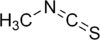This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 09:29, 25 February 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers from ChemSpider, CommonChemistry and FDA for the Chem/Drugbox validation project - Updated: ChEMBL.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 09:29, 25 February 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers from ChemSpider, CommonChemistry and FDA for the Chem/Drugbox validation project - Updated: ChEMBL.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Methylisothiocyanate | |||
| Other names MITC | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.303 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C2H3NS | ||
| Molar mass | 73.12 | ||
| Appearance | colourless solid | ||
| Density | 1.07 g cm | ||
| Melting point | 31 °C (88 °F; 304 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 117 °C (243 °F; 390 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | low | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Methyl isothiocyanate is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3N=C=S. This low melting colorless solid is a powerful lachrymator. As a precursor to a variety of valuable bioactive compounds, it is the most important organic isothiocyanate in industry.
Synthesis
It is prepared industrially by two routes. Annual production in 1993 was estimated to be 4M kg. The main method involves the thermal rearrangement of methyl thiocyanate:
- CH3S-C≡N → CH3N=C=S
It is also prepared via with the reaction of methylamine with carbon disulfide followed by oxidation of the resulting dithiocarbamate with hydrogen peroxide. A related method is useful to prepare this compound in the laboratory.
MITC forms naturally upon the enzymatic degradation of glucocapparin, a modified sugar found in capers.
Reactions
A characteristic reaction is with amines to give methyl thioureas:
- CH3NCS + R2NH → R2NC(S)NHCH3
Other nucleophiles add similarly.
Applications
Solutions of MITC is used in agriculture as a soil fumigant, mainly for protection against fungi and nematodes.
MITC is a building block for the synthesis of 1,3,4-thiadiazoles, which are heterocyclic compounds used as herbicides. Commercial products include "Spike", "Ustilan," and "Erbotan." Well known pharmaceuticals prepared using MITC include Zantac and Tagamet.
Safety
MITC is a dangerous lachrymator as well as being poisonous.
References
- ^ F. Romanowski, H. Klenk "Thiocyanates and Isothiocyanates, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim.
- Moore, M. L.; Crossley, F. S. (1955). "Methyl Isothiocyanate". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 3, p. 599.