This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 00:55, 22 October 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:55, 22 October 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)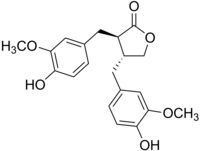 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (3R,4R)-3,4-bisoxolan-2-one | |
| Other names (αR,βR)-α,β-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)butyrolactone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C20H22O6 |
| Molar mass | 358.390 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Matairesinol is a plant lignan. It occurs with secoisolariciresinol in numerous foods such as oil seeds, whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
The plant lignans are precursors of the enterolignans (mammalian lignans). A number of plant lignans are metabolized to the enterolignans (enterodiol and enterolactone) that can potentially reduce the risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases.
Although there are studies which indicate the disease prevention (cardio-protective and hormone associated cancers like breast cancer) benefits of lignans, the results are not yet conclusive.
References
- Matairesinol at Sigma-Aldrich
- Niemeyer HB, Honig DM, Kulling SE, Metzler M (2003). "Studies on the metabolism of the plant lignans secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". J. Agric. Food Chem. 51 (21): 6317–25. doi:10.1021/jf030263n. PMID 14518962.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Milder IE, Arts IC, van de Putte B, Venema DP, Hollman PC (2005). "Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: a database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". Br. J. Nutr. 93 (3): 393–402. doi:10.1079/BJN20051371. PMID 15877880.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University