alcohol. It is produced industrially as an intermediate to 3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol (prenol): global production in 2001 can be estimated as 6–13 thousand tons.
Synthesis
Isoprenol is produced by the reaction between isobutene (2-methylpropene) and formaldehyde, in what is arguably the simplest example of the Prins reaction.

The thermodynamically preferred prenol with the more substituted double bond cannot be directly formed in the above reaction, but is produced via a subsequent isomerisation:
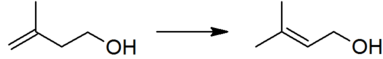
This isomerisation reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an allyl complex without excessive hydrogenation of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.
Uses
Isoprenol is primarily a feedstock used in the production of other more valuable chemicals. Isoprenol and its prenol isomer are used together in the formation of ionones such as vitamin A. It is also used in the synthesis of pyrethroid pesticides , vitamin E, and citral.
Notes
- Sigma-Aldrich Co. gives a value for the flash point of isoprenol of 42 °C (108 °F). The difference in the two values does not alter the safety classification of isoprenol as a category 3 flammable liquid under the GHS; but the lower value quoted here (from the New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority) would make it a class IC flammable liquid instead of a class II combustible liquid under the U.S. OSHA classification (29 C.F.R § 1910.106), and F3 rather than F2 under the NFPA 704 standard.
References
- Sigma-Aldrich Co., 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol. Retrieved on 2009-08-31..
- HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database, New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority, retrieved 2009-08-31.
- 3-Methyl-2-buten-1-ol (PDF), SIDS Initial Assessment Report, Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme, May 2005. Major produce in a world is BASF(Germany) and Kuraray(Japan).
- See, e.g., Kogan, S. B.; Kaliya, M.; Froumin, N. (2006), "Liquid phase isomerization of isoprenol into prenol in hydrogen environment", Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 297 (2): 231–36, doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2005.09.010.
- Bonrath, Werner; Gao, Bo; Houston, Peter; McClymont, Tom; Müller, Marc-André; Schäfer, Christian; Schweiggert, Christiane; Schütz, Jan; Medlock, Jonathan A. (15 September 2023). "75 Years of Vitamin A Production: A Historical and Scientific Overview of the Development of New Methodologies in Chemistry, Formulation, and Biotechnology". Organic Process Research & Development. 27 (9): 1557–1584. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.3c00161.