This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Latebird (talk | contribs) at 13:58, 8 December 2007 (Undid revision 176501844 by 99.130.8.150 (talk) - please provide sources for the implied chinese empire to the black sea). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:58, 8 December 2007 by Latebird (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 176501844 by 99.130.8.150 (talk) - please provide sources for the implied chinese empire to the black sea)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. You can assist by editing it. (June 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Genghis Khan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khagan of the Mongol Empire (Khan of the Mongols) | |||||
 | |||||
| Reign | 1206 – 18 August, 1227 | ||||
| Coronation | 1206 during khurultai at Khentii Province, Mongolia | ||||
| Predecessor | (title created) | ||||
| Successor | Ögedei Khan | ||||
| Burial | (unknown) | ||||
| Issue | Jochi Chagatai Ögedei Tolui others | ||||
| |||||
| House | Borjigin | ||||
| Father | Yesükhei | ||||
| Mother | Ho'elun | ||||
Genghis Khan (IPA: [ʧiŋgɪs χaːŋ]; Template:Lang-mn; classic Mongolian: ![]() (properly transliterated "Chinggis Khaγan", see below for alternative spellings); ca. 1162–August 18, 1227) born Temujin was the founder, Khan (ruler) and posthumously declared Khagan (emperor) of the Mongol Empire, the largest contiguous empire in history.
(properly transliterated "Chinggis Khaγan", see below for alternative spellings); ca. 1162–August 18, 1227) born Temujin was the founder, Khan (ruler) and posthumously declared Khagan (emperor) of the Mongol Empire, the largest contiguous empire in history.
Temujin came to power by uniting many of the nomadic tribes of north-east Asia and Central Asia. After founding the Mongol Nation and being proclaimed "Genghis Khan", he pursued an aggressive foreign policy by starting the Mongol invasion of East Asia and Central Asia. During his life, the Mongol Empire eventually occupied most of Asia.
Temujin died of unknown causes in 1227 after a campaign to subjugate the Xi Xia and Jin dynasties in China. He was buried in an unmarked grave somewhere in his native Mongolia. His descendants went on to stretch the Mongol Empire across most of Eurasia, conquering all of modern-day China and Mongolia, as well as substantial portions of modern Russia, southern Asia, Eastern Europe and the Middle East.
Early life
Birth

Due to the lack of contemporary written records, there is very little factual information about the early life of Temüjin. The few sources that provide insight into this period often disagree about many facts.
Temüjin was born around 1162 in a Mongol tribe near Khentii Province near the Burhan Haldun mountain range, not far from the current capital of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar, near the Onon and the Kherlen Rivers. Popular legend recorded in The Secret History of the Mongols purports that Temüjin was born with a blood clot grasped in his fist, an indication in the traditional Mongolian folklore that he was destined to become a great leader. He was the eldest son of Yesükhei, a minor tribal chief of the Kiyad and a nöker (vassal) of Ong Khan of the Kerait tribe, and was, again according to the Secret History, named after a Tartar chieftain that his father had just captured. The name also suggests that they may have descended from a family of blacksmiths (see section Name and title below).
Yesükhei's clan was called Borjigin (Боржигин), and Temüjin's mother, Hoelun, was from the Olkhunut tribe of the Mongol confederation. Like other tribes, they were nomads. Because his father was a chieftain, as were his predecessors, Temüjin was of a royal or noble background. This relatively higher social standing made it easier to solicit help from and eventually consolidate the other Mongol tribes.
No accurate portraits of Genghis exist today, and any surviving depictions are considered to be artistic interpretations. The physical descriptions of Genghis Khan from contemporary historians are quite different than what is found in the portraits. Muslim historian Rashid al-Din, foremost contemporary historian on Genghis Khan, recorded in his "Chronicles" that the legendary "glittering" ancestor of Genghis was tall, long-bearded, red-haired, and green-eyed. Rashid al-Din also described the first meeting of Genghis and Kublai Khan, when Genghis was shocked to find Kublai had not inherited his red hair. Genghis's Borjigid clan, al-Din also revealed, had a legend involving their clan: it began as the result of an affair (technically an immaculate conception) between Alan-ko and a stranger to her land, a glittering man who happened to have red hair and bluish-green eyes. Modern historian Paul Ratchnevsky has suggested in his Genghis biography that the "glittering man" may have been from the Kyrgyz people, who historically displayed these same characteristics. Controversies aside, the closest depiction generally accepted by most historians is the portrait currently in the National Palace Museum in Taipei, Taiwan (see above).
Family and lineage
Main article: Family tree of Genghis KhanTemüjin was related on his father's side to Qabul Khan, Ambaghai and Qutula Khan who had headed the Mongol confederation. When the Jin dynasty switched support from the Mongols to the Tatars in 1161 they destroyed Qabul Khan. Genghis' father, Yesükhei (leader of the Borjigin and nephew to Ambaghai and Qutula Khan) emerged as the head of the ruling clan of the Mongols, but this position was contested by the rival Tayichi’ud clan, who descended directly from Ambaghai. When the Tatars grew too powerful after 1161, the Jin moved their support from the Tatars to the Kerait.
Childhood and Family
Early life
Temüjin had three brothers, Khasar (or Qasar), Khajiun, and Temüge, and one sister, Temülen (or Temülin), as well as two half-brothers, Bekhter and Belgutei.
Like many of the nomads of Mongolia, Temüjin's early life was difficult. At nine years old, as part of the marriage arrangement, his father delivered him to the family of his future wife Börte, who were members of the Onggirat tribe. He was to live there in service to Deisechen, the head of the household, until he reached the marriageable age of 12. At this time, none of the tribal confederations of Mongolia were united politically, and arranged marriages were often used to solidify temporary alliances. Temujin grew up observing the tough political climate of Mongolia, surrounded by tribal warfare, thievery, raids, and continuing acts of revenge carried out between the various confederations, all compounded by interference from foreign forces such as the Chinese dynasties to the south.
While heading home, his father was poisoned during a meal with the neighbouring Tatars, who had long been enemies of the Mongols. Temüjin had to return home to claim the position of clan chief. However, his father's clan refused to be led by a boy so young. They abandoned him and his family, including his mother Hoelun, leaving them without protection.
For the next several years, Temüjin and his family lived in poverty, surviving primarily on wild fruits, marmots, and other small game hunted by Temüjin and his brothers. It was during one of these hunting incidents that 13 year old Temüjin murdered his half-brother, Bekhter, in a dispute over hunting spoils. This incident cemented his position as head of the household.
In another incident in 1182 he was captured in a raid and held prisoner by his father's former allies, the Ta'yichiut. The Ta'yichiut enslaved Temüjin (reportedly with a cangue), but he escaped with the help of a sympathetic watcher, the father of Chilaun (who would later become general of Genghis Khan), by escaping from the ger and hiding in a river crevice. It was around this time that Jelme and Bo'orchu, two of Genghis Khan's future generals, joined forces with him. Along with his brothers, they provided the manpower needed for early expansion. Temüjin's reputation also became relatively widespread after his escape from the Ta'yichiut.
Family
His mother Hoelun taught him many lessons about survival in the harsh landscape, and the even more grim political climate of Mongolia, especially the need for alliances with others, a lesson which would shape his understanding in his later years. One of the most important lessons he received occurred when she showed him an arrow, and told him to break it. He did so easily. Then she got a quiver-full of arrows and asked him to break them. He tried repeatedly but could not. His mother told him, "A single arrow breaks easily, just like one man. But when there are many men, nobody can break them."
As previously arranged by his father, Temüjin married Börte of the Konkirat tribe around when he was 16 in order to cement alliances between their respective tribes. Börte had four sons, Jochi (1185–1226), Chagatai (?—1241), Ögedei (?—1241), and Tolui (1190–1232). Genghis Khan also had many other children with his other wives, but they were excluded from the succession, and records of daughters are nonexistent. Soon after Börte's marriage to Temüjin, she was kidnapped by the Merkits, and reportedly given away as a wife. Temüjin rescued her with the help of his friend and future rival, Jamuka, and his protector, Ong Khan of the Kerait tribe. She gave birth to a son, Jochi, nine months later, clouding the issue of his parentage. Despite speculation over Jochi, Börte would be his only empress, though Temujin did follow tradition by taking several morganatic wives.
According to traditional historical accounts, the issue over Jochi's paternity was voiced most strongly by Chagatai. In The Secret History of the Mongols, just before the invasion of the Khwarezmid Empire by Genghis Khan, Chagatai declares before his father and brothers that he would never accept Jochi as Genghis Khan's successor. In response to this tension and possibly for other reasons, it was Ögedei who was appointed as successor. He subsequently ruled as Khagan after Genghis Khan's death.
Jochi died in 1226, during his father's lifetime. Some scholars, notably Ratchnevsky, have commented on the possibility that Jochi was secretly poisoned by an order from Genghis Khan. Rashid al-Din reports that the great Khan sent for his sons in the spring of 1223, and while his brothers heeded the order, Jochi remained in Khorasan. Juzjani suggests that the disagreement arose from a quarrel between Jochi and his brothers in the siege of Urgench. Jochi had attempted to protect Urgench from destruction, as it belonged to territory allocated to him as a fief. He concludes his story with the clearly apocryphal statement by Jochi: "Genghis Khan is mad to have massacred so many people and laid waste so many lands. I would be doing a service if I killed my father when he is hunting, made an alliance with Sultan Muhammad, brought this land to life and gave assistance and support to the Muslims." Juzjani claims that it was in response to hearing of these plans that Genghis Khan ordered his son secretly poisoned; however, as Sultan Muhammad was already dead in 1223, the accuracy of this story is questionable.
Temüjin put absolute trust in generals, such as Muqali, Jebe and Subutai, and regarded them as brothers, often extending them the same privileges and trust normally reserved for close family members. He allowed them to make decisions on their own when they embarked on campaigns far from the Mongol Empire capital Karakorum. Temüjin also became blood brother (anda) with Jamuka, and they vowed to remain eternally faithful.
Religion
Genghis Khan's religion is widely speculated to be Shamanism, which was very likely among nomadic Mongol-Turkic tribes of Central Asia. Later, Genghis Khan would become interested in the ancient Buddhism and Taoism religion from China. One Taoist monk, Ch'ang Ch'un, who had rejected invitations from Song and Jin leaders, travelled more than 5000 kilometres to meet Genghis Khan near the Afghanistan border. Genghis Khan asked if the monk had secret medicine that could make him immortal. The monk's negative answer disheartened Genghis Khan, and he lost interest in the monk thereafter.
Uniting the confederations

The Central Asian plateau (north of China) around the time of Temüjin was divided into several tribes or confederations, among them Naimans, Merkits, Uyghurs, Tatars, Mongols, Keraits that were all prominent in their own right and often unfriendly toward each other as evidenced by random raids, revenges, and plundering.
Temüjin began his slow ascent to power by offering himself as an ally (or, according to others sources, a vassal) to his father's anda (sworn brother or blood brother) Toghrul, who was Khan of the Kerait, and is better known by the Chinese title Ong Khan (or "Wang Khan"), which the Jin Empire granted him in 1197. This relationship was first reinforced when Börte was captured by the Merkits; it was to Toghrul that Temüjin turned for support. In response, Toghrul offered his vassal 20,000 of his Kerait warriors and suggested that he also involve his childhood friend Jamuka, who had himself become Khan (ruler) of his own tribe, the Jadaran. Although the campaign was successful and led to the recapture of Börte and utter defeat of the Merkits, it also paved the way for the split between the childhood friends, Temüjin and Jamuka.
The main opponents of the Mongol confederation (traditionally the "Mongols") circa 1200 were the Naimans to the west, the Merkits to the north, Tanguts to the south, the Jin and Tatars to the east. By 1190, Temüjin, his followers and advisors united the smaller Mongol confederation only. As an incentive for absolute obedience and following his rule of law, the Yassa code, Temüjin promised civilians and soldiers a wealth from future possible war spoils.
Toghrul's (Wang Khan) son Senggum was jealous of Temüjin's growing power, and his affinity with his father. He allegedly planned to assassinate Temüjin. Toghrul, though allegedly saved on multiple occasions by Temüjin, gave in to his son and became uncooperative with Temüjin. Temüjin learned of Senggum's intentions and eventually defeated him and his loyalists. One of the later ruptures between Toghrul and Temüjin was Toghrul's refusal to give his daughter in marriage to Jochi, the eldest son of Temüjin, a sign of disrespect in the Mongolian culture. This act led to the split between both factions, and was a prelude to war. Toghrul allied himself with Jamuka, who already opposed Temüjin's forces; however the internal dispute between Toghrul and Jamuka, plus the desertion of a number of their allies to Temüjin, led to Toghrul's defeat. Jamuka escaped during the conflict. This defeat was a catalyst for the fall and eventual dissemination of the Kerait tribe.
The next direct threat to Temüjin was the Naimans (Naiman Mongols), with whom Jamuka and his followers took refuge. The Naimans did not surrender, although enough sectors again voluntarily sided with Temüjin. In 1201, a kurultai elected Jamuka as Gur Khan, universal ruler, a title used by the rulers of the Kara-Khitan Khanate. Jamuka's assumption of this title was the final breach with Temüjin, and Jamuka formed a coalition of tribes to oppose him. Before the conflict, however, several generals abandoned Jamuka, including Subutai, Jelme's well-known younger brother. After several battles, Jamuka was finally turned over to Temüjin by his own men in 1206.
According to the Secret History, Temüjin again offered his friendship to Jamuka, asking him to return to his side. Temüjin had killed the men who betrayed Jamuka, stating that he did not want disloyal men in his army. Jamuka refused the offer of friendship and reunion, saying that there can only be one Sun in the sky, and he asked for a noble death. The custom is to die without spilling blood, which is granted by breaking the back. Jamuka requested this form of death, despite the fact that in the past Jamuka had been infamously known to have boiled his opponent's generals alive. The rest of the Merkit clan that sided with the Naimans were defeated by Subutai, a member of Temüjin's personal guard who would later become one of the successful commanders of Genghis Khan. The Naimans' defeat left Genghis Khan as the sole ruler of the Mongol plains, which means all the prominent confederations fell and/or united under Temüjin's Mongol confederation. Accounts of Genghis Khan's life are marked by claims of a series of betrayals and conspiracies. These include rifts with his early allies such as Jamuka (who also wanted to be a ruler of Mongol tribes) and Wang Khan (his and his father's ally), his son Jochi, and problems with the most important Shaman who was allegedly trying break him up with brother Qasar who was serving Genghis Khan loyally. Many modern scholars doubt that all of the conspiracies existed and suggest that Genghis Khan was probably inclined towards paranoia as a result of his experiences.
His military strategies showed a deep interest in gathering good intelligence and understanding the motivations of his rivals as exemplified by his extensive spy network and Yam route systems. He seemed to be a quick student, adopting new technologies and ideas that he encountered, such as siege warfare from the Chinese. Many legends claim that Genghis Khan always was in the front in battles, but these may not be historically accurate.
As a result by 1206 Temüjin had managed to unite the Merkits, Naimans, Mongols, Uyghurs, Keraits, Tatars and disparate other smaller tribes under his rule. It was a monumental feat for the "Mongols" (as they became known collectively), who had a long history of internecine dispute, economic hardship, and pressure from Chinese dynasties and empires. At a Kurultai, a council of Mongol chiefs, he was acknowledged as "Khan" of the consolidated tribes and took the new title Genghis Khan. The title Khagan was not conferred on Genghis until after his death, when his son and successor, Ögedei took the title for himself and extended it posthumously to his father (as he was also to be posthumously declared the founder of the Yuan Dynasty). This unification of all confederations by Genghis Khan established peace between previously warring tribes and a single political and military force under Genghis Khan.
See also: Mongols before Genghis Khan and MongolsExpansion and military campaigns
See also: Mongol invasionsConquest of the Western Xia Dynasty
Main article: Mongol Nation
During the 1206 political rise for Genghis Khan, the Mongol nation or Mongol Empire created by Genghis Khan and his allies was neighboured to the west by the Tanguts' Western Xia Dynasty. To its east and south was the Jin Dynasty, founded by the Manchurian Jurchens, who ruled northern China as well as being the traditional overlord of the Mongolian tribes for centuries.
Temüjin organised his people, army, and his state to first prepare for war with Western Xia, or Xi Xia, which was closer to the Mongolian lands. He correctly believed that the more powerful Jin Dynasty's young ruler would not come to the aid of Xi Xia. When the Tanguts requested help from the Jin Dynasty, they were flatly refused. Despite initial difficulties in capturing its well-defended cities, Genghis Khan forced the surrender of Western Xia by 1209.
Conquest of the Jin Dynasty
Main articles: Jin Dynasty, 1115–1234 and Yuan DynastyIn 1211, after the conquest of Western Xia, Genghis Khan planned again to conquer the Jin Dynasty. The commander of the Jin Dynasty army made a tactical mistake in not attacking the Mongols at the first opportunity. Instead, the Jin commander sent a messenger, Ming-Tan, to the Mongol side, who promptly defected and told the Mongols that the Jin army was waiting on the other side of the pass. At this engagement fought at Badger Pass the Mongols massacred thousands of Jin troops. In 1215 Genghis besieged, captured, and sacked the Jin capital of Yanjing (later known as Beijing). This forced the Emperor Xuanzong to move his capital south to Kaifeng, abandoning the northern half of his kingdom to the Mongols.
Defeat of the Kara-Khitan Khanate
Main article: Kara-Khitan Khanate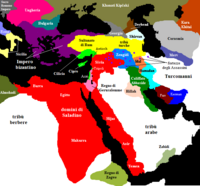
Meanwhile, Kuchlug, the deposed Khan of the Naiman confederation that Temüjin defeated and folded into the Mongol nation, fled west and usurped the khanate of Kara-Khitan (also known as Kara Kitay). Genghis Khan decided to conquer the Kara-Khitan khanate and defeat Kuchlug possibly to take him out of power. By this time the Mongol army was exhausted from ten years of continuous campaigning in China against the Western Xia and Jin Dynasty. Therefore, Genghis sent only two tumen (20,000 soldiers) against Kuchlug, under his younger general, Jebe, known as "The Arrow".
With such a small force, the invading Mongols were forced to change strategies and resort to inciting internal revolt among Kuchlug's supporters, leaving the Khara-Khitan khanate more vulnurable to Mongol conquest. As a result Kuchlug's army was defeated in west of Kashgar. Kuchlug fled again, but was soon hunted down by Jebe's army and executed. By 1218 as a result of defeat of Kara-Khitan khanate, the Mongol Empire and its control extended as far west as Lake Balkhash, which bordered the Khwarezmia (Khwarezmid Empire), a Muslim state that reached the Caspian Sea to the west and Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea to the south.
Destruction of the Khwarezmid Empire
Main article: Mongol invasion of Central AsiaAt this time the Khwarezmian Dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarezmia as a commercial trading partner, and, instead of sending an invasion force, he initially sent a 500-man caravan to establish trade ties with the empire. However, Inalchuq, the governor of the Khwarezmian city of Otrar, attacked the caravan that came from Mongolia, claiming that the caravan was a conspiracy against Khwarezmia. The situation became more complicated as the governor later refused to make repayments for the looting of the caravan and murder of its members. Genghis Khan then sent again a second group of ambassadors to meet the Shah himself. The Shah had all the men shaved and all but one beheaded. This was seen as an affront and insult to Genghis Khan. Outraged, Genghis Khan planned one of his largest invasion campaigns by organising together around 200,000 soldiers (20 tumens), his most capable generals and some of his sons.
The Mongol army under personal command of Genghis Khan, generals and son(s) crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarezmid Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarezmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarzemia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on Samarkand. The third division under Genghis Khan and Tolui marched to the northwest and attacked Khwarzemia from that direction.
The Shah's army was split by diverse internal disquisitions and by the Shah's decision to divide his army into small groups concentrated in various cities This fragmentation was decisive in Khwarezmia's defeats, as it allowed the Mongols, although exhausted from the long journey, to immediately set about defeating small fractions of the Khwarzemi forces instead of facing a unified defense. The Mongol army quickly seized the town of Otrar, relying on superior strategy and tactics. Genghis Khan ordered the execution of many of the inhabitants and executed Inalchuq by pouring molten silver into his ears and eyes, as retribution for his actions. Near the end of the battle the Shah fled rather than surrender. Genghis Khan charged Subutai and Jebe with hunting him down, giving them two years and 20,000 men. The Shah died under mysterious circumstances on a small island within his empire.
The Mongols' conquest, even by their own standards, was relatively brutal. After the capital Samarkand fell, the capital was moved to Bukhara by the remaining men, and Genghis Khan dedicated two of his generals and their forces to completely destroying the remnants of the Khwarezmid Empire, including not only royal buildings, but entire towns and even vast swaths of farmland. According to stories, Genghis Khan even went so far as to divert a river through the Khwarezmid emperor's birthplace, erasing it from the map.
The heir Shah Jalal Al-Din, who was supported by a nearby town, battled the Mongols several times with his father's armies. However, internal disputes once again split his forces apart, and they were forced to flee Bukhara after yet another devastating defeat, effectively bringing the Khwarezmid Empire to an end.
In the meantime, Genghis Khan selected his third son Ögedei as his successor before his army set out, and specified that subsequent Khans should be his direct descendants. Genghis Khan also left Muqali, one of his most trusted generals, as the supreme commander of all Mongol forces in Jin China while he was out battling the Khwarezmid Empire to the west.
Attacks on Georgia and Volga Bulgaria
After the complete defeat of the Khwarezmid Empire in 1220, the Mongol army was split into two component forces. Genghis Khan led a division on a raid through Afghanistan, Pakistan and northern India, while another contingent marched through the Caucasus and into Russia. As Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes, the second force of 20,000 troops (two tumen), commanded by generals Jebe and Subutai, pushed deep into Armenia and Azerbaijan. The Mongols destroyed Georgia, sacked the Genoese trade-fortress of Caffa in Crimea, and overwintered near the Black Sea. Heading home, Subutai's forces attacked the Kipchaks and were intercepted by the allied but poorly coordinated troops of Mstislav the Bold of Halych and Mstislav III of Kiev, along with about 80,000 Kievan Rus' to stop their actions. Subutai sent emissaries to the Slavic princes calling for a separate peace, but the emissaries were executed. At the Battle of Kalka River in 1223, Subutai's forces defeated the larger Kievan force, while losing the battle of Samara Bend against the neighboring Volga Bulgars..
The Mongols learned from captives of the abundant green pastures beyond the Bulgar territory, allowing for the planning for conquest of Hungary and Europe. The Russian princes then sued for peace. Subutai agreed but was in no mood to pardon the princes. As was customary in Mongol society for nobility, the Russian princes were given a bloodless death. Subutai had a large wooden platform constructed on which he ate his meals along with his other generals. Six Russian princes, including Mstislav of Kiev, were put under this platform and crushed to death.
Genghis Khan recalled Subutai back to Mongolia soon afterwards, and Jebe died on the road back to Samarkand. Subutai and Jebe's famous cavalry expedition, in which they encircled the entire Caspian Sea defeating all armies in their path, except for that of the Volga Bulgars, remains unparalleled to this day, and word of the Mongol triumphs began to trickle to other nations, particularly Europe.
These two campaigns are generally regarded as reconnaissance campaigns that tried to get the feel of the political and cultural elements of the regions. In 1225 both divisions returned to Mongolia. These invasions ultimately added Transoxiana and Persia to an already formidable empire while destroying any resistance along the way.
Under Genghis Khan's grandson Batu and Golden Horde, the Mongols returned to definitively conquer Volga Bulgaria and the Kievan Rus in 1237, concluding the campaign in 1240.
Second war with the Western Xia and Jin Dynasty coalition
Main articles: Jin Dynasty, 1115–1234 and Yuan DynastyThe vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had refused to take part in the war against the Khwarezmid Empire. While most of the Mongol forces under Genghis Khan and his generals were out on campaign against the Khwarezmid Empire, the Western Xia and defeated Jin Dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarezmids to drain the Mongols' ability to respond effectively. Their cause was further emboldened by the Khan's expeditions further East, which had drawn the bulk of his army off into prolonged campaigns in Persia and Eastern Europe.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the east, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui, Ganzhou and Suzhou, and in the autumn he took Xiliang-fu. One of the Tangut generals challenged the Mongols to a battle near Helanshan, but were soundly defeated. In November, Genghis laid siege to the Tangut city Lingzhou, and crossed the Yellow River, defeating the Tangut relief army. According to legend, it was here that Genghis Khan reportedly saw a line of five stars arranged in the sky, and interpreted it as an omen of his victory.
In 1227, Genghis Khan's army attacked and destroyed the Tangut capital of Ning Hia, and continued to advance, seizing Lintiao-fu, Xining province, Xindu-fu, and Deshun province in quick succession in the Spring. At Deshun, the Tangut general Ma Jianlong put up a fierce resistance for several days and personally led charges against the invaders outside the city gate. Ma Jianlong later died from wounds received from arrows in battle. Genghis Khan, after conquering Deshun, went to Liupanshan (Qingshui County, Gansu Province) to escape the severe summer. The new Tangut emperor quickly surrendered to the Mongols, and the rest of the Tanguts officially surrendered soon after. Not happy with their betrayal and resistance, Genghis Khan ordered the entire imperial family to be executed, effectively ending the Tangut lineage.
Death and burial
Main article: Tomb of Genghis Khan
On August 18, 1227, during his last campaign against the coalition of Jin Dynasty and Western Xia, Genghis Khan died. The reason for his death is uncertain and speculations abound. Some histories maintain that he fell off his horse due to old age and physical fatigue, ultimately dying of his injuries. Others contend that he was felled by a protracted illness such as pneumonia. The Galician-Volhynian Chronicle alleges he was killed by the Tanguts in battle. There are persistent folktales that a Tangut princess, to avenge her people and prevent her rape, castrated him with a knife hidden inside her vagina and that he never recovered.
Genghis Khan asked to be buried without markings, according the customs of his tribe. After he died, his body was returned to Mongolia and presumably to his birthplace in Khentii Aimag, where many assume he is buried somewhere close to the Onon River and the Burkhan Khaldun mountain (part of the Kentii mountain range). According to legend, the funeral escort killed anyone and anything across their path to conceal where he was finally buried. The Genghis Khan Mausoleum, constructed many years after his death, is his memorial, but not his burial site.
On October 6, 2004, A joint Japanese-Mongolian archaeological dig uncovered what is believed to be Genghis Khan's palace in rural Mongolia, which raises the possibility of actually locating the ruler's long-lost burial site. Folklore says that a river was diverted over his grave to make it impossible to find (the same manner of burial of Sumerian King Gilgamesh of Uruk.) Other tales state that his grave was stampeded over by many horses, over which trees were then planted, and the permafrost also did its bit in hiding the burial site.
Genghis Khan left behind an army of more than 129,000 men; 28,000 were given to his various brothers and his sons. Tolui, his youngest son, inherited more than 100,000 men. This force contained the bulk of the elite Mongolian cavalry. By tradition, the youngest son inherits his father's property. Jochi, Chagatai, Ögedei Khan, and Kulan's son Gelejian received armies of 4,000 men each. His mother and the descendants of his three brothers received 3,000 men each.
Mongol Empire under Genghis

Politics and economics
Main article: Organization of state under Genghis KhanThe Mongol Empire was governed by a civilian and military code, called the Yassa, created by Genghis Khan.
The Mongol Empire did not emphasize the importance of ethnicity and race in the administrative realm, instead adopting an approach grounded in meritocracy. The exception was the role of Genghis Khan and his family. The Mongol Empire was one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse empires in history, as befitted its size. Many of the empire's nomadic inhabitants considered themselves Mongols in military and civilian life, including Turks, Mongols, and others and included many diverse Khans of various ethnicities as part of the Mongol Empire such as Muhammad Khan.
There were tax exemptions for religious figures and, to some extent, teachers and doctors. The Mongol Empire practiced religious tolerance to a large degree because Mongol tradition had long held that religion was a very personal concept, and not subject to law or interference. Sometime before the rise of Genghis Khan, Ong Khan, his mentor and eventual rival, had converted to Nestorian Christianity. Various Mongol tribes were Buddhist, Muslim, shamanist or Christian. Religious tolerance was a well established concept on the Asian steppe.
Modern Mongolian historians say that towards the end of his life, Genghis Khan attempted to create a civil state under the Great Yassa that would have established the legal equality of all individuals, including women. However, there is no contemporary evidence of this, or of the lifting of discriminatory policies towards sedentary peoples such as the Chinese. Women played a relatively important role in Mongol Empire and in family, for example Torogene Khatun was briefly in charge of the Mongol Empire when next male Khagan was being chosen. Modern scholars refer to the alleged policy of encouraging trade and communication as the Pax Mongolica (Mongol Peace).
Genghis Khan realized that he needed people who could govern cities and states conquered by him. He also realised that such administrators could not be found among his Mongol people because they were nomads and thus had no experience governing cities. For this purpose Genghis Khan invited a Khitan prince, Chu'Tsai, who worked for the Jin and had been captured by Mongol army after the Jin Dynasty were defeated. Jin had captured power by displacing Khitan. Genghis told Chu'Tsai, who was a lineal descendant of Khitan rulers, that he had avenged Chu'Tsai's forefathers. Chu'Tsai responded that his father served the Jin Dynasty honestly and so did he; he did not consider his own father his enemy, so the question of revenge did not apply. Genghis Khan was very impressed by this reply. Chu'Tsai administered parts of the Mongol Empire and became a confidant of the successive Mongol Khans.
Genghis Khan expected unwavering loyalty from his generals, and granted them a great deal of autonomy in making command decisions. Muqali, a trusted general, was given command of the Mongol forces against the Jin Dynasty while Genghis Khan was fighting in Central Asia, and Subutai and Jebe were allowed to pursue the Great Raid into the Caucausus and Kievan Rus, an idea they had presented to the Khagan on their own initiative. The Mongol military also was successful in siege warfare, cutting off resources for cities and towns by diverting certain rivers, taking enemy prisoners and driving them in front of the army, and adopting new ideas, techniques and tools from the people they conquered, particularly in employing Muslim and Chinese siege engines and engineers to aid the Mongol cavalry in capturing cities. Also one of the standard tactics of Mongol military was the commonly practiced feigned retreat to break enemy formations and to lure small enemy groups away from larger group and defended position for ambush and counterattack.
Another important aspect of the military organization of Genghis Khan was the communications and supply route or Yam, adapted from previous Chinese models. Genghis Khan dedicated special attention to this in order to speed up the gathering of military intelligence and official communications. To this end, Yam waystations were established all over the empire.
Division of the Empire into Khanates
Before his death, Genghis Khan divided his empire among his sons Ögedei, Chagatai, Tolui, and Jochi (Jochi's death several months before Genghis Khan meant that his lands were instead split between his sons, Batu and Orda) into several Khanates designed as sub-territories: their Khans were expected to follow the Great Khan, who was, initially, Ögedei.

Following are the Khanates in the way in which Genghis Khan assigned after his death:
- Empire of the Great Khan - Ögedei Khan, as Great Khan, took most of Eastern Asia, including China; this territory later to comprise the Yuan Dynasty under Kubilai Khan.
- Mongol homeland (present day Mongolia, including Karakorum) - Tolui Khan, being the youngest son, received a small territory near the Mongol homeland, following Mongol custom.
- Chagatai Khanate - Chagatai Khan, Genghis Khan's second son, was given Central Asia and northern Iran.
- Blue Horde - Batu Khan, and White Horde - Orda Khan, both were later combined into the Kipchak Khanate, or Khanate of the Golden Horde, under Toqtamysh. Genghis Khan's eldest son, Jochi, had received most of the distant Russia and Ruthenia. Because Jochi died before Genghis Khan, his territory was further split up between his sons. Batu Khan launched an invasion of Russia, and later Hungary and Poland, and crushed several armies before being summoned back by the news of Ögedei's death.
After Genghis Khan
Contrary to popular belief, Genghis Khan did not conquer all of the areas of Mongol Empire. At the time of his death, the Mongol Empire stretched from the Caspian Sea to the Sea of Japan. The empire's expansion continued for a generation or more after Genghis's death in 1227. Under Genghis's successor Ögedei Khan the speed of expansion reached its peak. Mongol armies pushed into Persia, finished off the Xi Xia and the remnants of the Khwarezmids, and came into conflict with the imperial Song Dynasty of China, starting a war that would last until 1279 and that would conclude with the Mongols gaining control of all of China.
Controversy
| This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (November 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Like other notable conquerors, such as Hernán Cortés, Genghis Khan's portrayal differs from those he conquered, as opposed to those who conquered with him. Additionally, unlike Hitler, whose regime was overthrown, and Napoleon I of France, who was defeated, Genghis Khan was never completely vanquished, and created an empire that evolved into a modern nation. Therefore, there is an entire culture that identifies with Khan as a leader and founder, much as George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, and others are viewed as the “founding fathers” of The United States of America. Genghis Khan is undisputedly both the creator and destroyer of nations, and remains a debatable figure, even to modern scholars.
Positive perception of Genghis Khan
Negative views of Genghis Khan are very persistent with histories written by many different cultures, from various different geographical regions. They often cite the cruelties and destructions brought upon by Mongol armies. However, there are positive aspects to Genghis Khan's conquests. Genghis Khan is credited with bringing the Silk Road under one cohesive political environment. This allowed increased communication and trade between the West, Middle East and Asia by expanding the horizon of all three areas. Some historians have noted that Genghis Khan instituted certain levels of meritocracy in his rule, and was tolerant of different religions. In much of modern-day Turkey, Genghis Khan is looked on as a great military leader, and it is popular for male children to carry his name.
Genghis Khan as an icon in Mongolia


Traditionally Genghis Khan had been revered for centuries among the Mongols and other ethnic groups like the Turks largely because of his association with the Mongol culture, political and military organization, and his historic victories in war. He eventually evolved into a larger-than-life figure chiefly among the Mongols.
During the communist period, Genghis Khan was often described as reactionary, and positive statements on him were generally avoided. In 1962, the erection of a monument at his birthplace and a conference held in commemoration of his 800th birthday led to criticism from the Soviet Union, and resulted in the dismissal of Tömör-Ochir, a secretary of the ruling Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party Central Committee. In the early 1990s, when democracy was established in Mongolia, the memory of Genghis Khan with the Mongolian traditional national identity has had a powerful revival. Genghis Khan became the central figure of the national identity. He is now a source of pride for Mongolians with ties to their historic roots. For example, it is not uncommon for Mongolians to refer to Mongolia as "Genghis Khan's Mongolia," to themselves as "Genghis Khan's children," and to Genghis Khan as "father of the Mongols" especially among the younger generation. His name and likeness are endorsed on products, streets, buildings, and other places. His face can be found on everyday commodities, from liquors to the largest denominations of 500, 1000, 5000 and 10,000 Mongolian tögrög (₮). Mongolia's main international airport in the capital Ulaanbaatar has been renamed Chinggis Khaan International Airport, and major Genghis Khan statues have been erected before the parliament and near Ulaanbaatar. There have been repeated discussions about regulating the use of his name and image to avoid trivialization. In summary, Mongolians see him as the fundamental figure in the founding of the Mongol nation, and therefore the basis for Mongolia as a country.

Genghis Khan is now widely regarded as one of Mongolia's greatest and most legendary leaders. He is responsible for the emergence of the Mongols as a political and ethnic identity. He reinforced many Mongol traditions and provided stability and unity during a time of great uncertainty, due to both internal and external factors. He is also given credit for the introduction of the traditional Mongolian script and the creation of the Ikh Zasag, the first written Mongolian law. There is a chasm in the perception of his brutality - Mongolians maintain that the historical records written by non-Mongolians are unfairly biased against Genghis Khan; and that his butchery is exaggerated, while his positive role is underrated.
In China
The People's Republic of China considers Genghis Khan to be an ethnic minority hero. The rationale for this claim is the fact that there are more ethnic Mongols living inside the PRC than outside, including Mongolia. While Genghis Khan never conquered all of China, his grandson Kublai Khan completed that conquest, and also had a natural affinity for the people of China proper and their various lifestyles, and established a sinicized Yuan Dynasty that is often credited with re-uniting China . There has also been much artwork and literature praising him as a great military leader and political genius. The years of the Mongol-established Yuan Dynasty left an indelible imprint on Chinese political and social structures for subsequent generations. However, the legacy of Genghis Khan and his successors who conquered the militarily advanced Chinese dynasties, particularly the Southern Song after 65 years of struggle remains a mixed topic, even to this day.
Recognitions in publications
Genghis Khan is recognized in number of large and popular publications and by other authors, which include the following:
- Genghis Khan is ranked #29 on Michael H. Hart's list of the most influential people in history.
- An article that appeared in the Washington Post on December 31, 1995 selected Genghis Khan as "Man of the Millennium".
- Genghis Khan was nominated for the "Top 10 Cultural Legends of the Millennium" in 1998 by Dr G. Ab Arwel, voted by the five Judges, Prof. D Owain, Mr. G. Parry, OBE, Dr. C Campbell of Oxford University, and Mr S Evans and Sir B. Parry of the International Museum of Culture, Luxembourg.
- National Geographic's 50 Most Important Political Leaders of All Time.
Negative perceptions of Genghis Khan
In Iraq and Iran, he is looked on as a destructive and genocidal warlord who caused enormous damage and destruction. Similarly, in Afghanistan and Pakistan (along with other non-Turkic Muslim countries) he is viewed unfavorably. It is believed that the Hazara of Afghanistan are descendants of a large Mongol garrison stationed therein. The invasions of Baghdad and Samarkand caused mass murders, such as when portions of southern Khuzestan was completely destroyed. His descendant Hulagu Khan destroyed much of Iran's northern part. Among the Iranian peoples he is regarded as one of the most despised conquerors of Iran, along with Alexander and Tamerlane. In much of Russia, Ukraine, Poland and Hungary, Genghis Khan and his regime are credited with considerable damage and destruction. Presently Genghis Khan, his descendants, his generals, and the Mongol people are remembered for their ferocious and destructive conquests by the region's history books.
Claimed descendants study
Main article: Descent from Genghis KhanZerjal et al identified a Y-chromosomal lineage present in about 8% of the men in a large region of Asia (about 0.5% of the men in the world). The paper suggests that the pattern of variation within the lineage is consistent with a hypothesis that it originated in Mongolia about 1,000 years ago. Such a spread would be too rapid to have occurred by genetic drift, and must therefore be the result of natural selection. The authors propose that the lineage is carried by likely male-line descendants of Genghis Khan, and that it has spread through social selection.
In addition to the Khanates and other descendants, the Mughal emperor Babur's mother was a descendant. Timur, the 14th century military leader, claimed descent from Genghis Khan.
Name and title
There are many theories about the origins of Temüjin's title. Since people of the Mongol nation later associated the name with ching (Mongolian for strength), such confusion is obvious, though it does not follow etymology.
One theory suggests the name stems from a palatalised version of the Mongolian and Turkic word tenggiz, meaning "ocean", "oceanic" or "wide-spreading". (Lake Baikal and ocean were called tenggiz by the Mongols. However, it seems that if they had meant to call Genghis tenggiz they could have said (and written) "Tenggiz Khan", which they did not. Zhèng (Chinese: 正) meaning "right", "just", or "true", would have received the Mongolian adjectival modifier -s, creating "Jenggis", which in medieval romanization would be written "Genghis" . It is likely that the 13th century Mongolian pronunciation would have closely matched "Chinggis". See Lister and Ratchnevsky, referenced below, for further reading.
"Genghis" as popularly spelled and pronounced in Western media and text is supposedly derived from the original Persian reports of an invading army, led by a man in 1219 against the Khwarezmid Empire. The Persian people pronounced the man's name "Genghis", as there was no "ch" sound in the Persian tongue. Henceforth, the Persian version of the name of the leader of the Mongol Empire became known and widespread in the Western hemisphere as "Genghis".
According to to the Secret History, Temüjin was named after a powerful warrior of a rival tribe that his father Yesükhei had taken prisoner. The name "Temüjin" is believed to derive from the Turkic word temur, meaning iron (modern Mongolian: төмөр, tömör). This name would imply skill as a blacksmith.
More likely, as no evidence has survived to indicate that Genghis Khan had any exceptional training or reputation as a blacksmith, the name indicated an implied lineage in a family once known as blacksmiths. The latter interpretation is supported by the names of Genghis Khan's siblings, Temülin and Temüge, which are derived from the same root word.
Name and spelling variations
Genghis Khan's name is spelled in variety of ways in different languages such as Chinese: 成吉思汗; pinyin: Chéngjísī Hán, Turkic: Cengiz Han, Chengez Khan, Chinggis Khan, Chinggis Xaan, Chingis Khan, Jenghis Khan, Chinggis Qan, Djingis Kahn etc. Temüjin is written in Chinese as simplified Chinese: 铁木真; traditional Chinese: 鐵木眞; pinyin: Tiěmùzhēn.
Short timeline
- c. 1155-1167—Temüjin born in Hentiy, Mongolia.
- c. 1171—Temüjin's father Yesükhei poisoned by the Tatars, leaving him and his family destitute
- c. 1184—Temüjin's wife Börte kidnapped by Merkits; calls on blood brother Jamuka and Wang Khan (Ong Khan) for aid, and they rescued her.
- c. 1185—First son Jochi born, leading to doubt about his paternity later among Genghis' children, because he was born shortly after Börte's rescue from the Merkits.
- 1190—Temüjin unites the Mongol tribes, becomes leader, and devises code of law Yassa.
- 1201—Wins victory over Jamuka's Jadarans.
- 1202—Adopted as Ong Khan's heir after successful campaigns against Tatars.
- 1203—Wins victory over Ong Khan's Keraits. Ong Khan himself is killed by accident by allied Naimans.
- 1204—Wins victory over Naimans (all these confederations are united and become the Mongols).
- 1206—Jamuka is killed. Temüjin given the title Genghis Khan by his followers in Kurultai (around 40 years of age).
- 1207-1210—Genghis leads operations against the Western Xia, which comprises much of northwestern China and parts of Tibet. Western Xia ruler submits to Genghis Khan. During this period, the Uyghurs also submit peacefully to the Mongols and became valued administrators throughout the empire.
- 1211—After kurultai, Genghis leads his armies against the Jin Dynasty that ruled northern China.
- 1215—Beijing falls, Genghis Khan turns to west and the Khara-Kitan Khanate.
- 1219-1222—Conquers Khwarezmid Empire.
- 1226—Starts the campaign against the Western Xia for forming coalition against the Mongols, being the second battle with the Western Xia.
- 1227—Genghis Khan dies leading fight against Western Xia. How he died is uncertain, although legend states that he was thrown off his horse in the battle, and contracted a deadly fever soon after.
Notes
- Rashid al-Din asserts that Genghis Khan lived to the age of 72, placing his year of birth at 1155. The Yuanshi (元史, History of the Yuan dynasty, not to be confused with the era name of the Han Dynasty), records his year of birth as 1165. According to Ratchnevsky, accepting a birth in 1155 would render Genghis Khan a father at the age of 30 and would imply that he personally commanded the expedition against the Tanguts at the age of 72. Also, according to the Altan Tobci, Genghis Khan's sister, Temülin, was nine years younger than he; but the Secret History relates that Temülin was an infant during the attack by the Merkits, during which Genghis Khan would have been 18, had he been born in 1155. Zhao Hong reports in his travelogue that the Mongols he questioned did not know and had never known their ages.
- Conferred posthumously by his son Ögedei Khan when he took the new title
- Morgan, David, The Mongols (Peoples of Europe), 1990, p.58.
- http://www.republicanchina.org/Mongols.html
- Ratchnevsky, Paul (1991). Genghis Khan: His Life and Legacy. Blackwell Publishing. pp. 9–10. ISBN 0-631-16785-4.
- http://www.csuchico.edu/~cheinz/syllabi/fall99/kong/Index1.htm
- Ratchnevsky, Paul. Genghis Khan: His Life and Legacy, 1991, p. 126.
- (Ratchnevsky, p. 136-7)
- Grousset, Rene. Conqueror of the World: The Life of Chingis-khan (New York: The Viking Press, 1944) SBN 670-00343-3.
- Man, John. Genghis Khan : Life, Death and Resurrection (London; New York : Bantam Press, 2004) ISBN 0-593-05044-4.
- Man, John. Genghis Khan: Life, Death and Resurrection (London; New York: Bantam Press, 2004) ISBN 0-593-05044-4.
- De Hartog, Leo (1988). Genghis Khan: Conqueror of the World. London, UK: I.B. Tauris & Co. Ltd. pp. 122–123.
- Palace of Genghis Khan unearthed
- Mongolia sees Genghis Khan's good side
- Christopher Kaplonski: The case of the disappearing Chinggis Khaan
- Once Shunned, Genghis Khan Conquers Mongolia Again
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/5412410.stm
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/1967201.stm
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/6252741.stm?lsf
- Kublai Khan
- Inner Mongolia Travel Guide
- "The Legacy of Genghis Khan" at Los Angeles County Museum of Art--again
- Phoenix From the Ashes: A Tale of the Book in Iran
- Civilizations: How we see others, how others see us
- Zerjal et. al, (2003) The Genetic Legacy of the Mongols. American Journal of Human Genetics 72(3):717-721 (PubMed)
External links
- Book Review of Genghis Khan by Leo De Hartog
- Genghis Khan and the Mongols
- Welcome to The Realm of the Mongols
- Parts of this biography were taken from the Area Handbook series at the Library of Congress
- Coverage of Temüjin's Earlier Years
- Estimates of Mongol warfare casualties
- Genghis Khan on the Web (directory of some 250 resources)
- Mongol Arms
- LeaderValues
- ‘Ala’ al-Din ‘Ata Malik Juvayni (A History of the World-Conqueror Ghengis Genghis Khan, Ata al-Mulk Juvayni and Rashid al-Din Hamadani)
- iExplore.com: The search for the missing tomb of Genghis Khan
- BBC Radio 4 programme "In Our Time", topic was "Genghis Khan", 1 February 2007. With Peter Jackson, Professor of Medieval History at Keele University, Naomi Standen, Lecturer in Chinese History at Newcastle University, and George Lane, Lecturer in History at the School of Oriental and African Studies and presented by Melvyn Bragg.
References
- Brent, Peter. The Mongol Empire: Genghis Khan: His Triumph and his Legacy. Book Club Associates, London. 1976.
- Weatherford, Jack. Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World (New York : Crown, 2004) ISBN 0-609-61062-7.
- Kennedy, Hugh. Mongols, Huns & Vikings (London : Cassell, 2002) ISBN 0-304-35292-6.
- "Genghis Khan and the Mongols". Genghis Khan and the Mongols. Retrieved June 30.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - Man, John. Genghis Khan : Life, Death and Resurrection (London; New York : Bantam Press, 2004) ISBN 0-593-05044-4.
- Lister, R. P. Genghis Khan (Lanham, Md. : Cooper Square Press, 2000 ) ISBN 0-8154-1052-2.
- Eric Jameson professeur of ancient Asian rulers at Harvard
- "Mongol Arms". Mongol Arms. Retrieved June 24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - Template:PDFlink
- Ratchnevsky, Paul. Genghis Khan: His Life and Legacy (Oxford, UK ; Cambridge, Mass., USA : B. Blackwell, 1992, c1991) tr. & ed. Thomas Nivison Haining, ISBN 0-631-16785-4.
- Bretschneider, Emilii. Mediæval Researches from Eastern Asiatic Sources. London: K. Paul, Trench, Trübner & Co. ISBN 81-215-1003-1.
- History of the Mongol Conquests, JJ Saunders, U. Pennsylvania Press, 1972
- Genocide: A Critical Bibliographic Review edited by Israel W Charney, 1994
- Final Solutions: Mass Killing and Genocide in the Twentieth Century by Benjamin A Valentino
- Zerjal, Xue, Bertorelle, Wells, Bao, Zhu, Qamar, Ayub, Mohyuddin, Fu, Li, Yuldasheva, Ruzibakiev, Xu, Shu, Du, Yang, Hurles, Robinson, Gerelsaikhan, Dashnyam, Mehdi, Tyler-Smith (2003). "The Genetic Legacy of the Mongols" (PDF). The American Journal of Human Genetics (72): 717–721, .
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - De Hartog, Leo (1988). Genghis Khan: Conqueror of the World. London, UK: I.B. Tauris & Co. Ltd.
- Morgan, David (1986). The Mongols (Peoples of Europe). Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-631-17563-6.
Primary sources
- Juvaynī, Alā al-Dīn Atā Malik, 1226-1283. Genghis Khan: The History of the World-Conqueror (Seattle : UWashington Press, 1997) tr. John Andrew Boyle, ISBN 0-295-97654-3.
- The Secret History of the Mongols (Leiden; Boston : Brill, 2004) tr. Igor De Rachewiltz, Brill's Inner Asian Library. v.7, ISBN 90-04-13159-0.
- A Compendium of Chronicles: Rashid al-Din's Illustrated History of the World Jami' al-Tawarikh (Oxford : Oxford University Press, 1995) The Nasser D. Khalili Collection of Islamic Art, Vol. XXVII, ed. Sheila S. Blair, ISBN 0-19-727627-X.
- Tabib, Rashid al-Din. The Successors of Genghis Khan (New York : Columbia University Press, 1971) tr. from the Persian by John Andrew Boyle, , UNESCO collection of representative works: Persian heritage series, ISBN 0-231-03351-6.http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=109217551
Further reading
- Cable, Mildred and Francesca French. The Gobi Desert (London: Landsborough Publications, 1943).
- Lamb, Harold, Genghis Khan: The Emperor of All Men, 1927.
- Man, John. Gobi : Tracking the Desert (London : Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1997) hardbound; (London : Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1998) paperbound, ISBN 0-7538-0161-2; (New Haven: Yale, 1999) hardbound.
- Stewart, Stanley. In the Empire of Genghis Khan: A Journey among Nomads (London: Harper Collins, 2001) ISBN 0-00-653027-3.
- History Channel's biography of Genghis Khan
- Secret History of the Mongols: The Origin of Chingis Khan (expanded edition) (Boston: Cheng & Tsui Asian Culture Series, 1998) adapted by Paul Kahn, ISBN 0-88727-299-1.
| Genghis Khan House of Borjigin (Боржигин) (1206-1402)Born: 1162 Died: 1227 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byPosition Established | Khagan of Mongol Empire 1206-1227 |
Succeeded byThe Ögedei Khan |
| Khagan of the Mongol Empire | |
|---|---|
| Early Khagans | |
| Yuan (Kublaid) Khagans | |
| Mongol Empire | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Timeline of the Mongol Empire | |||||||||||
| Emperors of the Yuan dynasty | ||
|---|---|---|
| Yuan | Early Mongol rulers posthumously honoured by Kublai as Yuan emperors
Following Kublai's enthronement as Khagan-Emperor in 1260, proclamation of the dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, and conquest of Southern Song in 1279, Yuan ruled all of China. | 元 |
| Northern Yuan |
| |
| Note: Before Kublai announced the dynastic name "Great Yuan" in 1271, Khagans (Great Khans) of the "Great Mongol State" (Ikh Mongol Uls) already started to use the Chinese title of Emperor (Chinese: 皇帝; pinyin: Huángdì) practically in the Chinese language since the enthronement of Genghis Emperor (成吉思皇帝) in 1206.
Xia → Shang → Zhou → Qin → Han → 3 Kingdoms → Jìn / 16 Kingdoms → S. Dynasties / N. Dynasties → Sui → Tang → 5 Dynasties & 10 Kingdoms → Liao / Song / W. Xia / Jīn → Yuan → Ming → Qing → ROC / PRC | ||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: