This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 13:12, 24 February 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:12, 24 February 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation ()(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)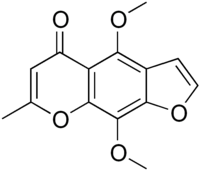
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4,9-Dimethoxy-7-methylfurochromen-5-one | |
| Other names
Amicardine Corafurone Methafrone Kelourin Rykellin Visammin Ammispasmin Ammivisnagen Gynokhellan Interkellin Interkhellin Amikellin Ammipuran Benecardin Deltoside Kelicorin Khelangin Khellamine Khellanals Khellinorm Medekellin Visammimix Viscardan Visnagalin Kalangin Kelincor | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.267 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 260.24 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Khellin is a furanochromone, an organic compound which is derivative of chromone (1,4-benzopyrone) and furan.
It has lipophilic properties and causes vasodilation (widening of blood vessels). It is found in the plant Ammi visnaga which has been used in Egyptian folk medicine.
It is not used as a medication because it is difficult to absorb and causes a range of undesirable side effects such as dizziness, headache, gastrointestinal disorders and nausea.
In Egypt, the plant "Khella" was used for renal colic. The incidence of renal colic was due mostly to schistosomiasis infections and stone formation. The plant mixture had diuretic properties that were seen to relieve renal colic in Egyptian folk medicine. After the chemical compound khellin was identified, people began to study its properties. It was found to relax the ureter and coronary arteries.
In the early 20th century, researchers searched for khellin analogues with lower toxicities and better efficacy. A number of drugs were discovered in researching khellin analogues. Amiodarone and cromolyn sodium are khellin analogues used in current medical practice.
See also
- Ammi (genus)
- Amikhelline, an antimitotic drug