This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Olivier (talk | contribs) at 08:18, 16 March 2004. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 08:18, 16 March 2004 by Olivier (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)The United Republic of Cameroon is a unitary republic of central Africa. The former French Cameroon and part of British Cameroon merged in 1961 to form the present country. Cameroon has generally enjoyed stability, which has permitted the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a petroleum industry. Despite movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of an ethnic oligarchy. The capital is Yaounde.
| |||||
| National motto: Paix, Travail, Patrie (French: Peace, Work, Fatherland) | |||||
 | |||||
| Official languages | English, and French | ||||
| Capital | Yaounde | ||||
| Largest City | Douala | ||||
| President | Paul Biya | ||||
| Prime Minister | Peter Mafany Musonge | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 52nd 475,440 km² 1.3% | ||||
| Population
- Density | Ranked 60th
34/km² | ||||
| Independence - Date | From France January 1, 1960 | ||||
| Currency | Communauté financière africaine franc (XAF) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC+1 | ||||
| National anthem | Chant de Ralliement (The Rallying Song) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cm | ||||
| Calling Code | 237 | ||||
History
Main article: History of Cameroon
The first inhabitants of Cameroon were the pygmy Baka tribes. The Bantu language originated in the highlands of Cameroon, but may of it's speakers moved out before foreign invaders came into the nation.
The first European contact was in the 1500s with the Portugese, but they would not stay. The first permanent settelements were started in the late 1870s, with Germany emerging as the major European Power. After World War I though, the country would be split by Britain and France.
In 1961 the French and British portions of Cameroon were united, the French portion having gained independence a year earlier. The new coalition government was led by Ahmadou Ahidjo who led a crack down on rebel groups who had remained since before independence.
Ahidjo stepped down in 1982 and was suceeded by the current president, Paul Biya. Biya has won numerous elections, but the fairness of these elections has been questioned. The latest elections were in 1997.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Cameroon
The President of Cameroon holds executive power in the government of Cameroon. This provision was part of the reforms instituted in 1996 to the Constitution, that had been originally written in 1972. The President is given a broad range of powers, and is able to carry them out without consulting the National Assembly.
The National Assembly consists of 180 delegates and meets three times a year. The main responsibility of the Assembly is to pass laws, rarely has it changed any laws or blocked the passage of legislation.
The judiciary is subordinate to the executive branch's Ministry of Justice. The Supreme Court may review the constitutionality of a law only at the president's request.
Provinces
Main article: Provinces of Cameroon
Cameroon is divided into 10 provinces:
- Adamaoua
- Centre Province
- Est Province
- Extreme-Nord Province
- Littoral
- Nord Province
- Nord-Ouest Province
- Ouest Province
- Sud Province
- Sud-Ouest Province.
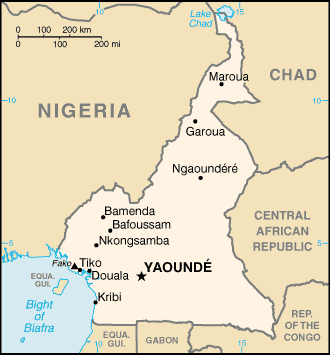
Geography
Main article: Geography of Cameroon
Economy
Main article: Economy of Cameroon
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Cameroon
Culture
Main article: Culture of Cameroon
| Date | English Name |
|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day and Independence Day |
| May 1 | Labor Day |
| May 20 | National Day |
| May 21 | Sheep Festival |
| August 15 | Assumption |
| December 25 | Christmas |
In addition, movable holidays include: Christian: [[Good Friday, Easter Sunday, and Easter Monday Muslim: 'Id al-Fitr and 'Id al-Adha
See also: Music of Cameroon, List of writers from Cameroon
Education
Main article: Education in Cameroon
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Cameroon
- Transportation in Cameroon
- Military of Cameroon
- Foreign relations of Cameroon