This is an old revision of this page, as edited by WikitanvirBot (talk | contribs) at 18:00, 18 December 2011 (r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding nl:1-broombutaan). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:00, 18 December 2011 by WikitanvirBot (talk | contribs) (r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding nl:1-broombutaan)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)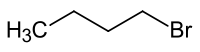
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1-Bromobutane | |
| Other names Butyl bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.357 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H9Br |
| Molar mass | 137.020 g·mol |
| Density | 1.2686 g cm, liquid |
| Melting point | −112 °C (−170 °F; 161 K) |
| Boiling point | 101.4 °C (214.5 °F; 374.5 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
1-Bromobutane (CH3(CH2)3Br) is a colorless liquid that is insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. As a primary alkyl halide, it is especially prone to SN2 type reactions. It is commonly used as an alkylating agent, or in combination with magnesium metal in dry ether (Grignard reagent) to form carbon-carbon bonds.
1-Bromobutane may also be used to form organometallic compounds, such as n-butyllithium:
- 2 Li + C4H9X → C4H9Li + LiX
- where X = Cl, Br
The lithium for this reaction contains 1-3% sodium. When bromobutane is the precursor, the product is a homogeneous solution, consisting of a mixed cluster containing both LiBr and LiBu. It can be formed by reaction of butanol with concentrated hydrobromic acid in presence of strong acid, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4), by reaction of dibutyl ether with hydrobromic acid, or bromination of butane in presence of peroxide.
References
- Brandsma, L.; Verkraijsse, H. D. (1987). Preparative Polar Organometallic Chemistry I. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-16916-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article about an organic halide is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |