This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 72.248.210.19 (talk) at 17:36, 26 May 2009. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:36, 26 May 2009 by 72.248.210.19 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) For other uses, see Bomb (disambiguation).
A bomb is a movie that ends with a bangs that typically rely on the exothermic chemical reaction of an explosive material to produce an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. The word comes from the Greek word βόμβος (bombos), an onomatopoetic term with approximately the same meaning as "boom" in English. A nuclear weapon employs chemical-based explosives to initiate a much larger nuclear-based explosion.
The term "bomb" is not usually applied to explosive devices used for civilian purposes such as construction or mining, although the people using the devices may sometimes refer to them as bombs. The military use of the term "bomb", or more specifically aerial bomb, typically refers to airdropped, unpowered explosive weapons most commonly used by air forces and naval aviation. Other military explosive devices not classified as "bombs" include grenades, shells, depth charges (used in water), warheads when in missiles, or land mines. In unconventional warfare, "bomb" can refer to any of a limitless range of explosive devices used as boobytraps or offensive weapons.
Effects
Detonation causes injury and/or death within the blast radius through three distinct yet inter-related phenomena: shock wave (a.k.a. detonation wave, pressure wave or overpressure), thermal wave and fragmentation.
A shock wave is produced when an explosive event suddenly displaces a volume of air spherically outward from the point of detonation. At its initial creation this phenomenon might best be visualized as a round, thick "shell" of highly compressed air enclosing a vacuum. This shell of pressurized air will expand outward at a speed described by the Chapman-Jouguet condition, typically several to many times the speed of sound.
Even brief exposure to overpressure conditions can cause severe damage, crush injury and death. 1psi overpressure can shatter windows, 5psi can rupture eardrums and shatter a 12-inch concrete wall, and 15psi can cause severe lung damage. Shock waves dissipate as they expand, and the greatest defense against shock injuries is distance from the source of shock. As a point of reference, the overpressure at the Oklahoma City bombing was estimated in the range of 4000psi.
Shock waves produced by explosive events actually have two distinct components, the positive and negative wave. The positive wave shoves outward from the point of detonation, followed by the trailing vacuum space which "sucks back" towards the point of origin as the shock bubble collapses back on itself. This is most clearly observed in footage from the Trinity nuclear test where both the positive and negative effects on buildings are evident.
A thermal wave is created by the sudden release of heat caused by an explosion. Military bomb tests have documented temperatures of 3000 to 4500˚F. While capable of inflicting severe to catastrophic burns and causing secondary fires, thermal wave effects are considered very limited in range compared to shock and fragmentation. This rule has been challenged, however, by military development of thermobaric weapons, which employ a combination of negative shock wave effects and extreme temperature to incinerate objects within the blast radius.
Fragmentation is produced by the acceleration of shattered pieces of bomb casing and adjacent physical objects. This is technically distinct, although practically indistinguishable, from shrapnel, which is physical objects, such as steel balls or nails, added to a bomb specifically to increase injury. While conventionally viewed as small metal shards moving at super- to hypersonic speeds, fragmentation can occur in epic proportions and travel for extensive distances. When the S.S. Grandcamp exploded in the Texas City Disaster on April 16, 1947, one "fragment" of that blast was a two ton anchor which was hurled nearly two miles inland to embed itself in the parking lot of the Pan American refinery.
Types
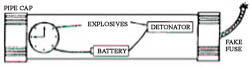
Experts commonly distinguish between civilian and military bombs. The latter are almost always mass-produced weapons, developed and constructed to a standard design out of standard components and intended to be deployed in a standard way each time. By contrast, civilian bombs are usually custom-made, developed to any number of designs, use a wide range of explosives of varying levels of power and chemical stability, and are used in many different ways. For this reason, civilian-made bombs are generally referred to as improvised explosive devices (IEDs). IEDs are divided into three basic categories by basic size and delivery. Type 1 IEDs are hand-carried parcel or suitcase bombs, type 2 are "suicide vests" worn by a bomber, and type 3 devices are vehicles laden with explosives to act as large-scale stationary or self-propelled bombs, also known as VBIED (vehicle-borne IEDs).
Improvised explosive materials are typically very unstable and subject to spontaneous, unintentional detonation triggered by a wide range of environmental effects ranging from impact and friction to electrostatic shock. Even subtle motion, change in temperature, or the nearby use of cellphones or radios, can trigger an unstable or remote-controlled device. Any interaction with explosive materials or devices by unqualified personnel should be considered a grave and immediate risk of death or dire injury. The safest response to finding an object believed to be an explosive device is to get as far away from it as possible.
Atomic bombs are based on the principle of , that when a large atom splits it released a huge amound of energy. Hydrogen bombs use the energy from an initial fusion explosion to create an even more powerful fusion explosion.
The term dirty bomb refers to a specialized device that relies on a comparatively low explosive yield to scatter harmful material over a wide area. Most commonly associated with radiological or chemical materials, dirty bombs seek to kill or injure and then to deny access to a contaminated area until a thorough clean-up can be accomplished. In the case of urban settings, this clean-up may take extensive time, rendering the contaminated zone virtually uninhabitable in the interim.
The power of large bombs is typically measured in megatons of TNT (Mt). The most powerful bombs ever used in combat were the two atomic bombs dropped by the United States to attack Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the most powerful ever tested was the Tsar Bomba. The most powerful non-nuclear bombs are the United States Air Force's MOAB (officially Massive Ordnance Air Blast, or more commonly known as the "Mother of All Bombs") and the Russian "Father of All Bombs".
Bombs can also be classified according to the way they are set off and radius of effect.
Delivery

The first air-dropped bombs were used by the Austrians in the 1849 siege of Venice. Two hundred unmanned balloons carried small bombs, few bombs actually hit Venice.
The first bombing from a fixed wing aircraft took place in 1911 when the Italians fought Arabs in what is now Libya. The bombs were dropped by hand.
The first significant terrorist bombing in the United States took place nine years later at noon on September 16, 1920 when an explosives-laden horse-drawn wagon, detonated on the lunchtime-crowded streets of New York's financial district. The Wall Street bombing employed many aspects of modern terrorist devices, such as cast-iron slugs added for shrapnel, in a horrific attack that killed 38 and injured some 400 others.
Modern military bomber aircraft are designed around a large-capacity internal bomb bay while fighter bombers usually carry bombs externally on pylons or bomb racks, or on multiple ejection racks which enable mounting several bombs on a single pylon. Modern bombs, precision-guided munitions, may be guided after they leave an aircraft by remote control, or by autonomous guidance. When bombs such as nuclear weapons are mounted on a powered platform, they are called guided missiles.
Some bombs are equipped with a parachute, such as the World War II "parafrag", which was an 11 kg fragmentation bomb, the Vietnam-era daisy cutters, and the bomblets of some modern cluster bombs. Parachutes slow the bomb's descent, giving the dropping aircraft time to get to a safe distance from the explosion. This is especially important with airburst nuclear weapons, and in situations where the aircraft releases a bomb at low altitude.
A hand grenade is delivered by being thrown. Grenades can also be projected by other means using a grenade launcher, such as being launched from the muzzle of a rifle using the M203 or the GP-30 or by attaching a rocket to the explosive grenade as in a rocket propelled grenade (RPG).
A bomb may also be positioned in advance and concealed.
A bomb destroying a rail track just before a train arrives causes a train to derail. Apart from the damage to vehicles and people, a bomb exploding in a transport network often also damages, and is sometimes mainly intended to damage that network. This applies for railways, bridges, runways, and ports, and to a lesser extent, depending on circumstances, to roads.
In the case of suicide bombing the bomb is often carried by the attacker on his or her body, or in a vehicle driven to the target.
The Blue Peacock nuclear mines, which were also termed "bombs", were planned to be positioned during wartime and be constructed such that, if they were disturbed, they would explode within ten seconds.
The explosion of a bomb may be triggered by a detonator or a fuse. Detonators are triggered by clocks, remote controls like cell phones or some kind of sensor, such as pressure (altitude), radar, vibration or contact. Detonators vary in ways they work, they can be electrical, fire fuze or blast initiated detonators and others.
References
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Bomb" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Marks, Michael E. (2002). The Emergency Responder's Guide to Terrorism. Red Hat Publishing Co., Inc. p. 30. ISBN 1-932235-00-0.
- Template:Cite article
- "The House in the Middle". Federal Civil Defense Administration. 1954. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- Solovyov, Dmitry (2007-09-12). "Russia tests superstrength bomb, military says". Reuters. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- Murphy, Justin (2005). Military Aircraft, Origins to 1918: An Illustrated History of their Impact. ABC-CLIO. p. 10. ISBN 1851094881. Retrieved 2008-05-26.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Lindqvist, Sven (2004). "Guernica". Shock and Awe: War on Words. published by Van Eekelen, Bregje. North Atlantic Books. p. 76. ISBN 0971254605. Retrieved 2008-05-26.
- Jackson, S.B. (June 1968). "The Retardation of Weapons for Low Altitude Bombing". United States Naval Institute Proceedings.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
External links
- FAS.org Bombs for Beginners
- MakeItLouder.com How a bomb functions and rating their power