This is an old revision of this page, as edited by The chemistds (talk | contribs) at 21:44, 17 October 2011 (added CSID, (Std)InChI & (Std)InChIKey). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:44, 17 October 2011 by The chemistds (talk | contribs) (added CSID, (Std)InChI & (Std)InChIKey)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound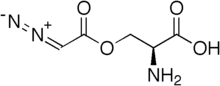 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.692 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H7N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 173.127 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Azaserine is a carcinogen primarily used for researching pancreatic cancer in animal models. It is a glutamine analogue that irreversibly inhibits glutamine utilizing enzymes such as Gln: Phosphoribosyl Amidotransferase, which is involved in the biosynthesis of Inosine monophosphate (IMP). IMP is an important precursor to the purine nucleotides which include Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and Guanosine monophosphate (GMP).
Further enzymes of purine and pyrimidine metabolism are inhibited as well. Therefore it was tested as anti-cancer drug by different authors in different indications (not only pancreatic cancer) in pre-clinical settings. Further glutamine analogues that were tested as anti-cancer drugs are DON and Acivicin.
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |