This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Template namespace initialisation script (talk | contribs) at 05:37, 4 June 2004. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:37, 4 June 2004 by Template namespace initialisation script (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
A ribosome is an organelle composed of RNA and ribosomal proteins. It translates mRNA into a polypeptide chain (e.g., a protein).
They can be thought of as a factory that builds a protein from a set of genetic instructions. Ribosomes are found in the cytosol (the internal fluid of the cell) of all cells.
Overview
Ribosomes consist of two subunits (Figure 1) that fit together (Figure 2) and work as one to translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain (Figure 3). Each subunit consists of one or two very large RNA molecules (known as ribosomal RNA or rRNA) and several smaller protein molecules.
The structure and function of ribosomes, and their attendant molecules, known as the translational apparatus, has been of ongoing research interest since the mid 20th century on through the early 21st century. A triennial conference is held to discuss the ribosome. In 1999, the conference was held in Helsingør, Denmark. The 2002 conference was held in Queenstown, New Zealand .
| Ribosome structure | Figure 1: The subunits of a ribosome. Side and front view. |
Free ribosomes
Free ribosomes occur in all cells, and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells. Several free ribosomes can associate on a single mRNA molecule to form a polyribosome or polysome. Free ribosomes usually produce proteins that are used in the cytosol or in the organelle they occur in.
Membrane bound ribosomes
When certain proteins are synthesized by a ribosome, it can become "membrane-bound", associated with the membrane of the nucleus and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (in eukaryotes only) for the time of synthesis. They insert the freshly produced polypeptide chains directly into the ER, from where they are transported to their destinations Bound ribosomes usually produce proteins that are used within the cell membrane or are expelled from the cell via exocytosis.
The ribosomal subunits of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are quite similar. However, prokaryotes use 70S ribosomes, each consisting of a (small) 30S and a (large) 50S subunit, whereas eukaryotes use 80S ribosomes, each consisting of a (small) 40S and a (large) 60S subunit.

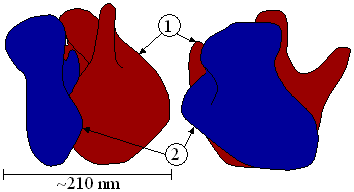
Figure 3 : Translation (1) of mRNA by a ribosome (2) into a polypeptide chain (3). The mRNA begins with a start codon (AUG) and ends with a stop codon (UAG).
In Figure 3, both ribosomal subunits (small and large) assemble at the start codon (the 5' end of the mRNA). The ribosome uses tRNA (transfer RNAs which are RNA molecules that carry an amino acid and present the matching codon, according to the genetic code, to the ribosome) which matches the current triplet on the mRNA to append an amino acid to the polypeptide chain. This is done for each triplet on the mRNA, while the ribosome moves towards the 3' end of the mRNA. Usually, several ribosomes are working parallel on a single mRNA.
See also: protein assembly
| Structures of the cell / organelles | |
|---|---|
| Endomembrane system | |
| Cytoskeleton | |
| Endosymbionts | |
| Other internal | |
| External | |