This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Nudge67 (talk | contribs) at 23:49, 4 August 2007 (→Pre-Federation: fixed some dates ~~~~). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:49, 4 August 2007 by Nudge67 (talk | contribs) (→Pre-Federation: fixed some dates ~~~~)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (November 2006) |
This is a list of the evolution of the borders of Australia. It lists each change to the internal and external borders of the country.
Pre-Federation

The colony of New South Wales is founded. New South Wales, according to Arthur Phillip's amended Commission dated 25 April 1787, includes "all the islands adjacent in the Pacific Ocean" and running westward to the 135th meridian.
New South Wales's western border is extended to 129° E.
The colony of Van Diemen's Land is proclaimed
Swan River Colony is declared by Charles Fremantle for Britain.
Swan River Colony has its name changed to Western Australia.
The colony of South Australia is proclaimed with its western border set at 132° E.
New Zealand is formally annexed to New South Wales.
- Nov 16 1840 The colony of New Zealand is proclaimed by Letters Patent. Although not represented on a map here, New South Wales was significantly reduced in size by this proclamation. Seperation was effected on May 3 1841

The colony of North Australia was proclaimed by Letters Patent on 17 February. This was all of New South Wales north of 26° S.

The colony of North Australia was revoked and reincorporated into New South Wales
The colony of Victoria is proclaimed.
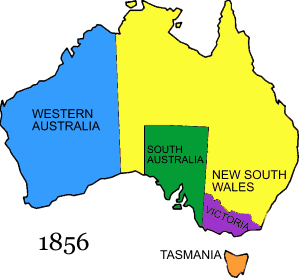
Van Diemen's Land name is changed to Tasmania.
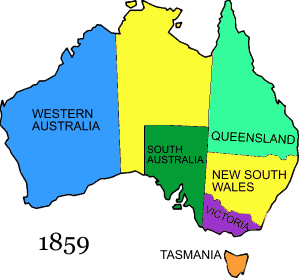
The colony of Queensland is proclaimed by Letters Patent, with its western border set at 141° E, and settlement began on December 10 that year.

South Australia border changed from 132° E to 129° E.

Queensland's western border is moved to 139° E.

That part of New South Wales to the north of South Australia was annexed to South Australia as the Northern Territory by Letters Patent.
Post-Federation

The Commonwealth of Australia was formed, uniting the British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia. Note that the Northern Territory was under South Australian administration at Federation.
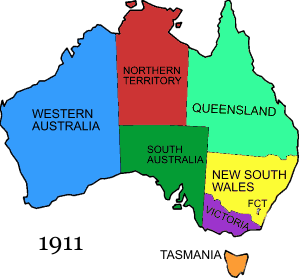
The Federal Capital Territory was created within New South Wales, and the Northern Territory was split off from South Australia.

The coastal area now known as the Jervis Bay Territory is added to the Federal Capital Territory.

The Northern Territory was split into the territories of North Australia and Central Australia.
North Australia and Central Australia were reunited as the Northern Territory.
The Federal Capital Territory's name is changed to the Australian Capital Territory.
The Jervis Bay Territory becomes Australia's third mainland territory when the Australian Capital Territory is granted self government.
External Territories
July 1 1914 – Norfolk Island is transferred from New South Wales to the Commonwealth of Austalia
July 23 1931 - Ashmore Island and the Cartier Islands are transferred from Britain to Australia
June 13 1933 – The Australian Antarctic Territory is transferred from Britain
June 26 1947 – Heard Island and the McDonald Islands are transferred from Brtiain
November 23 1955 - The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are transferred from Singapore to Australia
October 1 1958 - Christmas Island is transferred from Britain
September 30 1969 - The Coral Sea Islands Territory is transferred from Queensland to the Commonwealth of Australia
Former External Territories
- Territory of Papua (1906-42)
- Territory of New Guinea (1920-42)
- Territory of Nauru (1920-68)
- Territory of Papua and New Guinea (1942-71)
- Territory of Papua New Guinea (1971-75)
See also
External links
- States of Australia - Statoids.com
- Acting under instructions from England, Captain Freemantle took possession of the Swan River, to found a new colony; and formally laid claim to "all that part of New Holland which is not included within the territory of New South Wales".