This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Jeff Dahl (talk | contribs) at 02:46, 29 March 2008 (→New Kingdom: we wouldn't want to confuse 18th Dynasty|first dynasty, making the prose smoother). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 02:46, 29 March 2008 by Jeff Dahl (talk | contribs) (→New Kingdom: we wouldn't want to confuse 18th Dynasty|first dynasty, making the prose smoother)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
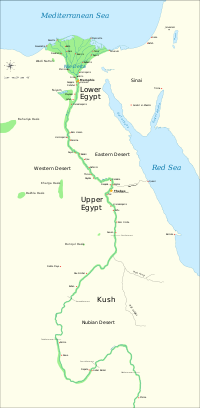
Ancient Egypt was a civilization in eastern North Africa concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in the modern nation of Egypt. The civilization began around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh. Its more than three millennia of history is divided into a series of golden ages, known as Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods. After the end of the last golden age, the New Kingdom, ancient Egyptian civilization entered a period of slow, steady decline, during which Egypt was conquered by a succession of foreign powers. The rule of the pharaohs officially ended in 31 BC when the early Roman Empire conquered Egypt and made it a province.
The civilization of ancient Egypt thrived from adaptation to the conditions of the Nile River Valley, leading to the development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military that defeated foreign enemies. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a divine pharaoh. Ancient Egyptian achievements include a system of mathematics, medicine and architecture, faience and glass technology, literary traditions, irrigation techniques, and the earliest known peace treaty. Egypt left a lasting legacy: art and architecture were copied, and monuments have inspired the imaginations of tourists and writers for centuries. A newfound respect for antiquities and excavations in the modern period led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy.
History
Template:Small Egyptian Dynasty List
Main articles: History of ancient Egypt and History of EgyptBy the late Paleolithic period, the arid climate of northern Africa had become increasingly hot and dry, forcing the populations of the area to concentrate along the Nile valley, and since nomadic hunter-gatherers began living in the region during the Pleistocene some 1.8 million years ago, the Nile has been the lifeline of Egypt. The fertile floodplain of the Nile gave humans the opportunity to develop a settled agricultural economy and a more sophisticated, centralized society that became a cornerstone in the history of human civilization.

Predynastic Period
By about 5500 BC, small tribes living in the Nile valley had developed into a series of unique cultures demonstrating firm control of agriculture and animal husbandry. The earliest were established in Lower Egypt at el-Omari north of Helwan, Merimda in the western Nile Delta, and in the Faiyum region. The Faiyum Neolithic was noted for advanced stone tools which shaped prehistoric lithic industry in Egypt. Faiyum lay at the intersection of three routes: from the Nile Valley itself, from the eastern Sahara and from the Near East, thus displaying characteristics of all three. Merimda was one of the largest northern communities, comparable in size and structure to predynastic Nekhen. In addition to its lithic technology, its culture was characterized by sophisticated forms of vases and pottery ring-stands and ladles, and the stone maceheads that became popular in later Egyptian history.
Many centuries later, the southern predynastic cultures began to establish. They were contemporaneous with later predynastic settlements in northern Egypt, such as Maadi, Buto and Heliopolis. The earliest southern community, Badari, was known for its high quality ceramics, stone tools, and its use of copper. Badarian burials, simple pit graves with signs of social stratification, suggest that the culture was coming under the control of more powerful leaders. In the north, Maadian pottery was a local development, made from Nile silt and occasionally decorated with birds and serekhs bearing the first Horus names. Maadi was also the main source of basalt vessels, whose distribution becomes more widespread in the south after northern Egypt falls under the control of the Upper Egyptian rulers.
The Naqada culture began to expand along the Nile by about 4000 BC. Over a period of about 1000 years, the Naqada culture developed from a few small farming communities into a powerful civilization whose leaders were in complete control of the people and resources of the Nile valley. Establishing a power center at Nekhen, and later at Abydos, Naqada leaders expanded their control of Egypt northwards and engaged in trade with Nubia, the oases of the western desert, and the Levant. Naqada manufactured painted pottery, high quality decorative stone vases, cosmetic palettes, and jewelry made of gold, lapis, and ivory. They also developed a ceramic glaze known as faience, which was used well into the Roman Period to decorate cups, amulets, and figurines. During the last phase of the predynastic, the Naqada culture began using written symbols that evolved into a full system of hieroglyphs for writing the Egyptian language.
Early Dynastic Period

The ancient Egyptians chose to begin their official history with a king named "Meni" (or Menes in Greek) who they believed had united the two kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt. The transition to a unified state actually happened more gradually than the ancient Egyptian writers would have us believe, and there is no contemporary record of Menes. Scholars now believe, however, that the mythical Menes may have actually been the pharaoh Narmer, who is depicted wearing royal regalia on the ceremonial Narmer Palette in a symbolic act of unification. The third century BC Egyptian priest Manetho grouped the long line of pharaohs following Menes into 30 dynasties, a system still in use today.
In the Early Dynastic Period about 3150 BC, the first pharaohs solidified their control over lower Egypt by establishing a capital at Memphis, from which they could control the labor force and agriculture of the fertile delta region as well as the lucrative and critical trade routes to the Levant. The increasing power and wealth of the pharaohs during the early dynastic period was reflected in their elaborate mastaba tombs and mortuary cult structures at Abydos, which were used to celebrate the deified pharaoh after his death. The strong institution of kingship developed by the pharaohs served to legitimize state control over the land, labor, and resources that were essential to the survival and growth of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Old Kingdom

Stunning advances in architecture, art, and technology were made during the Old Kingdom, fueled by the increased agricultural productivity made possible by a well developed central administration. Under the direction of the vizier, state officials collected taxes, coordinated irrigation projects to improve crop yield, drafted peasants to work on construction projects, and established a justice system to maintain peace and order. With the surplus resources made available by a productive and stable economy, the state was able to sponsor construction of colossal monuments and to commission exceptional works of art from the royal workshops. The pyramids built by Djoser, Khufu, and their descendants are the most memorable symbols of ancient Egyptian civilization, and power of the pharaohs that controlled it.
Along with the rising importance of a central administration arose a new class of educated scribes and officials who were granted estates by the pharaoh in payment for their services. Pharaohs also made land grants to their mortuary cults and local temples to ensure that these institutions would have the necessary resources to worship the pharaoh after his death. By the end of the Old Kingdom, five centuries of these feudal practices had slowly eroded the economic power of the pharaoh, who could no longer afford to support a large centralized administration. As the power of the pharaoh diminished, regional governors called nomarchs began to challenge the supremacy of the pharaoh. This, coupled with severe droughts between 2200 and 2150 BC, ultimately caused the country to enter a 140-year period of famine and strife known as the First Intermediate Period.
First Intermediate Period
After Egypt's central government collapsed at the end of the Old Kingdom, the administration could no longer support or stabilize the country's economy. Regional governors could not rely on the king for help in times of crisis, and the ensuing food shortages and political disputes escalated into famines and small-scale civil wars. Yet despite difficult problems, local leaders, owing no tribute to the pharaoh, used their newfound independence to establish a thriving culture in the provinces. Once in control of their own resources, the provinces became economically richer—a fact demonstrated by larger and better burials among all social classes. In bursts of creativity, provincial artisans adopted and adapted cultural motifs formerly restricted to the royalty of the Old Kingdom, and scribes developed literary styles that expressed the optimism and originality of the period.
Free from their loyalties to the pharaoh, local rulers began competing with each other for territorial control and political power. By 2160 BC, rulers in Hierakonpolis controlled Lower Egypt, while a rival clan based in Thebes, Intef I, took control of Upper Egypt. As the Intefs grew in power and expanded their control northward, a clash between the two rival dynasties became inevitable. Around 2055 BC the Theban forces under Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II finally defeated the Herakleopolitan rulers, reuniting the Two Lands and inaugurating a period of economic and cultural renaissance known as the Middle Kingdom.
Middle Kingdom

The pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom restored the country's prosperity and stability, thereby stimulating a resurgence of art, literature, and monumental building projects. Mentuhotep II and his 11th Dynasty successors ruled from Thebes, but the vizier Amenemhet I, upon assuming kingship at the beginning of the 12th Dynasty around 1985 BC, shifted the nation's capital to the city of Itjtawy located in Faiyum. From Itjtawy, the pharaohs of the 12th Dynasty undertook a far-sighted land reclamation and irrigation scheme to increase agricultural output in the region. Moreover, the military reconquered territory in Nubia rich in quarries and gold mines, while laborers built a defensive structure in the Eastern Delta, called the "Walls-of-the-Ruler", to defend against foreign attack.
Having secured military and political security and vast agricultural and mineral wealth, the nation's population, arts, and religion flourished. In contrast to elitist Old Kingdom attitudes towards the gods, the Middle Kingdom experienced an increase in expressions of personal piety and what could be called a democratization of the afterlife, in which all people possessed a soul and could be welcomed into the company of the gods after death. Middle Kingdom literature featured sophisticated themes and characters written in a confident, eloquent style, and the relief and portrait sculpture of the period captured subtle, individual details that reached new heights of technical perfection.
The last great ruler of the Middle Kingdom, Amenemhat III, allowed Asiatic settlers into the delta region to provide a sufficient labor force for his especially active mining and building campaigns. These ambitious building and mining activities, however, combined with inadequate Nile floods later in his reign, strained the economy and precipitated the slow decline into the Second Intermediate Period during the later 13th and 14th dynasties. During this decline, the foreign Asiatic settlers began to seize control of the delta region, eventually coming to power in Egypt as the Hyksos.
Second Intermediate Period and the Hyksos
Around 1650 BC, as the power of the Middle Kingdom pharaohs weakened, Asiatic immigrants living in the Eastern Delta town of Avaris seized control of the region and forced the central government to retreat to Thebes, where the pharaoh was treated as a vassal and expected to pay tribute. The Hyksos ("foreign rulers") imitated Egyptian models of government and portrayed themselves as pharaohs, thus integrating Egyptian elements into their Middle Bronze Age culture.
After their retreat, the Theban kings found themselves trapped between the Hyksos to the north and the Hyksos' Nubian allies, the Kushites, to the south. Nearly 100 years of tenuous inaction followed, and it was not until 1555 BC that the Theban forces gathered enough strength to challenge the Hyksos in a conflict that would last more than 30 years. The pharaohs Seqenenre Tao II and Kamose were ultimately able to defeat the Nubians, but it was Kamose's successor, Ahmose I, who successfully waged a series of campaigns that permanently eradicated the Hyksos' presence in Egypt. In the New Kingdom that followed, the military became a central priority for the pharaohs seeking to expand Egypt’s borders and secure her complete dominance of the Near East.

New Kingdom
The New Kingdom pharaohs established a period of prosperity by securing their borders and strengthening diplomatic ties with their neighbors. Military campaigns waged under Tuthmosis I and his grandson Tuthmosis III extended the influence of the pharaohs into Syria and Nubia, cementing loyalties and opening access to critical imports such as bronze and wood. The New Kingdom pharaohs began a large-scale building campaign to promote the god Amun, whose growing cult was based in Karnak. They also constructed monuments to glorify their own achievements, both real and imagined. The female pharaoh Hatshepsut used such propaganda to legitimize her claim to the throne. Her successful reign was marked by trading expeditions to Punt, an elegant mortuary temple, a colossal pair of obelisks and a chapel at Karnak. Despite her achievements, Hatshepsut's nephew-stepson Tuthmosis III sought to erase her legacy near the end of his reign, possibly in retaliation for her usurping of his throne.

Around 1350 BC, the stability of the New Kingdom was briefly threatened when Amenhotep IV unexpectedly ascended the throne and instituted a series of radical and chaotic reforms. Changing his name to Akhenaten, he touted the previously obscure sun god Aten as the supreme deity, suppressed the worship of other deities, and attacked the power of the priestly establishment. Moving the capital to the new city of Akhetaten (modern-day Amarna), Akhenaten turned a deaf ear to foreign affairs and absorbed himself in his new religion and artistic style. After his death, the cult of the Aten was quickly abandoned, and the subsequent pharaohs Tutankhamun, Aye, and Horemheb quietly erased all mention of Akhenaten's heresy, now known as the Amarna Period.
The 18th Dynasty ended when its last three kings—Tutankhamun, Aye, and Horemheb—all died without an heir. Ramesses II, also known as Ramesses the Great, ascended the throne around 1279 BC at the age of 18 and built more temples, erected more statues and obelisks, and sired more children than any other pharaoh in history. A bold military leader, Ramesses II led his army against the Hittites in the Battle of Kadesh and, after fighting to a stalemate, eventually concluded the first recorded peace treaty in 1258 BC. Egypt's wealth, however, made it a tempting target for invasion, particularly by the Libyans and the Sea Peoples. Initially, the military was able to repel these invasions, but Egypt eventually lost control of Syria and Palestine. The impact of external threats was exacerbated by internal problems such as corruption, tomb robbery and civil unrest. The high priests at the temple of Amun in Thebes accumulated vast tracts of land and wealth, and their growing power splintered the country during the Third Intermediate Period.

Third Intermediate Period
Following the death of Ramesses XI in 1078 BC, Smendes assumed authority over the northern part of Egypt, ruling from the city of Tanis. The southern part was effectively controlled by the High Priests of Amun at Thebes, who recognized Smendes in name and title only. During this time, Libyans had been settling in the western delta, and chieftains of these settlers began increasing their autonomy. Libyan princes took control of the delta under Shoshenq I in 945, founding the so-called Libyan or Bubastite dynasty that would rule for some 200 years. Sheshonq also gained control of southern Egypt by placing his family members in important priestly positions. Libyan control began to erode as a rival dynasty in the delta arose in Leontopolis, and Kushites threatened from the south. Around 727 BC the Kushite king Piye invaded northward, seizing control of Thebes and eventually the Delta.
Egypt's far-reaching prestige declined considerably by the end of the Third Intermediate Period. Its foreign allies had fallen under the Assyrian sphere of influence, and by 700 BC war between the two states became inevitable. Between 671 and 667 BC the Assyrians began their attack on Egypt. The reigns of both Taharqa and his successor, Tanutamun, were filled with constant conflict with the Assyrians, against whom Egypt enjoyed several victories. Ultimately, the Assyrians pushed the Kushites back into Nubia, occupied Memphis, and sacked the temples of Thebes.
Late Period
With no permanent plans for conquest, the Assyrians left control of Egypt to a series of vassals who became known as the Saite kings of the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty. By 653 BC, the Saite king Psamtik I was able to oust the Assyrians with the help of Greek mercenaries, who were recruited to form Egypt's first navy. Greek influence expanded greatly as the city of Naukratis became the home of Greeks in the delta. The Saite kings based in the new capital of Sais witnessed a brief but spirited resurgence in the economy and culture, but in 525 BC, the powerful Persians, led by Cambyses II, began their conquest of Egypt, eventually capturing the pharaoh Psamtik III at the battle of Pelusium. Cambyses II then assumed the formal title of pharaoh, but ruled Egypt from his home of Susa, leaving Egypt under the control of a satrapy. A few successful revolts against the Persians marked the 5th century BC, but Egypt was never able to permanently overthrow the Persians.
Following its annexation by Persia, Egypt was joined with Cyprus and Phoenicia in the sixth satrapy of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. This first period of Persian rule over Egypt, also known as the Twenty-Seventh dynasty, ended in 402 BC, and from 380–343 BC the Thirtieth Dynasty ruled as the last native royal house of dynastic Egypt, which ended with the kingship of Nectanebo II. A brief restoration of Persian rule, sometimes known as the Thirty-First Dynasty, began in 343 BC, but shortly after, in 332 BC, the Persian ruler Mazaces handed Egypt over to Alexander the Great without a fight.
Ptolemaic Dynasty

In 332 BC, Alexander III of Macedon conquered Egypt with little resistance from the Persians and was welcomed by the Egyptians as a deliverer. The Greek government established by Alexander's successors, the Ptolemies, was based on an Egyptian model and based in the new capital city of Alexandria. The city was to showcase the power and prestige of Greek rule, and became a seat of learning and culture, centered at the famous Library of Alexandria. The Lighthouse of Alexandria lit the way for the many ships, which kept trade flowing through the city, as the Ptolemies made commerce and revenue-generating enterprises, such as papyrus manufacturing, their top priority.
Greek culture did not supplant native Egyptian culture, as the Ptolemies supported time-honored traditions in an effort to secure the loyalty of the populace. They built new temples in Egyptian style, supported traditional cults, and portrayed themselves as pharaohs. Some traditions merged, as Greek and Egyptian gods were syncretized into composite deities, such as Serapis, and classical Greek forms of sculpture influenced traditional Egyptian motifs. Despite their efforts to appease the Egyptians, the Ptolemies were challenged by native rebellion, bitter family rivalries, and the powerful mob of Alexandria which had formed following the death of Ptolemy IV. In addition, as Rome relied more heavily on imports of grain from Egypt, the Romans took great interest in the political situation in the country. Continued Egyptian revolting, ambitious politicians, and powerful Syrian opponents made this situation unstable, leading Rome to send forces to secure the country as a province of its empire.

Roman domination
Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire in 30 BC, following the defeat of Marc Antony and Ptolemaic Queen Cleopatra VII by Octavian (later Emperor Augustus) in the Battle of Actium. The Romans relied heavily on grain shipments from Egypt, and the Roman army, under the control of a prefect appointed by the Emperor, quelled rebellions, strictly enforced the collection of heavy taxes, and prevented attacks by bandits, which had become a notorious problem during the period. Alexandria became an increasingly important center on the trade route with the orient, as exotic luxuries were in high demand in Rome.
Although the Romans had a more hostile attitude towards the Egyptians than the Greeks, some traditions such as mummification and worship of the traditional gods continued. The art of mummy portraiture flourished, and some of the Roman emperors had themselves depicted as pharaohs, though not to the extent that the Ptolemies had. The former lived outside Egypt and did not perform the ceremonial functions of Egyptian kingship. Local administration became Roman in style and closed to native Egyptians.
From the mid-first century AD, Christianity took root in Alexandria and spread. Incompatible with paganism, Christianity sought to win converts and threatened popular religious traditions. This led to persecution of converts to Christianity, culminating in the great purges of Diocletian starting in 303 AD, but eventually Christianity won out. As a consequence, Egypt's pagan culture was continually in decline. While the native population continued to speak their language, the ability to read hieroglyphic writing slowly disappeared as the role of the Egyptian temple priests and priestesses diminished. The temples themselves were sometimes converted to churches or abandoned to the desert.
Government and economy
Administration and commerce

The pharaoh was the absolute monarch of the country and, at least in theory, wielded complete control of the land and its resources. The king was also the supreme military commander, who relied on a bureaucracy of officials to manage his affairs. In charge of the administration was his second in command, the vizier, who acted as the king's representative and coordinated land surveys, the treasury, building projects, the legal system, and the archives. At a local level, the country was divided into 42 administrative regions called nomes each governed by a nomarch, who was accountable to the vizier for his jurisdiction. The temples formed the backbone of the economy. Not only were they houses of worship, but were also responsible for collecting and storing the nation's wealth in a system of granaries and treasuries administered by overseers, who distributed grain and goods to the populace.
Much of the economy was centrally organized and strictly controlled. Although the ancient Egyptians did not use coinage until the Late period, they did use a type of money-barter system, with standard sacks of grain and the deben, a weight of roughly 91 grams (3 oz) of copper or silver, forming a common denominator. Workers were paid in grain; a simple laborer might earn 5½ sacks (200 kg or 400 lb) of grain per month, while a foreman might earn 7½ sacks (250 kg or 550 lb). Prices were fixed across the country and recorded in lists to facilitate trading; for example a shirt cost five copper deben, while a cow cost 140 deben. Grain could be traded for other goods, according to the fixed price list. During the 5th century BC coined money was introduced into Egypt from abroad. At first the coins were used as standardized pieces of precious metal rather than true money, but in the following centuries international traders came to rely on coinage.
Social status
Egyptian society was highly stratified, and social status was expressly displayed. Farmers made up the bulk of the population, but agricultural produce was owned directly by the state, temple, or noble family that owned the land. Farmers were also subject to a labor tax and were required to work on irrigation or construction projects in a corvée system. Artists and craftsmen were of higher status than farmers, but they were also under state control, working in the shops attached to the temples and paid directly from the state treasury. Scribes and officials formed the upper class in ancient Egypt, the so-called "white kilt class" in reference to the bleached linen garments that served as a mark of their rank. The upper class prominently displayed their social status in art and literature. Below the nobility were the priests, physicians, and engineers with specialized training in their field. Slavery was known in ancient Egypt, but the extent and prevalence of its practice are unclear.
The ancient Egyptians viewed men and women, including people from all social classes except slaves, as essentially equal under the law, and even the lowliest peasant was entitled to petition the vizier and his court for redress. Both men and women had the right to own and sell property, make contracts, marry and divorce, receive inheritance, and pursue legal disputes in court. Married couples could own property jointly and protect themselves from divorce by agreeing to marriage contracts, which stipulated the financial obligations of the husband to his wife and children should the marriage end. Compared with their counterparts in ancient Greece, Rome, and even more modern places around the world, ancient Egyptian women had a greater range of personal choices and opportunities for achievement. Women such as Hatshepsut and Cleopatra even became pharaohs, while others wielded power as Divine Wives of Amun. Despite these freedoms, ancient Egyptian women did not take part in official roles in the administration, served only secondary roles in the temples, and were not as likely to be as educated as men.

Legal system
The head of the legal system was officially the pharaoh, who was responsible for enacting laws, delivering justice, and maintaining order (ma'at). Although no legal codes from ancient Egypt survive, court documents show that Egyptian law was based on a common-sense view of right and wrong that emphasized reaching agreements and resolving conflicts rather than strictly adhering to a complicated set of statutes. Local councils of elders, known as Kenbet in the New Kingdom, were responsible for ruling in court cases involving small claims and minor disputes. More serious cases involving murder, major land transactions, and tomb robbery were referred to the Great Kenbet, over which the vizier or pharaoh presided. Plaintiffs and defendants were expected to represent themselves and were required to swear an oath that they had told the truth.
Punishment for minor crimes involved either imposition of fines, beatings, facial mutilation, or exile, depending on the severity of the offense. Serious crimes such as murder and tomb robbery were punished by execution, carried out by decapitation, drowning, or impaling the criminal on a stake. Punishment could also be extended to the criminal's family. Beginning in the New Kingdom, oracles played a major role in the legal system, dispensing justice in both civil and criminal cases. The procedure was to ask the god a "yes" or "no" question concerning the right or wrong of an issue. The god, carried by a number of priests, rendered judgment by choosing one or the other, moving forward or backward, or pointing to one of the answers written on a piece of papyrus or an ostracon.
Agriculture
See also: Ancient Egyptian cuisine
A combination of favorable geographical features contributed to the success of ancient Egyptian culture, the most important of which was the rich fertile soil resulting from annual inundations of the Nile river. The ancient Egyptians were thus able to produce an abundance of food, allowing the population to devote more time and resources to cultural, technological, and artistic pursuits. Land management was crucial in ancient Egypt because taxes were assessed based on the amount of land a person owned.
Farming in Egypt was dependent on the cycle of the Nile River. The Egyptians recognized three seasons: Akhet (flooding), Peret (planting), and Shemu (harvesting). The flooding season lasted from June to September, depositing on the river's banks a layer of mineral-rich silt perfect for growing crops. After the floodwaters had receded, the growing season lasted from October to February. Farmers plowed and planted seeds in the fields, which were irrigated with ditches and canals. Egypt received little rainfall, so farmers relied on the Nile to water their crops. From March to May, farmers used sickles to harvest their crops, which were then threshed with a flail to separate the straw from the grain. Winnowing removed the chaff from the grain, and the grain was then ground into flour, brewed to make beer, or stored for later use.
The ancient Egyptians cultivated emmer and barley, and several other cereal grains, all of which were used to make the two main food staples of bread and beer. Flax plants, uprooted before they started flowering, were grown for the fibers of their stems. These fibers were split along their length and spun into thread, which was used to weave sheets of linen and to make clothing. Papyrus growing on the banks of the Nile River was used to make paper. Vegetables and fruits were grown in garden plots, close to habitations and on higher ground, and had to be watered by hand. Vegetables included leeks, garlic, melons, squashes, pulses, lettuce, and other crops, in addition to grapes that were made into wine.

Animals
The Egyptians believed that a balanced relationship between people and animals was an essential element of the cosmic order; thus humans, animals and plants were believed to be members of a single whole. Animals, both domesticated and wild, were therefore a critical source of spirituality, companionship, and sustenance to the ancient Egyptians. Cattle were the most important livestock; the administration collected taxes on livestock in regular censuses, and the size of a herd reflected the prestige and importance of the estate or temple that owned them. In addition to cattle, the ancient Egyptians kept sheep, goats, and pigs. Poultry such as ducks, geese, and pigeons were captured in nets and bred on farms, where they were force-fed with dough to fatten them. The Nile provided a plentiful source of fish. Bees were also domesticated from at least the Old Kingdom, and they provided both honey and wax.
The ancient Egyptians used donkeys and oxen as beasts of burden, and they were responsible for plowing the fields and trampling seed into the soil. The slaughter of a fattened ox was also a central part of an offering ritual. Horses were introduced by the Hyksos in the Second Intermediate Period, and the camel, although known from the New Kingdom, was not used as a beast of burden until the Late Period. Dogs, cats and monkeys were common family pets, while more exotic pets imported from the heart of Africa, such as lions, were reserved for royalty. Herodotus observed that the Egyptians were the only people to keep their animals with them in their houses. During the Predynastic and Late periods, the worship of the gods in their animal form was extremely popular, such as the cat goddess Bastet and the ibis god Thoth, and these animals were bred in large numbers on farms for the purpose of ritual sacrifice.
Natural resources
Further information: Mining in EgyptEgypt is rich in building and decorative stone, copper and lead ores, gold, and semiprecious stones. These natural resources allowed the ancient Egyptians to build monuments, sculpt statues, make tools, and fashion jewelry. Embalmers used salts from the Wadi Natrun for mummification, which also provided the gypsum needed to make plaster. Ore-bearing rock formations were found in distant, inhospitable wadis in the eastern desert and the Sinai, requiring large, state-controlled expeditions to obtain natural resources found there. The Wadi Hammamat was a notable source of granite, greywacke, and gold. Flint was the first mineral collected and used to make tools, and flint handaxes are the earliest pieces of evidence of habitation in the Nile valley. Nodules of the mineral were carefully flaked to make blades and arrowheads of moderate hardness and durability even after copper was adopted for this purpose.
The Egyptians worked deposits of the lead ore galena at Gebel Rosas to make net sinkers, plumb bobs, and small figurines. Copper was the most important metal for toolmaking in ancient Egypt and was smelted in furnaces from malachite ore mined in the Sinai. Workers collected gold by washing the nuggets out of sediment in alluvial deposits, or by the more labor-intensive process of grinding and washing gold-bearing quartzite. Iron deposits found in upper Egypt were utilized in the Late Period. High-quality building stones were abundant in Egypt; the ancient Egyptians quarried limestone all along the Nile valley, granite from Aswan, and basalt and sandstone from the wadis of the eastern desert. Deposits of decorative stones such as porphyry, greywacke, alabaster, and carnelian dotted the eastern desert and were collected even before the First Dynasty. In the Ptolemaic and Roman Periods, miners worked deposits of emeralds in Wadi Sikait and amethyst in Wadi el-Hudi.
Language
Main article: Egyptian languageDevelopment
| ||||||
| r n kmt 'Egyptian language' in hieroglyphs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Egyptian language is a northern Afro-Asiatic language closely related to Berber and Semitic. It has the longest documented history of any language, having remained in written use from c. 3200 BC to the Middle Ages and as a spoken language for longer. Two major phases of the language are identified: Earlier Egyptian comprising Old and Middle Egyptian (Classical Egyptian), and Later Egyptian, which includes the Late, Demotic and Coptic stages of the language. While pre-Coptic writing does not convey dialectal differences, it is likely that Egyptian was spoken in several regional dialects centered around Memphis and later Thebes.
The transition from Earlier to Later Egyptian displays a number of innovations, namely a change from synthetic to more analytic patterns, and the development of different scripts for writing the language. Later Egyptian develops prefixal definite and indefinite articles, which replace the earlier suffix markers of inflectional categories, and undergoes a change from the older VSO word order to SVO. The older Egyptian writing systems, namely the native hieroglyphic, hieratic, and demotic scripts, eventually give way to the more phonetic Coptic alphabet. The last phase of Egyptian, Coptic, continues to be used in the liturgy of the Egyptian Orthodox Church, and traces of it are found in modern Egyptian Arabic.
Sounds and grammar
Egyptian has a phonemic inventory of about 25 consonants similar to those of other Afro-Asiatic languages. These include the characteristic pharyngeal and to a lesser extent emphatic consonants, in addition to voiced and voiceless stops, voiceless fricatives and voiced and voiceless affricates. Three long and three short vowels, which expanded in Later Egyptian to about nine, are distinguished. The basic word in Egyptian, similar to Semitic and Berber, is a triliteral or biliteral root made up of a sequence of consonants and semiconsonants to which several affixes are attached to indicate a morphosyntactic category such as tense, gender, voice and number.
Verbs take finite and non-finite forms. Egyptian finite verbs correspond to the forms of the personal pronouns, yielding a paradigm of 11. The triconsonantal skeleton S-Ḏ-M, for example, is the semantic core of the word 'hear'; its basic conjugation is sḏm=f 'he hears'. In contrast to other Afro-Asiatic languages, a non-finite verb heads a clause if the subject is a noun regardless of its grammatical number. Adjectives are formed derivationally from a noun stem through a process that Egyptologists call nisbation. The typical order of constituents in Egyptian syntax is PREDICATE-SUBJECT in sentences with verbal and adjectival predicates, and SUBJECT-PREDICATE in sentences in which the predicate is a noun phrase or an adpositional phrase. Verb arguments in Egyptian are frequently topicalized and are followed by a coreferential pronoun. Stress falls on the ultimate or penultimate syllable, which can be open (CV) or closed (CVC).
Writing
Main article: Egyptian hieroglyphs
Hieroglyphic writing dates to c. 3200 BC, and is composed of some 500 symbols. Each hieroglyph is a pictogram, such as a bird, tool, or body part that usually corresponds to a letter or letter combination. Hieroglyphs were a formal script, used on stone monuments and in tombs, that could be as detailed as individual works of art. In day-to-day writing, scribes used a cursive form of writing, called hieratic, which was quicker and easier. While formal hieroglyphs may be read in rows or columns in either direction (though typically written from right to left), hieratic was always written from right to left, usually in horizontal rows. A new form of writing, Demotic, became the prevalent writing style, and it is this form of writing—along with formal hieroglyphs—that accompany the Greek text on the Rosetta Stone.
Around the 1st century AD, the native demotic script gave way to the Coptic alphabet, a modified Greek alphabet with the addition of demotic graphemes. Although formal hieroglyphs were used in a ceremonial role until the 4th century AD, towards the end only a small handful of priests could still read them. As the traditional religious establishments were disbanded, knowledge of hieroglyphic writing was mostly lost. Attempts to decipher them date to the Byzantine and Islamic periods in Egypt, but only in 1822, after the discovery of the Rosetta stone and years of research by Thomas Young and Jean-François Champollion, were hieroglyphs almost fully deciphered.

Literature
Main article: Ancient Egyptian literatureWriting first appeared in association with kingship on labels and tags for items found in royal tombs. It was primarily an occupation of the scribes, who worked out of the Per Ankh institution or the House of Life. The latter comprised offices, libraries (called House of Books), laboratories and observatories. Some of the most well-known pieces of ancient Egyptian literature, such as the Pyramid and Coffin Texts, were written in Classical Egyptian, which continued to be the language of writing until about 1300 BC. Later Egyptian was spoken from the New Kingdom onward and is represented in Ramesside administrative documents, love poetry and tales, as well as in Demotic and Coptic texts. During this period, the tradition of writing had evolved into the tomb autobiography, such as those of Harkhuf and Weni. The genre known as Sebayt (Instructions) was developed to communicate teachings and guidance from famous nobles; the Ipuwer papyrus, a poem of lamentations describing natural disasters and social upheaval, is a famous example.
The Story of Sinuhe, written in Middle Egyptian, might be the classic of Egyptian literature. Also written at this time was the Westcar Papyrus, a set of stories told to Khufu by his sons relating the marvels performed by priests. Towards the end of the New Kingdom, the vernacular language was more often employed to write popular pieces like the Story of Wenamun and the Instructions of Ani. The former tells the story of a noble who is robbed on his way to buy cedar from Lebanon and of his struggle to return to Egypt. From about 700 BC, narrative stories and instructions, such as the popular Instructions of Onchsheshonqy, as well as personal and business documents were written in the demotic script and phase of Egyptian. Many stories written in demotic during the Graeco-Roman period were set in previous historical eras, when Egypt was an independent nation and ruled by great pharaohs such as Ramesses II.
Culture
Daily life

Most ancient Egyptians were farmers tied to the land. Their dwellings were restricted to immediate family members, and were constructed of mud-brick designed to remain cool in the heat of the day. Each home had a kitchen with an open roof, which contained a grindstone for milling flour and a small oven for baking bread. Walls were painted white and could be covered with dyed linen wall hangings. Floors were covered with reed mats, and wooden stools, beds raised from the floor, and individual tables comprised the furniture.
The ancient Egyptians placed a great value on hygiene and appearance. Most bathed in the Nile and used a pasty soap made from animal fat and chalk. Men shaved their entire bodies for cleanliness, and aromatic perfumes and ointments covered bad odors and soothed skin. Clothing was made from simple linen sheets that were bleached white, and both men and women of the upper classes wore wigs, jewelry, and cosmetics. Children went without clothing until maturity, at about age 12, and at this age males were circumcised and had their heads shaved. Mothers were responsible for taking care of the children, while the father provided the family's income.
The staple of the diet consisted of bread and beer, supplemented with vegetables such as onions and garlic, and fruit such as dates and figs. Wine and meat were enjoyed by all on feast days while the upper classes indulged on a more regular basis. Fish, meat, and foul could be salted or dried, and could be cooked in stews or roasted on a grill. Music and dance were popular entertainments for those who could afford them. Early instruments included flutes and harps, while instruments similar to trumpets, oboes, and pipes developed later and became popular. In the New Kingdom, the Egyptians played on bells, cymbals, tambourines, and drums and imported lutes and lyres from Asia. The sistrum was a rattle-like musical instrument that was especially important in religious ceremonies.
The ancient Egyptians enjoyed a variety of leisure activities, including games and music. Senet, a board game where pieces moved according to random chance, was particularly popular from the earliest times; another similar game was mehen, which had a circular gaming board. Juggling and ball games were popular with children, and wrestling is also documented in a tomb at Beni Hasan. The wealthy members of ancient Egyptian society enjoyed hunting and boating as well.

Architecture
Main article: Ancient Egyptian architectureThe architecture of ancient Egypt includes some of the most famous structures in the world: the Great Pyramids of Giza and the temples at Thebes. Building projects were organized and funded by the state for religious and commemorative purposes, but also to reinforce the power of the pharaoh. The ancient Egyptians were skilled builders; using simple but effective tools and sighting instruments, architects could build large stone structures with accuracy and precision.
The domestic dwellings of elite and ordinary Egyptians alike were constructed from perishable materials such as mud bricks and wood, and have not survived. Peasants lived in simple homes, while the palaces of the elite were more elaborate structures. A few surviving New Kingdom palaces, such as those in Malkata and Amarna, show richly decorated walls and floors with scenes of people, birds, water pools, deities and geometric designs. Important structures such as temples and tombs that were intended to last forever were constructed of stone instead of bricks. The architectural elements used in the world's first large-scale stone building, Djoser's mortuary complex, include post and lintel supports in the papyrus and lotus motif.
The earliest preserved ancient Egyptian temples, such as those at Giza, consist of single, enclosed halls with roof slabs supported by columns. In the New Kingdom, architects added the pylon, the open courtyard, and the enclosed hypostyle hall to the front of the temple's sanctuary, a style that was standard until the Graeco-Roman period. The earliest and most popular tomb architecture in the Old Kingdom was the mastaba, a flat-roofed rectangular structure of mudbrick or stone built over an underground burial chamber. The step pyramid of Djoser is a series of stone mastabas stacked on top of each other. Pyramids were built during the Old and Middle Kingdoms, but later rulers abandoned them in favor of less conspicuous rock-cut tombs.
Art

The ancient Egyptians produced art to serve functional purposes. For over 3500 years, artists adhered to artistic forms and iconography that were developed during the Old Kingdom, following a strict set of principles that resisted foreign influence and internal change. These artistic standards—simple lines, shapes, and flat areas of color combined with the characteristic flat projection of figures with no indication of spatial depth—created a sense order and balance within a composition. Images and text were intimately interwoven on tomb and temple walls, coffins, stelae, and even statues. The Narmer Palette, for example, displays figures which may also be read as hieroglyphs. Because of the rigid rules that governed its highly stylized and symbolic appearance, ancient Egyptian art served its political and religious purposes with precision and clarity.
Ancient Egyptian artisans used stone to carve statues and fine reliefs, but used wood as a cheap and easily carved substitute. Paints were obtained from minerals such as iron ores (red and yellow ochres), copper ores (blue and green), soot or charcoal (black), and limestone (white). Paints could be mixed with gum arabic as a binder and pressed into cakes, which could be moistened with water when needed. Pharaohs used reliefs to record victories in battle, royal decrees, and religious scenes. Common citizens had access to pieces of funerary art, such as shabti statues and books of the dead, which they believed would protect them in the afterlife. During the Middle Kingdom, wooden or clay models depicting scenes from everyday life became popular additions to the tomb. In an attempt to duplicate the activities of the living in the afterlife, these models show laborers, houses, boats, and even military formations that are scale representations of the ideal ancient Egyptian afterlife.
Despite the homogeneity of ancient Egyptian art, the styles of particular times and places sometimes reflected changing cultural or political attitudes. After the invasion of the Hyksos in the Second Intermediate Period, Minoan-style frescoes were found in Avaris. The most striking example of a politically driven change in artistic forms comes from the Amarna period, where figures were radically altered to conform to Akhenaten's revolutionary religious ideas. This style, known as Amarna art, was quickly and thoroughly erased after Akhenaten's death and replaced by the traditional forms.
Religious beliefs
Main article: Ancient Egyptian religion
Beliefs in the divine and in the afterlife were ingrained in ancient Egyptian civilization from its inception; pharaonic rule was based on the divine right of kings. The Egyptian pantheon was populated by gods who had supernatural powers and were called on for help or protection. However, the gods were not always viewed as benevolent, and Egyptians believed they had to be appeased with offerings and prayers. The structure of this pantheon changed continually as new deities were promoted in the hierarchy, but priests made no effort to organize the diverse and sometimes conflicting creation myths and stories into a coherent system.

Gods were worshiped in cult temples administered by priests acting on the king's behalf. At the center of the temple was the cult statue in a shrine. Temples were not places of public worship or congregation, and only on select feast days and celebrations was a shrine carrying the statue of the god brought out for public worship. Normally, the god's domain was sealed off from the outside world and was only accessible to temple officials. Common citizens could worship private statues in their homes, and amulets offered protection against the forces of chaos. After the New Kingdom, the pharaoh's role as a spiritual intermediary was de-emphasized as religious customs shifted to direct worship of the gods. As a result, priests developed a system of oracles to communicate the will of the gods directly to the people. An oracle could be a statue of a god that could be asked a yes or no question, to which it would "respond" by hidden manipulations of a priest, who could also pose questions behind closed doors. Oracles became very popular for appealing legal verdicts or for justifying military actions and political decisions.
The Egyptians believed that every human being was composed of physical and spiritual parts or aspects. In addition to the body, each person had a šwt (shadow), a ba (personality or soul), a ka (life-force), and a name. The heart, rather than the brain, was considered the seat of thoughts and emotions. After death, the spiritual aspects were released from the body and could move at will, but they required the physical remains (or a substitute, such as a statue) as a permanent home. The ultimate goal of the deceased was to rejoin his ka and ba and become one of the "blessed dead", living on as an akh, or "effective one". In order for this to happen, the deceased had to be judged worthy in a trial, in which the heart was weighed against a "feather of truth". If deemed worthy, the deceased could continue their existence on earth in spiritual form.

Burial customs
Main article: Ancient Egyptian burial customsThe ancient Egyptians maintained an elaborate set of burial customs that they believed were necessary to ensure immortality after death. These customs involved preserving the body by mummification, performing burial ceremonies, and interring, along with the body, goods to be used by the deceased in the afterlife. Before the Old Kingdom, bodies buried in desert pits were naturally preserved by desiccation. The arid, desert conditions continued to be a boon throughout the history of ancient Egypt for the burials of the poor, who could not afford the elaborate burial preparations available to the elite. Wealthier Egyptians began to bury their dead in stone tombs and, as a result, they made use of artificial mummification, which involved removing the internal organs, wrapping the body in linen, and burying it in a rectangular stone sarcophagus or wooden coffin. Beginning in the Fourth Dynasty, some parts were preserved separately in canopic jars.

By the New Kingdom, the ancient Egyptians had perfected the art of mummification; the best technique took 70 days and involved removing the internal organs, removing the brain through the nose, and desiccating the body in a mixture of salts called natron. The body was then wrapped in linen with protective amulets inserted between layers and placed in a decorated anthropoid coffin. Mummies of the Late Period were also placed in painted cartonnage mummy cases. Actual preservation practices declined during the Ptolemaic and Roman eras, while greater emphasis was placed on the outer appearance of the mummy, which was decorated.
Wealthy Egyptians were buried with larger quantities of luxury items, but all burials, regardless of social status, included goods for the deceased. Beginning in the New Kingdom, books of the dead were included in the grave, along with shabti statues that were believed to perform manual labor for them in the afterlife. Rituals in which the deceased was magically re-animated accompanied burials. After burial, living relatives were expected to occasionally bring food to the tomb and recite prayers on behalf of the deceased.
Foreign relations
Trade
The ancient Egyptians engaged in trade with their foreign neighbors to obtain rare, exotic goods not found in Egypt. In the Predynastic Period, they established trade with Nubia to obtain gold and incense. They also established trade with Palestine, as evidenced by Palestinian-style oil jugs found in the burials of the First Dynasty pharaohs. By the Second Dynasty, the ancient Egyptians had established trade with Byblos, a critical source of quality timber not found in Egypt. In the Fifth Dynasty, trade was established with the Land of Punt, which provided gold, aromatic resins, ebony, ivory, and wild animals such as monkeys and baboons.
Egypt relied on trade with Anatolia for essential quantities of tin as well as supplementary supplies of copper, both metals being necessary for the manufacture of bronze. The ancient Egyptians prized the blue stone lapis lazuli, which had to be imported from far-away Afghanistan. Egypt's Mediterranean trade partners also included Greece and Crete, which provided, among other goods, supplies of olive oil. In exchange for its luxury imports and raw materials, Egypt mainly exported grain, gold, linen, and papyrus, in addition to other finished goods including glass and stone objects.
Military
Main article: Military history of Ancient Egypt
The ancient Egyptian military was responsible for defending Egypt against foreign invasion, and for maintaining Egypt's domination in the ancient Near East. The military protected mining expeditions to the Sinai during the Old Kingdom and fought civil wars during the First and Second Intermediate Periods. The military was responsible for maintaining fortifications along important trade routes, such as those found at the city of Buhen on the way to Nubia. Forts also were constructed to serve as military bases, such as the fortress at Sile, which was a base of operations for expeditions to the Levant. In the New Kingdom, a series of pharaohs used the standing Egyptian army to attack and conquer Kush and parts of the Levant.
Typical military equipment included bows and arrows, spears, and round-topped shields made by stretching animal skin over a wooden frame. In the New Kingdom, the military began using chariots that had earlier been introduced by the Hyksos invaders. Weapons and armor continued to improve after the adoption of bronze: shields were now made from solid wood with a bronze buckle, spears were tipped with a bronze point, and the Khopesh was adopted from Asiatic soldiers. The pharaoh was usually depicted in art and literature riding at the head of the army, and there is evidence that at least a few pharaohs, such as Seqenenre Tao II and his sons, did do so. Soldiers were recruited from the general population, but during, and especially after, the New Kingdom, mercenaries from Nubia, Kush, and Libya were hired to fight for Egypt.
Technology, medicine, and mathematics
Main article: Ancient Egyptian technologyIn technology, medicine and mathematics, ancient Egypt achieved a relatively high standard of productivity and sophistication. Traditional empiricism, as evidenced by the Edwin Smith and Ebers papyri (c. 1600 BC), is first credited to Egypt, and the roots of the scientific method can also be traced back to the ancient Egyptians. The Egyptians created their own alphabet and decimal system.

Faience and glass
Even before the Old Kingdom, the ancient Egyptians had developed a glassy material known as faience, which they treated as a type of artificial semi-precious stone. Faience is a non-clay ceramic made of silica, small amounts of lime and soda, and a colorant, typically copper. The material was used to make beads, tiles, figurines, and small wares. Several methods can be used to create faience, but typically production involved application of the powdered materials in the form of a paste over a clay core, which was then fired. By a related technique, the ancient Egyptians produced a pigment known as Egyptian Blue, also called blue frit, which is produced by fusing (or sintering) silica, copper, lime, and an alkali such as natron. The product can be ground up and used as a pigment. The ancient Egyptians could fabricate a wide variety of objects from glass with great skill, but it is not clear whether they developed the process independently. It is also unclear whether they made their own raw glass or merely imported pre-made ingots, which they melted and finished. However, they did have technical expertise in making objects, as well as adding trace elements to control the color of the finished glass. A range of colors could be produced, including yellow, red, green, blue, purple, and white, and the glass could be made either transparent or opaque.
Medicine
Main article: Ancient Egyptian medicine
The medical problems of the ancient Egyptians stemmed directly from their environment. Living and working close to the Nile brought hazards from malaria and debilitating schistosomiasis parasites, which caused liver and intestinal damage. Dangerous wildlife such as crocodiles and hippos were also a common threat. The life-long labors of farming and building put stress on the spine and joints, and traumatic injuries from construction and warfare all took a significant toll on ancient Egyptians. The grit and sand from stone-ground flour abraded teeth, leaving them susceptible to abscesses (though caries were rare). The diets of the wealthy were rich in sugars, which promoted periodontal disease. Despite the flattering physiques portrayed on tomb walls, the overweight mummies of many of the upper class show the effects of a life of overindulgence. Life expectancy was about 35 for men and 30 for women, but reaching adulthood was difficult as about one-third of the population died in infancy.
Ancient Egyptian physicians were renowned in the ancient Near East for their healing skills. Herodotus remarked that there was a high degree of specialization among Egyptian physicians, with some treating only the head or the stomach, while others were eye-doctors and dentists. One of the earliest Egyptian physicians who came to have profound influence on the history of Egyptian medicine was Imhotep. Training of physicians took place at the Per Ankh or the House of Life institution, most notably those headquartered in Per-Bastet during the New Kingdom and at Abydos and Saïs in the Late period. Medical papyri show empirical knowledge of the human anatomy, injuries, including different types of fractures, and how to treat them. Wounds were treated by bandaging with raw meat, white linen, sutures, nets, pads and swabs soaked with honey to prevent infection, while opium was used to relieve pain. Garlic and onions were used regularly to promote good health and were thought to relieve asthma symptoms. Ancient Egyptian surgeons stitched wounds, set broken bones, and amputated diseased limbs, but they recognized that some injuries were so serious that they could only make the patient comfortable until he died.
Mathematics
Main article: Egyptian mathematicsUnderstanding of Egyptian mathematics is incomplete due to paucity of available material and lack of exhaustive study of the texts that have been uncovered. The earliest attested examples of mathematical calculations date to the predynastic Naqada period, and they show the same numbering system that was later used. The importance of mathematics to an educated Egyptian is suggested by a New Kingdom fictional letter in which the writer proposes a scholarly competition between himself and another scribe regarding the mathematical knowledge required to undertake everyday tasks such as accounting of land, labor and grain. Texts such as the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus and the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus show that the ancient Egyptians could perform the four basic mathematical operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division—use fractions, compute the volumes of boxes and pyramids, and calculate the surface areas of rectangles, triangles, circles and even spheres. They understood basic concepts of algebra and geometry, and could solve simple sets of simultaneous equations.
| ||
| 2⁄3 in hieroglyphs | ||
|---|---|---|
Mathematical notation was decimal, and based on hieroglyphic signs for each power of ten up to one million. Each of these could be written as many times as necessary to add up to the desired number; so to write the number eighty or eight hundred, the symbol for ten or one hundred was written eight times respectively. Because ancient Egyptian methods of calculation could not handle most fractions with a numerator greater than one, these types of fractions had to be written as the sum of several fractions. For example, the fraction 2⁄5 was resolved into the sum of 1⁄3 + 1⁄15; this was facilitated by standard tables of values. Some common fractions, however, were written with a special glyph; the equivalent of the modern 2⁄3 is shown on the right.
The Egyptians had a grasp of the principles underlying the Pythagorean theorem such that they knew that a triangle had a right angle opposite the hypotenuse when its sides were of a 3-4-5 ratio. They were able to get very close to the value of the area of a circle by subtracting 1⁄9 of its diameter and squaring the result. In modern notation, this would be expressed as Area ≈ , yielding a result of 256⁄81 ≈ 3.16 as compared to the modern approximation 3.14. The golden ratio seems to be reflected in many Egyptian constructions, including the pyramids, but its use may have been an unintended consequence of the ancient Egyptian practice of combining the use of knotted ropes with an intuitive sense of proportion and harmony.
Legacy

The culture and monuments of ancient Egypt have left a lasting legacy on the world. The cult of the goddess Isis, for example, became popular in the Roman empire, as obelisks and other relics were transported back to Rome. The Romans also imported building materials from Egypt to erect structures in Egyptian style. Early historians such as Herodotus, Strabo, Diodorus Siculus and Pliny the Elder were fascinated by Egypt and studied and wrote about the land. During the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, the pagan culture of ancient Egypt was in decline after the rise of Christianity and later Islam, but interest in Egyptian antiquity continued as evidenced in the writings of medieval Islamic scholars such as Dhul-Nun al-Misri and al-Maqrizi.
In the 17th and 18th centuries, European travelers and tourists brought back antiquities and wrote stories of their journeys, leading to a wave of Egyptomania that swept across Europe. This renewed interest sent travelers and museum collectors into Egypt, who took, purchased, or were given many important antiquities. Although the European colonial occupation of Egypt destroyed a significant portion of the country's historical legacy, some collection programs had more positive results. Napoleon, for example, arranged the first studies in Egyptology when he brought some 150 scientists and artists to study and document Egypt's natural history, which was published in the Description de l'Ėgypte. The decipherment of hieroglyphs in 1822 was also a great step in the modern scientific investigation of ancient Egyptian civilization. In 19th century, the Egyptian Government and archaeologists alike recognized the importance of cultural respect and integrity in excavations. The Supreme Council of Antiquities now approves and oversees all excavations, and supervises museums and monument reconstruction programs designed to preserve the historical legacy of ancient Egypt.
Notes and references
References
- Only after 664 BC are dates secure. See Egyptian chronology for details. "Chronology". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- Dodson (2004) p. 46
- Clayton (1994) p. 217
- James (2005) p. 8
- Clayton (1994) p. 153
- James (2005) p. 84
- Shaw (2002) p. 17
- Shaw (2002) pp. 17, 67–69
- Hayes (1964) p. 220
- Midant-Reynes (2000) p. 106
- Hayes (1964) p. 230
- Midant-Reynes (2000) pp. 210–19
- "The Badarian Civilisation". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Shaw (2002) p. 39
- Midant-Reynes (2000) p. 211
- Mallory-Greenough (2002), p. 84
- "Chronology of the Naqada Period". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Shaw (2002) p. 61
- "Faience in different Periods". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Allen (2000) p. 1
- Robins (1997) p. 32
- Shaw (2002) pp. 78–80
- Clayton (1994) pp. 12–13
- Clayton (1994) p. 6
- Shaw (2002) p. 70
- "Early Dynastic Egypt". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- James (2005) p. 40
- Shaw (2002) p. 102
- Shaw (2002) pp. 116–7
- Fekri Hassan. "The Fall of the Old Kingdom". British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
- Clayton (1994) p. 69
- Shaw (2002) p. 120
- ^ Shaw (2002) p. 146
- Clayton (1994) p. 29
- Shaw (2002) p. 148
- Clayton (1994) p. 79
- Shaw (2002) p. 158
- Shaw (2002) pp. 179–82
- Robins (1997) p. 90
- Shaw (2002) p. 188
- ^ Ryholt (1997) p. 310
- Shaw (2002) p. 189
- Shaw (2002) p. 224
- James (2005) p. 48
- "Hatshepsut". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2007-12-09.
- Clayton (1994) p. 108
- Aldred (1988) p. 259
- Cline (2001) p. 273
- From his two principal wives and large harem, Ramesses II sired more than 100 children. Clayton (1994) p. 146
- Tyldesley (2001) pp. 76–7
- James (2005) p. 54
- Cerny (1975) p. 645
- Shaw (2002) p. 345
- Shaw (2002) p. 358
- Shaw (2002) p. 383
- Shaw (2002) p. 385
- Shaw (2002) p. 405
- Shaw (2002) p. 411
- Shaw (2002) p. 418
- James (2005) p. 62
- James (2005) p. 63
- Shaw (2002) p. 426
- ^ Shaw (2002) p. 422
- Shaw (2002) p. 441
- Shaw (2002) p. 445
- ^ Manuelian (1998) p. 358
- Manuelian (1998) p. 363
- Meskell (2004) p. 23
- ^ Manuelian (1998) p. 372
- Walbank (1984) p. 125
- Manuelian (1998) p. 383
- James (2005) p. 136
- Billard (1978) p. 109
- "Social classes in ancient Egypt". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2007-12-11.
- ^ Janet H. Johnson. "Women's Legal Rights in Ancient Egypt". University of Chicago. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Oakes (2003) p. 472
- McDowell (1999) p. 168
- Manuelian (1998) p. 361
- Nicholson (2000) p. 514
- Nicholson (2000) p. 506
- Nicholson (2000) p. 510
- Nicholson (2000) pp. 577 and 630
- ^ Strouhal (1989) p. 117
- ^ Manuelian (1998) p. 381
- Nicholson (2000) p. 409
- Oakes (2003) p. 229
- Greaves (1929) p. 123
- Lucas (1962) p. 413
- Nicholson (2000) p. 28
- Scheel (1989) p. 14
- Nicholson (2000) p. 166
- Nicholson (2000) p. 51
- Loprieno (1995b) p. 2137
- Loprieno (2004) p. 161
- Loprieno (2004) p. 162
- Loprieno (1995b) p. 2137-38
- Vittman (1991) pp. 197–227
- Loprieno (1995a) p. 46
- Loprieno (1995a) p. 74
- Loprieno (2004) p. 175
- Allen (2000) pp. 67, 70, 109
- Loprieno (2005) p. 2147
- Loprieno (2004) p. 173
- Allen (2000) p. 13
- Allen (2000) p. 7
- Loprieno (2004) p. 166
- El-Daly (2005) p. 164
- Allen (2000) p. 8
- Strouhal (1989) p. 235
- Lichtheim (1975) p. 11
- Lichtheim (1975) p. 215
- Lichtheim (1980) p. 159
- Manuelian (1998) p. 401
- Manuelian (1998) p. 403
- Manuelian (1998) p. 405
- Manuelian (1998) pp. 406–7
- Manuelian (1998) pp. 399–400
- "Music in Ancient Egypt". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Manuelian (1998) p. 126
- Clarke (1990) pp. 94–7
- Badawy (1968) p. 50
- "Types of temples in ancient Egypt". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Dodson (1991) p. 23
- Robins (1997) p. 29
- Robins (1997) p. 21
- Robins (2001) p. 12
- Nicholson (2000) p. 105
- ^ James (2005) p. 122
- Robins (1998) p. 74
- Shaw (2002) p. 216
- Robins (1998) p. 149
- Robins (1998) p. 158
- James (2005) p. 102
- James (2005) p. 117
- ^ Shaw (2002) p. 313
- Allen (2000) pp. 79, 94–5
- Wasserman, et al (1994) pp. 150–3
- "Mummies and Mummification: Old Kingdom". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- "Mummies and Mummification: Late Period, Ptolemaic, Roman and Christian Period". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- "Shabtis". Digital Egypt for Universities, University College London. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- James (2005) p. 124
- Shaw (2002) p. 72
- Shaw (2002) p. 322
- Manuelian (1998) p. 145
- Harris (1990) p. 13
- Shaw (2002) p. 245
- Manuelian (1998) pp. 366–7
- Clayton (1994) p. 96
- Shaw (2002) p. 400
- Nicholson (2000) p. 177
- Nicholson (2000) p. 109
- Nicholson (2000) p. 195
- Nicholson (2000) p. 215
- Filer (1995) p. 94
- Filer (1995) pp. 78–80
- Filer (1995) p. 21
- Filer (1995) p. 25
- Filer (1995) p. 39
- Strouhal (1989) p. 243
- Stroual (1989) pp. 244–46
- Stroual (1989) p. 250
- "Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus Translation". Retrieved 2008-03-01.
- Imhausen et al. (2007) p. 7
- Imhausen et al. (2007) p. 13
- Imhausen et al. (2007) p. 11
- Clarke (1990) p. 222
- Clarke (1990) p. 217
- Clarke (1990) p. 218
- Gardiner (1957) p. 197
- ^ Strouhal (1989) p. 241
- Imhausen et al. (2007) p. 31
- "The Egyptian Pyramids - Mathematics and the Liberal Arts". Truman State University. Retrieved 2008-03-09.
- Kemp (1989) p. 138
- Siliotti (1998) p. 8
- Siliotti (1998) p. 10
- El-Daly (2005) p. 112
- Siliotti (1998) p. 13
- Siliotti (1998) p. 100
Bibliography
- Aldred, Cyril (1988). Akhenaten, King of Egypt. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05048-1.
- Allen, James P. (2000). Middle Egyptian : An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-77483-7.
- Andrews, Carol (1994). Amulets of ancient Egypt. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-70464-X.
- Badawy, Alexander (1968). A History of Egyptian Architecture. Vol III. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-00057-9.
- Baines, John and Jaromir Malek (2000). The Cultural Atlas of Ancient Egypt (revised edition ed.). Facts on File. ISBN 0816040362.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Bard, KA (1999). Encyclopedia of the Archaeology of Ancient Egypt. NY, NY: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-18589-0.
- Bierbrier, Morris (1984). The Tomb Builders of the Pharaohs. New York, NY: Charles Scribner's Sons. ISBN 0-684-18229-7.
- Billard, Jules B. (1978). Ancient Egypt: Discovering its Splendors. Washington D.C.: National Geographic Society.
- Booth, Charlotte (2005). The Hyksos Period in Egypt. Shire Egyptology. ISBN 0-7478-0638-1.
- Bowman, Alan K (1996). Egypt after the Pharaohs 332 BC – AD 642 (2nd ed. ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 25–26. ISBN 0520205316.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Cerny, J (1975). Egypt from the Death of Ramesses III to the End of the Twenty-First Dynasty' in The Middle East and the Aegean Region c.1380–1000 BC. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-08691-4.
- Clarke, Somers (1990). Ancient Egyptian Construction and Architecture. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-26485-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|couthors=ignored (help) - Clayton, Peter A. (1994). Chronicle of the Pharaohs. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05074-0.
- Cline, Eric H.; O'Connor, David Kevin (2001). Amenhotep III: Perspectives on His Reign. Ann Arbor, Mich: University of Michigan Press. p. 273. ISBN 0-472-08833-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Dodson, Aidan (1991). Egyptian Rock Cut Tombs. Buckinghamshire, UK: Shire Publications Ltd. ISBN 0-7478-0128-2.
- Dodson, Aidan (2004). The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0500051283.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Edgerton, William F. (1951). "The Strikes in Ramses III's Twenty-Ninth Year". JNES 10 (No. 3 ed.).
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - El-Daly, Okasha (2005). Egyptology: The Missing Millennium. London: UCL Press. ISBN 1-844-72062-4.
- Filer, Joyce (1996). Disease. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-72498-5.
- Gardiner, Sir Alan (1957). Egyptian Grammar: Being an Introduction to the Study of Hieroglyphs. Oxford: Griffith Institute. ISBN 0-900416-35-1.
- Gillings, Richard J. (1972). Mathematics in the Time of the Pharaohs. New York. ISBN 048624315X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|publiser=ignored (|publisher=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Greaves, R.H. (1929). Gold Resources of Egypt, Report of the XV International Geol. Congress, South Africa.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Grimal, Nicolas (1992). A History of Ancient Egypt. Blackwell Books. ISBN 0631193960.
- Hölbl, Günther (trans. Tina Saavedra) (2001). A History of the Ptolemaic Empire. London: Routledge. ISBN 0415234891.
- Harris, Geraldine (1990). Ancient Egypt. New York: Facts on File. ISBN 0-8160-1971-1.
- Hayes, W. C. (1964). "Most Ancient Egypt: Chapter III. The Neolithic and Chalcolithic Communities of Northern Egypt". JNES (No. 4 ed.): 217–272.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|vol=ignored (|volume=suggested) (help) - Imhausen, Annette (2007). The Mathematics of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, India, and Islam: A Sourcebook. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-11485-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - James, T.G.H. (2005). The British Museum Concise Introduction to Ancient Egypt. Ann Arbor, Mich: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-03137-6.
- Kemp, Barry (1991). Ancient Egypt: Anatomy of a Civilization. Routledge. ISBN 0415063469.
- Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson (1996). The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100–650 BC) (3rd ed. ed.). Warminster: Aris & Phillips Limited. ISBN 0856682985.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Lehner, Mark (1997). The Complete Pyramids. London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0500050848.
- Lichtheim, Miriam (1975). Ancient Egyptian Literature, vol 1. London, England: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-02899-6.
- Lichtheim, Miriam (1980). Ancient Egyptian Literature, A Book of Readings. Vol III: The Late Period. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-24844-1.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: checksum (help) - Loprieno, Antonio (1995a). Ancient Egyptian: A linguistic introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-44849-2.
- Loprieno, Antonio (1995b), "Ancient Egyptian and other Afroasiatic Languages", in Sasson, J. M. (ed.), Civilizations of the Ancient Near East, vol. 4, New York: Charles Scribner, pp. 2137–2150, ISBN 1-565-63607-4
- Loprieno, Antonio (2004), "Ancient Egyptian and Coptic", in Woodward, Roger D. (ed.), The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 160–192, ISBN 0-52-156256-2
- Clayton, Peter A. (1994). Chronicle of the Pharaohs. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05074-0.
- Lucas, Alfred (1962). Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, 4th Ed. London: Edward Arnold Publishers. ISBN 1854170465.
- Mallory-Greenough, Leanne M. (2002). "The Geographical, Spatial, and Temporal Distribution of Predynastic and First Dynasty Basalt Vessels". The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology. 88. London: Egypt Exploration Society: 67–93.
- Manuelian, Peter Der (1998). Egypt: The World of the Pharaohs. Bonner Straße, Cologne Germany: Könemann Verlagsgesellschaft mbH. ISBN 3-89508-913-3.
- McDowell, A. G. (1999). Village life in ancient Egypt: laundry lists and love songs. Oxford : Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-814998-0.
- Meskell, Lynn. Object Worlds in Ancient Egypt: Material Biographies Past and Present (Materializing Culture). Oxford, UK: Berg Publishers. ISBN 1-85973-867-2.
- Midant-Reynes, Béatrix (2000). The Prehistory of Egypt: From the First Egyptians to the First Pharaohs. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 0-631-21787-8.
- Myśliwiec, Karol (2000). The Twighlight of Ancient Egypt: First Millennium B.C.E. (trans. by David Lorton). Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801486300.
- Nicholson, Paul T.; et al. (2000). Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521452570.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - Oakes, Lorna (2003). Ancient Egypt: An Illustrated Reference to the Myths, Religions, Pyramids and Temples of the Land of the Pharaohs. New York: Barnes & Noble. ISBN 0-7607-4943-4.
- Robins, Gay (2000). The Art of Ancient Egypt. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00376-4.
- Ryholt, Kim (1997). The Political Situation in Egypt During the Second Intermediate Period. Museum Tusculanum. ISBN 8772894210.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Scheel, Bernd (1989). Egyptian Metalworking and Tools. Haverfordwest, Great Britain: Shire Publications Ltd. ISBN 0747800014.
- Shaw, Ian (2003). The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-500-05074-0.
- Siliotti, Alberto (1998). The Discovery of Ancient Egypt. Edison, New Jersey: Book Sales, Inc. ISBN 0-7858-1360-8.
- Simpson (2003). Simpson, William Kelly (ed.). The Literature of Ancient Egypt. Ritner, Tobin & Wente. New Haven & London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300099207.
- Stanwick, Paul Edmond (2003). Portraits of the Ptolemies: Greek kings as Egyptian pharaohs. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0292777728.
- Stierlin, Anne; Stierlin, Henri. The Pharaohs Master-Builders. Vilo International. ISBN 2-87939-020-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Strouhal, Eugen (1989). Life in Ancient Egypt. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-2475-x.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Tyldesley, Joyce A. (2001). Ramesses: Egypt's greatest pharaoh. Harmondsworth : Penguin. pp. 76–77. ISBN 0-14-028097-9.
- Vittman, G. (1991). "Zum koptischen Sprachgut im Ägyptisch-Arabisch". Wiener Zeitschrift für die Kunde des Morgenlandes. 81. Vienna: Institut für Orientalistik, Vienna University: 197–227.
- Walbank, Frank William (1984). The Cambridge ancient history. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-23445-X.
- Wasserman, James; Faulkner, Raymond Oliver; Goelet, Ogden; Von Dassow, Eva (1994). The Egyptian Book of the dead, the Book of going forth by day: being the Papyrus of Ani. San Francisco: Chronicle Books. ISBN 0-8118-0767-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wilkinson, R. H. (2000). The Complete Temples of Ancient Egypt. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0500051003.
- Wilkinson, R.H. (2003). The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0500051208.
- Yurco, Frank J. (1999). "End of the Late Bronze Age and Other Crisis Periods: A Volcanic Cause". SAOC 58.
External links
- Ancient Egypt – maintained by the British Museum, this site provides a useful introduction to Ancient Egypt for older children and young adolescents
- BBC History: Egyptians – provides a reliable general overview and further links
- Texts from the Pyramid Age Door Nigel C. Strudwick, Ronald J. Leprohon, 2005, Brill Academic Publishers
- Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book Door Marshall Clagett, 1989
- Digital Egypt for Universities. Outstanding scholarly treatment with broad coverage and excellent cross references (internal and external). Artifacts used extensively to illustrate topics.
- Ancient Egyptian Metallurgy A site that shows the history of Egyptian metalworking
