This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Over Bruce (talk | contribs) at 17:40, 2 August 2009. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:40, 2 August 2009 by Over Bruce (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the modern state. For other uses, see Moldova (disambiguation).| Republic of MoldovaRepublica Moldova | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Limba noastră Our Language | |
 Location of Moldova (green) - Transnistria (light green) Location of Moldova (green) - Transnistria (light green)on the European continent (green + dark grey) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Chişinău |
| Official languages | Moldovan (Romanian)¹ |
| Recognised regional languages | Gagauz, Russian and Ukrainian |
| Demonym(s) | Moldovan, Moldavian |
| Government | Parliamentary republic |
| • President | Vladimir Voronin (PCRM) (acting) |
| • Speaker of the Parliament | vacant |
| • Prime Minister | Zinaida Greceanîi (PCRM) (acting) |
| Consolidation | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33,846 km (13,068 sq mi) (139th) |
| • Water (%) | 1.4 |
| Population | |
| • 2008 estimate | 4,128,047 (121st) |
| • 2004 census | 3,383,332 |
| • Density | 1,219/km (3,157.2/sq mi) (87th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $10.746 billion |
| • Per capita | $3,173 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $6.124 billion |
| • Per capita | $1,808 |
| Gini (2007) | 37.1 medium inequality |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (111th) |
| Currency | Moldovan leu (MDL) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | 373 |
| ISO 3166 code | MD |
| Internet TLD | .md |
| |
Moldova /mɒlˈdoʊvə/, officially the Republic of Moldova (Republica Moldova) is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east and south.
In the Middle Ages, most of the present territory of Moldova was part of the Principality of Moldavia. In 1812, it was annexed by the Russian Empire, and became known as Bessarabia. Between 1856 and 1878, the southern part was returned to Moldavia. In 1859 it united with Wallachia to form modern Romania.
Upon the dissolution of the Russian Empire in 1917, an autonomous, then-independent Moldavian Democratic Republic was formed, which joined Romania in 1918. Part of Romania during the interwar period, in 1940, Bessarabia was occupied and annexed by the Soviet Union and was split between the Ukrainian SSR and the newly created Moldavian SSR, following the carve-up of Romania in the Ribbentrop-Molotov pact between Hitler's Germany and Stalin's USSR.
After changing hands in 1941 and 1944 during World War II, the territory of the modern country was subsumed by the Soviet Union until its declaration of independence on August 27, 1991. Moldova was admitted to the UN in March 1992.
Although independent from the USSR since 1991, Russian forces have remained on Moldovan territory east of the Dniester River supporting the Slavic majority population, mostly Ukrainians and Russians, who have proclaimed a "Transnistria" republic. Most of today's Moldova was once part of Romania and about 800,000 Moldovans, responding to an offer from Bucharest, have either secured or applied for Romanian citizenship.
The country is a parliamentary democracy with a president as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. Moldova is a member state of the United Nations, Council of Europe, WTO, OSCE, GUAM, CIS, BSEC and other international organizations. Moldova currently aspires to join the European Union, and has implemented the first three-year Action Plan within the framework of the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP). The population in Moldova, which held parliamentary elections in July, 2009, wants reunification with Romania - and the EU membership it would bring.
History
Main article: History of Moldova
Antiquity and early middle ages
Main article: Dacia Main article: Roman DaciaIn Antiquity Moldova's territory was inhabited by Dacian tribes. Between the 1st and 7th centuries AD, the south was intermittently under the Roman, then Byzantine Empires. Due to its strategic location on a route between Asia and Europe, Moldova was repeatedly invaded, including by the Bastarns, Sarmatians, Goths, Huns, Avars, Magyars, Kievan Rus', Pechenegs, Cumans, and the Mongols.
Principality of Moldavia
Main article: MoldaviaTatar invasions continued after the establishment of the Principality of Moldavia in 1359, bounded by the Carpathian mountains in the west, Dniester river in the east, and Danube and Black Sea in the south. Its territory comprised the present-day territory of the Republic of Moldova, the eastern eight of the 41 counties of Romania, and the Chernivtsi oblast and Budjak region of Ukraine. Like the present-day republic, it is known to the locals as Moldova. In 1538, the principality became a tributary to the Ottoman Empire, but it retained internal and partial external autonomy.
19th century

In 1812, according to the Treaty of Bucharest between the Ottoman Empire (of which Moldavia was a vassal) and the Russian Empire, the former ceded the eastern half of the territory of the Principality of Moldavia, along Khotyn and old Bessarabia (modern Budjak), despite numerous protests by Moldavians. At first, the Russians used the name "'Oblast' of Moldavia and Bessarabia", allowing a large degree of autonomy, but later (in 1828) suspended the self-administration and called it Guberniya of Bessarabia, or simply Bessarabia, starting a process of Russification. The western part of Moldavia (which is not a part of present-day Moldova) remained an autonomous principality, and in 1859, united with Wallachia to form the Kingdom of Romania. In 1856, the Treaty of Paris saw three counties of Bessarabia, Cahul, Bolgrad and Ismail, returned to Moldavia, but in 1878, the Treaty of Berlin saw the Kingdom of Romania returning them to the Russian Empire.
Upon annexation, after the expulsion of the large Nogai Tatar population of Budjak (Little Tartary), the Moldovan/Romanian population of Bessarabia was predominant. The colonization of the region in the 19th century, generated by the need to better exploit the resources of the land,, and by the absence of serfdom in Bessarabia, lead to an increase in the Russian, Ukrainian, Lipovan, and Cossack populations in the region; this together with a large influx of Bulgarian immigrants, saw an increase of the Slavic population to more than a fifth of the total population by 1920. With the settling of other nationals such as Gagauz, Jews (Bessarabian Jews), and Germans (Bessarabian Germans), the proportion of the Moldovan population decreased from around 86% to 52% by some sources or to 70% by others during the course of the century. According to the census of 1897, the capital Kishinev had a Jewish population of 50,000, or 46%, out of a total of approximately 110,000. The Tsarist policy in Bessarabia was in part aimed at denationalization of the Romanian element by forbidding after the 1860s education and religious mass in Romanian. However, the effect was an extremely low literacy rate (in 1897 approx. 18% for males, approx. 4% for females) rather than a denationalization.
Union with Romania
Main articles: Union of Bessarabia with Romania and Greater Romania Main article: Sfatul ŢăriiWorld War I brought in a rise in political and cultural (national) awareness of the locals, as 300,000 Bessarabians were drafted into the Russian Army formed in 1917; within bigger units several "Moldavian Soldiers' Committees" were formed. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917, a Bessarabian parliament, Sfatul Ţării, which was elected in October-November 1917 and opened on December 3 [O.S. November 21] 1917, proclaimed the Moldavian Democratic Republic (December 15 [O.S. December 2] 1917) within a federal Russian state, and formed its government (December 21 [O.S. December 8] 1917). Bessarabia proclaimed independence from Russia (February 6 [O.S. January 24] 1918), and, on April 9 [O.S. March 27] 1918, in presence of the Romanian army that entered the region to counter a Bolshevik coup attempt in early January, Sfatul Ţării decided with 86 votes for, 3 against and 36 abstaining, to unite with the Kingdom of Romania, conditional upon the fulfilment of the agrarian reform, local autonomy, and respect for universal human rights. The conditions were dropped after Bukovina and Transylvania also joined the Kingdom of Romania.


After 1918 Bessarabia was under Romanian jurisdiction for the next 22 years. This fact was recognized in the Treaty of Paris (1920) which, however, some today argue has never come into force since it was not ratified by Japan. The newly-communist Russia did not recognize the Romanian rule over Bessarabia. Furthermore, Russia and later, the Soviet Union, considered the region to be Soviet territory under foreign occupation and conducted numerous diplomatic attempts to reclaim it. No diplomatic relations existed between the two states until 1934. Nonetheless, both countries subscribed to the principle of non-violent resolution of territorial disputes in the Kellogg-Briand Treaty of 1928 and the Treaty of London of July 1933. Meanwhile, the neighboring region of Transnistria, part of the Ukrainian SSR at the time, was formed into the Moldavian ASSR after the failure of the Tatarbunary Uprising in 1924.
The agrarian (land) reform, implemented by Sfatul Ţării in 1918-1919, resulted in a rise of a middle class, as 87% of the region's population lived in rural areas. Together with peace and favorable economic circumstances, this reform resulted in a small economic boom. However, urban development and industry were insignificant, and the region remained primarily an agrarian rural region throughout the interwar period. Certain improvements were achieved in the area of education, the literacy rate rising from 15.6% in 1897 to 37% by 1930; however, Bessarabia continued to lag behind the rest of the country, the national literacy rate being 60%. During the inter-war period, Romanian authorities also conducted a program of Romanianization that sought to assimilate ethnic minorities throughout the country. The enforcement of this policy was especially pervasive in Bessarabia due to its highly diverse population, and resulted in the closure of minority educational and cultural institutions.
Soviet era
Main article: Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina Main article: Moldavian Soviet Socialist RepublicIn August 1939, the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact and its secret Additional Protocol were signed, by which Nazi Germany recognized Bessarabia as being within the Soviet sphere of influence, which led the latter to actively revive its claim to the region. On June 26, 1940, Romania received an ultimatum from the Soviet Union, demanding the evacuation of the Romanian military and administration from Bessarabia and, unexpectedly, from the northern part of Bukovina, with an implied threat of invasion in the event of non-compliance. Under pressure from Moscow and Berlin, the Romanian administration and the army retreated from these territories, and on June 28, 1940 they were occupied by the Soviet Union. During the retreat, the Romanian Army was attacked by the Soviet Army, which entered Bessarabia before the Romanian administration finished retreating. Some 42,876 Romanian soldiers and officers were unaccounted for after the retreat. The northern and southern parts, which had sizable minorities (Ukrainians, Bessarabian Bulgarians, Bessarabian Germans, or Lipovans), were transferred to the Ukrainian SSR as the Chernivtsi and Izmail Oblasts. At the same time, the Moldavian ASSR was disbanded, and up to half its territory, where Moldovans were a majority, was joined with the remaining territory of Bessarabia to form the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic (MSSR), contiguous with present-day Moldova.
By participating in the 1941 Axis invasion of the Soviet Union, Romania seized the lost territories of Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina, as well as those of the former MASSR, and established its administration there. In occupied Transnistria, Romanian forces, working with the Germans, deported or exterminated ca. 300,000 Jews, including 147,000 from Bessarabia and Bukovina (of the latter, over 90,000 perished). The Soviet Army reconquered and re-annexed the area in February-August 1944.
Under early Soviet rule, deportations of locals to the northern Urals, to Siberia, and Kazakhstan occurred regularly throughout the Stalinist period, with the largest ones on 12–13 June 1941, and 5-6 July 1949, accounting for 19,000 and 35,000 deportees respectively (from MSSR alone). According to Russian historians, in 1940-1941, ca. 90,000 inhabitants of the annexed territories were subject to political persecutions, such as arrests, deportations, or executions. In 1946, as a result of a severe drought and excessive delivery quota obligations and requisitions imposed by the Soviet government, the southwestern part of the USSR suffered from widespread famine resulting in 216,000 deaths and about 350,000 cases of dystrophy in the Moldavian SSR alone. Similar events occurred in 1930s in the Moldavian ASSR. In 1944-53, there were numerous anti-Communist armed resistance groups active in Moldova; however the NKVD and later MGB managed to arrest, execute or deport most of them and their power base.
The postwar period saw a wide scale migration of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians into the new Soviet republic, especially into urbanized areas, partly to compensate the demographic loss caused by the emigration of 1940 and 1944. The Soviet government conducted a campaign to promote a Moldovan ethnic identity, different from that of the Romanians, based on a theory developed during the existence of the Moldavian ASSR (1924-1940). Official Soviet policy asserted that the language spoken by Moldovans was distinct from the Romanian language (see Moldovenism). To distinguish the two, during the Soviet period, Moldovan was written in the Cyrillic alphabet, in contrast with Romanian, which since 1860 was written in the Latin alphabet. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Moldavian SSR received substantial allocations from the budget of the USSR to develop industrial and scientific facilities as well as housing. In 1971, the Council of Ministers of the USSR adopted a decision "About the measures for further development of the city of Kishinev" (modern Chişinău), that allotted more than one billion Soviet rubles from the USSR budget for building projects; subsequent decisions also directed substantial funding and brought qualified specialists from other parts of the USSR to develop Moldova's industry. This influx of investments stopped in 1991 with the dissolution of the Soviet Union, when Moldova became independent.
Independence
Main article: Politics of MoldovaIn the new political conditions created after 1985 by the glasnost policy introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev, in 1986, to support perestroika (restructuring), a Democratic Movement of Moldova (Template:Lang-ro) was formed, which in 1989 became known as the nationalist Popular Front of Moldova (FPM; Template:Lang-ro). Along with several other Soviet republics, from 1988 onwards, Moldova started to move towards independence. On August 27, 1989, the FPM organized a mass demonstration in Chişinău, that became known as the Great National Assembly (Template:Lang-ro), which pressured the authorities of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic to adopt a language law on August 31, 1989 that proclaimed the Moldovan language written in the Latin script to be the state language of the MSSR. Its identity with the Romanian language was also established.
The first independent elections for the local parliament were held in February and March 1990. Mircea Snegur was elected as Speaker of the Parliament, and Mircea Druc as Prime Minister. On June 23, 1990, the Parliament adopted the Declaration of Sovereignty of the Soviet Socialist Republic Moldova, which, among other things, stipulated the supremacy of Moldovan laws over those of the Soviet Union. After the failure of the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, on August 27, 1991, Moldova declared its independence. On December 21 of the same year Moldova, along with most of the former Soviet republics, signed the constitutive act that formed the post-Soviet Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Declaring itself a neutral state, it did not join the military branch of the CIS. Three months later, on March 2, 1992, the country gained formal recognition as an independent state at the United Nations. In 1994, Moldova became a member of NATO's Partnership for Peace program and also a member of the Council of Europe on June 29, 1995.
Transnistria
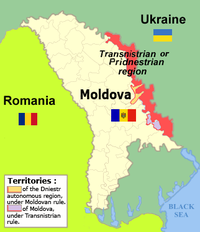
In the region east of the Dniester river, Transnistria, which includes a large proportion of predominantly Russophone ethnic Russians and Ukrainians (51%, as of 1989, with ethnic Moldovans forming a 40% plurality), and where the headquarters and many units of the Soviet 14th Guards Army were stationed, an independent "Transdnestrian Moldovan Republic" (TMR) was proclaimed on August 16, 1990, with its capital in Tiraspol. The motives behind this move were fear of the rise of nationalism in Moldova and the country's expected reunification with Romania upon secession from the USSR. In the winter of 1991-1992 clashes occurred between Transnistrian forces, supported by elements of the 14th Army, and the Moldovan police. Between March 2 and July 26, 1992, the conflict escalated into a military engagement.
The Russian military remains in the breakaway region east of the Dniester to this day, despite Russia having signed international agreements to withdraw, and against the will of Moldovan government. The postwar status quo remains to this day: Chişinău offers extensive autonomy, while Tiraspol demands independence. De jure, Transnistria is internationally recognized as part of Moldova, but de facto, the authorities in Chişinău do not exercise any control over that territory.
Post-independence politics (1992-2009)
On January 2, 1992, Moldova introduced a market economy, liberalizing prices, which resulted in huge inflation. From 1992 to 2001, the young country suffered its worst economic crisis, leaving most of the population below the poverty line. In 1993, a national currency, the Moldovan leu, was introduced to replace the Soviet ruble. The end of the planned economy also meant that industrial enterprises would have to buy supplies and sell their goods by themselves, and most of the management was unprepared for such a change. Moldova's industry, especially machine building, became all but defunct, and unemployment skyrocketed. The economic fortunes of Moldova began to change in 2001; since then the country has seen a steady annual growth of between 5% and 10%. The early 2000s also saw a considerable growth of emigration of Moldovans looking for work (mostly illegally) in Italy, Portugal, Spain, Greece, Cyprus, Turkey, and other countries, in addition to work in Russia. Remittances from Moldovans abroad account for almost 38% of Moldova's GDP, the second-highest percentage in the world. Officially, Moldova's annual GDP is on the order of $1,000 per capita; however, a significant part of the economy goes unregistered due to corruption.
The pro-nationalist governments of prime-ministers Mircea Druc (May 25, 1990 - May 28, 1991), and Valeriu Muravschi (May 28, 1991 - July 1, 1992), were followed by a more moderate government of Andrei Sangheli, which saw the decline of the pro-Romanian nationalist sentiment. After the 1994 elections, Moldovan Parliament adopted measures that distanced Moldova from Romania. The new Moldovan Constitution also provided for autonomy for Transnistria and Gagauzia. On December 23, 1994, the Parliament of Moldova adopted a "Law on the Special Legal Status of Gagauzia", and in 1995 it was constituted.
After winning the presidential elections of 1996, on January 15, 1997, Petru Lucinschi, the former First Secretary of the Moldavian Communist Party in 1989-91, became the country's second president. After the legislative elections on March 22, 1998, an Alliance for Democracy and Reform was formed by non-Communist parties. However, activity of the new government of prime-minister Ion Ciubuc (January 24, 1997- February 1, 1999) was marked by chronic political instability, which prevented a coherent reform program. The 1998 financial crisis in Russia, Moldova's main economic partner at the time, produced an economic crisis in the country. The standard of living plunged, with 75% of population living below the poverty line, while the economic disaster caused 600,000 people to eventually leave the country.
New governments were formed by Ion Sturza (February 19 - November 9, 1999) and Dumitru Braghiş (December 21, 1999 - April 19, 2001). On July 21, 2000, the Parliament adopted an amendment to the Constitution that transformed Moldova from a presidential to a parliamentary republic, in which the president is elected by 3/5 of the votes in the parliament, and no longer directly by the people.
Only 3 of the 31 political parties passed the 6% threshold of the February 25, 2001 early elections. Winning 49.9% of the vote, the Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova (reinstituted in 1993 after being outlawed in 1991), gained 71 of the 101 MPs, and on April 4, 2001, elected Vladimir Voronin as the country's third president. A new government was formed on April 19, 2001 by Vasile Tarlev. The country became the first post-Soviet state where a non-reformed Communist Party returned to power. In March-April 2002, in Chişinău, several mass protests took place against the plans of the government to fulfill its electoral promise and introduce Russian as the second state language along with its compulsory study in schools. The government mainly renounced these plans. Relationship between Moldova and Russia deteriorated in November 2003 over a Russian proposal for the solution of the Transnistrian conflict, which Moldovan authorities refused to accept because it stipulated a 20-year Russian military presence in Moldova. The federalization plan for Moldova would have also turned Transnistria and Gagauzia into a blocking minority over all major policy matters of Moldova. As of 2006, approximately 1,200 of the 14th army personnel remain stationed in Transnistria, guarding a large ammunitions depot at Colbasna. In the last years, negotiations between the Transnistrian and Moldovan leaders have been going on under the mediation of the OSCE, Russia, and Ukraine; lately observers from the European Union and the United States have become involved, creating a 5+2 format.
In the wake of the November 2003 deadlock with Russia, a series of shifts in the external policy of Moldova occurred, targeted at rapprochement with the European Union. In the context of the EU's expansion to the east, Moldova wants to sign a Stability an Association Agreement. It implemented its first three-year Action Plan within the framework of the European Neighborhood Policy (ENP) of the EU.
In the March 2005 elections, the Party of the Communists (PCRM) won 46% of the vote, (56 of the 101 seats in the Parliament), Democratic Moldova Block (BMD) won 28.5% of the vote (34 MPs), and the Christian Democratic People Party (PPCD) won 9.1% (11 MPs). On April 4, 2005, Vladimir Voronin was re-elected as country's president, supported by a part of the opposition, and on April 8, Vasile Tarlev was again charged as head of government. On March 31, 2008, Vasile Tarlev was replaced by Zinaida Greceanîi as head of the government.
2009 election protests
Main article: 2009 Moldova civil unrestFollowing the parliamentary elections on April 5, 2009 the Communist Party won 49.48% of the votes, followed by the Liberal Party with 13.14% of the votes, the Liberal Democratic Party with 12.43% and the Alliance "Moldova Noastră" with 9.77%. The opposition leaders have protested against the outcome calling it fraudulent and demanded a repeated election.
A preliminary report by OSCE observers called the vote generally free and fair. However, one member of the OSCE observation team expressed concerns over that conclusion and said that she and a number of other team members feel that there had been some manipulation, but they were unable to find any proof.
On April 6, 2009, several NGOs and opposition parties organized a protest in Chişinău, gathering a crowd of about 15,000 with the help of social network sites such as Twitter and Facebook. The protesters accused the Communist government of electoral fraud. Anti-communist and pro-Romanian slogans were widely used. The demonstration had spun out of control on April 7 and escalated into a riot when a part of the crowd attacked the presidential offices and broke into the parliament building, looting and setting its interior on fire. Police had regained control on the night of April 8, arresting and detaining several hundred protesters. Numerous detainees reported beatings by the police when released. The violence on both sides (demonstrators and police) was condemned by the OSCE and other international organizations. Three young people have died during the day the protests took place. The opposition blamed police abuse for these deaths, while the government claimed they were either unrelated to the protests, or accidents. Government officials, including President Vladimir Voronin, have called the rioting a coup d'état attempt and have accused Romania of organizing it. The opposition accused the government of organizing the riots by introducing agent provocateur among the protesters.
The political climate in Moldova remains unstable. The parliament failed to elect a new president. For this reason, the parliament was dissolved and new general elections were held on July 29, 2009, with the Communists again attaining a substantial, although weakened, plurality both in popular vote and in parliamentary seats; similar unproved allegations of voting manipulations were prevalent.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Moldova
The largest part of the country lies between two rivers, the Dniester and the Prut. Moldova's rich soil and temperate continental climate (with warm summers and mild winters) have made the country one of the most productive agricultural regions since ancient times, and a major supplier of agricultural products in southeastern Europe. The western border of Moldova is formed by the Prut river, which joins the Danube before flowing into the Black Sea. In the north-east, the Dniester is the main river, flowing through the country from north to south, receiving the waters of Răut, Bâc, Ichel, Botna. Ialpug flows into one of the Danube limans, while Cogâlnic into the Black Sea chain of limans.
The country is landlocked, even though it is very close to the Black Sea. While the northern part of the country is hilly, elevations never exceed 430 meters (1,411 ft)—the highest point being the Bălăneşti Hill. Moldova's hills are part of the Moldavian Plateau, which geologically originate from the Carpathian Mountains. Its subdivisions in Moldova include Dniester Hills (Northern Moldavian Hills and Dniester-Rāut Ridge), Moldavian Plain (Middle Prut Valley and Bălţi Steppe), and Central Moldavian Plateau (Ciuluc-Soloneţ Hills, Corneşti Hills (Codri Massive) - Codri, meaning "forests" -, Lower Dniester Hills, Lower Prut Valley, and Tigheci Hills). In the south, the country has a small flatland, the Bugeac Plain. The territory of Moldova east of the river Dniester is split between parts of the Podolian Plateau, and parts of the Eurasian Steppe.
Phytogeographically, Moldova is shared between the Central European and Eastern European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the WWF, the territory of Moldova can be subdivided into three ecoregions: the Central European mixed forests, the East European forest steppe (the most territory of the country), and Pontic steppe (in the south and southeast).
The country's main cities are the capital Chişinău, in the center of the country, Tiraspol (in Transnistria), Bălţi and Tighina.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of MoldovaMoldova is a unitary parliamentary representative democratic republic. The Constitution of Moldova, adopted in 1994, sets the framework for the government of the country. A parliamentary majority of at least two thirds is required to amend the constitution, which cannot be revised in time of war or national emergency. Amendments to the Constitution affecting the state's sovereignty, independence, or unity can only be made after a majority of voters support the proposal in a referendum. Furthermore, no revision can be made to limit the fundamental rights of people enumerated in the Constitution.
The country's central legislative body is the unicameral Moldovan parliament (Parlament), which has 101 seats, and whose members are elected by popular vote on party lists every four years.
The head of state is the president, who is elected by Parliament, requiring the support of three fifths of the deputies (at least 61 votes). The president appoints a prime minister who functions as the head of government, and who in turn assembles a cabinet, both subject to parliamentary approval.
The Constitution also establishes an independent Constitutional Court, composed of six judges (two appointed by the President, two by Parliament, and two by the Supreme Council of Magistrature), serving six-year terms, during which they are irremovable and not subordinate to any power. The Court is invested with the power of judicial review over all acts of the parliament, over presidential decrees, and over international treaties, signed by the country.
The 2005 parliamentary elections were won by the Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova, which held a majority of 55 seats. Other parties represented in the Parliament were the Our Moldova Alliance (13 seats), the Democratic Party (Moldova) (11 seats), the Christian-Democratic People's Party (7 seats), with 15 unaffiliated members of parliament.
The most recent parliamentary elections occurred on April 5, 2009. The Party of Communists won these as well, claiming 60 seats. The PCRM majority makes Moldova one of only three countries with democratically-elected Communist leaders, the other two being Cyprus and Nepal. Opposition is represented by the Liberal Party (PL, 15 seats), Liberal Democratic Party of Moldova (PLDM, 15 seats) and Party Alliance Our Moldova (AMN, 11 seats).
The President of Moldova is Vladimir Voronin, who has held this post since 2001.
Foreign relations
Main articles: Foreign Relations of Moldova and Moldova and the European UnionAfter achieving independence from the Soviet Union, Moldova established relations with other European countries. A course for European Union integration and neutrality define the country's foreign policy guidelines. In 1995 the country became the first post-Soviet state admitted to the Council of Europe. In addition to its participation in NATO's Partnership for Peace program, Moldova is also a member state of the United Nations, the OSCE, the North Atlantic Cooperation Council, the World Trade Organization, the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the Francophonie and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. In 2005 Moldova and EU established an action plan that sought to improve the collaboration between the two neighboring structures. In June 2007 the Vice President of the Moldovan Parliament Iurie Roşca signed a bilateral agreement with the International Parliament for Safety and Peace, an intergovernmental organization for the promotion of world peace, based in Italy. After the War of Transnistria, Moldova had sought a peaceful resolution to the conflict in the Transnistria region by working with Romania, Ukraine, and Russia, calling for international mediation, and cooperating with the OSCE and UN fact-finding and observer missions. The foreign minister of Moldova, Andrei Stratan, had repeatedly stated that the Russian troops stationed in the breakaway region are there against the will of the Moldovan Government and called on them to leave "completely and unconditionally."
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of Moldova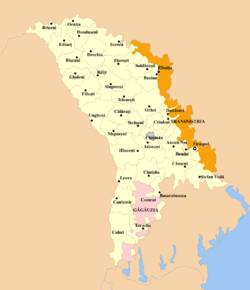
Moldova is divided into thirty-two districts (raioane, singular raion); three municipalities (Bălţi, Chişinău, Bender); and two autonomous regions (Găgăuzia and Transnistria). The cities of Comrat and Tiraspol, the administrative seats of the two autonomous territories also have municipality status. The 32 districts are:
The final status of Transnistria is still disputed, as the central government does not control that territory.
Largest cities and their population:
| # | City | without suburbs | with suburbs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chişinău | 647,513 (2005) | 712,218 (2004) |
| 2. | Tiraspol | 159,163 (2004) | 159,163 (2004) |
| 3. | Bălţi | 122,778 (2005) | 127,561 (2004) |
| 4. | Tighina | 97,027 (2004) | 100,000 (2004) |
| 5. | Rîbniţa | 53,648 (2004) | 53,648 (2004) |
| 6. | Cahul | 35,488 (2004) | 35,488 (2004) |
| 7. | Ungheni | 32,530 (2004) | 32,530 (2004) |
| 8. | Soroca | 28,362 (2004) | 28,362 (2004) |
| 9. | Orhei | 25,641 (2004) | 25,641 (2004) |
| 10. | Dubăsari | 23,650 (2004) | 23,650 (2004) |
| 11. | Comrat | 23,327 (2004) | 23,327 (2004) |
| 12. | Ceadîr-Lunga | 19,401 (2004) | 19,401 (2004) |
| 13. | Străşeni | 18,320 (2004) | 19,090 (2004) |
| 14. | Căuşeni | 17,757 (2004) | 17,757 (2004) |
| 15. | Drochia | 16,606 (2004) | 16,606 (2004) |
| 16. | Edineţ | 15,624 (2004) | 17,292 (2004) |
Economy
Main article: Economy of Moldova
Moldova enjoys a favorable climate and good farmland but has no major mineral deposits. As a result, the economy depends heavily on agriculture, featuring fruits, vegetables, wine, and tobacco. The economy contracted dramatically following the fall of the Soviet Union. Currently, Moldova is the poorest country in Europe.
Energy
Moldova must import all of its supplies of petroleum, coal, and natural gas, largely from Russia. Moldova is a partner country of the EU INOGATE energy programme, which has four key topics: enhancing energy security, convergence of member state energy markets on the basis of EU internal energy market principles, supporting sustainable energy development, and attracting investment for energy projects of common and regional interest.
Economic reforms
After the break up of the Soviet Union in 1991, energy shortages contributed to sharp production declines. As part of an ambitious economic liberalization effort, Moldova introduced a convertible currency, liberalized all prices, stopped issuing preferential credits to state enterprises, backed steady land privatization, removed export controls, and liberalized interest rates. The government entered into agreements with the World Bank and the IMF to promote growth. Recent trends indicate that the Communist government intends to reverse some of these policies, and recollectivise land while placing more restrictions on private business. The economy returned to positive growth, of 2.1% in 2000 and 6.1% in 2001. Growth remained strong in 2007 (6%), in part because of the reforms and because of starting from a small base. The economy remains vulnerable to higher fuel prices, poor agricultural weather, and the skepticism of foreign investors.
Following the regional financial crisis in 1998, Moldova has made significant progress towards achieving and retaining macroeconomic and financial stabilization. It has, furthermore, implemented many structural and institutional reforms that are indispensable for the efficient functioning of a market economy. These efforts have helped maintain macroeconomic and financial stability under difficult external circumstances, enabled the resumption of economic growth and contributed to establishing an environment conducive to the economy’s further growth and development in the medium term. Despite these efforts, and despite the recent resumption of economic growth, Moldova still ranks low in terms of commonly-used living standards and human development indicators in comparison with other transition economies. Although the economy experienced a constant economic growth after 2000: with 2.1%, 6.1%, 7.8% and 6.3% between 2000 and 2003 (with a forecast of 8% in 2004), one can observe that these latest developments hardly reach the level of 1994, with almost 40% of the GDP registered in 1990. Thus, during the last decade little has been done to reduce the country’s vulnerability. After a severe economic decline, social and economic challenges, energy uprooted dependencies, Moldova continues to occupy one of the last places among European countries in income per capita.
In 2005 (Human Development Report 2008), the registered GDP per capita US $ 2,100 PPP, which is 4.5 times lower than the world average (US $ 9,543). Moreover, GDP per capita is under the average of its statistical region (US $ 9,527 PPP). In 2005, about 20.8% of the population were under the absolute poverty line and registered an income lower than US $ 2.15 (PPP) per day. Moldova is classified as medium in human development and is at the 111th spot in the list of 177 countries. The value of the Human Development Index (0.708) is below the world average. Moldova remains the poorest country in Europe in terms of official (i.e. excluding the black and grey economy) per capita which currently stands at $1,808.729
The GDP in 2007 constituted $4,104 mln. That constituted a growth of 3% from 2006.
Agriculture
In agriculture, the economic reform started with the land cadastre reform.
Wine industry
Main article: Moldovan wine See also: Moldovan wine producersMoldova is famous for its wines. For many years viticulture and winemaking in Moldova were the general occupation of the population. Evidence of this is present in historical memorials and documents, folklore, and the Moldovan spoken language.
The country has a well established wine industry. It has a vineyard area of 147,000 hectares (360,000 acres), of which 102,500 ha (253,000 acres) are used for commercial production. Most of the country's wine production is made for export. Many families have their own recipes and strands of grapes that have been passed down through the generations.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Moldova
Cultural and ethnic composition
The last reference data is that of the 2004 Moldovan Census (areas controlled by the central government), and the 2004 Census in Transnistria (areas controlled by the breakaway authorities, including Transnistria, Bender/Tighina, and four neighboring communes):
| # | Self-identification | Moldovan census |
% Core Moldova |
Transnistrian census |
% Transnistria + Bender |
Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moldovans | 2,564,849 | 75.81% | 177,382 | 31.94% | 2,742,231 | 69.62% |
| 2. | Romanians | 73,276 | 2.17% | 253 | 0.05% | 73,529 | 1.87% |
| 3. | Ukrainians | 282,406 | 8.35% | 160,069 | 28.82% | 442,475 | 11.23% |
| 4. | Russians | 201,218 | 5.95% | 168,678 | 30.37% | 369,896 | 9.39% |
| 5. | Gagauz | 147,500 | 4.36% | 4,096 | 0.74% | 151,596 | 3.85% |
| 6. | Bulgarians | 65,662 | 1.94% | 13,858 | 2.50% | 79,520 | 2.02% |
| 7. | Roma | 12,271 | 0.36% | 507 | 0.09% | 12,778 | 0.32% |
| 8. | Jews | 3,608 | 0.11% | 1,259 | 0.23% | 4,867 | 0.12% |
| 9. | Poles | 2,383 | 0.07% | 1,791 | 0.32% | 4,174 | 0.11% |
| 10. | Others/undeclared | 30,159 | 0.89% | 27,454 | 4.94% | 57,613 | 1.46% |
| — | TOTAL | 3,383,332 | 100% | 555,347 | 100% | 3,938,679 | 100% |
There is an ongoing controversy over whether Romanians and Moldovans are the same ethnic group, namely whether Moldovans' self-identification constitutes an ethnic group distinct and apart from Romanians or a subset. At the census, citizens could declare only one nationality. Consequently, one could not declare oneself both Moldovan and Romanian.
Languages
Main article: Romanian languageThe Constitution of Moldova states that the Moldovan language is the official language, while the Declaration of Independence of the Republic of Moldova names the official language Romanian. The 1989 State Language Law speaks of a Moldo-Romanian linguistic identity.
In 2003, the Communist government of Moldova adopted a national political conception which states that one of the priorities of the national politics of the Republic of Moldova is the insurance of the existence of a Moldovan language. (See also Controversy over national identity in Moldova)
Russian is provided with the status of a "language of interethnic communication" (alongside the official language), and in practice remains widely used on all levels of the society and the state. The above-mentioned national political conception also states that Russian-Moldovan bilingualism is characteristic for Moldova.
Gagauz and Ukrainian have significant regional speaker populations and are granted official status together with Russian in Gagauzia and Transnistria respectively.
| Population of Moldova | Romanian | Russian | Ukrainian | Gagauz | Bulgarian | Other languages, non-declared |
| by native language | 2,588,355 76.51% |
380,796 11.26% |
186,394 5.51% |
137,774 4.07% |
54,401 1.61% |
35,612 1.04% |
| by language of first use | 2,543,354 75.17% |
540,990 15.99% |
130,114 3.85% |
104,890 3.10% |
38,565 1.14% |
25,419 0.75% |
Religion
Main articles: Religion in Moldova and Romanian Orthodox ChurchFor the 2004 census, Eastern Orthodox Christians, who make up over 90% of Moldova's population, were not required to declare the particular of the two main churches they belong to. The Moldovan Orthodox Church, autonomous and subordinated to the Russian Orthodox Church, and the Orthodox Church of Bessarabia, autonomous and subordinated to the Romanian Orthodox Church, both claim to be the national church of the country.
Culture

Located geographically at the crossroads of Latin, Slavic and other cultures, Moldova has enriched its own culture adopting and maintaining some of the traditions of its neighbors and of other influence sources.
The country's cultural heritage was marked by numerous churches and monasteries build by the Moldavian ruler Stephen the Great in the 15th century, by the works of the later renaissance Metropolitans Varlaam and Dosoftei, and those of scholars such as Grigore Ureche, Miron Costin, Nicolae Milescu, Dimitrie Cantemir, Ion Neculce. In the 19th century, Moldavians from the territories of the medieval Principality of Moldavia, then split between Austria, Russia, and an Ottoman-vassal Moldavia (after 1859, Romania), made the largest contribution to the formation of the modern Romanian culture. Among these were many Bessarabians, such as Alexandru Donici, Alexandru Hâjdeu, Bogdan Petriceicu Hasdeu, Constantin Stamati, Constantin Stamati-Ciurea, Costache Negruzzi, Alecu Russo, Constantin Stere.
Mihai Eminescu, a late Romantic poet, and Ion Creangă, a writer, are the most influential Romanian language artists, considered national writers both in Romania and Moldova.
Moldova has produced artists with works that are recognized worldwide: composers (Gavriil Musicescu, Ştefan Neaga, Eugen Doga), sculptors (Alexandru Plămădeală), and architects (Alexey Shchusev, a Moldovan-born Russian architect).
In the field of popular music, Moldova has produced the boyband O-Zone, who came to prominence in 2004, with their hit song Dragostea Din Tei, also known as "The Numa Numa Song".
Ethnic Moldovans, 78.3% of the population, are Romanian-speakers and share the Romanian culture. Their culture has been also influenced (through Eastern Orthodoxy) by the Byzantine culture. The country has also important minority ethnic communities. Gagauz, 4.4% of the population, are the only Christian Turkic people. Greeks, Armenians, Poles, Jews, Ukrainians, although not numerous, were present since as early as 17th century, and had left cultural marks. The 19th century saw the arrival of many more Ukrainians and Jews from Podolia and Galicia, as well as new communities, such as Lipovans, Bulgarians and Germans. In the second part of the 20th century, Moldova saw a massive Soviet immigration, which brought with it many elements of the Soviet culture. The country has now important Russian (6%) and Ukrainain (8.4%) populations. 50% of ethnic Ukrainians, 27% of Gagauzians, 35% of Bulgarians, and 54% of smaller ethnic groups speak Russian as first language. In total, there are 541,000 people (or 16% of the population) in Moldova who use Russian as first language, including 130,000 ethnic Moldovans. By contrast, only 47,000 ethnic minorities use Moldovan/Romanian as first language.
Military
Main article: Military of MoldovaThe Moldovan armed forces consist of the Ground Forces and Air and Air Defense Forces. Moldova has accepted all relevant arms control obligations of the former Soviet Union. On October 30, 1992, Moldova ratified the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of conventional military equipment and provides for the destruction of weapons in excess of those limits. It acceded to the provisions of the nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in October 1994 in Washington, DC. It does not have nuclear, biological, or chemical weapons. Moldova joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation's Partnership for Peace on March 16, 1994.
Crime
Main article: Crime in MoldovaThe CIA World Factbook lists widespread crime and underground economic activity among major crime issues in Moldova.
See also
Main article: Outline of Moldova| Moldova articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |  | ||||
| Geography |
| ||||
| Politics | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Society |
| ||||
Notes
- Template:Ro iconSituaţia demografică în Republica Moldova pentru anul 2007 Demographyc situation in the Republic od Moldova as for January 1, 2008 and 2004 census of Transnistrian region
- ^ "Moldova". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- Template:Ro iconNational Bureau of Statistics of Moldova
- http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/07/26/AR2009072601078.html Moldova, at east-west crossroads, heads for polls
- "Moldova will prove that it can and has chances to become EU member," Moldpress News Agency, June 19, 2007
- "Moldova-EU Action Plan Approved by European Commission", moldova.org, December 14, 2004, retrieved July 2, 2007
- Soldier Khan, Mike Bennighof, Ph.D.
-
- Following the Peace concluded in Bucharest, in 1812, a part of this territory was assigned to Czarist Russia
- Selection of encyclopedias in Russian language on the Treaty of Bucharest
- again "transferred/passed over to the Russian Empire
- Asociaţia Oamenilor de Ştiinţa din Moldova N. Milescu Spa︣taru. V. E. Andruşceac. (2002). History of the Republic of Moldova: from most ancient times till our days - Association of Moldavian scientists "Milescu-Spataru" - Second reviewed and added edition. Elan Poligraf. pp. 95–360. ISBN 9975-9719-5-4.
- Vasile Stati. (2002). Stati V.:History of Moldavia. Tipografia Centrală. pp. 218–220. ISBN 9975-9504-1-8. both use the phrasing According to the Article 4, Porta ceded to Russia the eastern part of the Moldavian Principality - the territory between Prut and Danube
- Article 4 of the Treaty
- what Britannica Encyclopedia concessions of Mahmud II , History of Moldova, History of Ottoman Empire, History of Russo-Turkish wars
- what Columbia Encyclopedia sixth edition 2008
- Batiushkov, P. Bessarabiia: Istoricheskoe opisanie (Saint Petersburg 1892)
- Berg, L. Bessarabiia (Petrograd 1918)
- Dembo, V. Nikoly ne zabuty: Kryvavyi litopys Besarabiï. Z ofitsiinykh dokumentiv (Kharkiv 1923)
- Berg, L. Naselenie Bessarabii, etnograficheskii sostav i chislennost' (Petrograd 1925)
- Babel, A. La Bessarabie (Paris 1926)
- Uhlig, C. Die bessarabische Frage: Eine geopolitische Betrachtung (Breslau 1926)
- Iorga, N. La vérité sur le passé et le présent de la Bessarabie (Bucharest 1931)
- Nistor, I. La Bessarabie et la Bucovine (Bucharest 1937)
- Mokhov, N. Ocherki istorii moldavsko-russko-ukrainskikh sviazei (s drevneishikh vremen do nachala XIX veka) (Kishinev 1961)
- Istoriia Moldavskoi SSR, 1–2 (Kishinev 1965–8)
- Smishko, P. Borot'ba trudiashchykh ukraintsiv prydunais'kykh zemel' za vozz'iednannia z URSR (1917–1940) (Lviv 1969)
- Zelenchuk, V. Nasalenie Moldavii (Demograficheskie protsesy i etnicheshii sostav) (Kishinev 1973)
- Jewsbury, G.F. The Russian Annexation of Bessarabia 1774–1828: A Study of Imperial Expansion (Boulder, Col, 1976)
- Khotinskoe vosstanie (Sbornik dokumentov i materialov) (Kishinev 1976)
- Moldavskaia SSR v Velikoi Otechestvennoi voine Sovetskogo Soiuza, 2 (Kishinev 1976)
- Meurs, W. van. The Bessarabian Question in Communist Historiography: Nationalist and Communist Politics and History-Writing (New York 1994)
- Mennonite-Nogai Economic Relations, 1825-1860
- Bessarabia by Charles Upson Clark, 1927, chapter 8: "The first Russian census after the annexation (1816) revealed a province almost solidly Romanian-of a population of about half a million, 921/2% Moldavian and Ukrainian, 11/2% Lipovans (Russian heterodox), 41/2% Jews, 1.6% other races."
- Marcel Mitrasca, Moldova: A Romanian Province Under Russian Rule, Algora, 2002, ISBN 1892941864, pg. 25
- Ion Nistor, Istoria Basarabiei, Cernăuţi, 1921
- Bessarabia by Charles Upson Clark, 1927, chapter 8: "Today, the Bulgarians form one of the most solid elements in Southern Bessarabia, numbering (with the Gagauzes, i.e. Turkish-speaking Christians also from the Dobrudja) nearly 150,000. Colonization brought in numerous Great Russian peasants, and the Russian bureaucracy imported Russian office-holders and professional men; according to the Romanian estimate of 1920, the Great Russians were about 75,000 in number (2.9%), and the Lipovans and Cossacks 59,000 (2.2%); the Little Russians (Ukrainians) came to 254,000 (9.6%). That, plus about 10,000 Poles, brings the total number of Slavs to 545,000 in a population of 2,631,000, or about one-fifth"
- Ion Nistor, Istoria Bassarabiei, Cernăuţi, 1921
- Template:De icon Flavius Solomon, Die Republik Moldau und ihre Minderheiten (Länderlexikon), in: Ethnodoc-Datenbank für Minderheitenforschung in Südostosteuropa, p. 52
- Bessarabia by Charles Upson Clark, 1927, chapter 7
- Jewish Moldova
- Bessarabia by Charles Upson Clark, 1927, chapter 10: "Naturally, this system resulted not in acquisition of Russian by the Moldavians, but in their almost complete illiteracy in any language."]
- Template:Ro iconprm.md:"Sfatul Tarii ... proclaimed the Moldavian Democratic Republic"
- Charles Upson Clark (1927). "24:The Decay of Russian Setiment". Bessarabia: Russia and Romania on the Black Sea - View Across Dniester From Hotin Castle. New York: Dodd, Mead & Company.
- Pelivan (Chronology)
- Cazacu (Moldova, pp. 240-245).
- Cristina Petrescu, "Contrasting/Conflicting Identities:Bessarabians, Romanians, Moldovans" in Nation-Building and Contested Identities, Polirom, 2001, pg. 156
- Malbone W. Graham (1944). "The Legal Status of the Bukovina and Bessarabia" (– ). The American Journal of International Law. 38 (4). American Society of International Law. Retrieved 2007-12-08.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|format=|month=ignored (help) - Ioan Bulei (March 1998). "Roma, 1924-1927". Magazin Istoric (3). Fundaţia Culturală Magazin Istoric. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
- Wayne S Vucinich, Bessarabia In: Collier's Encyclopedia (Crowell Collier and MacMillan Inc., 1967) vol. 4, p. 103
- ^ Cristina Petrescu, "Contrasting/Conflicting Identities:Bessarabians, Romanians, Moldovans" in Nation-Building and Contested Identities, Polirom, 2001, pg. 159
- ^ Charles King, The Moldovans: Romania, Russia, and the politics of culture, Hoover Institution Press, Stanford University, 2000. ISBN 0-8179-9792-X. p. 23 Cite error: The named reference "CKing" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Olson, James (1994). An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. p. 483.
- Nagy-Talavera, Nicolas M. (1970). Green Shirts and Others: a History of Fascism in Hungary and Romania. p. 305.
- Tismăneanu Report, pages 585
- Template:Ro icon Tismăneanu Report, pages 584 and 587
- ^ Template:Ro icon Comisia Prezidenţială pentru Analiza Dictaturii Comuniste din România: Raport Final / ed.: Vladimir Tismăneanu, Dorin Dobrincu, Cristian Vasile, Bucureşti: Humanitas, 2007, 879 pp., ISBN 978-973-50-1836-8 (Tismăneanu Report)
- Pal Kolsto, National Integration and Violent Conflict in Post-Soviet Societies: The Cases of Estonia and Moldova, Rowman & Littlefield, 2002, ISBN 0742518884, pg. 202
- Architecture of Chişinău on Kishinev.info, Retrieved on 2008-10-12
- ^ Template:Ro Horia C. Matei, "State lumii. Enciclopedie de istorie." Meronia, Bucureşti, 2006, p. 292-294
- "Romanian Nationalism in the Republic of Moldova" by Andrei Panici, American University in Bulgaria, 2002; pages 40 and 41
- Legea cu privire la functionarea limbilor vorbite pe teritoriul RSS Moldovenesti Nr.3465-XI din 01.09.89 Vestile nr.9/217, 1989 (Law regarding the usage of languages spoken on the territory of the Republic of Moldova): "Moldavian SSR supports the desire of the Moldovans that live across the borders of the Republic, and considering the existing linguistic Moldo-Romanian identity — of the Romanians that live on the territory of the USSR, of doing their studies and satisfying their cultural needs in their native language."
- ^ Statement by H.E. Mr. Andrei Stratan at the General Debate of the Sixty Second Session of the UN General Assembly, New-York, 1 October 2007: "I would like to reiterate on this occasion the position of the Republic of Moldova according to which the withdrawal of the Russian troops that remain on the Moldovan territory against its will, in conformity with the obligations assumed by the Russian Federation in 1999 in Istanbul, would create the necessary premises for ratifying and applying the Adapted CFE Treaty."
- http://www.jamestown.org/edm/article.php?article_id=2368523 Jamestown: "Moldovan President wants out of Russia's orbit"
- "Moldova: Information Campaign to Increase the Efficiency of Remittance Flows", International Organization for Migration, 10 December 2008
- Helen Fedor, ed. Moldova: A Country Study. Government. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1995.
- Dr. Mihai Gribincea: "Russian troops in Transnistria – a threat to the security of the Republic of Moldova"
- Moldova-EU Action Plan Approved by European Commission, http://www.azi.md, December 14, 2004, retrieved July 2, 2007
- EU/MOLDOVA ACTION PLAN
- ^ BBC: "Romania blamed over Moldova riots", 8 April 2009
- SevenTimes.ro: "Supporting actions for Moldova's riot", 08 April 2009
- ^ "The protest initiative group: LDPM is the guilty one for the devastations in the Chişinău downtown", April 08, 2009
- Al Jazeera English: "Violent protests after Moldova poll", 7 April 2009.
- OSCE press release: "OSCE Mission to Moldova condemns post-election violence and appeals to all sides for restraint"
- "Moldova: MEPs condemn grave violations of human rights following parliamentary elections".
- "Moldova parliament fails to elect president, crisis deepens"
- ^ Parliament of the Republic of Moldova. The Constitution of the Republic of Moldova 2000. Retrieved 11-14, 2007
- Parliament of the Republic of Moldova. Parliamentary Factions Retrieved 11-14, 2007
- "Moldova Calls On Russian Troops To Leave Transdniestr"
- ^ World Gazetteer. Moldova: largest cities 2004. Retrieved 11-14, 2007
- ^ Pridnestrovie.net 2004 Census 2004. Retrieved 11-14, 2007
- ^ Template:Ro icon Official results of 2004 Moldovan census
- http://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/public/story_page/030-53410-103-04-16-903-20090403STO53395-2009-13-04-2009/default_en.htm
- INOGATE website
- World Economic Outlook Database, April 2009
- 2007 evaluation
- Article 13, line 1 - of Constitution of Republic of Moldova
- Template:Ro Declaraţia de independenţa a Republicii Moldova, Moldova Suverană
- A Field Guide to the Main Languages of Europe - Spot that language and how to tell them apart, on the website of the European Commission
- The law regarding approval of the National Political Conception of the Republic of Moldova stipulates that "The conception is rooted in the historically established truth and confirmed by the common literary treasure: Moldovan nation and Romanian nation use a common literary form "which is based on the live spring of the popular talk from Moldova" - a reality which impregnates the national Moldovan language with a specific peculiar pronunciation, a certain well known and appreciated charm. Having the common origin; common basic lexical vocabulary, the national Moldovan language and national Romanian language keep each their lingvonim/glotonim as the identification sign of each nation: Moldovan and Romanian."
- ^ Template:Ro icon "Concepţia politicii naţionale a Republicii Moldova" Moldovan Parliament
- Prince Dimitrie Cantemir was one of the most important figures of Moldavian culture of the 18th century. He wrote the first geographical, ethnographic and economic description of the country. Template:La icon Descriptio Moldaviae, (Berlin, 1714), at Latin Wikisource
- Moldova
External links
Template:WikinewsPortalMoldova
Government
- Official site
- Official governmental site
- Official web site of the Parliament
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- The Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- Embassy of the Republic of Moldova in the United States of America
General information
- "Moldova". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Best gateway to discover Moldova
- Country information from the United States Department of State
- Travel information from the United States Department of State
- Portals to the World from the United States Library of Congress
- Moldova at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Moldova
Wikimedia Atlas of Moldova- Template:Wikitravel
International rankings
- Bertelsmann: Bertelsmann Transformation Index 2006, ranked 75th out of 119 countries
- Reporters without borders: Annual worldwide press freedom index (2005), ranked 74th out of 167 countries
- The Wall Street Journal: 2005 Index of Economic Freedom, ranked 77th out of 155 countries
- The Economist: The World in 2005 - Worldwide quality-of-life index, 2005, ranked 99th out of 111 countries
- Transparency International: Corruption Perceptions Index 2005, ranked 88th out of 158 countries
- United Nations Development Programme: Human Development Index 2005, ranked 116th out of 177 countries
- World Economic Forum: Global Competitiveness Report 2005-2006 - Growth Competitiveness Index Ranking, ranked 82nd out of 117 countries
- World Bank: Doing Business 2006, ranked 83rd out of 155
- World Bank: Ease of Starting a Business 2006, ranked 69th out of 155
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Foreign Direct Investment Performance Index 2004, ranked 35th out of 140
News media
- Moldova In The World - online journal
- Moldpres - state owned news agency
- Stiri.md - News Aggregator for all online news agencies
Other
- Tourism in Moldova
- Guide to Moldova's Hotels
- Sport in Moldova
- Igor Pivovar’s Blog: Interethnic relations in Moldova
- ECMI Moldova, European Centre for Minority Issues (ECMI) (Information about Minority Issues in Moldova)
- Dimitrie Cantemir-Descrierea Moldovei
- "Moldova 2006 Investment Climate Statement", Iulian Bogasieru, Business Information Service For The Newly Independent States (BISNIS) Representative (January 2006).
- "Moldova: Young Women From Rural Areas Vulnerable To Human Trafficking", Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (October 6, 2004).
- Country population portal
- OurNet — Moldova Internet Resources
- Business.md - National Business Portal
- Moldova, allcountries.eu (Information about Moldova)
- Various panoramas of Chisinau and Moldova, panorama.md
| International organizations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||