This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 15:32, 19 October 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEMBL').). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:32, 19 October 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEMBL').)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Names | |
|---|---|
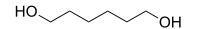
| IUPAC name hexane-1,6-diol | |
| Other names Hexamethylene glycol; 1,6-Dihydroxyhexane; 1,6-Hexylene glycol; Hexamethylenediol; HDO | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.068 |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H14O2 |
| Molar mass | 118.176 g·mol |
| Melting point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
1,6-Hexanediol (HOCH2(CH2)4CH2OH) is a colorless crystalline solid that melts at 42 °C and boils at 250 °C. It is well soluble in water.
Production
1,6-Hexanediol is prepared industrially by the hydrogenation of adipic acid.
Uses
1,6-Hexanediol is widely used for industrial polyester and polyurethane production.
References
| This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "1,6-Hexanediol" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |