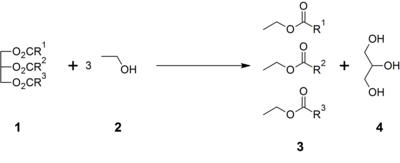This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Arnavchaudhary (talk | contribs) at 14:19, 6 December 2011 (Reverted edits by 216.254.70.154 (talk) to last revision by Christian75 (HG)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:19, 6 December 2011 by Arnavchaudhary (talk | contribs) (Reverted edits by 216.254.70.154 (talk) to last revision by Christian75 (HG))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name propane-1,2,3-triol | |
| Other names
glycerin glycerine 1,2,3-propanetriol 1,2,3-triglycerol 1,2,3-trihydroxypropane glyceritol glycyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.263 |
| E number | E422 (thickeners, ...) |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H8O3 |
| Molar mass | 92.094 g·mol |
| Appearance | clear, colorless solid hygroscopic |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.261 g/cm |
| Melting point | 17.8 °C, 291.0 K, 64.0 °F |
| Boiling point | 290 °C, 563 K, 554°F |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4746 |
| Viscosity | 1.412 Pa·s |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | 160 °C (closed cup) 176 °C (open cup) |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Glycerol (data page) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
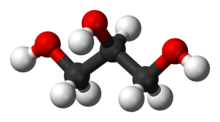
Glycerol (or glycerin, glycerine) is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids known as triglycerides. Glycerol is sweet-tasting and of low toxicity.
Production
Glycerol forms the backbone of triglycerides, and is chiefly produced by saponification of fats as a byproduct of soap-making.
It is also a byproduct of the production of biodiesel via transesterification. This form of crude glycerin is often dark in appearance with a thick, syrup-like consistency. Triglycerides (1) are treated with an alcohol such as ethanol (2) with catalytic base to give ethyl esters of fatty acids (3) and glycerol (4):
Glycerol is also produced by various routes from propylene. The epichlorohydrin process is the most important; it involves the chlorination of propylene to give allyl chloride, which is oxidized with hypochlorite to dichlorohydrins, which reacts with a strong base to give epichlorohydrin. Epichlorohydrin is then hydrolyzed to give glycerol.
Because of the emphasis on biodiesel, where glycerol is a waste product, the market for glycerol is depressed, and the old epichlorohydrin process for glycerol synthesis is no longer economical on a large scale. Glycerol can be removed from the process by using a special enzyme that breaks down phytol and starches. This enzyme is biologically produced using a genetically engineered bacterium. Because there is no glycerin produced as a by-product, the biodiesel purity is greatly improved and costs can be reduced.
Only one producer for synthetic glycerol is left, because high-quality glycerol is needed in highly sensitive pharmaceutical, technical and personal care applications. Raw materials used to make glycerol include animal fats, such as beef tallow, and vegetable oils, such as coconut and soybean. Approximately 950,000 tons per annum are produced in the USA and Europe; 350,000 tons of glycerol were produced per year in the United States alone from 2000-2004. Production will increase as the EU directive 2003/30/EC is implemented, which requires the replacement of 5.75% of petroleum fuels with biofuel across all Member States by 2010. It is projected that by the year 2020, production will be six times more than demand.
Applications
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (March 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Food industry
In foods and beverages, glycerol serves as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, and may help preserve foods. It is also used as filler in commercially prepared low-fat foods (e.g., cookies), and as a thickening agent in liqueurs. Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of leaves. As a sugar substitute, it has approximately 27 calories per teaspoon (sugar has 20) and is 60% as sweet as sucrose. Although it has about the same food energy as table sugar, it does not raise blood sugar levels, nor does it feed the bacteria that form plaques and cause dental cavities. As a food additive, glycerol is labeled as E number E422.
Glycerol is also used to manufacture mono- and di-glycerides for use as emulsifiers, as well as polyglycerol esters going into shortenings and margarine.
It is also used as a humectant (along with propylene glycol labelled as E1520 and/or E422) in the production of snus, a Swedish-style smokeless tobacco product.
As used in foods, glycerol is categorized by the American Dietetic Association as a carbohydrate. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) carbohydrate designation includes all caloric macronutrients excluding protein and fat. Glycerol has a caloric density similar to table sugar, but a lower glycemic index and different metabolic pathway within the body, so some dietary advocates accept glycerol as a sweetener compatible with low carbohydrate diets.
Pharmaceutical and personal care applications
Glycerol is used in medical and pharmaceutical and personal care preparations, mainly as a means of improving smoothness, providing lubrication and as a humectant. It is found in allergen immunotherapies, cough syrups, elixirs and expectorants, toothpaste, mouthwashes, skin care products, shaving cream, hair care products, soaps and water-based personal lubricants. In solid dosage forms like tablets, glycerol is used as a tablet holding agent. For human consumption, glycerol is classified by the U.S. FDA among the sugar alcohols as a caloric macronutrient.
Glycerol is a component of glycerin soap, which is made from denatured alcohol, glycerol, sodium castorate (saponified Castor bean oil), saponified cocoa butter, saponified tallow, sucrose, water, and sometimes sodium laureth sulfate. Essential oils are added for fragrance. This kind of soap is used by people with sensitive, easily-irritated skin because it prevents skin dryness with its moisturizing properties. It draws moisture up through skin layers and slows or prevents excessive drying and evaporation. It is possible to make glycerol soap at home.
Used as a laxative when introduced into the rectum in suppository or small-volume (2–10 ml)(enema) form; irritates the anal mucosa and induces a hyperosmotic effect.
Topical pure or nearly pure glycerol is an effective treatment for psoriasis, burns, bites, cuts, rashes, bedsores, and calluses. It can be used orally to eliminate halitosis, as it is a contact bacterial desiccant. The same property makes it very helpful with periodontal disease; it penetrates biofilm quickly and eliminates bacterial colonies.
Surface science
Glycerol is shown to reduce the coefficient of friction of polymer coated surfaces by several orders of magnitude. This effect is attributed to the enhanced viscosity of glycerol-water solutions as compared to the pure water.
Botanical extracts
When utilized in 'tincture' method extractions, specifically as a 10% solution, glycerol prevents tannins from precipitating in ethanol extracts of plants (tinctures). It is also used as a substitute for ethanol as a solvent in preparing herbal extractions. It is less extractive when utilized in tincture methodology and is approximately 30% more slowly absorbed by the body resulting in a much lower glycemic load. Fluid extract manufacturers often extract herbs in hot water before adding glycerin to make glycerites.
When used as a primary true alcohol-free (e.g. no alcohol (i.e. ethanol) ever being used) botanical extraction solvent in innovative non-tincture based 'dynamic' methodologies, glycerol has been shown, both in literature and through extraction applications, to possess a high degree of extractive versatility for botanicals including removal of numerous constituents and complex compounds, with an extractive power that can rival that of alcohol or water/alcohol solutions. That Glycerol possess such high extractive power assumes that Glycerol, with its tri-atomic structure, is utilized with dynamic methodologies as opposed to standard passive 'tincturing' methodologies that are better suited to alcohol's di-atomic structure. Glycerol possesses the intrinsic property of not denaturing or rendering a botanical's constituents inert. Glycerol is a stable preserving agent for botanical extracts that, when utilized in proper concentrations in an extraction solvent base, does not allow inverting or REDOX of a finished extract's constituents over several years. Both Glycerol and ethanol are viable preserving agents. Glycerol is bacteriostatic in its action, and ethanol is bactericidal in its action.
Antifreeze
Main article: antifreezeLike ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, glycerol is a non-ionic kosmotrope that forms strong hydrogen bonds with water molecules, competing with water-water hydrogen bonds. This disrupts the crystal lattice formation of ice unless the temperature is significantly lowered. The minimum freezing point temperature is at about −36 °F / −37.8 °C corresponding to 60–70% glycerol in water.
Glycerol was historically used as an anti-freeze for automotive applications before being replaced by ethylene glycol, which has a lower freezing point. While the minimum freezing point of a glycerol-water mixture is higher than an ethylene-glycol mixture, glycerol is not toxic and is being re-examined for use in automotive applications.
In the laboratory, glycerol is a common component of solvents for enzymatic reagents stored at temperatures below 0 °C due to the depression of the freezing temperature of solutions with high concentrations of glycerol. It is also used as a cryoprotectant where the glycerol is dissolved in water to reduce damage by ice crystals to laboratory organisms that are stored in frozen solutions, such as bacteria, nematodes, and fruit flies.
Chemical intermediate
Glycerol is used to produce nitroglycerin, or glycerol trinitrate (GTN), which is an essential ingredient of smokeless gunpowder and various explosives such as dynamite, gelignite, and propellants like cordite. Reliance on soap-making to supply co-product glycerine made it difficult to increase production to meet wartime demand. Hence, synthetic glycerin processes were national defence priorities in the days leading up to World War II. GTN is commonly used to relieve angina pectoris, taken in the form of sub-lingual tablets, or as an aerosol spray.
A great deal of research is being conducted to try to make value-added products from crude glycerol (typically containing 20 % water and residual esterification catalyst) obtained from biodiesel production, as an alternative to disposal by incineration. The use of crude glycerin as an additive to biomass for a renewable energy source when combusted or gasified is also being explored.
- Hydrogen gas production unit
- Glycerine acetate (as a potential fuel additive)
- Conversion to propylene glycol
- Conversion to acrolein
- Conversion to ethanol
- Conversion to epichlorhydrin, a raw material for epoxy resins
Fuel
A Kent (UK) company has claimed that glycerol can be used as an alternative to diesel.
Metabolism
Glycerol is a precursor for synthesis of triacylglycerols and of phospholipids in the liver and adipose tissue. When the body uses stored fat as a source of energy, glycerol and fatty acids are released into the bloodstream. In some organisms, the glycerol component can be converted into glucose by the liver and, thus, provide energy for cellular metabolism .
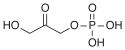
Before glycerol can enter the pathway of glycolysis or gluconeogenesis (depending on physiological conditions), it must be converted to their intermediate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in the following steps:
| Glycerol | Glycerol kinase | Glycerol-3-phosphate | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate | Triosephosphate isomerase | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate | |||
| ATP | ADP | FAD | FADH2 |
|

| ||||
|

|

| |||||||
| NAD | NADH |
||||||||
The enzyme glycerol kinase is present only in the liver. In adipose tissue, glycerol 3-phosphate is obtained from dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) with the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Glycerol has very low toxicity when ingested; its LD50 oral dose for rats is 12600 mg/kg and 8700 mg/kg for mice.
Historical cases of contamination with diethylene glycol
Glycerine and diethylene glycol are similar in appearance, smell, and taste. The US Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed following the 1937 "Elixir Sulfanilamide" incident of poisoning caused by diethylene glycol contamination of medicine.
On May 4, 2007, the US Food and Drug Administration advised all US makers of medicines to test all batches of glycerine for the toxic diethylene glycol. This follows an occurrence of 100 fatal poisonings in Panama resulting from a Chinese factory deliberately falsifying records in order to export the cheaper diethylene glycol as the more expensive glycerol.
Additional physical properties
Its surface tension is 64.00 mN/m at 20 °C, and it has a temperature coefficient of -0.0598 mN/(m K). The surface tension makes it useful in bubble-blowing solutions.
See also
- Biodiesel by-product
- Epichlorohydrin
- Nitroglycerin
- Oleochemicals
- Saponification/Soap making
- Sugar alcohol
- Transesterification
References
- Lide, D. R., Ed. CRC Handbook of Data on Organic Compounds, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1994; p 4386.
- "Viscosity of Glycerol and its Aqueous Solutions". Retrieved 2011-04-19.
- ^ Christoph, Ralf; Schmidt, Bernd; Steinberner, Udo; Dilla, Wolfgang; Karinen, Reetta (2006). "Glycerol". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_477.pub2.
- "Biosynthesis of Biodiesel without Glycerin By-Product". University of Minnesota. Retrieved 27 May 2011.
- Information of the DOW Chemical Company
- Dave Nilles (2005). "A Glycerin Factor". Biodiesel Magazine.
- Walter S. Long. The Composition of Commercial Fruit Extracts Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science (1903-), Vol. 28, Jan. 14, 1916 – Jan. 13, 1917 (Jan. 14, 1916 - Jan. 13, 1917), pp. 157–161 doi:10.2307/3624347
- Does Alcohol Belong In Herbal Tinctures?
- GLYCEROL AND THE GLYCOLS – Production, Properties and Analysis by, James W. Lawrie, Ph.D. (1928 The Chemical Catalog Company, Inc., New York, NY)
- GLYCERIN – Its Industrial and Commercial Applications, by Georgia Leffingwell, Ph.D. and Miton Lesser, B.S. (1945 Chemical Publishing Co., Inc., Brooklyn, NY)
- The Manufacture of GLYCEROL – Vol. III (1956 The Technical Press, LTD., London, UK)
- Glycerol Freezing Point
- Hudgens, R. Douglas; Hercamp, Richard D.; Francis, Jaime; Nyman, Dan A.; Bartoli, Yolanda (2007). doi:10.4271/2007-01-4000.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - A. T. Marshall and R. G. Haverkamp (2008). "Production of hydrogen by the electrochemical reforming of glycerol-water solutions in a PEM electrolysis cell". International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 33 (17): 4649–4654. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.029.
- J. A. Melero, R. vanGrieken, G. Morales and M. Paniagua (2007). "Acidic mesoporous silica for the acetylation of glycerol: Synthesis of bioadditives to petrol fuel". Energy Fuels. 21 (3): 1782–1791. doi:10.1021/ef060647q.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Dow achieves another major milestone in its quest for sustainable chemistries" (Press release). Dow Chemical Company. 15 March 2007.
- L. Ott, M. Bicker and H. Vogel (2006). "The catalytic dehydration of glycerol in sub- and supercritical water: a new chemical process for acrolein production". Green Chemistry. 8 (2): 214–220. doi:10.1039/b506285c.
- Watanabe, M.; et al. (2007). "Acrolein synthesis from glycerol in hot-compressed water". Bioresource Technology. 98 (6): 1285–1290. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.007. PMID 16797980.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - S. S. Yazdani and R. Gonzalez (2007). "Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol: a path to economic viability for the biofuels industry". Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 18 (3): 213–219. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2007.05.002. PMID 17532205.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - "Dow Epoxy advances glycerine-to-epichlorohydrin and liquid epoxy resins projects by choosing Shanghai site" (Press release). Dow Chemical Company. 26 March 2007.
- Is glycerine primed to end fossil fuel domination? on Environmental Expert
- Safety data for glycerol http://msds.chem.ox.ac.uk/GL/glycerol.html
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "FDA Advises Manufacturers to Test Glycerin for Possible Contamination." Released May 4, 2007. Last retrieved May 8, 2007.
- Walt Bogdanich. "From China to Panama, a Trail of Poisoned Medicine." New York Times. Published: May 6, 2007. Last retrieved May 8, 2007.
- "Surface tension values of some common test liquids for surface energy analysis". Retrieved 2010-09-05.