This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Aquamarinedew (talk | contribs) at 20:31, 3 January 2011. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:31, 3 January 2011 by Aquamarinedew (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound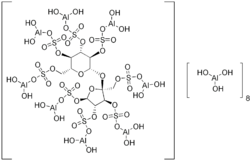 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, suspension, rectal suspension |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 3-5% (local acting) |
| Metabolism | GI; liver: unknown |
| Elimination half-life | unknown |
| Excretion | feces, urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.636 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H54Al16O75S8 |
| Molar mass | 2086.75 g/mol |
Sucralfate is an oral gastrointestinal medication primarily indicated for the treatment of active duodenal ulcers. Brand names include Sucramal in Italy; Carafate in U.S.A.,Pepsigard,Sucral,sucrafil, hapifate in India, Sutra in parts of South-East Asia, Sulcrate in Canada; and Antepsin in Turkey. Sucralfate is also used for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and stress ulcers. Unlike the other classes of medications used for treatment of peptic ulcers, sucralfate is a sucrose sulfate-aluminium complex that binds to the mucosa, thus creating a physical barrier that impairs diffusion of hydrochloric acid in the gastrointestinal tract and prevents degeradation of mucus by acid. It also stimulates bicarbonate output and acts like an acid buffer with cytoprotective properties. Sucralfate was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1981.
Mechanism of action
Sucralfate is a locally acting substance that in an acidic environment (pH < 4) reacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form a cross-linking, viscous, paste-like material capable of acting as an acid buffer for as long as 6 to 8 hours after a single dose. It also attaches to proteins on the surface of ulcers, such as albumin and fibrinogen, to form stable insoluble complexes. These complexes serve as protective barriers at the ulcer surface, preventing further damage from acid, pepsin, and bile. In addition, it prevents back diffusion of hydrogen ions, and adsorbs both pepsin and bile acids. Recently, it has been indicated that sucralfate also stimulates the increase of prostaglandin E2, epidermal growth factors (EGF), bFGF, and gastric mucus.
Clinical uses
The only FDA-approved indication for sucralfate is for the treatment of active duodenal ulcers not related to NSAID usage because the mechanism behind these ulcers is secondary to acid oversecretion. It is not technically approved for gastric ulcers because the main mechanism is not due to acid oversecretion but rather from diminished protection. The use for sucralfate in peptic ulcer disease has diminished recently, but it is still the preferred agent for stress ulcer prophylaxis.
- Active duodenal ulcer not related to NSAID use—1 g PO four times a day given 1 hr before meals and at bedtime for 4–8 weeks
- Maintenance therapy for resolved duodenal ulcers -- 1 g PO bid on empty stomach
- Gastric ulcer not related to NSAID use and gastritis due to GERD—1 g PO four times a day 1 hr before meals and at bedtime. Triple combination therapy with lansoprazole + cisapride + sucralfate can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life and was more cost-effective than ranitidine combination group.
- Aphthous ulcer and stomatitis due to radiation or chemotherapy -- 5-10 mL PO suspension swish and spit/swallow four times a day.
- Proctitis from radiation or ulcerative colitis -- 3 g/15 mL rectal suspension once or twice daily.
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease during pregnancy -- first-line drug therapy combined with lifestyle and diet modification.
- Stress ulcer prophylaxis -- The use of sucralfate rather than H2 antagonists for stress ulcer prophylaxis, and measures to prevent aspiration, such as semirecumbent positioning or continuous subglottic suctioning, have all been shown to reduce the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
- Prevention of stricture formation—Sucralfate has an inhibitory effect on stricture formation in experimental corrosive burns and can be used in the treatment of corrosive esophageal burns to enhance mucosal healing and suppress stricture formation
- Rectal bleeding and its management after irradiation for uterine cervical cancer
Grade 1 bleeding experienced immediate relief with sucrasulfate enema for 1 month. Grade 2 bleeding, sucrasulfate enema and/or coagulation were effective. Grade 3 bleeding lasted for 1 year despite frequent transfusions and coagulation. Grade 2 and 3 rectal bleeding occurred in 8.5% of patients. The most significant risk factor was the ICRU-CRBED. Prompt treatment with a combination of sucrasulfate enema and coagulation is effective in controlling Grade 1 and 2 rectal bleeding without the development of fistula or stricture.
Adverse reactions
The most common side effects seen are constipation and bezoar formation. Less commonly reported include flatulence, cephalalgia (headache), hypophosphatemia, and xerostomia (dry mouth). Nursing mothers: Uncertain.
Notes
- ^ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 9049.
- Maton PN (2003). "Profile and assessment of GERD pharmacotherapy". Cleve Clin J Med. 70 Suppl 5: S51–70. doi:10.3949/ccjm.70.Suppl_5.S51. PMID 14705381.
- Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Nov 1;22(9):749-57.
- Respir Care. 2005 Jun;50(6):725-39; discussion 739-41.
- Surg Today. 2005;35(8):617-22.
- International Journal Radiation Oncology Biological Physics, 2004 Jan 1;58(1):98-105
References
- Journal of Zhejiang University 2003 Sep-Oct; 4(5): 602-6
- Katzung, Bertram G. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 9th ed. (2004).
External links
- Medline Plus
- Mar Vista Animal Medical Center
- Medicine Net
- Rx List
- Drugs.com
- Whole Health MD
- Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- Carafate prescribing information
| Drugs for peptic ulcer and GERD/GORD (A02B) | |
|---|---|
| H2 antagonists ("-tidine") | |
| Prostaglandins (E)/ analogues ("-prost-") | |
| Proton-pump inhibitors ("-prazole") | |
| Potassium-competitive acid blockers ("-prazan") | |
| Others | |
| Combinations | |
| |