This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 03:43, 17 February 2012 (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to watched fields - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[user talk:CheMoB...). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 03:43, 17 February 2012 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (changes to watched fields - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[user talk:CheMoB...)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Indium(III) phosphide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.856 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | InP |
| Molar mass | 145.792 g/mol |
| Appearance | black cubic crystals |
| Density | 4.81 g/cm, solid |
| Melting point | 1,062 °C (1,944 °F; 1,335 K) |
| Solubility in water | slightly soluble in acids |
| Band gap | 1.344 eV (300 K; direct) |
| Electron mobility | 5400 cm/(V·s) (300 K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.68 W/(cm·K) (300 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 3.1 (infrared); 3.55 (632.8 nm) |
| Structure | |
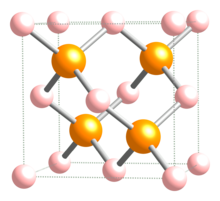
| Crystal structure | Zinc blende |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 45.4 J/(mol·K) |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
59.8 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-88.7 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Toxic, hydrolysis to phosphine |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Indium nitride Indium arsenide Indium antimonide |
| Other cations | Aluminium phosphide Gallium phosphide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Indium phosphide (InP) is a binary semiconductor composed of indium and phosphorus. It has a face-centered cubic ("zincblende") crystal structure, identical to that of GaAs and most of the III-V semiconductors.
InP is used in high-power and high-frequency electronics because of its superior electron velocity with respect to the more common semiconductors silicon and gallium arsenide. It also has a direct bandgap, making it useful for optoelectronics devices like laser diodes. InP is also used as a substrate for epitaxial indium gallium arsenide based opto-electronic devices.
Indium phosphide also has one of the longest-lived optical phonons of any compound with the zincblende crystal structure.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 4–61, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- Sheng Chao, Tien; Lee, Chung Len; Lei, Tan Fu (1993), "The refractive index of InP and its oxide measured by multiple-angle incident ellipsometry", Journal of Materials Science Letters, 12 (10): 721, doi:10.1007/BF00626698.
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 5–20, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
External links
- Extensive site on the physical properties of indium phosphide (Ioffe institute)
- InP conference series at IEEE
- Indium Phosphide and Indium Gallium Arsenide Help Break 600 Gigahertz Speed Barrier (2006 news)
| Indium compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Indium(I) |
| ||
| Indium(I,III) | |||
| Indium(III) |
| ||