This is an old revision of this page, as edited by NER~enwiki (talk | contribs) at 23:16, 6 September 2005 (→Storm development). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:16, 6 September 2005 by NER~enwiki (talk | contribs) (→Storm development)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. Feel free to improve this article or discuss changes on the talk page, but please note that updates without valid and reliable references will be removed. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- This article is about the 2005 hurricane. For other storms with this name, see Hurricane Katrina (disambiguation).
| Duration | Aug. 23 - 31, 2005 |
|---|---|
Hurricane Katrina, one of the worst natural disasters in U.S. history, devastated the Gulf Coast of the United States from New Orleans, Louisiana to Mobile, Alabama. Katrina made landfall in the early morning of August 29, 2005. The hurricane is believed to have killed thousands of people, and known to have displaced more than 1 million — a humanitarian crisis on a scale unseen in the U.S. since the American Civil War.
Katrina, a tropical cyclone, developed from a tropical wave about 175 miles east of Nassau, Bahamas. The hurricane strengthened to Category 1 before making landfall on the Miami-Dade/Broward county line in Florida on August 25. Katrina moved southwest across Florida and west into the Gulf of Mexico, where it intensified rapidly to Category 5. In the early morning of August 29, Katrina made its second landfall near Buras, Louisiana as a Category 4 storm featuring 145-mph winds, and its eyewall passed over the eastern edge of New Orleans as the hurricane made its way to water once again. A few hours later, it made landfall for a third time near the Louisiana/Mississippi border with 125-mph Category 3 winds. Katrina weakened thereafter, losing "hurricane" status more than 100 miles inland, near Laurel, Mississippi. It was downgraded to a tropical depression near Clarksville, Tennessee and continued to race northward.
As the hurricane approached landfall near New Orleans, Mayor Ray Nagin placed the city under a mandatory evacuation order. Many residents remained in the city. The vast majority of those who stayed were reported to have been unable to leave because they did not have vehicles, money for gas and other transportation. Also, many residents were unable to travel because they were elderly or infirm. As a result, the Louisiana Superdome was opened as a temporary shelter for those that were to stay in the city, though the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) failed to provide any provisions for those seeking shelter. Federal disaster declarations blanketed 90,000 square miles (233,000 km²) of the United States, an area almost as large as the United Kingdom. The hurricane left an estimated five million people without power, and it may be up to two months before all power is restored. Disaster relief plans are in operation in the affected areas.
Early in the morning of August 30 2005 and as a direct result of Hurricane Katrina, breaches in three places of the levee system on the Lake Pontchartrain side of New Orleans caused a second and even greater disaster. Heavy flooding covered almost the entire city over a sustained period, forcing the total evacuation of over a million people. Because 80% of the city's area is below sea level, all water that goes into the city must be directly pumped out--even water from an average rainstorm. Consequently, the city is now uninhabitable until the water is removed at the earliest.
On September 3, 2005 US Homeland Security Secretary Michael Chertoff described the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina as "probably the worst catastrophe, or set of catastrophes" in the country's history, referring to the Hurricane itself plus the flooding of New Orleans.
Hurricane Katrina may be the deadliest hurricane in the United States since the Galveston Hurricane of 1900, which killed around 8,000 (possibly up to 12,000) people. As of 7 PM CDT September 1, 2005, more than 20,000 are still reported missing. New Orleans mayor Ray Nagin stated on August 31 that the death toll of Katrina may be "in the thousands", an estimate also provided through a statement by Louisiana Governor Kathleen Blanco on September 1. Accurate numbers are not known. Damage was reported in at least 12 states. Hurricane Katrina will be remembered for its vast devastation of the Gulf Coast regions of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. The hurricane will also be remembered for the ineffective planning for hurricane preparedness, as well as the slow response on the part of federal, state and local governments to provide effective search and rescue and safe refuge for the storm's victims.
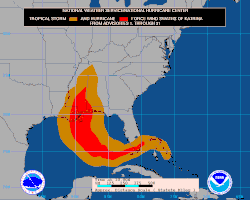
Storm development
| Hurricane Katrina |
|---|
 |
| 2005 Atlantic hurricane season |
| General |
| Impact |
| Relief |
| Analysis |
| External links |
|
The U.S. National Hurricane Center (NHC) issued a lucid statement on August 23 saying that Tropical Depression Twelve had formed over the southeastern Bahamas. The numbering of the system was debated, as Tropical Depression Twelve formed partially from the remains of Tropical Depression Ten. The naming and numbering rules at the NHC require a system to keep the same identity if it dies, then regenerates, which would normally have caused this storm to remain numbered Ten. However, the NHC gave this storm a new number because a second disturbance merged with the remains of Tropical Depression Ten on August 20, and there is no way to tell whether the remnants of T.D. Ten should be credited with this storm. (This is different from Hurricane Ivan in the 2004 season, when the NHC ruled that Ivan did indeed reform; the remnant of Ivan that regenerated in the Gulf of Mexico was a distinct system from the moment Ivan originally dissipated to the moment it regained tropical storm strength.) The system was upgraded to Tropical Storm Katrina on the morning of August 24. Katrina became the fourth hurricane of the 2005 season on August 25 and made landfall later that day around 6:30 p.m. between Hallandale Beach and Aventura, Florida.

On August 27, the storm was upgraded to category 3 intensity (major hurricane) and at 12:40 a.m. CDT (0540 UTC) on August 28, Katrina was upgraded to Category 4. Later that morning, Katrina went through a period of rapid intensification, with its maximum sustained winds peaking at 175 mph (280 km/h) (well above the Category 5 threshold of 156 mph (250 km/h)), gusts of 215 mph (344 km/h) and central pressure of 906 mb by 1:00 p.m. CDT. It later reached a minimum pressure of 902 mb, making it the fourth most intense Atlantic Basin hurricane on record. NER 23:16, 6 September 2005 (UTC)Minor edit of sentence structure at landfall The storm weakened just before landfall on August 29 as a Category 4 hurricane with winds of 145 mph at 6:10 a.m. CDT near Buras-Triumph, Louisiana.
Katrina, which affected a very wide swath of land covering a large portion of eastern North America, was last seen in the eastern Great Lakes region on August 31. Before being absorbed by the frontal boundary, Katrina's last known position was over southeast Quebec and northern New Brunswick.
Its lowest minimum pressure at landfall was 918 mb, making it the third strongest hurricane on record to make landfall on the United States. A 15 to 30 foot (5 to 9 m) storm surge came ashore on virtually the entire coastline from Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama to Florida. The 30 foot (10 m) storm surge recorded at Biloxi, Mississippi is the highest ever observed in America.
At 11 p.m. EDT on August 31 (0300 UTC, September 1), U.S. government weather officials announced that the center of the remnant low of what was Katrina had been completely absorbed by a frontal boundary in southeastern Canada, with no discernible circulation. The Hydrometeorological Prediction Center's last public advisory on Katrina was at 11 p.m. EDT Wed 31 August 2005 and the Canadian Hurricane Centre's last public advisory on Katrina was at 8 a.m. EDT Wed 31 August 2005.
Tornadoes

There were tornado reports near Adams and Cumberland Counties in Pennsylvania, in Fauquier, Virginia, in Atlanta, Georgia, in Carroll County, Georgia, in Carrollton, Georgia, in White County, Georgia, in Helen, Georgia, and in Mobile, Alabama. No deaths were reported from the tornadoes, but several injuries were reported in Georgia. 500,000 chickens were killed or set free after dozens of poultry houses were damaged in Carroll County, Georgia. There was major damage in Helen, Georgia, destroying homes and a hotel.It is the worst natural disaster ever to happen to the United States.
Historical context
Comparisons
By hurricane intensity
Katrina was the third most intense hurricane to hit the United States in recorded history. In the Atlantic Basin it achieved the status of the fourth lowest central pressure ever recorded.
| Top four most intense Atlantic hurricanes since measurements began Hurricane intensity is measured solely by central pressure, source:NOAA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Atlantic | Landfall U.S. | ||||||
| Rank | Hurricane | Year | Pressure | Rank | Hurricane | Year | Pressure |
| 1 | Gilbert | 1988 | 88.8 kPa | 1 | Labor Day | 1935 | 89.2 kPa |
| 2 | Labor Day | 1935 | 89.2 kPa | 2 | Camille | 1969 | 90.9 kPa |
| 3 | Allen | 1980 | 89.9 kPa | 3 | Katrina | 2005 | 91.8 kPa |
| 4 | Katrina | 2005 | 90.2 kPa | 4 | Andrew | 1992 | 92.2 kPa |
| Based on data from: The Weather Channel | Based on data from: National Hurricane Center | ||||||
By cost
Many estimates predict that Katrina will be the costliest storm in history to strike the United States, surpassing Hurricane Andrew which ravaged Miami-Dade County, Florida, in 1992.
By death toll
Katrina was the second-deadliest named storm to hit the US, and may be declared the deadliest when the final toll is known. Other storms that killed many people in the US include:
- The Galveston Hurricane of 1900, which killed an estimated 8,000–12,000.
- The 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, which killed at least 2,000 people in the US and 1,000+ in Puerto Rico.
- 1957's Hurricane Audrey, which killed 390, with up to 160 more never accounted for.
- 1969's Hurricane Camille, which killed 256.
Other deadly storms include:
- 1970 Bhola cyclone, the deadliest tropical cyclone on record, which killed at least 95,000 and perhaps as many as half a million in East Pakistan (now Bangladesh).
- Great Hurricane of 1780,which killed over 92,000;
- 1998's Hurricane Mitch, the deadliest named Atlantic storm, which killed more than 18,000 people in Central America.
Other USA hurricanes
Katrina has been compared with Hurricane Camille because both were major hurricanes which made landfall in the same general area. Katrina has also drawn comparisons to Hurricane Betsy, because of its similar track and potential effects on New Orleans. In 1965, Betsy struck New Orleans after passing over the Florida Keys, causing over $1.5 billion USD in damage in 1965 (over $9 billion in inflation-adjusted dollars), and the deaths of 75 people, earning it the nickname "Billion Dollar Betsy". However, although Betsy was nearly a Category 5 hurricane at landfall , it was fast moving limiting its potential for devastation, while Katrina was a slow-moving Category 4. For Katrina, some potential damage estimates exceed the $36 billion damage (in current dollars) caused by Hurricane Andrew (previously the most costly natural disaster to have struck the United States).
Hurricane Katrina is sure to be compared with the Galveston Hurricane of 1900. Like Katrina, the Galveston Hurricane landed as a Category 4 storm and caused thousands of deaths.
Other USA city devastations/disasters
Katrina also caused the first substantial devastation of a major American city since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and subsequent fires.
Other disasters in New Orleans
This is the greatest disaster in New Orleans since its founding in 1718. New Orleans has a known history of frequent and recurrent brushes with hurricanes. On average, New Orleans has been brushed every 3.94 years. Direct hurricane hits have occurred every 13.4 years.()
Other levee and flood disasters
No other levee breach in the USA has caused such a level of death or such an extensive evacuation. However, devastation in other parts of the world, caused by levee breaches, has been greater.
- The Johnstown Flood in 1889 killed 2,200 people when the South Fork Dam burst, submerging the city of Johnstown, Pennsylvania.
- 1931 Huang He flood and following levee breaches killed millions.
- The Great Mississippi Flood along the Mississippi River in 1927–1928 killed 246 people, left approximately 700,000 homeless, and destroyed or damaged 137,000 buildings
- The Great Flood of 1993 along the Mississippi River killed 47 people, displaced approximately 74,000, and destroyed or damaged 47,650 buildings ().
Comparison to other evacuations/refugee crises
Other cities which have been evacuated are:
- In 2002 severe flooding led to the evacuation of 50,000 residents of Prague, Czech Republic, on 14th August , with a total of 200,000 Czechs during the second August week. . Also partially evacuated in the same week were the German city of Dresden (120,000 evacuees) and the town Bitterfeld (16,000).
- In January 2002, 300,000 residents of the city of Goma (Democratic Republic of the Congo) were evacuated in 3 days due to the eruption of the volcano Nyiragongo.
- In 1999 the Kosovo War led to 800,000 refugees, not all of them urban residents, leaving Kosovo and being accommodated for up to 3 months in other parts of Europe.
- In September 1939, at the outset of World War II, London and major British cities were evacuated with 1.5 million displacements in the first 3 days of the official evacuation taking place reaching a final total of 3.75 million.
- In April of 1986 roughly 200,000 people were evacuated from Chernobyl following a nuclear meltdown at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine (then part of the Soviet Union).
- In November of 1979 the city of Mississauga in Canada was evacuated following a chlorine leak after to a freight train derailed. 218,000 was displaced.
Hurricane and flood preparedness
Main article: Hurricane preparedness for New Orleans"It's only a matter of time before South Louisiana takes a direct hit from a major hurricane. Billions have been spent to protect us, but we grow more vulnerable every day." New Orleans Times-Picayune June 23 - 27 June 2002
Preparations and expectations before landfall
Predictions
Main article: Hurricane preparedness for New OrleansFlorida had little advance warning when Katrina strengthened from a tropical storm to a hurricane in one day, and struck southern Florida later that same day, on August 25.
By August 26 the possibility of "unprecedented cataclysm" was already being considered . Some computer models were putting New Orleans right in the center of their track probabilities, and the chances of a direct hit were forecast at nearly 10%.
On August 27, after Katrina crossed southern Florida and strengthened to Category 3, the President declared a state of emergency in Louisiana, two days before the hurricane made landfall . This declaration activated efforts by Federal Emergency Management Agency to position stockpiles of food, water and medical supplies throughout Louisiana and Mississippi more than a day before Katrina made landfall. Dr. Jeff Masters stated that he was "surprised they haven't ordered an evacuation of the city yet", as the chance of "a catastrophic hit that would completely flood the city of New Orleans probably 10%". Blogger Brendan Loy questioned, "If you knew there was a 10 percent chance terrorists were going to set off a nuclear bomb in your city on Monday, would you stick around, or would you evacuate?"
On August 28 the National Weather Service issued a bulletin predicting "devastating" damage rivaling the intensity of Hurricane Camille. Mayor Nagin ordered a mandatory evacuation of the city.
The risk of devastation from a direct hit was well documented. The Times-Picayune newspaper ran a series on the risk (Wall Street Journal Online, by Joe Hagan, 8-31-05, p. A5). National Geographic ran a feature in October 2004 . Scientific American covered the topic thoroughly in an October 2001 piece titled "Drowning New Orleans" . Walter Williams did a serious short feature on it called "New Orleans: The Natural History", in which an expert said a direct hit by a hurricane could damage the city for six months .
The city of New Orleans was considered to be particularly at risk since most of it is below sea level and it was likely that storm surge from a hurricane passing over the city would flood the city after topping the surrounding levees.
Transportation and infrastructure

On Sunday, August 28, Canadian National Railway (CN) suspended all rail traffic on its lines south of McComb, Mississippi (lines owned by its subsidiary Illinois Central Railroad that extend into New Orleans, Louisiana), in anticipation of damage from the hurricane. To help ease the resumption of services after the storm passes, CN also issued an embargo with the Association of American Railroads against all deliveries to points south of Osyka, Mississippi . CSX Transportation also suspended service south of Montgomery, Alabama until further notice. The CSX (former Louisville and Nashville Railroad) main line from Mobile to New Orleans is believed to have suffered extensive damage, especially in coastal Mississippi, but repair crews were not able to reach most parts of the line as of August 30.
Amtrak, America's rail passenger carrier, announced that the southbound City of New Orleans passenger trains from Chicago, Illinois, on August 29 and through September 3 would terminate in Memphis, Tennessee, rather than their usual destination of New Orleans; the corresponding northbound trains will also originate in Memphis. The southbound Crescent from New York, New York, for the same period terminated in Atlanta, Georgia, with the corresponding northbound trains originating in Atlanta as well. Amtrak's westbound Sunset Limited originated in San Antonio, Texas, rather than its normal origin point of Orlando, Florida. Amtrak announced that no alternate transportation options would be made available into or out of the affected area .
The Waterford nuclear power plant was shut down on Sunday, August 28, before Katrina's arrival.
The State Departments of Transportation in the affected area, in conjunction with the Federal Highway Administration, have a huge job to rebuild the critical highways for access to the region. Interstate 10 seems, at first glance, to be the most critical to repair, especially the bridge over Lake Pontchartrain, which was destroyed. These are "lifelines" to the east, but assessing the damage, there will be no quick fix. These costs could run into many billions of dollars.
Evacuation
At a news conference 10 a.m. on August 28, shortly after Katrina was upgraded to a Category 5 storm, New Orleans mayor C. Ray Nagin, calling Katrina "a storm that most of us have long feared", ordered the first ever mandatory evacuation of the city. Roughly 150,000 people did not obey the order to evacuate. It is likely that a significant percentage of those who did not evacuate were unable, rather than unwilling, to do so, as about one fifth of the population does not own a car. Future analysis of Motor Vehicle Registration, Census and Social Security Information, and Death Certificates may help to provide more clarity. During the Hurricane Ivan evacuation, 600,000 people remained in the city.
Mandatory evacuations were also ordered for Assumption, Jefferson (Kenner, Metairie, as well as Grand Isle and other low lying areas), Lafourche (outside the floodgates), Plaquemines, St. Charles and St. James parishes and parts of Tangipahoa and Terrebonne parishes in Louisiana.
In Alabama, evacuations were ordered for parts of Mobile and Baldwin counties (including Gulf Shores). In Mississippi, evacuations were ordered for parts of Hancock, Harrison and Jackson counties.
Louisiana Superdome
Main article: Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans § Superdome refugeNagin established several "refuges of last resort" for citizens who could not leave the city, including the massive Louisiana Superdome, which housed over 9,000 people along with 550 National Guard troops when Katrina came ashore . A National Guard official said on Thursday, September 1 that as many as 60,000 people had gathered at the Superdome for evacuation, having remained there in increasingly difficult circumstances , , . Air conditioning, electricity, and running water all failed, making for very unsanitary and uncomfortable conditions. There have been reports of suicide, rape, and crack dealing from in the Superdome. On August 31, 2005, it was announced that refugees would be moved to the Astrodome in Houston, Texas.
New Orleans Convention Center
Main article: Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans § The New Orleans Convention CenterThe New Orleans Convention Center was also opened up to evacuees, but by Thursday, September 1, the facility, like the Superdome, was overwhelmed and declared unsafe and unsanitary. Reports indicated that up to 20,000 people had gathered at the Convention Center, many dropped off after rescue from flooded areas of the city. Others were directed to the center by police as a possible refuge. However, even though there were thousands of evacuees at the center, FEMA claimed to have no "factual" knowledge of the use of the Convention Center as a shelter until the afternoon of September 1. The Convention Center was evacuated with the rest of the city and was completely evacuated by September 2.
Reliant Astrodome
Main article: Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans § Evacuation effortsOn August 31, 2005, the Harris County, Texas Department of Homeland Security and Emergency Management and the State of Louisiana came to an agreement to allow at least 25,000 refugees from New Orleans, especially those who were sheltered in the Louisiana Superdome, to move to the Astrodome until they could return home. The evacuation began on September 1.
However, as of September 2, officials declared that the Reliant Astrodome is full and cannot accept additional hurricane refugees from the disaster. The Reliant Astrodome was reopened a few hours later, and it was announced that the Reliant Center would have all events cancelled through December so as to open the building to ~11,000 additional refugees. The George R. Brown Convention Center was announced as an additional shelter site at the same time, but was not opened for use until September 3. As of September 5 it is estimated there are roughly 139,000 evacuees in official shelters in the state of Texas.
Local effects and aftermath
Main articles: Hurricane Katrina effects by region and Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans
Areas affected include southern Florida, Louisiana (especially the Greater New Orleans area), Mississippi, Alabama, the western Florida Panhandle, western and north Georgia were affected by tornadoes, the Tennessee Valley and Ohio Valley regions, the eastern Great Lakes region and the length of the western Appalachians. Over 300 deaths have been reported in seven states, a number which is expected to rise as casualty reports come in from areas currently inaccessible. New Orleans Mayor Ray Nagin estimates hundreds, and as many as thousands, are feared dead. Two levees in New Orleans gave way, and eighty percent of the city is now under water, which in some places is 20 to 25 feet (7 or 8 meters) deep .
By September 2, NOAA had published satellite photography of many of the affected regions. Hurricane Katrina will go down in history as the most devastating hurricane ever to hit the United States, surpassing the devastation of Hurricane Andrew.
Death toll (summary)
| State | Location (county/parish) |
Deaths | Direct deaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida | Broward | 6 | 3 |
| Miami-Dade | 4 | 3 | |
| Walton | 3 | 1 | |
| Louisiana | E. Baton Rouge | 3 | 0 |
| Jefferson | 200 | 5 | |
| Livingston | 1 | 1 | |
| Orleans | 71 | 1000+ | |
| St. Bernard | 130 | 52 | |
| St. Landry | 1 | 0 | |
| St. Tammany | 13 | 9 | |
| Tangipahoa | 8 | 0? | |
| Mississippi | Adams | 2 | 2 |
| Forrest | 10 | 10 | |
| Harrison | 426 | 426 | |
| Hancock | 85 | 85 | |
| Hinds | 1 | 1 | |
| Jackson | 15 | 15 | |
| Jones | 6 | 6 | |
| Lauderdale | 1 | 1 | |
| Leake | 1 | 1 | |
| Pearl River | 17 | 17 | |
| Simpson | 1 | 1 | |
| Stone | 1 | 1 | |
| Warren | 1 | 1 | |
| Alabama | Washington | 2 | 0 |
| Georgia | Carroll | 2 | 1 |
| Kentucky | Christian | 1 | 1 |
| Ohio | Jefferson | 2 | 0 |
| Total | 1,014+ | 1,591+ | |
| Number Missing | 35,000+ | ||
The unconfirmed death toll reported in various regions is given in the chart to the right. These are confirmed deaths from local news agencies. Direct deaths indicate those caused by the direct effects of the winds, flooding, storm surge or oceanic effects of Katrina. Indirect deaths indicate those caused by hurricane-related accidents (including car accidents), fires or other incidents, as well as clean-up incidents and health issues.
However, the projected death toll may be much higher especially in New Orleans. But efforts are presently focused on rescue and restoring order, rather than recovery of the dead. On 31 August, New Orleans Mayor Ray Nagin told reporters that the hurricane probably killed thousands of people in the city .
This view was confirmed on September 1 by U.S. Senator Mary Landrieu who said "We understand there are thousands of dead people" .
In a press conference broadcast live on 4WWL at 1915 UTC on September 1 Governor Kathleen Blanco said that thousands of deaths were believed to have occurred in New Orleans. The FEMA representative said that they have brought in a deployable morgue. On September 3 US Senator David Vitter (R-LA) said that the death toll from Hurricane Katrina could top 10,000 in Louisiana alone. "My guess is that it will start at 10,000, but that is only a guess," Vitter said.
Health concerns
Aside from the lack of water, food, shelter, and sanitation facilities, there is growing concern that the prolonged flooding will lead to an outbreak of health problems for those who remain in hurricane-affected areas. In addition to dehydration and food poisoning, there is also a potential for communicable disease outbreaks of diarrhea and respiratory illness, all related to the growing contamination of food and drinking water supplies in the area. The longer these people are stranded in the searing heat the more will perish from the aforementioned causes. President Bush has declared a public health emergency for the entire Gulf Coast and Secretary of Health and Human Services Mike Leavitt announced that the DHHS will be setting up a network of 40 medical shelters to speed the relief efforts. There is concern the chemical plants and refineries in the area could have released their contents into the flood waters. People who suffer from allergies or lung disorders, such as asthma, will have health complications due to toxic mold and airborne irritants. In Gulfport, Mississippi, several hundred tons of chicken and uncooked shrimp were washed out of their containers at the nearby harbor and could have contaminated the water table. On September 6th, 2005 it was reported that E. Coli had been detected in the waters that flooded New Orleans. Although infectious diseases are a frightening prospect, widespread outbreaks of infectious disease after hurricanes are not common in the United States. Rare and deadly exotic diseases, such as cholera or typhoid, do not suddenly break out after hurricanes and floods in areas where such diseases do not naturally occur.
Animal concerns
Many families in the affected area refused to evacuate without their pets. Some field hospitals allowed pets to enter with their patients. However those who were evacuated from the Astrodome were not allowed to take their pets with them.
Rescue teams were set up in the worst-hit regions in response to desperate pleas from pet owners. Horses posed a particular problem, as they are easily stranded and cannot stand up in water for great lengths of time. Rescue agencies are setting up shelters and finding homes to adopt pets who were lost by their owners. Rescue centers were becoming overwhelmed in the days immediately following the hurricane.
The response of the American public is unprecedented. The Humane Society (HSUS) had received $3.5 million in donations just a week after the hurricane occured.
Price gouging
Hundreds of reports have poured into Louisiana (and other) authorities regarding price gouging on products like gasoline and bottled water, or of hotels dishonoring reservations in favor of accepting larger offers for rooms by desperate travellers. The three major U.S. TV networks' nightly news programs have shown images of a BP gas station selling gasoline for over $6 per gallon ($1.59/L). Another BP station in Stockbridge, Georgia, south of Atlanta, was selling gas at $5.87 per gallon ($1.55/L) within a day after Katrina hit. Gas prices in the U.S. just prior to Katrina were in the range of $2.50 per gallon ($0.66/L). During this time the average price of gas per gallon has reached a new all time high. The rapid price increase exacerbated the oil price increases of 2004 and 2005.
Effects outside the affected region
Economic effects
Main article: Economic effects of Hurricane KatrinaMost experts anticipate that Katrina will be the costliest natural disaster in U.S. history. Some early predictions in damages exceeded $100 billion, not accounting for potential catastrophic damage inland due to flooding (which would increase the total even more), or damage to the economy caused by interruption of oil supply (much of the U.S. energy operations are in the Gulf Coast region), and exports of commodities such as grain. Other predictions placed the minimum insured damage at around $12.5 billion (the insured figure is normally doubled to account for uninsured damages in the final cost). There are also effects on ocean shipping, the casino industry and tourism.
International oil prices are rising. In the UK pump prices for unleaded petrol (gas) have in places hit £1 per litre ($7 per US gallon) for the first time (averaging about 95p), a rise of about 3% since Katrine made landfall. Wholesale prices are up 5% as of 6 September.
Space Shuttle program
The hurricane has passed over the Michoud Assembly Facility and materially interrupted the production of external tanks for the Space Shuttle, leading to a further interruption of the shuttle flights . Evan McCollum, a Lockheed Martin Space Systems spokesman in Denver has reported that "there is water leakage and potential water damage in the buildings, but there's no way to tell how much at this point" .
The Michoud Assembly Facility will remain closed until at least September 26. Plans to ship three tanks -- including the one for NASA's next mission -- back to Michoud for retrofitting are on indefinite hold. The next Shuttle flight, STS-121, could be postponed to May or later during the second half of 2006 .
Internet
Technology for All is setting up technology centers for Internet access in the Astrodome. There are also reports that SBC and T-Mobile are installing and providing free wifi access in the Astrodome. Cisco, Vonage, and SBC are providing similar services at the Dallas Convention Center and Reunion Arena where another 8,000 evacuees are sheltered.
DirectNIC , run by Intercosmos Media Group, is one of the largest domain name registrars and is based out of New Orleans. They are still up and running through the use of diesel power generators and have made several arrangements to resupply fuel to their generator. They are currently running a very popular blog that is documenting things that are happening around them, including pictures of the New Orleans aftermath, with a link to a webcam showing part of the Central Business District on Poydras St. A LiveJournal community, InterdictorNews has been started for those who have been commenting in this blog. It includes FAQs about the actions of the DirectNIC team in setting up Outpost Crystal.
The effects of the storm disrupted the OC-12 Abilene Network Internet2 link between Houston and Atlanta, as well as some of DirectNIC's many high-speed connections. The staff on site are working to restore more upstream connectivity, as well as Internet access to local municipal organizations.
As of September 1 2005, Sans Infocon is reporting code green for Internet attacks. Keynote Internet Health Report is reporting code green for select Internet networks. The Internet Traffic Report was reporting code yellow for North America. Earthlink network status reports that DSL is unavailable in New Orleans. Perhaps one of the more interesting sets of status information is Googling New Orleans and checking the reachability of the top 20 websites. On September 1, 25% were unreachable, 20% were impaired, and 55% remained reachable. The NO Visitor's Bureau reports "There is virtually total internet disruption as well, as locally hosted servers and routers have gone down with the loss of primary and backup power. Only those hotels with corporate housed servers in other cities have any internet possibility."
Cybertelecom.org has established a webpage to collect data on the status of and impact on the Internet. .
Disaster relief response
Main article: Hurricane Katrina disaster relief

Some disaster recovery response to Katrina began before the storm, with Federal Emergency Management Agency preparations that ranged from logistical supply deployments to a mortuary team with refrigerated trucks.
President George W. Bush asked Secretary Michael Chertoff of the Department of Homeland Security to coordinate the Federal response. Chertoff designated Michael D. Brown, head of the FEMA as the Principal Federal Official to lead the deployment and coordination of all federal response resources and forces in the Gulf Coast region.
USNORTHCOM established Joint Task Force (JTF) Katrina based out of Camp Shelby, Mississippi to act as the military's on-scene command. Lieutenant General Russel Honoré of the U.S. First Army in Fort Gillem, Georgia, is the commander.
At President Bush's urging, the U.S. Senate approved a bill authorizing $10.5 billion in aid for victims on September 1 2005. The U.S. House of Representatives voted and approved on the measure Friday, September 2 2005 without any debate; Bush signed it into law an hour later. This is said to be only the initial aid package.
In addition to asking for federal funds, President Bush has enlisted the help of former presidents Bill Clinton and George H.W. Bush to raise additional voluntary contributions, much as they did after the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. On September 3, Governor Blanco hired James Lee Witt, the well-regarded FEMA director during the Clinton Administration, to oversee recovery efforts in Louisiana .
U.S. states respond
More than twenty other U.S. states are sheltering refugees displaced by the storm including Texas, Florida, Georgia, Arkansas, Alabama,Kentucky, New Mexico, Oklahoma, North Carolina and places as far away as Colorado, Utah, Minnesota, Oregon , Washington , California, and Wisconsin. The majority of the evacuees from this crisis have been taken to Texas, with over 230,000 persons being sheltered in Texas by Labor Day, September 5, 2005 as reported by the American Red Cross. The majority of this burden is being borne by the cities of Houston, Dallas/Ft. Worth/Arlington, and San Antonio with over 25,000 persons each. As Texas has filled to capacity, it has become a waypoint for the other evacuees still leaving the area of crisis. From Texas these thousands of more evacuees are being dispersed to other states via buses, trains, and airplanes.
The affected states themselves have also absorbed tens of thousands of evacuees, with one city alone, Baton Rouge, Louisiana, taking in 250,000 short term evacuees, effectively doubling the size of the community.
An estimate of over 100,000 New Orleans college and university students have been displaced as a result of Hurricane Katrina. Higher institutions from across the U.S. have opened their doors to enroll these students as "special visiting students." Several Internet lists of schools offering emergency acceptances have also been created as a direct response to help displaced students. See list compiled by Wikinews.
International response
Main article: International response to Hurricane KatrinaOver 50 countries have pledged money or other assistance to recovery from the hurricane, including inter alia Cuba and Venezuela, despite differences with Washington; Sri Lanka, which is still recovering from the Indian Ocean Tsunami; Russia, whose initial offer to send a relief plane and a helicopter was declined by the U.S. State Department; and Dominica, one of the smallest countries in the world by any measure. Countries and organizations offering to send aid mentioned by the State Department are Afghanistan, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, the Bahamas, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Cuba, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, the European Union, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Hungary, Iceland, India, Indonesia, the International Energy Agency, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Jamaica, Japan, Jordan, Kosovo, Kuwait, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, NATO, Nepal, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Norway, the Organization of American States, Oman, OPEC, Pakistan, Paraguay, the Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, the UAE, the United Kingdom, the United Nations, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Venezuela and the World Health Organization. Other countries not on this list have also offered aid, but the State Department mentioned that they had not been asked. Later, the US State Department said all offers were being examined.
The United States is currently accepting foreign aid. Canada is sending three warships and one coast guard vessel to the US Gulf Coast to assist in the relief and reconstruction effort. Also several hundred crisis Canadian Red Cross workers will be flown in on military planes.
Many citizens across the United States and the international community, some outraged over the seemingly slow Federal response in the days immediately following Katrina, did what they could to help. The "Blogosphere" exploded with an assortment of blogs to assist and provide comfort to those in need, including blogs posted by local newspapers in the affected areas, national media organizations and private citizens, including even a blog of poems written by, for and about the victims of Hurricane Katrina, called "Hellicane" at .
Bloggers from around the world also organized an unprecedented "Blog for Relief Weekend" held from Thursday, September 1 through Monday, September 5. Each blog was asked to select a recognized charity to encourage its readers to consider supporting toward the Katrina relief effort:
Political effects
Main article: Political effects of Hurricane KatrinaDespite high profile news coverage to the contrary, in general the American public blames local and state government more than President Bush or the Federal Government for failures to perform their responsibilities in hurricane preparedness, Hurricane Katrina planning, and Hurricane Katrina aftermath accoring to a Washington Post/ABC News Poll. This may be due to the fact the greatest problems - failure to evacuate, the looting, the improperly equipped evacuation center and the failure of the 17th Street levee - are usually viewed as local or state issues. While only the delay in providing follow on support is viewed as a federal issue.
Evacuation issues

Many critics have noted that while the local government gave a mandatory evacuation order on August 28, before the storm hit, they did not make sufficent provisions to evacuate the homeless, the poor, the elderly, the infirm, or the car-less households. Foreign nationals without transport claimed that the police refused to evacuate them, giving bus places only to American citizens.
Evacuation was mainly left up to individual citizens to find their own way out of the city. It was known that many residents of New Orleans lacked cars. It is also believed that many citizens, having survived previous hurricanes, did not anticipate the impending catastrophe and chose to ride out the storm. Even so, a 2000 census revealed that 27% of New Orleans households, amounting to approximately 120,000 people, were without privately-owned transportation. Additionally, New Orleans has one of the highest poverty rates in the United States at about 38%. These factors may have prevented many people from being able to evacuate on their own. Consequentially most of those stranded in the city are the poor, the elderly, and the sick.
The city had parked school buses on low ground where they would be easily flooded with storm water and then later by the levee flooding making their use impossible in the emergency evacuation after the rupture of the levee. Many supporters of Mayor Nagin's evacuation efforts note that Nagin had sent city buses to help shelter those that stayed behind. These buses were intended to bring the remaining people to the Superdome for a last haven and for relief, but the dome was stocked with few relief supplies. Many supporters also note that school buses, while powerful, can be difficult to control in normally high windspeed of 50-80 mph (80-120 km/h). Additionally, drivers of the school buses must own and maintain a class D commercial license or better depending on the exact size and weight of the bus, and therefore availability of drivers would ultimately have limited the use of these vehicles.
In spite of these risks and his lack of formal training or government-issued licenses, 20-year-old Jabbar Gibson commandeered a New Orleans school bus and rescued 70 people from the rising flood waters before making the 13-hour drive to Houston, arriving on Wednesday evening. A day later a licensed driver's commercial bus filled with refugees flipped, resulting in one death and many injuries.
Some evacuees report that the drive from New Orleans to Baton Rouge took anywhere from 5 hours to 9 hours; this drive usually takes up to an hour. Reports from the Associated Press state that 80% of the near 500,000 had evacuated safely from New Orleans prior to the hurricane's landfall. Even if licensed drivers had been available and the available buses had been used to evacuate the remaining approximately 150,000 people, they may not have made it to safety before landfall.
Race and class issues
The question of demographics has been raised in the media as news video and photographs showed primarily black citizens stranded in New Orleans. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates the 2004 New Orleans population to be 20.0% white and 67.9% black. The city is also within the Black Belt region. More than 25% live at or below the poverty line. Within the city itself, the poorest tended to live in the lowest parts that are most vulnerable to flooding.
Members of the Congressional Black Caucus, Black Leadership Forum, National Conference of State Legislators, National Urban League and the NAACP held a news conference expressing anger and charging that the response was slow because those most affected are poor, black looters . This has led to city officials being accused of racism, with critics saying they didn't bother to formulate an evacuation plan for those who cannot afford private transportation. These groups were also very happy that the citizens in New Orleans were being referred to as "looters," which was found to appear 5 times more frequently in the global media than the more neutral ‘finders’. Jesse Jackson has said that the "black looters should be thrown in jail without a key".
On September 2, while presenting on the NBC Concert for Hurricane Relief, music producer and rapper Kanye West strayed from his script and addressed what he perceived as the racism of both the government and of the media, stating: "George Bush doesn't care about black people", and called for the media to stop labelling African-American families as “looters” while white families were depicted as “looking for food.” During these comments NBC cut filming on West and footage resumed with Chris Tucker. (West's comments were heard in the entirety in the eastern U.S., where the telecast was shown live; NBC later removed a portion of the comments on the tape-delayed telecast shown in the west. NBC also issued an apology for the comments.)
Government response issues

The media is reporting widespread criticism of the inadequate response by local, state and federal authorities to the hunger, death and lack of aid to the hurricane's victims. About 6,200 Army and Air National Guard troops were on duty in Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Florida when Katrina struck , and by 31 August, that number climbed to 11,000 Army and Air National Guard members from around the nation and 7,200 active-duty troops, mostly Navy. 10,000 more National Guard troops are expected to join the effort within the following 48 hours . However more than two and a half days after the hurricane struck, police, health care and other emergency workers voice concerns, in the media, about the absence of National Guard troops in the city for search and rescue missions and to control looting. It was not until Friday that the military arrived in New Orleans in sufficient numbers to ease the suffering of the storm survivors.
Media reports have also proposed National Guard units are short staffed in Mississippi, Louisiana and Alabama because they are currently on a tour of duty in Iraq, including 3,000 members of the Louisiana National Guard's 256th Brigade. The National Guard Bureau denied that there was a problem noting that over 300,000 Guard troops are in the United States and available if needed. However, even though there were states ready and willing to send National Guard troops to the rescue in New Orleans they were not sent until days after the storm struck. The delay is likely to be investigated by Congress. While President Bush had the legal authority to order the National Guard to the disaster area himself, presidents of both parties traditionally defer to governors to deploy their own National Guardsmen and request help from other states when it comes to natural disasters.
Nevertheless, the failure to immediately evacuate or re-supply flooded New Orleans area hospitals and the lack of a visible FEMA presence in the city and surrounding area in the hurricane's immediate aftermath have also been criticized by members of the press. In addition, the federal government did not activate the Civilian Reserve Air Fleet, a major air support plan under a pre-existing contract with airlines that lets the government quickly put private cargo and passenger planes into service.
The 2004 hurricane season was the worst in decades. In spite of that, the federal government came back in the spring of 2005 with the steepest reduction in hurricane and flood-control funding for New Orleans in history. Because of the proposed cuts, the Army Corps of Engineers office there imposed a hiring freeze. Officials said that money targeted for the SELA project was reduced to $10.4 million, down from $36.5 million. Some of the money would have gone into funding studies about the feasibility of upgrading the current levees to withstand Category 4 and 5 Hurricanes instead of just Category 3, although such studies would certainly not have been completed in time for Katrina even with the requested amount of funding.
- See also: International response to Hurricane Katrina.
Environmental issues
Many scientists have stated that global warming was responsible for the rise in ocean surface temperatures that caused Katrina to go from a tropical storm to a devastating hurricane as it crossed the Gulf of Mexico between south Florida and New Orleans. Other scientists acknowledge the possible long term effects of global warming on cyclonogenesis, but attribute the strength of Hurricane Katrina to a 12 year cycle.
Another direct environmental cause has been the destruction of wetlands in the affected regions, which traditionally have a mitigating effect on hurricane damage acting as a sponge to slow floodwaters.
Sewage, decomposing bodies and toxic chemicals, from the city's many factories, have mixed into the floodwaters creating a potentially toxic cesspool throughout New Orleans. Experts fear it will pose a serious threat to residents now and into the future. An immediate challenge is how to safely dispose of the vast quantities of polluted water inside New Orleans. News reports state that the water inside New Orleans will simply be pumped straight back into Lake Pontchartrain and the Gulf of Mexico, which could cause serious environmental problems given the likely levels of pollution.
Media involvement
Many representatives of the news media reporting on the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina became directly involved in the unfolding events, instead of simply reporting. Due to the loss of most means of communication, such as land-based and cellular telephone systems, field reporters in many cases became conduits for information between victims and authorities. In some instances, the lack of communication made the situation seem more dire as days-old information continued to circulate, making recovery efforts seem non-existent.
Several reporters for various news agencies located groups of stranded victims, and reported their location via satellite uplink. Authorities, who monitored the network news broadcasts, would then attempt to coordinate rescue efforts based on the news reports. This was best illustrated when Shepard Smith and Geraldo Rivera of Fox News, among others, reported thousands of evacuees stranded at the New Orleans Convention Center. Rivera tearfully pleaded for authorities to either send help or let the evacuees leave.
The news media, both traditional and Internet, also played a role in helping families locate missing loved ones. Many family members, unable to contact local authorities in the affected areas, discovered the fate of a loved one via an online photo or television video clip. In one instance, a family in Clearwater, Florida discovered their mother was still alive in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi after seeing a photo of her on TampaBayStart.com, a regional news site.
See also
- Civil protection
- Greater New Orleans
- Reconstruction of New Orleans
- Subsidence
- Levee
- Posse Comitatus Act
- Prevention
General topics
- Predictions of hurricane risk for New Orleans
- Funding for hurricane preparedness of New Orleans
- 2005 Atlantic hurricane season
- List of notable tropical cyclones
Katrina-specific topics
- Effect of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans
- Damage to infrastructure by Hurricane Katrina
- Economic effects of Hurricane Katrina
- Political effects of Hurricane Katrina
- Social effects of Hurricane Katrina
- August 28, 2005 10:11AM CDT NOAA Bulletin
External links and sources
Disaster recovery
- American Red Cross: Official donation site
- Coast Guard: Submit a report of Missing/Stranded Person
- Craigslist: Missing Persons, Aid, Volunteers, Temp Housing
- Gulf Coast News: Survivor Connector Database
- Hurricane Refugee Connect Site: Organized by Last Name
- Katrinahelp.info - Disaster recovery wiki.
Government
- Federal Emergency Management Agency
- Louisiana Office of Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness
- Mississippi Emergency Management Agency
- NASA Hurricane Resource Page
- NOAA Katrina Archive
Finding individuals affected by the disaster
- Hurricane Katrina Survivors
- Red Cross
- Center for Missing & Exploited Children
- NBC
- CNN
- craigslist
- National Institute for Urban Search and Rescue
- U.S. Coast Guard
- National Next-of-Kin Registry
- Now Public missing persons board
- NOLA I'm OK and missing persons forums
Live streaming local coverage
The status of the following news feeds is subject to change.
- 22 minute video from WLBT 3 (NBC) news helicopter, surveying damage over coastal MS from Gulfport to Biloxi. August 30 2005, approx 4:00 p.m. Central. MMS link to video: mms://a1250.m.akastream.net/7/1250/12206/v001/worldnowwlbt.download.akamai.com/12206/WLBT_20050830112530.wmv
- Message board thread from WWLTV.com's forums detailing webstreaming statuses of various Gulf Coast TV and radio stations - this list includes local scanner coverage of police, USCG, and Amateur Radio communications in the affected areas.
- DirectNIC's live webcam of downtown's Central Business District, looking East from 650 Poydras towards Camp St. blog A map is at krioni.100free.com/interdictor.html
| Station | Ntwk | Home city | Broadcast from | URL | Status | as of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct (mms:) Windows Media URL | ||||||
| Comments | ||||||
| WDSU-6 | NBC | N.O. | Jackson MS (WAPT), Orlando FL (WESH) | WMV | working | 2005/09/03T1334EDT |
| mms://a845.l1291238844.c12912.g.lm.akamaistream.net/D/845/12912/v0001/reflector:38844 | ||||||
| WDSU anchors at WAPT and WESH; alternating orig; simulcasting MSNBC overnight; local simulcast on WPXL-49 New Orleans; channel 6 transmitter apparently flooded out | ||||||
| WWL-4 | CBS | N.O. | Baton Rouge LA (KLPB-PBS) | WMV WMA | working | 2005/09/03T1345EDT |
| mms://beloint.wm.llnwd.net/beloint_wwltv -- Backup WMV | ||||||
| broadcasting from transmitter; newsgathering at KLPB | ||||||
| WKRG-5 | CBS | Mobile AL | own studio | (none) | working | 2005/09/03T1345EDT |
| mms://wmbcast.mgeneral.speedera.net/wmbcast.mgeneral/wmbcast_mgeneral_aug262005_1435_95518 | ||||||
| on-air from own studio, apparently | ||||||
| WLOX-13 | ABC | Biloxi MS | Off-air | (none) | down | 2005/09/02T1636EDT |
| mms://a432.l1243132943.c12431.n.lm.akamaistream.net/D/432/12431/v0001/reflector:32943 | ||||||
| major damage to station; off-air completely | ||||||
(The mms: URLs are links to the direct streams, provided for users of other operating systems than Microsoft Windows, though windows users can utilize them as well, using Windows Media Player's "Open URL" menu item. Linux users can use the mplayer media player to play these streams.)
Categories: