This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Dbachmann (talk | contribs) at 20:37, 3 March 2008 (cats. is this the article on the 2008 Republic now, or what?). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:37, 3 March 2008 by Dbachmann (talk | contribs) (cats. is this the article on the 2008 Republic now, or what?)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| It has been suggested that this article be split into articles titled Kosovo (region) and Republic of Kosovo. (discuss) |
For other uses, see Kosovo (disambiguation). "Republic of Kosova" redirects here. For other uses, see Republic of Kosova (1990–2000). "Kosova" redirects here. For other uses, see Kosova (disambiguation).
| Republic of Kosovo Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) Косово и Метохија / Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
 Location of Kosovo in Europe Location of Kosovo in Europe | |
| Capitaland largest city | Pristina |
| Official languages | Albanian, Serbian |
| Recognised regional languages | Turkish, Gorani, Romani, Bosnian |
| Ethnic groups (2007) | 92% Albanians 5.3% Serbs 2.7% others |
| Demonym(s) | Kosovar |
| Government | international protectorate |
| • Special Representative of the Secretary-General | Joachim Rücker |
| • President | Fatmir Sejdiu (LDK) |
| • Prime Minister | Hashim Thaçi (PDK) |
| Independence from Serbia | |
| • Declared | 17 February 2008 |
| • Recognized | by 22 countries |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,887 km (4,203 sq mi) (166) |
| • Water (%) | n/a |
| Population | |
| • 2007 estimate | 1,900,000 (141) |
| • 1991 census | 1,956,196 |
| • Density | 220/km (569.8/sq mi) (55) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | 381 |
| Internet TLD | None assigned |
| |
Kosovo (Template:Lang-sq or Kosovë, Template:Lang-sr, Kosovo, see: Names of Kosovo), is a region in the Balkans, presently under the ad interim control of the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo and protection of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's Kosovo Force. Its Provisional Institutions of Self-Government have recently declared independence from the Republic of Serbia, which contested the act, and, as the Republic of Kosovo, received partial recognition.
Kosovo has a population of about two million people, predominantly ethnic Albanians, with smaller populations of Serbs, Romani people, Goranis, Bosniaks, Turks and other ethnic communities. Pristina is the capital and largest city. Kosovo is landlocked, bordering Montenegro to the west, Albania to the southwest, the Republic of Macedonia to the south and Central Serbia to the north and east.
Following the Kosovo War in 1999, United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244 placed Kosovo under the authority of the UNMIK, with security provided by the NATO-led Kosovo Force (KFOR), and legally reaffirmed Serbia's sovereignty over the region and committed the UN Member States to its territorial integrity. After UN-sponsored negotiations failed to reach a consensus on an acceptable constitutional status, Kosovo's provisional government unilaterally declared independence from Serbia on 17 February 2008 and received partial international recognition as a sovereign state (notably from the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Albania, Italy, and Turkey). As of February 29th, 2008, 22 states formally recognise the Republic of Kosovo while at least another 13 have declared their intention to do so at a later date.
Kosovo's unilateral declaration of independence is disputed by Serbia, Russia, Spain and 18 other nations. The official position of these countries is that Kosovo is a Serbian province under ad interim UN control, formally known as Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija (Template:Lang-sr, Autonomna pokrajina Kosovo i Metohija, also Космет, Kosmet; Template:Lang-sq). Other countries, including the People's Republic of China, have called for further negotiations or have stated they have made no decision yet.
History
Main article: History of KosovoEarly history
Main articles: Prehistoric Balkans, Moesia Superior, History of Medieval Kosovo, First Bulgarian Empire, and History of Medieval SerbiaDuring the Neolithic period, the region of Kosovo lay within the extent of the Vinča-Turdaş culture. In the 4th to 3rd centuries BC, it was the territory of the Thraco-Illyrian tribe of the Dardani, forming part of the kingdom of Illyria. The Illyrians were conquered by Rome in the 160s BC, and made the Roman province of Illyricum in 59 BC. The Kosovo region became part of Moesia Superior in AD 87. The Slavic migrations reached the Balkans in the 6th to 7th century. The area was absorbed into the Byzantine empire in the 850s. As the center of Slavic resistance to Constantinople in the region, it often switched between Serbian and Bulgarian rule on one hand and Byzantine on the other until the Serb principality of Rascia conquered it by the end of the 11th century.
Fully absorbed into the Serbian Kingdom until the end of the 12th, it became the secular and spiritual center of the Serbian medieval state of the Nemanyiden dynasty in the 13th century, with the Patriarchate of the Serbian Orthodox Church in Peć, while Prizren was the secular center. The zenith was reached with the formation of a Serbian Empire in 1346, which after 1371 transformed from a centralized absolutist medieval monarchy to a feudal realm. Kosovo became the hereditary land of the House of Branković and Vučitrn and Priština flourished.
In the 1389 Battle of Kosovo, Ottoman forces defeated a coalition led by Lazar Hrebeljanović. In 1402 a Serbian Despotate was raised and Kosovo became its richest territory, famous for mines. The local House of Branković came to prominence as the local lords of Kosovo, under Vuk Branković, with the temporary fall of the Serbian Despotate in 1439. During the first fall of Serbia Novo Brdo and Kosovo offered last resistance to the invading Ottomans in 1441, in 1455 it was finally and fully conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
Ottoman Kosovo (1455 to 1912)
Main article: History of Ottoman Kosovo Further information: Vilayet of Kosovo and History of Ottoman Serbia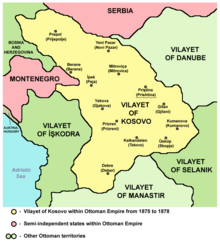
Kosovo was part of the Ottoman Empire from 1455 to 1912, at first as part of the eyalet of Rumelia, and from 1864 as a separate province. Ottoman influence included gradual Islamisation with them, particularly in towns.
Kosovo was briefly taken by the Austrian forces during the Great War of 1683–1699 with help of 6,000 led by Pjetër Bogdani. In 1690, the Serbian Patriarch of Peć Arsenije III led 37,000 families out of Kosovo. Other migrations of Orthodox Christians from the Kosovo area continued throughout the 18th century. In 1766, the Ottomans abolished the Patriarchate of Peć and the position of Christians in Kosovo deteriorated, including full imposition of jizya (taxation of non-Muslims).
In the 19th century, Kosovo along with the rest of the Balkans saw an "awakening" of ethnic nationalism, in the case of Kosovo ethnic Albanian nationalism, including Romantic notions of ancient Illyria.
In 1871, a Serbian meeting was held in Prizren at which the possible retaking and reintegration of Kosovo and the rest of "Old Serbia" was discussed, as the Principality of Serbia itself had already made plans for expansions towards Ottoman territory. In 1878, a Peace Accord was drawn that left the cities of Priština and Kosovska Mitrovica under civil Serbian control, and outside Ottoman jurisdiction, while the rest of Kosovo remained under Ottoman control. As a response, ethnic Albanians formed the League of Prizren, pursuing political aspirations of a unified Albanian people under the Ottoman umbrella. By the end of the 19th century the Albanians replaced the Serbs as the dominant people within the current Kosovo territory, though not the entire Ottoman Province.
20th century
Main article: 20th century history of KosovoBalkan Wars to World War I

The Young Turk movement supported a centralist rule and opposed any sort of autonomy desired by Kosovars, and particularly the Albanians. In 1910, an Albanian uprising spread from Priština and lasted until the Ottoman Sultan's visit to Kosovo in June of 1911. In 1912, during the Balkan Wars, most of Kosovo was taken by the Kingdom of Serbia, while the region of Metohija (Albanian: Dukagjini Valley) was taken by the Kingdom of Montenegro. An exodus of the local Albanian population occurred. This was described by Leon Trotsky, who was a reporter for the Pravda newspaper at the time. The Serbian authorities planned a recolonization of Kosovo. Numerous colonist Serb families moved into Kosovo, equalizing the demographic balance between Albanians and Serbs. Kosovo's status within Serbia was finalised the following year at the Treaty of London.
In the winter of 1915-1916, during World War I, Kosovo saw a large exodus of the Serbian army which became known as the Great Serbian Retreat, as Kosovo was occupied by Bulgarians and Austro-Hungarians. The Albanians joined and supported the Central Powers. In 1918, the Serbian Army pushed the Central Powers out of Kosovo. After World War I ended, the Monarchy was then transformed into the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenians on 1 December 1918.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia and World War II
The 1918–1929 period of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenians witnessed a rise of the Serbian population in the region. Kosovo was split into four counties, three being a part of Serbia (Zvečan, Kosovo and southern Metohija) and one of Montenegro (northern Metohija). However, the new administration system since 26 April 1922 split Kosovo among three Areas of the Kingdom: Kosovo, Rascia and Zeta. In 1929, the Kingdom was transformed into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia and the territories of Kosovo were reorganised among the Banate of Zeta, the Banate of Morava and the Banate of Vardar. The Kingdom of Yugoslavia lasted until the World War II Axis invasion of 1941, when the greatest part of Kosovo became a part of Italian-controlled Fascist Albania, and smaller bits by the Tsardom of Bulgaria and German-occupied Kingdom of Serbia. After numerous uprisings of Partisans led by Fadil Hoxha, Kosovo was liberated after 1944 with the help of the Albanian partisans of the Comintern, and became a province of Serbia within the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia.
Communist Yugoslavia
Main articles: Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija (1946-1974) and Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo
The province was first formed in 1945 as the Autonomous Kosovo-Metohian Area to protect its regional Albanian majority within the People's Republic of Serbia as a member of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia under the leadership of the former Partisan leader, Josip Broz Tito, but with no actual autonomy. After Yugoslavia's name change to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Serbia's to the Socialist Republic of Serbia in 1953, Kosovo gained internal autonomy in the 1960s. In the 1974 constitution, the Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo's government received higher powers, including the highest governmental titles — President and Prime Minister and a seat in the Federal Presidency which made it a de facto Socialist Republic within the Federation, but remaining a Socialist Autonomous Province within the Socialist Republic of Serbia. (Similar rights were extended to Vojvodina). In Kosovo Serbo-Croatian, Albanian and Turkish were defined as official languages on the provincial level. The ethnic balance of Kosovo tilted as the number of Albanians tripled, rising from almost 75% to over 90%, but the number of Serbs barely increased, dropping from 15% to 8% of the total population. Even though Kosovo was the least developed area of the former Yugoslavia, the living and economic prospects and freedoms were far greater than under the totalitarian Hoxha regime in Albania. Beginning in March 1981, Kosovar Albanian students organized protests seeking that Kosovo become a republic within Yugoslavia. During the 1980s, ethnic tensions continued with frequent violent outbreaks against Serbs and Yugoslav state authorities resulting in increased emigration of Kosovo Serbs and other ethnic groups. The Yugoslav leadership tried to suppress protests of Kosovo Serbs seeking protection from ethnic discrimination and violence.
Breakup of Yugoslavia and the Kosovo War
Main articles: Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija (1990-1999), Republic of Kosova (1990–2000), and Kosovo WarInter-ethnic tensions continued to worsen in Kosovo throughout the 1980s. The 1986 SANU Memorandum warned that Yugoslavia was suffering from ethnic strife and the disintegration of the Yugoslav economy into separate economic sectors and territories, which was transforming the federal state into a loose confederation. On June 28, 1989, Milošević delivered a speech in front of a large number of Serb citizens at the main celebration marking the 600th anniversary of the Battle of Kosovo, held at Gazimestan. Many think that this speech helped Milošević consolidate his authority in Serbia. In 1989, Milošević, employing a mix of intimidation and political maneuvering, drastically reduced Kosovo's special autonomous status within Serbia. Soon thereafter Kosovo Albanians organized a non-violent separatist movement, employing widespread civil disobedience, with the ultimate goal of achieving the independence of Kosovo. On July 2 1990, an unconstitutional Kosovo parliament declared Kosovo an independent country, the Republic of Kosova. The Republic of Kosova was formally disbanded in 2000 when its institutions were replaced by the Joint Interim Administrative Structure established by the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). During its lifetime, the Republic of Kosova was only recognized by Albania.
The Kosovo War was a conflict between Serbian and Yugoslav security forces and the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA), an ethnic Albanian guerrilla group and a terrorist organisation, supported by NATOseeking secession from the former Yugoslavia. In 1998 western interest increased and the Serbian authorities were forced to sign a unilateral cease-fire and partial retreat. Under an agreement devised by Richard Holbrooke, OSCE observers moved into Kosovo to monitor the ceasefire, while Yugoslav military forces partly pulled out of Kosovo. However, the ceasefire was systematically broken shortly thereafter by KLA forces, which again provoked harsh counterattacks by the Serbs.
NATO intervention between March 24 and June 10 1999, combined with continued skirmishes between Albanian guerrillas and Yugoslav forces resulted in a massive displacement of population in Kosovo. During the conflict roughly a million ethnic Albanians fled or were forcefully driven from Kosovo, several thousand were killed (the numbers and the ethnic distribution of the casualties are uncertain and highly disputed). Some 3,000 people are still missing, of which 2,500 are Albanian, 400 Serbs and 100 Roma.
Recent history (1999 to present)
Main articles: Kosovo (UNMIK) and Kosovo status processAfter the war ended, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 1244 that placed Kosovo under transitional UN administration (UNMIK) and authorized KFOR, a NATO-led peacekeeping force. Resolution 1244 also delivered that Kosovo will have autonomy within Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (today legal successor of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia is Republic of Serbia).
Some 200,000-280,000, representing the vast majority of the Serb population, left when the Serbian forces left. There was also some looting of Serb properties and even violence against some of those Serbs and Roma who remained. The current number of internally displaced persons is disputed, with estimates ranging from 65,000 to 250,000. Many displaced Serbs are afraid to return to their homes, even with UNMIK protection. Around 120,000-150,000 Serbs remain in Kosovo, but are subject to ongoing harassment and discrimination. According to Amnesty International, the aftermarth of the war resulted in an increase in the trafficking of women for sexual exploitation.
In 2001, UNMIK promulgated a Constitutional Framework for Kosovo that established the Provisional Institutions of Self-Government (PISG), including an elected Kosovo Assembly, Presidency and office of Prime Minister. Kosovo held its first free, Kosovo-wide elections in late 2001 (municipal elections had been held the previous year).
In March 2004, Kosovo experienced its worst inter-ethnic violence since the Kosovo War. The unrest in 2004 was sparked by a series of minor events that soon cascaded into large-scale riots.
International negotiations began in 2006 to determine the final status of Kosovo, as envisaged under UN Security Council Resolution 1244. The UN-backed talks, lead by UN Special Envoy Martti Ahtisaari, began in February 2006. Whilst progress was made on technical matters, both parties remained diametrically opposed on the question of status itself.
In February 2007, Ahtisaari delivered a draft status settlement proposal to leaders in Belgrade and Pristina, the basis for a draft UN Security Council Resolution which proposes 'supervised independence' for the province. A draft resolution, backed by the United States, the United Kingdom and other European members of the Security Council, was presented and rewritten four times to try to accommodate Russian concerns that such a resolution would undermine the principle of state sovereignty. Russia, which holds a veto in the Security Council as one of five permanent members, had stated that it would not support any resolution which was not acceptable to both Belgrade and Kosovo Albanians. Whilst most observers had, at the beginning of the talks, anticipated independence as the most likely outcome, others have suggested that a rapid resolution might not be preferable.
After many weeks of discussions at the UN, the United States, United Kingdom and other European members of the Security Council formally 'discarded' a draft resolution backing Ahtisaari's proposal on 20 July 2007, having failed to secure Russian backing. Beginning in August, a "Troika" consisting of negotiators from the European Union (Wolfgang Ischinger), the United States (Frank Wisner) and Russia (Alexander Botsan-Kharchenko) launched a new effort to reach a status outcome acceptable to both Belgrade and Pristina. Despite Russian disapproval, the U.S., the United Kingdom, and France appeared likely to recognize Kosovar independence. A declaration of independence by Kosovar Albanian leaders was postponed until the end of the Serbian presidential elections (4 February 2008). Most EU members and the US had feared that a premature declaration could boost support in Serbia for the ultra-nationalist candidate, Tomislav Nikolic.
Declaration of Independence
Main articles: 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence and International reaction to the 2008 Kosovo declaration of independenceThe Kosovar Assembly approved a declaration of independence on 17 February 2008. Over the following days, several countries (the United States, Turkey, Albania, Austria, Germany, Italy, France, the United Kingdom, Republic of China (Taiwan), Australia and others) announced their recognition, despite protests by Serbia in the UN Security Council.
The UN Security Council remains divided on the question (as of 25 February 2008). Of the five members with veto power, three (USA, UK, France) recognize the declaration of independence, and two (Russia and China) consider it illegal.
The European Union has no official position towards Kosovo's status, but has decided to deploy the European Union Rule of Law Mission in Kosovo to ensure a continuation of international civil presence in Kosovo.
Of Kosovo's immediate neighbour states (other than Serbia), Albania recognizes the declaration of independence, Macedonia announced they will likely recognize it within "a few weeks" and Montenegro stated they will wait for a decision of the European Union.
Serbs, like Russians, are mainly Slavs by ethnicity while Kosovars are mostly ethnic Albanians.

Geography
Main article: Geography of Kosovo
Kosovo has an area of 10,887 square kilometers (4,203 sq mi) and a population of about 2.2 million. The largest cities are Priština, the capital, with an estimated 170,000 inhabitants, Prizren in the south west with a population of 110,000, Peć in the west with 70,000, and Kosovska Mitrovica in the north with 70,000.
The climate in Kosovo is continental, with warm summers and cold and snowy winters. There are two main plains in Kosovo. The Metohija basin is located in the western part of the Kosovo, and the Plain of Kosovo occupies the eastern part.
Much of Kosovo's terrain is mountainous. The Šar Mountains are located in the south and south-east, bordering the Republic of Macedonia. This is one of the region's most popular tourist and skiing resorts, with Brezovica and Prevalac as the main tourist centers. Kosovo's mountainous area, including the highest peak Đeravica, at 2656 m above sea level, is located in the south-west, bordering Montenegro and Albania.
The Kopaonik mountains are located in the north. The central region of Drenica, Crnoljeva and the eastern part of Kosovo, known as Goljak, are mainly hilly areas. There are several notable rivers and lakes in Kosovo. The main rivers are the White Drin, running towards the Adriatic Sea, with the Erenik among its tributaries), the Sitnica, the South Morava in the Goljak area, and Ibar in the north. The main lakes are Gazivoda (380 million m³) in the north-western part, Radonjić (113 million m³) in the south-west part, Batlava (40 million m³) and Badovac (26 million m³) in the north-east part.

List of largest cities in Kosovo (with population figures for 2003-12-31):
- Priština (Prishtina): 165,844
- Prizren : 107,614
- Uroševac (Ferizaj) : 71,758
- Kosovska Mitrovica : 68,929
- Đakovica (Gjakova) : 68,645
- Peć (Peja) : 68,551
- Gnjilane (Gjilan): 55,781
- Vučitrn (Vushtrri) : 39,642
- Podujevo : 37,203
Politics and governance
Main article: Politics of Kosovo See also: United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo and Provisional Institutions of Self-Government| Politics of Kosovo |
|---|
 |
| Constitution and law |
| Executive |
| Legislature |
| Judiciary |
| Administrative divisions |
| Recent elections |
| Foreign policy |
In 1999, UN Security Council Resolution 1244 placed Kosovo under transitional UN administration pending a determination of Kosovo's future status. This Resolution entrusted the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) with sweeping powers to govern Kosovo, but also directed UNMIK to establish interim institutions of self-governance. Resolution 1244 permits Serbia no role in governing Kosovo and since 1999 Serbian laws and institutions have not been valid in Kosovo. NATO has a separate mandate to provide for a safe and secure environment.
In May 2001, UNMIK promulgated the Constitutional Framework, which established Kosovo's Provisional Institutions of Self-Government (PISG). The PISG replaced the Joint Interim Administrative Structure (JIAS) established a year earlier. Since 2001, UNMIK has been gradually transferring increased governing competencies to the PISG, while reserving some powers that are normally carried out by sovereign states, such as foreign affairs. Kosovo has also established municipal government and an internationally-supervised Kosovo Police Service.
According to the Constitutional Framework, Kosovo shall have a 120-member Kosovo Assembly. The Assembly includes twenty reserved seats: ten for Kosovo Serbs and ten for non-Serb minorities (Bosniaks, Roma, etc). The Kosovo Assembly is responsible for electing a President and Prime Minister of Kosovo.
The largest political party in Kosovo, the Democratic League of Kosovo (LDK), has its origins in the 1990s non-violent resistance movement to Miloševic's rule. The party was led by Ibrahim Rugova until his death in 2006. The two next largest parties have their roots in the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA): the Democratic Party of Kosovo (PDK) led by former KLA leader Hashim Thaci and the Alliance for the Future of Kosovo (AAK) led by former KLA commander Ramush Haradinaj. Kosovo publisher Veton Surroi formed his own political party in 2004 named "Ora." Kosovo Serbs formed the Serb List for Kosovo and Metohija (SLKM) in 2004, but have boycotted Kosovo's institutions and never taken their seats in the Kosovo Assembly.
In November 2001, the OSCE supervised the first elections for the Kosovo Assembly. After that election, Kosovo's political parties formed an all-party unity coalition and elected Ibrahim Rugova as President and Bajram Rexhepi (PDK) as Prime Minister.
After Kosovo-wide elections in October 2004, the LDK and AAK formed a new governing coalition that did not include PDK and Ora. This coalition agreement resulted in Ramush Haradinaj (AAK) becoming Prime Minister, while Ibrahim Rugova retained the position of President. PDK and Ora were critical of the coalition agreement and have since frequently accused the current government of corruption.

Ramush Haradinaj resigned the post of Prime Minister after he was indicted for war crimes by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) in March 2005. He was replaced by Bajram Kosumi (AAK). But in a political shake-up after the death of President Rugova in January 2006, Kosumi himself was replaced by former Kosovo Protection Corps commander Agim Ceku. Ceku has won recognition for his outreach to minorities, but Serbia has been critical of his wartime past as military leader of the KLA and claims he is still not doing enough for Kosovo Serbs. The Kosovo Assembly elected Fatmir Sejdiu, a former LDK parliamentarian, president after Rugova's death. Slaviša Petkovic, Minister for Communities and Returns, was previously the only ethnic Serb in the government, but resigned in November 2006 amid allegations that he misused ministry funds. Today two of the total thirteen ministries in Kosovo's Government have ministers from the minorities. Branislav Grbic, ethnic Serb, leads Minister of Returns and Sadik Idriz, ethnic Bosnjak, leads Ministry of Health
Parliamentary elections were held on 17 November 2007. After early results, Hashim Thaçi who was on course to gain 35 per cent of the vote, claimed victory for PDK, the Albanian Democratic Party, and stated his intention to declare independence. Thaci is likely to form a coalition with current President Fatmir Sejdiu's Democratic League which was in second place with 22 percent of the vote. The turnout at the election was particularly low with most Serbs refusing to vote.
Health
Access to health care is free for all residents of Kosovo. Currently there is no health insurance, however, the Ministry of Health is in the process of preparing a legislative infrastructure, which is scheduled to be implemented in 2008.
There are hospitals in all major cities. A total of 6 regional hospitals provide tertiary health care, and family centers in small municipalities.
Medical Education is available at the University Clinical Center of Kosovo (UCCK), in Pristina.
Economy
Main article: Economy of KosovoKosovo has one of the most under-developed economies in Europe, with a per capita income estimated at €1,565 (2004). Despite substantial development subsidies from all Yugoslav republics, Kosovo was the poorest province of Yugoslavia. Additionally, over the course of the 1990s a blend of poor economic policies, international sanctions, poor external commerce and ethnic conflict severely damaged the economy.
Kosovo's economy remains weak. After a jump in 2000 and 2001, growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was negative in 2002 and 2003 and is expected to be around 3 percent 2004-2005, with domestic sources of growth unable to compensate for the declining foreign assistance. Inflation is low, while the budget posted a deficit for the first time in 2004. Kosovo has high external deficits. In 2004, the deficit of the balance of goods and services was close to 70 percent of GDP. Remittances from Kosovars living abroad accounts for an estimated 13 percent of GDP, and foreign assistance for around 34 percent of GDP.
Most economic development since 1999 has taken place in the trade, retail and the construction sectors. The private sector that has emerged since 1999 is mainly small-scale. The industrial sector remains weak and the electric power supply remains unreliable, acting as a key constraint. Unemployment remains pervasive, at around 40-50% of the labor force.
UNMIK introduced de-facto an external trade regime and customs administration on September 3, 1999 when it set customs border controls in Kosovo. All goods imported in Kosovo face a flat 10% customs duty fee. These taxes are collected from all Tax Collection Points installed at the borders of Kosovo, including those between Kosovo and Serbia. UNMIK and Kosovo institutions have signed Free Trade Agreements with Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania and Republic of Macedonia.
The Republic of Macedonia is Kosovo's largest import and export market (averaging €220 million and €9 million, respectively), followed by Serbia-Montenegro (€111 million and €5 million), Germany and Turkey.
The euro is the official currency of Kosovo and used by UNMIK and the government bodies. The Serbian dinar is used in the Serbian-populated parts.
The economy is hindered by Kosovo's still-unresolved international status, which has made it difficult to attract investment and loans. The province's economic weakness has produced a thriving black economy in which smuggled petrol, cigarettes and cement are major commodities. The prevalence of official corruption and the pervasive influence of organised crime gangs has caused serious concern internationally. The United Nations has made the fight against corruption and organised crime a high priority, pledging a "zero tolerance" approach.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Kosovo
According to the Kosovo in Figures 2005 Survey of the Statistical Office of Kosovo, Kosovo's total population is estimated between 1.9 and 2.2 million in the following ethnic proportions:
Islam (mostly Sunni, with a Bektashi minority) is the predominant religion, professed by most of the majority ethnic Albanian population, the Bosniak, Gorani, and Turkish communities, and some of the Roma/Ashkali/Egyptian community. The Serb population, estimated at 100,000 to 120,000 persons, is largely Serbian Orthodox. Approximately 3 percent of ethnic Albanians are Roman Catholic. Catholic communities are concentrated around Catholic churches in Prizren, Klina, and Gjakova. Protestants make up less than 1 percent of the population and have small populations in most cities, with the largest concentration located in Pristina. There are no synagogues or Jewish institutions; there are reportedly two families whose members have Jewish roots. The number of atheists or those who do not practice any religion are difficult to determine, and estimates are largely unreliable.
Ethnic Albanians in Kosovo have the largest population growth in Europe. The people’s growth rate in Kosovo is 1.3%. Over an 82-year period (1921-2003) the population grew 4.6 times. If growth continues at such a pace, based on some estimations, the population will be 4.5 million by 2050.
In 1948 to 1991 period, Serb population on Kosovo incresed for 12% (3 times less than in Serbia), while Albanian population increased for 300% in the same time period.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Subdivisions of Kosovo See also: Municipalities of KosovoKosovo, for administrative reasons, is considered as consisting of seven districts. North Kosovo maintains its own government, infrastructure and institutions by its dominant ethnic Serb population in the Mitrovica District, viz. in the Leposavic, Zvecan and Zubin Potok municipalities and the northern part of Kosovska Mitrovica.
Kosovo is also divided into 30 municipalities :
| Municipalities of Kosovo | ||
|---|---|---|
| District of Ferizaj |  | |
| District of Gjakova | ||
| District of Gjilan | ||
| District of Mitrovica | ||
| District of Peja | ||
| District of Pristina | ||
| District of Prizren | ||
Culture
Music
Main article: Music of Kosovo Further information: Music of SerbiaAlthough in Kosovo the music is diverse (influenced to an extent by the cultures of the various regimes who controlled the region), authentic Albanian music (see World Music) and Serbian music do still exist. Albanian music is characterized by the use of the çiftelia (an authentic Albanian instrument), mandolin, mandola and percussion. In Kosovo, folk music is very popular alongside modern music. There are a number of folk singers and ensembles (both Albanian and Serbian). Classical music is also well known in Kosovo and has been taught at universities (at the University of Priština Faculty of Arts and the University of Priština at Kosovska Mitrovica Faculty of Arts) and several pre-college music schools
There are some notable music festivals in Kosovo:
- Rock për Rock - contains rock and metal music
- Polifest - contains all kinds of genres (usually hip hop and commercial pop)
- Showfest - contains all kinds of genres (usually hip hop and commercial pop)
- Videofest - contains all kinds of genres
- Kush Këndon Lutet Dy Herë - contains Christian music
- North City Jazz & Blues festival, an international music festival held annually in Zvečan (Template:Lang-sq), near Kosovska Mitrovica,
Kosovo Radiotelevisions like RTK, 21 and KTV have their musical charts.
Sport
Several sports federations have been formed in Kosovo within the framework of Law No. 2003/24 "Law on Sport" passed by the Assembly of Kosovo in 2003. The law formally established a national Olympic Committee, regulated the establishment of sports federations and established guidelines for sports clubs. At present only some of the sports federations established have gained international recognition.
Federations that have so far gained membership or recognition by their international governing body:
Federations that have not yet gained international recognition:
- Basketball Federation of Kosovo
- Football Federation of Kosovo and the Kosovo national football team
- Olympic Committee of Kosovo
- Tennis Federation of Kosovo
References
- Enti i Statistikës së Kosovës
- US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice (2008-02-18). "U.S. Recognizes Kosovo as Independent State". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Britain, France recognise Kosovo". Associated Press. 2008-02-18. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Castle, Stephen (2008-02-18). "Kosovo is Recognised by U.S., France and Britain". Retrieved 2008-02-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - See: UN estimate, Kosovo’s population estimates range from 1.9 to 2.4 million. The last two population census conducted in 1981 and 1991 estimated Kosovo’s population at 1.6 and 1.9 million respectively, but the 1991 census probably undercounted Albanians. The latest estimate in 2001 by OSCE puts the number at 2.4 Million. The World Factbook gives an estimate of 2,126,708 for the year 2007 (see "Kosovo". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.).
- BBC News: Kosovo MPs proclaim independence - February 17, 2008
- Elsie, R. (ed.) (2002): "Gathering Clouds. The roots of ethnic cleansing in Kosovo. Early twentieth-century documents". Dukagjini Balkan Books, Peja (Kosovo, Serbia). ISBN 9951-05-016-6
- Treaty of London, 1913
- New York Times 1981-04-19, "One Storm has Passed but Others are Gathering in Yugoslavia"
- Reuters 1986-05-27, "Kosovo Province Revives Yugoslavia's Ethnic Nightmare"
- Christian Science Monitor 1986-07-28, "Tensions among ethnic groups in Yugoslavia begin to boil over"
- New York Times 1987-06-27, "Belgrade Battles Kosovo Serbs"
- SANU (1986): Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts Memorandum. GIP Kultura. Belgrade.
- The Economist, June 05, 1999, U.S. Edition, 1041 words, "What's next for Slobodan Milošević?"
- "Operation Allied Force". NATO.
- Larry Minear, Ted van Baarda, Marc Sommers (2000). "NATO and Humanitarian Action in the Kosovo Crisis" (PDF). Brown University.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Rape victims' babies pay the price of war". The Observer. Guardian News and Media. 2000-04-16. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- KiM Info-Service (07/06/00). "3,000 missing in Kosovo".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "RESOLUTION 1244 (1999)". BBC News. 1999-06-17. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - "Kosovo: The Human Rights Situation and the Fate of Persons Displaced from Their Homes (.pdf) ", report by Alvaro Gil-Robles, Council of Europe Commissioner for Human Rights, Strasbourg, October 16, 2002, p. 30.
- UNHCR, Critical Appraisal of Responsee Mechanisms Operating in Kosovo for Minority Returns, Pristina, February 2004, p. 14.
- U.S. Committee for Refugees (USCR), April 2000, Reversal of Fortune: Yugoslavia's Refugees Crisis Since the Ethnic Albanian Return to Kosovo, p. 2-3.
- "Kosovo: The human rights situation and the fate of persons displaced from their homes (.pdf) ", report by Alvaro Gil-Robles, Council of Europe Commissioner for Human Rights, Strasbourg, October 16, 2002.
- International Relations and Security Network (ISN): Serbians return to Kosovo not impossible, says report (.pdf) , by Tim Judah, June 7, 2004.
- European Stability Initiative (ESI): The Lausanne Principle: Multiethnicity, Territory and the Future of Kosovo's Serbs (.pdf) , June 7, 2004.
- Coordinating Centre of Serbia for Kosovo-Metohija: Principles of the program for return of internally displaced persons from Kosovo and Metohija .
- UNHCR: 2002 Annual Statistical Report: Serbia and Montenegro, pg. 9
- U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants (USCRI): Country report: Serbia and Montenegro 2006.
- Kosovo UN troops 'fuel sex trade', BBC.
- Kosovo: Trafficked women and girls have human rights, Amnesty International.
- Nato force 'feeds Kosovo sex trade', Guardian Unlimited.
- U.S State Department Report, published in 2007.
- "UN frustrated by Kosovo deadlock ", BBC News, October 9, 2006.
- Southeast European Times (29/06/2007). "Russia reportedly rejects fourth draft resolution on Kosovo status".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Southeast European Times (09/07/07). "UN Security Council remains divided on Kosovo".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - James Dancer (30/03/07). "A long reconciliation process is required". Financial Times.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Simon Tisdall (13/11/07). "Bosnian nightmare returns to haunt EU". The Guardian.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6386467.stm
- "Kosovo MPs proclaim independence", BBC News Online, 17 February 2008
- http://www.taipeitimes.com/News/taiwan/archives/2008/02/20/2003402059
- "Recognition for new Kosovo grows", BBC News Online, 18 February 2008
- Independent Commission for Mines and Minerals. "Welcome to the Independent Commission for Mines and Minerals (ICMM), Kosovo".
- City Population. "Kosovo".
- "Kosovo: Serb minister resigns over misuse of funds ", Adnkronos international (AKI), November 27, 2006
- "Sole Kosovo Serb cabinet minister resigns: PM ", Agence France-Presse (AFP), November 24, 2006.
- Fillimi
- EuroNews: Ex-guerrilla chief claims victory in Kosovo election. Retrieved 18 November 2007.
- The World Bank (2006). "Kosovo Brief 2006".
- Christian Science Monitor 1982-01-15, "Why Turbulent Kosovo has Marble Sidewalks but Troubled Industries"
- The World Bank (2006/2007). "World Bank Mission in Kosovo".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - eciks (04/05/06). "May finds Kosovo with 50% unemployed".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ U.S. Commercial Service. "Doing Business in Kosovo".
- Economic Reconstruction and Development in South East Europe. "External Trade and Customs" (PDF).
- B92 (02/10/06). "Croatia, Kosovo sign Interim Free Trade Agreement". mrt.com.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - EU in Kosovo (17/02/06). "UNMIK and Bosnia and Herzegovina Initial Free Trade Agreement" (PDF). UNMIK.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - The World Bank (April 2006). "Kosovo Monthly Economic Briefing: Preparing for next winter" (PDF).
- EU in Kosovo. "Invest in Kosovo".
- BBC News (03/05/05). "Brussels offers first Kosovo loan".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - UNMIK. "Kosovo in figures 2005" (PDF). Ministry of Public Services.
- BBC News (23/12/05). "Muslims in Europe: Country guide".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - BBC News (20/11/07). "Regions and territories: Kosovo".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - International Crisis Group (31/01/01). "Religion in Kosovo".
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - International Religious Freedom Report 2007 (U.S. Department of States) - Serbia (includes Kosovo)
- International Religious Freedom Report 2006 (U.S. Department of States) - Serbia and Montenegro (includes Kosovo)
- Albanian Population Growth
- Demographic explosion in Kosovo
- Kosovo-Hotels, Prishtina - Kosova-Hotels, Prishtinë
Further reading
Malcolm, Noel (1999). Kosovo: A Short History. Harper Perennial. ISBN 0060977752.
See also
- Assembly of Kosovo
- Government of Kosovo
- Prime Minister of Kosovo
- President of Kosovo
- Serbs in Kosovo
- Albanians in Kosovo
- Post and Telecom of Kosovo
- National awakening and the birth of Albania
- Demographic history of Kosovo
- Unrest in Kosovo during March 2004
- Metohija
- North Kosovo
- Flag of Kosovo
- 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence
External links
 Wikimedia Atlas of Kosovo
Wikimedia Atlas of Kosovo- United Nations Interim Administration in Kosovo
- The Government of Kosovo and Prime minister's office
- Assembly of Kosovo
- President of Kosovo
- Serbian Government for Kosovo and Metohija
- The CIA World Factbook
- Visit Kosovo - Tourism Website
- Template:Wikitravel
| Geographic locale | |
|---|---|
| Template:Kosovo |
| Municipalities of Kosovo | ||
|---|---|---|
| District of Ferizaj |  | |
| District of Gjakova | ||
| District of Gjilan | ||
| District of Mitrovica | ||
| District of Peja | ||
| District of Pristina | ||
| District of Prizren | ||