This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 14:01, 7 August 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'DrugBank').). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:01, 7 August 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'DrugBank').)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound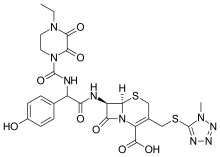 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.057.936 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H27N9O8S2 |
| Molar mass | 645.67 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefoperazone is a third generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid, and also marked by pharco B international under the name of Cefazoneand also marketed by "sigmatec " under the name " cefoperazone" . It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating Pseudomonas bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics.
Cefina-SB is a combination of sulbactam and cefoperazone. Cefoperazone exerts its bactericidal effect by inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis, and sulbactam acts as a beta-lactamase inhibitor, to increase the antibacterial activity of cefoperazone against beta-lactamase producing organisms. In some countries, the combination is sold as Sulperazone. Gepach International markets this combination of Cefoperazone with Sulbactam under the brand name Bacperazone
Adverse effects
Cefoperazone contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.
References
- Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA (eds.) (ed.). Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|editor=has generic name (help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link)
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |