This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 144.82.46.118 (talk) at 19:33, 5 December 2011. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:33, 5 December 2011 by 144.82.46.118 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)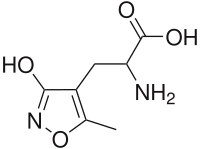
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
2-amino-3-(5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2- oxazol-4-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | AMPA |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H10N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 186.17 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
AMPA (2-amino-3-(5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2- oxazol-4-yl)propanoic acid) is a compound that is a specific agonist for the AMPA receptor, where it mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter glutamate.
There are two types of Ionotropic glutamate receptors that are ligand gated ion channels whose agonists include AMPA, Kainate and NMDA. In the synapse, these two classes of receptors serve very different purposes. AMPA can be used experimentally to distinguish the activity of one receptor from the other in order to understand their differing functions. AMPA generates fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP). AMPA activates AMPA receptors that are non-selective cationic channels allowing the passage of Na+ and K+ and therefore have an equilibrium potential near 0 mV.
References
- ^ Purves, Dale, George J. Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, William C. Hall, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James O. McNamara, and Leonard E. White (2008). Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sinauer Associates. pp. 128–33. ISBN 978-0-87893-697-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Dinh, L (2009). "Norepinephrine homogeneously inhibits alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate- (AMPAR-) mediated currents in all layers of the temporal cortex of the rat". Neurochem Res. 34 (11): 1896–906. doi:10.1007/s11064-009-9966-z. PMID 19357950.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)