This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 124.183.161.194 (talk) at 23:27, 6 October 2013 (→Capital flight). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:27, 6 October 2013 by 124.183.161.194 (talk) (→Capital flight)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)Template:Globalization sidebar
Globalization (or globalisation) is the process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas, and other aspects of culture. Advances in transportation and telecommunications infrastructure, including the rise of the telegraph and its posterity the Internet, are major factors in globalization, generating further interdependence of economic and cultural activities.
Though several scholars place the origins of globalization in modern times, others trace its history long before the European age of discovery and voyages to the New World. Some even trace the origins to the third millennium BCE. In the late 19th century and early 20th century, the connectedness of the world's economies and cultures grew very quickly.
The term globalization has been in increasing use since the mid-1980s and especially since the mid-1990s. In 2000, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified four basic aspects of globalization: trade and transactions, capital and investment movements, migration and movement of people and the dissemination of knowledge. Further, environmental challenges such as climate change, cross-boundary water, air pollution, and over-fishing of the ocean are linked with globalization. Globalizing processes affect and are affected by business and work organization, economics, socio-cultural resources, and the natural environment.
Overview

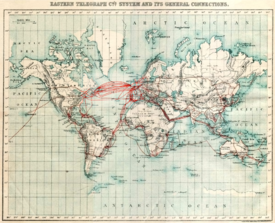
Humans have interacted over long distances for thousands of years. The overland Silk Road that connected Asia, Africa, and Europe is a good example of the transformative power of translocal exchange that existed in the "Old World". Philosophy, religion, language, the arts, and other aspects of culture spread and mixed as nations exchanged products and ideas. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans made important discoveries in their exploration of the oceans, including the start of transatlantic travel to the "New World" of the Americas. Global movement of people, goods, and ideas expanded significantly in the following centuries. Early in the 19th century, the development of new forms of transportation (such as the steamship and railroads) and telecommunications that "compressed" time and space allowed for increasingly rapid rates of global interchange. In the 20th century, road vehicles, intermodal transport, and airlines made transportation even faster. The advent of electronic communications, most notably mobile phones and the Internet, connected billions of people in new ways by the year 2010.

Etymology and usage
The term globalization is derived from the word globalize, which refers to the emergence of an international network of social and economic systems. One of the earliest known usages of the term as a noun was in a 1930 publication entitled, Towards New Education, where it denoted a holistic view of human experience in education. A related term, corporate giants, was coined by Charles Taze Russell in 1897 to refer to the largely national trusts and other large enterprises of the time. By the 1960s, both terms began to be used as synonyms by economists and other social scientists. It then reached the mainstream press in the later half of the 1980s. Since its inception, the concept of globalization has inspired competing definitions and interpretations, with antecedents dating back to the great movements of trade and empire across Asia and the Indian Ocean from the 15th century onwards. Due to the complexity of the concept, research projects, articles, and discussions often remain focused on a single aspect of globalization.
Roland Robertson, professor of sociology at University of Aberdeen, an early writer in the field, defined globalization in 1992 as:
...the compression of the world and the intensification of the consciousness of the world as a whole.
Sociologists Martin Albrow and Elizabeth King define globalization as:
...all those processes by which the peoples of the world are incorporated into a single world society.
In The Consequences of Modernity, Anthony Giddens uses the following definition:
Globalization can thus be defined as the intensification of worldwide social relations which link distant localities in such a way that local happenings are shaped by events occurring many miles away and vice versa.
In Global Transformations David Held, et al., study the definition of globalization:
Although in its simplistic sense globalization refers to the widening, deepening and speeding up of global interconnection, such a definition begs further elaboration. ... Globalization can be located on a continuum with the local, national and regional. At one end of the continuum lie social and economic relations and networks which are organized on a local and/or national basis; at the other end lie social and economic relations and networks which crystallize on the wider scale of regional and global interactions. Globalization can be taken to refer to those spatial-temporal processes of change which underpin a transformation in the organization of human affairs by linking together and expanding human activity across regions and continents. Without reference to such expansive spatial connections, there can be no clear or coherent formulation of this term. ... A satisfactory definition of globalization must capture each of these elements: extensity (stretching), intensity, velocity and impact.
Swedish journalist Thomas Larsson, in his book The Race to the Top: The Real Story of Globalization, states that globalization:
is the process of world shrinkage, of distances getting shorter, things moving closer. It pertains to the increasing ease with which somebody on one side of the world can interact, to mutual benefit, with somebody on the other side of the world.
The journalist Thomas L. Friedman popularized the term "flat world", arguing that globalized trade, outsourcing, supply-chaining, and political forces had permanently changed the world, for better and worse. He asserted that the pace of globalization was quickening and that its impact on business organization and practice would continue to grow.
Economist Takis Fotopoulos defined "economic globalization" as the opening and deregulation of commodity, capital and labor markets that led toward present neoliberal globalization. He used "political globalization" to refer to the emergence of a transnational elite and a phasing out of the nation-state. "Cultural globalization", he used to reference the worldwide homogenization of culture. Other of his usages included "ideological globalization", "technological globalization" and "social globalization".
In 2000, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified four basic aspects of globalization: trade and transactions, capital and investment movements, migration and movement of people and the dissemination of knowledge. With regards to trade and transactions, developing countries increased their share of world trade, from 19 percent in 1971 to 29 percent in 1999. However, there is great variation among the major regions. For instance, the newly industrialized economies (NIEs) of Asia prospered, while African countries as a whole performed poorly. The makeup of a country's exports is an important indicator for success. Manufactured goods exports soared, dominated by developed countries and NIEs. Commodity exports, such as food and raw materials were often produced by developing countries: commodities' share of total exports declined over the period.
Following from this, capital and investment movements can be highlighted as another basic aspect of globalization. Private capital flows to developing countries soared during the 1990s, replacing "aid" or "development assistance" which fell significantly after the early 1980s. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) became the most important category. Both portfolio investment and bank credit rose but they have been more volatile, falling sharply in the wake of the financial crisis of the late 1990s. The migration and movement of people can also be highlighted as a prominent feature of the globalization process. In the period between 1965–90, the proportion of the labor forces migrating approximately doubled. Most migration occurred between developing countries and Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
Manfred Steger, professor of Global Studies and research leader in the Global Cities Institute at RMIT University, identifies five dimensions of globalization: economic, political, cultural, ecological, and ideological. The ideological dimension, according to Steger, is filled with a range of norms, claims, beliefs, and narratives about the phenomenon itself.
History
Main article: History of globalization See also: Timeline of international tradeThere are both distal and proximate causes that can be traced in the historical factors affecting globalization. Large-scale globalization began in the 19th century.
Archaic
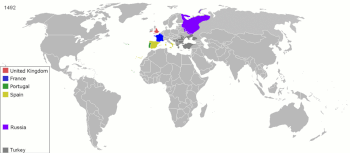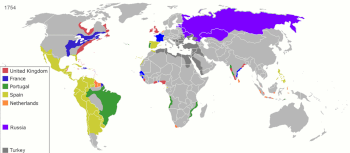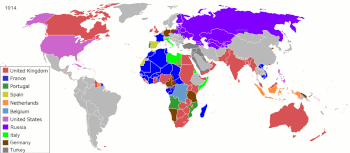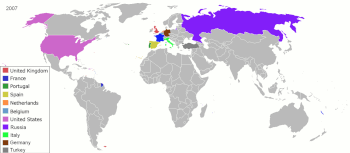
Archaic globalization is seen as a phase in the history of globalization conventionally referring to globalizing events and developments from the time of the earliest civilizations until roughly 1600. This term is used to describe the relationships between communities and states and how they were created by the geographical spread of ideas and social norms at both local and regional levels.
In this schema, three main prerequisites are posited for globalization to occur. The first is the idea of Eastern Origins, which shows how Western states have adapted and implemented learned principals from the East. Without the traditional ideas from the East, Western globalization would not have emerged the way it did. The second is distance. The interactions amongst states were not on a global scale and most often were confined to Asia, North Africa, the Middle East and certain parts of Europe. With early globalization it was difficult for states to interact with others that were not within close proximity. Eventually, technological advances allowed states to learn of others existence and another phase of globalization was able to occur. The third has to do with interdependency, stability and regularity. If a state is not depended on another then there is no way for them to be mutually affected by one another. This is one of the driving forces behind global connections and trade; without either globalization would not have emerged the way it did and states would still be dependent on their own production and resources to function. This is one of the arguments surrounding the idea of early globalization. It is argued that archaic globalization did not function in a similar manner to modern globalization because states were not as interdependent on others as they are today.
Also posited is a 'multi-polar' nature to archaic globalization, which involved the active participation of non-Europeans. Because it predated the Great Divergence of the nineteenth century, in which Western Europe pulled ahead of the rest of the world in terms of industrial production and economic output, archaic globalization was a phenomenon that was driven not only by Europe but also by other economically developed Old World centers such as Gujurat, Bengal, coastal China and Japan.

The German historical economist and sociologist Andre Gunder Frank argues that a form of globalization began with the rise of trade links between Sumer and the Indus Valley Civilization in the third millennium B.C.E. This archaic globalization existed during the Hellenistic Age, when commercialized urban centers enveloped the axis of Greek culture that reached from India to Spain, including Alexandria and the other Alexandrine cities. Early on, the geographic position of Greece and the necessity of importing wheat forced the Greeks to engage in maritime trade. Trade in ancient Greece was largely unrestricted: the state controlled only the supply of grain.

Proto-globalization
Main article: Proto-globalizationProto-globalization or 'early modern globalization' is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800. First introduced by historians A. G. Hopkins and Christopher Bayly, the term describes the phase of increasing trade links and cultural exchange that characterized the period immediately preceding the advent of so-called 'modern globalization' in the 19th century. Proto-globalization was characterized by the rise of maritime European empires, in the 16th and 17th centuries, first the Portuguese and Spanish Empires, and later the Dutch and British Empires. In the 17th century, world trade developed further when chartered companies like the British East India Company (founded in 1600) and the Dutch East India Company (founded in 1602, often described as the first multinational corporation in which stock was offered) were established.
Proto-globalization distinguished itself from modern globalization on the basis of expansionism, the method of managing global trade, and the level of information exchange. The period of proto-globalization is marked by such trade arrangements as the East India Company, the shift of hegemony to Western Europe, the rise of larger-scale conflicts between powerful nations such as the Thirty Year War, and a rise of new commodities—most particularly slave trade. The Triangular Trade made it possible for Europe to take advantage of resources within the western hemisphere. The transfer of plant and animal crops and epidemic diseases associated with Alfred Crosby's concept of The Columbian Exchange also played a central role in this process. Proto-globalization trade and communications involved a vast group including European, Muslim, Indian, Southeast Asian and Chinese merchants, particularly in the Indian Ocean region.

Modern
Main article: History of globalizationDuring the 19th century, globalization approached its modern form as a result of the industrial revolution. Industrialization allowed standardized production of household items using economies of scale while rapid population growth created sustained demand for commodities. Globalization in this period was decisively shaped by nineteenth-century imperialism. In the 19th century, steamships reduced the cost of international transport significantly and railroads made inland transport cheaper. The transport revolution occurred some time between 1820 and 1850. More nations embraced international trade. Globalization in this period was decisively shaped by nineteenth-century imperialism such as in Africa and Asia. The invention of shipping containers in 1956 helped advance the globalization of commerce.
After the Second World War, work by politicians led to the Bretton Woods conference, an agreement by major governments to lay down the framework for international monetary policy, commerce and finance, and the founding of several international institutions intended to facilitate economic growth multiple rounds of trade opening simplified and lowered trade barriers. Initially, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), led to a series of agreements to remove trade restrictions. GATT's successor was the World Trade Organization (WTO), which created an institution to manage the trading system. Exports nearly doubled from 8.5% of total gross world product in 1970 to 16.2% in 2001. The approach of using global agreements to advance trade stumbled with the failure of the Doha round of trade-negotiation. Many countries then shifted to bilateral or smaller multilateral agreements, such as the 2011 South Korea–United States Free Trade Agreement.
Since the 1970s, aviation has become increasingly affordable to middle classes in developed countries. Open skies policies and low-cost carriers have helped to bring competition to the market. In the 1990s, the growth of low cost communication networks cut the cost of communicating between different countries. More work can be performed using a computer without regard to location. This included accounting, software development, and engineering design.
In the late 19th century and early 20th century, the connectedness of the world's economies and cultures grew very quickly. This slowed down from the 1910s onward due to the World Wars and the Cold War but has picked up again since neoliberal policies began in the 1980s and perestroika and the Chinese economic reforms of Deng Xiaoping opened the old Eastern Bloc to western capitalism. In the early 2000s, much of the industrialized world entered into the Great Recession, which may have slowed the process, at least temporarily.
Trade and globalization have evolved tremendously today. Globalized society offers a complex web of forces and factors that bring people, cultures, markets, beliefs and practices into increasingly greater proximity to one another.
Aspects

Global business organization
Main article: International businessWith improvements in transportation and communication, international business grew rapidly after the beginning of the 20th century. International business includes all commercial transactions (private sales, investments, logistics, and transportation) that take place between two or more regions, countries and nations beyond their political boundaries. Such international diversification is tied with firm performance and innovation, positively in the case of the former and often negatively in the case of the latter. Usually, private companies undertake such transactions for profit. These business transactions involve economic resources such as capital, natural and human resources used for international production of physical goods and services such as finance, banking, insurance, construction and other productive activities.
International business arrangements have led to the formation of multinational enterprises (MNE), companies that have a worldwide approach to markets and production or one with operations in more than one country. A MNE may also be called a multinational corporation (MNC) or transnational company (TNC). Well known MNCs include fast food companies such as McDonald's and Yum Brands, vehicle manufacturers such as General Motors, Ford Motor Company and Toyota, consumer electronics companies like Samsung, LG and Sony, and energy companies such as ExxonMobil, Shell and BP. Most of the largest corporations operate in multiple national markets.
Businesses generally argue that survival in the new global marketplace requires companies to source goods, services, labor and materials overseas to continuously upgrade their products and technology in order to survive increased competition.
International trade
Main article: International trade

International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). Industrialization, advanced transportation, multinational corporations, offshoring and outsourcing all have a major impact on world trade. The growth of international trade is a fundamental component of globalization.
An absolute trade advantage exists when countries can produce a commodity with less costs per unit produced than could its trading partner. By the same reasoning, it should import commodities in which it has an absolute disadvantage. While there are possible gains from trade with absolute advantage, comparative advantage—that is, the ability to offer goods and services at a lower marginal and opportunity cost—extends the range of possible mutually beneficial exchanges. In a globalized business environment, companies argue that the comparative advantages offered by international trade have become essential to remaining competitive.
Trade agreements, economic blocks and special trade zones
Establishment of free trade areas has become an essential feature of modern governments to handle preferential trading arrangements with foreign and multinational entities.
A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic and other laws that are more free-market-oriented than a country's typical or national laws. "Nationwide" laws may be suspended inside these special zones. The category 'SEZ' covers many areas, including Free Trade Zones (FTZ), Export Processing Zones (EPZ), Free Zones (FZ), Industrial parks or Industrial Estates (IE), Free Ports, Urban Enterprise Zones and others. Usually the goal of a structure is to increase foreign direct investment by foreign investors, typically an international business or a multinational corporation (MNC). These are designated areas in which companies are taxed very lightly or not at all in order to encourage economic activity. Free ports have historically been endowed with favorable customs regulations, e.g., the free port of Trieste. Very often free ports constitute a part of free economic zones.
A FTZ is an area within which goods may be landed, handled, manufactured or reconfigured, and reexported without the intervention of the customs authorities. Only when the goods are moved to consumers within the country in which the zone is located do they become subject to the prevailing customs duties. Free trade zones are organized around major seaports, international airports, and national frontiers—areas with many geographic advantages for trade. It is a region where a group of countries has agreed to reduce or eliminate trade barriers.

A free trade area is a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free-trade agreement, which eliminates tariffs, import quotas, and preferences on most (if not all) goods and services traded between them. If people are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free-trade area, it would also be considered an open border. The European Union, for example, a confederation of 27 member states, provides both a free trade area and an open border.
Qualifying Industrial Zones (QIZ) are industrial parks that house manufacturing operations in Jordan and Egypt. They are a special free trade zones established in collaboration with neighboring Israel to take advantage of the free trade agreements between the United States and Israel. Under the trade agreements with Jordan as laid down by the United States, goods produced in QIZ-notified areas can directly access US markets without tariff or quota restrictions, subject to certain conditions. To qualify, goods produced in these zones must contain a small portion of Israeli input. In addition, a minimum 35% value to the goods must be added to the finished product. The brainchild of Jordanian businessman Omar Salah, the first QIZ was authorized by the United States Congress in 1997.
The Asia-Pacific has been described as "the most integrated trading region on the planet" because its intra-regional trade accounts probably for as much as 50-60% of the region's total imports and exports. It has also extra-regional trade: consumer goods exports such as televisions, radios, bicycles, and textiles into the United States, Europe, and Japan fueled the economic expansion.
The ASEAN Free Trade Area is a trade bloc agreement by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations supporting local manufacturing in all ASEAN countries. The AFTA agreement was signed on 28 January 1992 in Singapore. When the AFTA agreement was originally signed, ASEAN had six members, namely, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Vietnam joined in 1995, Laos and Myanmar in 1997 and Cambodia in 1999.

Tax havens

A tax haven is a state, country or territory where certain taxes are levied at a low rate or not at all, which are used by businesses for tax avoidance and tax evasion. Individuals and/or corporate entities can find it attractive to establish shell subsidiaries or move themselves to areas with reduced or nil taxation levels. This creates a situation of tax competition among governments. Different jurisdictions tend to be havens for different types of taxes and for different categories of people and companies. States that are sovereign or self-governing under international law have theoretically unlimited powers to enact tax laws affecting their territories, unless limited by previous international treaties. The central feature of a tax haven is that its laws and other measures can be used to evade or avoid the tax laws or regulations of other jurisdictions. In its December 2008 report on the use of tax havens by American corporations, the US Government Accountability Office was unable to find a satisfactory definition of a tax haven but regarded the following characteristics as indicative of it: nil or nominal taxes; lack of effective exchange of tax information with foreign tax authorities; lack of transparency in the operation of legislative, legal or administrative provisions; no requirement for a substantive local presence; and self-promotion as an offshore financial center.
A 2012 report from the Tax Justice Network estimated that between USD $21 trillion and $32 trillion is sheltered from taxes in unreported tax havens worldwide. If such wealth earns 3% annually and such capital gains were taxed at 30%, it would generate between $190 billion and $280 billion in tax revenues, more than any other tax shelter. If such hidden offshore assets are considered, many countries with governments nominally in debt are shown to be net creditor nations. However, the tax policy director of the Chartered Institute of Taxation expressed skepticism over the accuracy of the figures. Daniel J. Mitchell of the US-based Cato Institute says that the report also assumes, when considering notional lost tax revenue, that 100% money deposited offshore is evading payment of tax.
Tax havens have been criticized because they often result in the accumulation of idle cash that is expensive and inefficient for companies to repatriate. The tax shelter benefits result in a tax incidence disadvantaging the poor. Many tax havens are thought to have connections to "fraud, money laundering and terrorism." While investigations of illegal tax haven abuse have been ongoing, there have been few convictions. Lobbying pertaining to tax havens and associated transfer pricing has also been criticized. Accountants' opinions on the propriety of tax havens have been evolving, as have the opinions of their corporate users, governments, and politicians, although their use by Fortune 500 companies and others remains widespread. Reform proposals centering on the Big Four accountancy firms have been advanced. Some governments appear to be using computer spyware to scrutinize some corporations' finances.
International tourism
Main article: TourismTourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes". There are many forms of tourism such as agritourism, birth tourism, culinary tourism, cultural tourism, eco-tourism,extreme tourism, geotourism, heritage tourism, LGBT tourism, medical tourism, nautical tourism, pop-culture tourism, religious tourism, slum tourism, war tourism, and wildlife tourism.
Globalization has made tourism a popular global leisure activity. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that up to 500,000 people are in flight at any one time.

As a result of the late-2000s recession, international travel demand suffered a strong slowdown from the second half of 2008 through the end of 2009. After a 5% increase in the first half of 2008, growth in international tourist arrivals moved into negative territory in the second half of 2008, and ended up only 2% for the year, compared to a 7% increase in 2007. This negative trend intensified during 2009, exacerbated in some countries due to the outbreak of the H1N1 influenza virus, resulting in a worldwide decline of 4.2% in 2009 to 880 million international tourists arrivals, and a 5.7% decline in international tourism receipts. One notable exception to more free travel is travel from the United States to bordering countries Canada and Mexico, which had been semi-open borders. Now, by US law, travel to these countries requires a passport.
In 2010, international tourism reached US$919B, growing 6.5% over 2009, corresponding to an increase in real terms of 4.7%. In 2010, there were over 940 million international tourist arrivals worldwide.
International sports

Modern international sports events can be big business for as well as influencing the political, economical, and other cultural aspects of countries around the world. Especially with politics and sports, sports can affect countries, their identities, and in consequence, the world.
The ancient Olympic Games were a series of competitions held between representatives of several city-states and kingdoms from Ancient Greece, which featured mainly athletic but also combat and chariot racing events. During the Olympic games all struggles against the participating city-states were postponed until the games were finished. The origin of these Olympics is shrouded in mystery and legend. During the 19th century Olympic Games became a popular global event.
While some economists are skeptical about the economic benefits of hosting the Olympic Games, emphasizing that such "mega-events" often have large costs, hosting (or even bidding for) the Olympics appears to increase the host country's exports, as the host or candidate country sends a signal about trade openness when bidding to host the Games. Moreover, research suggests that hosting the Summer Olympics has a strong positive effect on the philanthropic contributions of corporations headquartered in the host city, which seems to benefit the local nonprofit sector. This positive effect begins in the years leading up to the Games and might persist for several years afterwards, although not permanently. This finding suggests that hosting the Olympics might create opportunities for cities to influence local corporations in ways that benefit the local nonprofit sector and civil society. The Games have also had significant negative effects on host communities; for example, the Centre on Housing Rights and Evictions reports that the Olympics displaced more than two million people over two decades, often disproportionately affecting disadvantaged groups.
Globalization has continually increased international competition in sports. The FIFA World Cup, for example, is the world's most widely viewed sporting event; an estimated 700 million people watched the final match of the 2010 FIFA World Cup held in South Africa.
According to a 2011 A.T. Kearney study of sports teams, leagues and federations, the global sports industry is worth between €350 billion and €450 billion (US$480-$620 billion). This includes infrastructure construction, sporting goods, licensed products and live sports events.
Illicit international trade
Main articles: Black market and Transnational organized crime
"Black markets" and organized crime often operate on a transnational basis, with global sales totaling almost US$2 trillion annually.
Drug trade
In 2010 the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reported that the global drug trade generated more than US$320 billion a year in revenues. Worldwide, the UN estimates there are more than 50 million regular users of heroin, cocaine and synthetic drugs. The international trade of endangered species was second only to drug trafficking among smuggling "industries". Traditional Chinese medicine often incorporates ingredients from all parts of plants, the leaf, stem, flower, root, and also ingredients from animals and minerals. The use of parts of endangered species (such as seahorses, rhinoceros horns, saiga antelope horns, and tiger bones and claws) resulted in a black market of poachers who hunt restricted animals.
Human smuggling and trafficking
Main article: Human trafficking
Human trafficking is the trade in humans, most commonly for the purpose of sexual slavery, forced labor or for the extraction of organs or tissues, including surrogacy and ova removal. Trafficking is a lucrative industry and one of the fastest growing, representing an estimated US$32 billion per year in international trade, compared to the estimated annual US$650 billion for all illegal international trade circa 2010. Human trafficking is a global issue that is shaped by economic hardships, cultures, laws, and immigration policies. In 2004, the total annual revenue for trafficking in persons was estimated to be between US$5 billion and $9 billion. In 2005, Patrick Belser of ILO estimated a global annual profit of US$31.6 billion. In 2008, the United Nations estimated nearly 2.5 million people from 127 different countries are being trafficked into 137 countries around the world.
Human trafficking differs from people smuggling. In the latter, people voluntarily request or hire an individual, known as a smuggler, to covertly transport them from one location to another. This generally involves transportation from one country to another, where legal entry would be denied at the international border. There may be no deception involved in the (illegal) agreement. After entry into the country and arrival at their ultimate destination, the smuggled person is usually free to find their own way. According to the International Centre for Migration Policy Development (ICMPD), human smuggling is a crime against the State due to violation of immigration laws and does not require violations of the rights of the smuggled migrants to be considered a crime. Human trafficking, on the other hand, is a crime against a person because of violation of the victim's rights through coercion and exploitation.
Economic globalization
Main article: Economic globalization
Economic globalization is the increasing economic interdependence of national economies across the world through a rapid increase in cross-border movement of goods, service, technology and capital. Whereas the globalization of business is centered around the diminution of international trade regulations as well as tariffs, taxes, and other impediments that suppresses global trade, economic globalization is the process of increasing economic integration between countries, leading to the emergence of a global marketplace or a single world market. Depending on the paradigm, economic globalization can be viewed as either a positive or a negative phenomenon. Economic globalization comprises the globalization of production, markets, competition, technology, and corporations and industries. Current globalization trends can be largely accounted for by developed economies integrating with less developed economies by means of foreign direct investment, the reduction of trade barriers as well as other economic reforms and, in many cases, immigration.
In 1944, 44 nations attended the Bretton Woods Conference with a purpose of stabilizing world currencies and establishing credit for international trade in the post World War II era. While the international economic order envisioned by the conference gave way to the neo-liberal economic order prevalent today, the conference established many of the organizations essential to advancement towards a close-knit global economy and global financial system, such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the International Trade Organization.
As an example, Chinese economic reform began to open China to globalization in the 1980s. Scholars find that China has attained a degree of openness that is unprecedented among large and populous nations, with competition from foreign goods in almost every sector of the economy. Foreign investment helped to greatly increase product quality and knowledge and standards, especially in heavy industry. China's experience supports the assertion that globalization greatly increases wealth for poor countries. As of 2005–2007, the Port of Shanghai holds the title as the World's busiest port.
As another example, economic liberalization in India and ongoing economic reforms began in 1991. As of 2009, about 300 million people—equivalent to the entire population of the United States—have escaped extreme poverty. In India, business process outsourcing has been described as the "primary engine of the country's development over the next few decades, contributing broadly to GDP growth, employment growth, and poverty alleviation".

Capital flight
Main articles: Capital flight and Liquidity crisis See also: Sudden stop (economics), Tax exporting, Capital strike, and Illicit financial flowsCapital flight occurs when assets or money rapidly flow out of a country because of that country's recent increase in taxes, tariffs, labor costs, or other unfavorable financial conditions such as government debt defaulting, which disturb investors. This leads to a sometimes very rapid disappearance of wealth and is usually accompanied by a sharp drop in the exchange rate of the affected country, leading in turn to depreciation in a variable currency exchange rate regime or a forced devaluation under fixed exchange rates. This can be particularly damaging when the capital belongs to the people of the affected country, because not only are the citizens now burdened by the loss of faith in the economy and devaluation of their currency, but probably also their assets have lost much of their nominal value. This leads to dramatic decreases in the purchasing power of the country's assets and makes it increasingly expensive to import goods.

A 2008 paper published by Global Financial Integrity estimated capital flight or illicit financial flows to be "out of developing countries" at a rate of "some US$850 billion to $1 trillion a year." But capital flight affects developing countries, too. A 2009 article in The Times reported that hundreds of wealthy financiers and entrepreneurs had recently fled the United Kingdom in response to recent tax increases, relocating in low tax destinations such as Jersey, Guernsey, the Isle of Man, and the British Virgin Islands. In May 2012 the scale of Greek capital flight in the wake of the first "undecided" legislative election was estimated at €4 billion a week and later that month the Spanish Central Bank revealed €97 billion in capital flight from the Spanish economy for the first quarter of 2012.
Capital flight can cause liquidity crises in the affected countries from which capital is flowing, the countries in which investors are trying to liquidate their assets, and other countries involved in international commerce such as shipping and finance. Market participants in need of cash find it hard to locate potential trading partners to sell their assets. This may result as a consequence of limited market participation or because of a decrease in cash held by financial market participants. Thus, asset holders may be forced to sell their assets at a price below the long term fundamental price. Borrowers typically face higher loan costs and collateral requirements, compared to periods of ample liquidity, and unsecured debt is nearly impossible to obtain. Typically, during a liquidity crisis, the interbank lending market does not function smoothly either.
Austerity
Main article: AusterityGovernments sometimes impose austerity policies to reduce budget deficits during adverse economic conditions. These can include spending cuts, tax increases, or a mixture of the two. Austerity policies demonstrate governments' liquidity to their creditors and credit rating agencies by bringing fiscal income closer to expenditure.
The economic effects of austerity are unclear due to its wide and non-specific definition, the limited historic sample of natural experiments and potential for conflation with the effects of other events that tend to precede austerity, such as recessions and financial crises. In macroeconomics, reducing government spending generally increases unemployment. This increases safety net spending and reduces tax revenues, to some extent. Government spending contributes to gross domestic product (GDP), so the debt-to-GDP ratio which signifies liquidity may not immediately improve. Short-term deficit spending, particularly, contributes to GDP growth when consumers and businesses are unwilling or unable to spend. Under the theory of expansionary fiscal contraction (EFC), a major reduction in government spending can change future expectations about taxes and government spending, encouraging private consumption and resulting in overall economic expansion. Since 2011, the International Monetary Fund has issued cautionary guidance against austerity measures imposed without regard to underlying economic fundamentals and many commentators have suggested that austerity measures have indeed been misguided and harmful to the economies where they have been imposed.
Measuring globalization
Indices
Main article: Globalization IndexMeasurement of economic globalization focuses on variables such as trade, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), portfolio investment, and income. However, newer indices attempt to measure globalization in more general terms, including variables related to political, social, cultural, and even environmental aspects of globalization.
One index of globalization is the KOF Index, which measures the three main dimensions of globalization: economic, social, and political. Another is the A.T. Kearney / Foreign Policy Magazine Globalization Index.
|
|
Free trade policies
Main article: Global Enabling Trade ReportThe Enabling Trade Index measures the factors, policies and services that facilitate the trade in goods across borders and to destinations. It is made up of four sub-indexes: market access; border administration; transport and communications infrastructure; and business environment. The top 20 countries (as of the 2010 report) are:
|
|
Sociocultural globalization

Culture
Main article: Cultural globalizationCultural globalization has increased cross-cultural contacts but may be accompanied by a decrease in the uniqueness of once-isolated communities. For example, sushi is available in Germany as well as Japan but Euro-Disney outdraws the city of Paris, potentially reducing demand for "authentic" French pastry. Globalization's contribution to the alienation of individuals from their traditions may be modest compared to the impact of modernity itself, as alleged by existentialists such as Jean-Paul Sartre and Albert Camus. Globalization has expanded recreational opportunities by spreading pop culture, particularly via the Internet and satellite television.
Religious movements were among the earliest cultural elements to globalize, being spread by force, migration, evangelists, imperialists and traders. Christianity, Islam, Buddhism and more recently sects such as Mormonism, which have taken root and influenced endemic cultures in places far from their origins.

Conversi claimed in 2010 that globalization was predominantly driven by the outward flow of culture and economic activity from the United States and was better understood as Americanization, or Westernization. For example, the two most successful global food and beverage outlets are American companies, McDonald's and Starbucks, are often cited as examples of globalization, with over 32,000 and 18,000 locations operating worldwide, respectively as of 2008.
The term globalization implies transformation. Cultural practices including traditional music can be lost or turned into a fusion of traditions. Globalization can trigger a state of emergency for the preservation of musical heritage. Archivists must attempt to collect, record or transcribe repertoires before melodies are assimilated or modified. Local musicians struggle for authenticity and to preserve local musical traditions. Globalization can lead performers to discard traditional instruments. Fusion genres can become interesting fields of analysis.
Globalization gave support to the World Music phenomenon by allowing locally-recorded music to reach Western audiences searching for new ideas and sounds. For example, Western musicians have adopted many innovations that originated in other cultures.
The term "World Music" was originally intended for ethnic-specific music. Now, globalization is expanding its scope such that the term often includes hybrid sub-genres such as World fusion, Global fusion, Ethnic fusion and Worldbeat

Music flowed outward from the West as well. Anglo-American pop music spread across the world through MTV. Dependency Theory explained that the world was an integrated, international system. Musically, this translated into the loss of local musical identity.
Bourdieu claimed that the perception of consumption can be seen as self-identification and the formation of identity. Musically, this translates into each being having his own musical identity based on likes and tastes. These likes and tastes are greatly influenced by culture as this is the most basic cause for a person's wants and behavior. The concept of one's own culture is now in a period of change due to globalization. Also, globalization has increased the interdependency of political, personal, cultural and economic factors.
A 2005 UNESCO report showed that cultural exchange is becoming more frequent from Eastern Asia but Western countries are still the main exporters of cultural goods. In 2002, China was the third largest exporter of cultural goods, after the UK and US. Between 1994 and 2002, both North America's and the European Union's shares of cultural exports declined while Asia's cultural exports grew to surpass North America. Related factors are the fact that Asia's population and area are several times that of North America. Americanization related to a period of high political American clout and of significant growth of America's shops, markets and object being brought into other countries.
So, globalization, a diverse phenomenon, relates to a multilateral political world and to the increase of cultural objects and markets between countries. The Indian experience particularly reveals the plurality of the impact of cultural globalization.
Multilingualism and the emergence of lingua francas
Main articles: Multilingualism, Lingua franca, and List of lingua francasMultilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. Today most people in the world are multilingual. Language contact occurs when two or more languages or varieties interact. Language contact occurs in a variety of phenomena, including language convergence, borrowing, and relexification. The most common products are pidgins, creoles, code-switching, and mixed languages.
Multilingualism is becoming a social phenomenon governed by the needs of globalization and cultural openness. Thanks to the ease of access to information facilitated by the Internet, individuals' exposure to multiple languages is becoming more and more frequent, triggering, therefore, the need to acquire more and more languages.
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues. Today, the most popular second language is English. Some 3.5 billion people have some acquaintance of the language. English is the dominant language on the Internet. About 35% of the world's mail, telexes, and cables are in English; approximately 40% of the world's radio programs are in English.
While multilingualism is common among individuals, globally the number of spoken languages is decreasing. The top 20 languages spoken by more than 50 million speakers each are spoken by some 50% of the world's population, whereas many of the other languages are spoken in small communities, most with less than 10,000 speakers. Historically, these less widespread languages were afforded protection through geographical isolation. Today, speakers of regional and minority languages are increasingly unable to compete with those who speak dominant languages such that these languages are now considered endangered languages. The total number of languages in the world is not precisely known and estimates vary depending on many factors. The current estimate is that there are between 6000 and 7000 languages spoken and between 50-90% of those will have become extinct by the year 2100.
Politics
Main article: Global politics
In general, globalization may ultimately reduce the importance of nation states. Supranational institutions such as the European Union, the WTO, the G8 or the International Criminal Court replace or extend national functions to facilitate international agreement. Some observers attribute the relative decline in US power to globalization, particularly due to the country's high trade deficit. This led to a global power shift towards Asian states, particularly China, which unleashed market forces and achieved tremendous growth rates. As of 2011, the Chinese economy was on track to overtake the United States by 2025.
Increasingly, Non-Governmental Organizations influence public policy across national boundaries, including humanitarian aid and developmental efforts. Philanthropic organizations with global missions are also coming to the forefront of humanitarian efforts; charities such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Accion International, the Acumen Fund (now Acumen) and the Echoing Green have combined the business model with philanthropy, giving rise to business organizations such as the Global Philanthropy Group and new associations of philanthropists such as the Global Philanthropy Forum. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation projects include a current multi-billion dollar commitment to funding immunizations in some of the world's more impoverished but rapidly growing countries. and hundreds of millions of dollars in the next few years to programs aimed at encouraging saving by the world's poor. The Hudson Institute estimates total private philanthropic flows to developing countries at US$59 billion in 2010.
As a response to globalization, some countries have embraced isolationist policies. For example, the North Korean government makes it very difficult for foreigners to enter the country and strictly monitors their activities when they do. Aid workers are subject to considerable scrutiny and excluded from places and regions the government does not wish them to enter. Citizens cannot freely leave the country.
Media and public opinion
Main articles: Media (communication) and Public opinionA 2005 study by Peer Fiss and Paul Hirsch found a large increase in articles negative towards globalization in the years prior. In 1998, negative articles outpaced positive articles by two to one. In 2008 Greg Ip claimed this rise in opposition to globalization can be explained, at least in part, by economic self-interest. The number of newspaper articles showing negative framing rose from about 10% of the total in 1991 to 55% of the total in 1999. This increase occurred during a period when the total number of articles concerning globalization nearly doubled.
A number of international polls have shown that residents of developing countries tend to view globalization more favorably. The BBC found a growing feeling in developing countries that globalization was proceeding too rapidly. Only in a few countries, including Mexico, the countries of Central America, Indonesia, Brazil and Kenya, did a majority feel that globalization is increasing too slowly.
Philip Gordon stated that " a clear majority of Europeans believe that globalization can enrich their lives, while believing the European Union can help them take advantage of globalization's benefits while shielding them from its negative effects." The main opposition consisted of socialists, environmental groups, and nationalists.
Residents of the EU did not appear to feel threatened by globalization in 2004. The EU job market was more stable and workers were less likely to accept wage/benefit cuts. Social spending was much higher than in the US.
In a Danish poll in 2007, 76% responded that globalisation is a good thing.
Fiss, et al., surveyed U.S. opinion in 1993. Their survey showed that, in 1993, more than 40% of respondents were unfamiliar with the concept of globalization. When the survey was repeated in 1998, 89% of the respondents had a polarized view of globalization as being either good or bad. At the same time, discourse on globalization, which began in the financial community before shifting to a heated debate between proponents and disenchanted students and workers. Polarization increased dramatically after the establishment of the WTO in 1995; this event and subsequent protests led to a large-scale anti-globalization movement. Initially, college educated workers were likely to support globalization. Less educated workers, who were more likely to compete with immigrants and workers in developing countries, tended to be opponents. The situation changed after the financial crisis of 2007. According to a 1997 poll 58% of college graduates said globalization had been good for the U.S. By 2008 only 33% thought it was good. Respondents with high school education also became more opposed.
According to Takenaka Heizo and Chida Ryokichi, as of 1998 there was a perception in Japan that the economy was "Small and Frail". However Japan was resource poor and used exports to pay for its raw materials. Anxiety over their position caused terms such as internationalization and globalization to enter everyday language. However, Japanese tradition was to be as self-sufficient as possible, particularly in agriculture.
The situation may have changed after the 2007 financial crisis. A 2008 BBC World Public Poll as the crisis began suggested that opposition to globalization in developed countries was increasing. The BBC poll asked whether globalization was growing too rapidly. Agreement was strongest in France, Spain, Japan, South Korea, and Germany. The trend in these countries appears to be stronger than in the United States. The poll also correlated the tendency to view globalization as proceeding too rapidly with a perception of growing economic insecurity and social inequality.
Many in developing countries see globalization as a positive force that lifts them out of poverty. Those opposing globalization typically combine environmental concerns with nationalism. Opponents consider governments as agents of neo-colonialism that are subservient to multinational corporations. Much of this criticism comes from the middle class; the Brookings Institute suggested this was because the middle class perceived upwardly mobile low-income groups as threatening to their economic security.
Although many critics blame globalization for a decline of the middle class in industrialized countries, the middle class is growing rapidly in developing countries. Coupled with growing urbanization, this leads to increasing disparities in wealth between urban and rural areas. In 2002, in India, 70% of the population lived in rural areas and depended directly on natural resources for their livelihood. As a result, mass movements in the countryside at times express objections to the process.
The nonprofit Reporters Without Borders publishes a Press Freedom Index, an annual ranking of countries based upon the organization's assessment of the countries' press freedom records in the previous year. It reflects the degree of freedom that journalists, news organizations, and netizens enjoy in each country, and the efforts made by the authorities to respect and ensure respect for this freedom.
Internet

Both a product of globalization as well as a catalyst, the Internet connects computer users around the world. From 2000 to 2009, the number of Internet users globally rose from 394 million to 1.858 billion. By 2010, 22 percent of the world's population had access to computers with 1 billion Google searches every day, 300 million Internet users reading blogs, and 2 billion videos viewed daily on YouTube. According to research firm IDC, the size of total worldwide e-commerce, when global business-to-business and -consumer transactions are added together, will equate to US$16 trillion in 2013. IDate, another research firm, estimates the global market for digital products and services at US$4.4 trillion in 2013. A report by Oxford Economics adds those two together to estimate the total size of the digital economy at $20.4 trillion, equivalent to roughly 13.8% of global sales.
While much has been written of the economic advantages of Internet-enabled commerce, there is also evidence that some aspects of the internet such as maps and location-aware services may serve to reinforce economic inequality and the digital divide. Electronic commerce may be partly responsible for consolidation and the decline of mom-and-pop, brick and mortar businesses resulting in increases in income inequality.
An online community is a virtual community that exists online and whose members enable its existence through taking part in membership ritual. Significant socio-technical change may have resulted from the proliferation of such Internet-based social networks.
Population growth
Main articles: World population and OverpopulationThe world population has experienced continuous growth since the end of the Great Famine and the Black Death in 1350, when it stood at around 370 million. The highest rates of growth – global population increases above 1.8% per year – were seen briefly during the 1950s, and for a longer period during the 1960s and 1970s. The growth rate peaked at 2.2% in 1963, and had declined to 1.1% by 2011. Total annual births were highest in the late 1980s at about 138 million, and are now expected to remain essentially constant at their 2011 level of 134 million, while deaths number 56 million per year, and are expected to increase to 80 million per year by 2040. Current projections show a continued increase in population (but a steady decline in the population growth rate), with the global population expected to reach 7.5 and 10.5 billion by 2050.

The head of the International Food Policy Research Institute, stated in 2008 that the gradual change in diet among newly prosperous populations is the most important factor underpinning the rise in global food prices. From 1950 to 1984, as the Green Revolution transformed agriculture around the world, grain production increased by over 250%. World population has grown by about 4 billion since the beginning of the Green Revolution and without it, there would be greater famine and malnutrition than the UN presently documents (approximately 850 million people suffering from chronic malnutrition in 2005). With human consumption of seafood having doubled in the last 30 years, seriously depleting multiple seafood fisheries and destroying the marine ecosystem as a result, awareness is prompting steps to be taken to create a more sustainable seafood supply.
It is becoming increasingly difficult to maintain food security in a world beset by a confluence of "peak" phenomena, namely peak oil, peak water, peak phosphorus, peak grain and peak fish. Growing populations, falling energy sources and food shortages will create a "perfect storm" by 2030, according to UK chief government scientist John Beddington, who noted that food reserves were at a 50-year low and the world would require 50% more energy, food and water by 2030. The world will have to produce 70% more food by 2050 to feed a projected extra 2.3 billion people and as incomes rise, according to the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO). Social scientists have warned of the possibility that global civilization is due for a period of contraction and economic re-localization due to a decline in fossil fuels and resulting crises in transportation and food production. Helga Vierich has predicted a restoration of sustainable local economic activities based on hunting and gathering, shifting horticulture, and pastoralism.
Health
Main articles: Global health and Globalization and diseaseGlobal health is the health of populations in a global context that transcends the perspectives and concerns of individual nations. Health problems that transcend national borders or have a global political and economic impact are emphasized. It has been defined as 'the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in health for all people worldwide'. Thus, global health is about worldwide improvement of health, reduction of disparities, and protection against global threats that disregard national borders. The application of these principles to the domain of mental health is called Global Mental Health.

The major international agency for health is the World Health Organization (WHO). Other important agencies with impact on global health activities include UNICEF, World Food Programme (WFP), United Nations University International Institute for Global Health and the World Bank. A major initiative for improved global health is the United Nations Millennium Declaration and the globally endorsed Millennium Development Goals.
International travel has helped to spread some of the deadliest infectious diseases. Modern modes of transportation allow more people and products to travel around the world at a faster pace, but they also open the airways to the transcontinental movement of infectious disease vectors. One example of this occurring is AIDS/HIV. Due to immigration, approximately 500,000 people in the United States are believed to be infected with Chagas disease. In 2006, the tuberculosis (TB) rate among foreign-born persons in the United States was 9.5 times that of U.S.-born persons. Starting in Asia, the Black Death killed at least one-third of Europe's population in the 14th century. Even worse devastation was inflicted on the American supercontinent by European arrivals. 90% of the populations of the civilizations of the "New World" such as the Aztec, Maya, and Inca were killed by small pox brought by European colonization.
Global natural environment
Main articles: Natural environment, Natural resource, and Natural capital See also: Human ecology and Coupled human–environment systemThe natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. The natural environment is contrasted with the built environment, which comprises the areas and components that are strongly influenced by humans. It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments; it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform but, instead, there exists a coupled human–environment system.

Human challenges to the natural environment, such as climate change, cross-boundary water and air pollution, over-fishing of the ocean, and the spread of invasive species require at least transnational and, often, global solutions. Since factories in developing countries increased global output and experienced less environmental regulation, globally there have been substantial increases in pollution and its impact on water resources.
State of the World 2006 report said India's and China's high economic growth was not sustainable. The report states, The world's ecological capacity is simply insufficient to satisfy the ambitions of China, India, Japan, Europe and the United States as well as the aspirations of the rest of the world in a sustainable way. In a 2006 news story, BBC reported, "...if China and India were to consume as much resources per capita as United States or Japan in 2030 together they would require a full planet Earth to meet their needs. In the longterm these effects can lead to increased conflict over dwindling resources and in the worst case a Malthusian catastrophe. International foreign investment in developing countries could lead to a "race to the bottom" as countries lower their environmental and resource protection laws to attract foreign capital. The reverse of this theory is true, however, when developed countries maintain positive environmental practices, imparting them to countries they are investing in and creating a "race to the top" phenomenon.

The time between distances is shrinking between continents and countries due to globalization, causing developing and developed countries to find new ways to solve problems on a global rather than regional scale. Agencies like the United Nations now must be the global regulators of pollution, whereas before, regional governance was enough. Action has been taken by the United Nations to monitor and reduce atmospheric pollutants through the Kyoto Protocol, the UN Clean Air Initiative, and studies of air pollution and public policy. Global traffic, production, and consumption are causing increased global levels of air pollutants. The northern hemisphere has been the leading producer of carbon monoxide and sulfur oxides.
Changes in natural capital are beginning to erode the economic logic of one major aspect of economic globalization: an international division of labor and production based on global supply chains. Planetary boundaries for several key environmental resources have been reached and others are near their limits. Over time, peak oil and climate change may result in "peak globalization," measured in terms of decreasing ton-miles of freight transported, particularly across oceans and continents. The economic logic of the comparative advantage of global supply chains could be overcome by both increasing transportation costs and interruptions and delays in the transit of freight.
China and India substantially increased their fossil fuel consumption as their economies switched from subsistence farming to industry and urbanization. Chinese oil consumption grew by 8% yearly between 2002 and 2006, doubling from 1996–2006. In 2007, China surpassed the United States as the top emitter of CO
2.
Only 1 percent of the country's 560 million city inhabitants (2007) breathe air deemed safe by the European Union. In effect, this means that developed countries may "outsource" some of the pollution associated with consumption in countries where pollution-intensive industries have been moved.
Societies utilize forest resources in order to reach a sustainable level of economic development. Historically, forests in earlier developing nations experience "forest transitions", a period of deforestation and reforestation as a surrounding society becomes more developed, industrialized and shift their primary resource extraction to other nations via imports. For nations at the periphery of the globalized system however, there are no others to shift their extraction onto, and forest degradation continues unabated. Forest transitions can have an effect on the hydrology, climate change, and biodiversity of an area by impacting water quality and the accumulation of greenhouse gases through the re-growth of new forest into second and third growth forests. A major source of deforestation is the logging industry, driven by China and Japan.
Without more recycling, zinc could be used up by 2037, both indium and hafnium could run out by 2017, and terbium could be gone by 2012. Other "peak" phenomena, such as peak oil, peak coal, peak gas, peak water, and peak wheat, also affect the availability and sustainability of natural capital.
In 2003, 29% of open sea fisheries were in a state of collapse. The journal Science published a four-year study in November 2006, which predicted that, at prevailing trends, the world would run out of wild-caught seafood in 2048. Conversely, globalization created a global market for farm-raised fish and seafood, which as of 2009 was providing 38% of global output, potentially reducing fishing pressure.
The global trade in goods depends upon reliable, inexpensive transportation of freight along complex and long-distance supply chains. Global warming and peak oil undermine globalization by their effects on both transportation costs and the reliable movement of freight. Countering the current geographic pattern of comparative advantage with higher transportation costs, climate change and peak oil would thus result in peak globalization, after which the volume of exports will decline as measured by ton-miles of freight.
Global workforce
Main articles: Global workforce and New international division of labourGlobal workforce refers to the international labor pool of workers, including those employed by multinational companies and connected through a global system of networking and production, immigrant workers, transient migrant workers, telecommuting workers, and those in contingent work and other precarious employment. As of 2012, the global labor pool consisted of approximately 3 billion workers, around 200 million unemployed.
The global workforce, or international labor pool, reflects a new international division of labor that has been emerging since the late 1970s in the wake of other forces of globalization. The global economic factors driving the rise of multinational corporations—namely, cross-border movement of goods, services, technology and capital—are changing ways of thinking about labor and the structure of today's workforce. With roots in the social processes surrounding the shift to standardization and industrialization, post-industrial society in the Western world has been accompanied by industrialization in other parts of the world, particularly in Asia. As industrialization takes hold worldwide and more cultures move away from traditional practices in respect to work and labor, the ways in which employers think about and utilize labor are changing.
The global workforce is competitive and has been described as "a war for talent." This competitiveness is due, in part, to communications technologies that assist companies to attain multinational status. Communication technologies also allow companies to find workers without limiting their search locally, a process known as global labor arbitrage.
However, production workers and service workers in advanced economies have been unable to compete directly with much lower-cost workers in developing countries. Low-wage countries gained the low-value-added element of work formerly done in rich countries, while higher-value work remained; for instance, the total number of people employed in manufacturing in the US declined, but value added per worker increased.
There are many examples of this movement of labor into developing economies. Two examples can be found in China and South Africa. Chinese success cost jobs in other developing countries as well as in the West. From 2000 to 2007, the U.S. lost a total of 3.2 million manufacturing jobs. As of 26 April 2005 "In regional giant South Africa, some 300,000 textile workers have lost their jobs in the past two years due to the influx of Chinese goods".
In Europe, in 2012, the unemployment rate hit a record high at 11.8% with 18.8 million people out of jobs with youth unemployment at a new high, according to Eurostat. The rate of unemployed youth in Spain increased to over 56%, and in Greece to 62.5% in early 2013. Research shows that young people in Europe, themselves, are also worried for their future.
Noble Prize winning economist Michale Spence writes, “The massive changes in the global economy since World War II have had overwhelmingly positive effects. Hundreds of millions of people in the developing world have escaped poverty, and more will in the future. The global economy will continue to grow -- probably at least threefold over the next 30 years. One person's gain is not necessarily another's loss; global growth is not even close to a zero-sum game. But globalization hurts some subgroups within some countries, including the advanced economies.”
International migration
Main articles: Human migration, Foreign worker, and List of countries by net migration rateMany countries have some form of guest worker program with policies similar to those found in the U.S. that permit U.S. employers to sponsor non-U.S. citizens as laborers for approximately three years, to be deported afterwards if they have not yet obtained a green card. As of 2009, over 1,000,000 guest workers reside in the US; the largest program, the H-1B visa, has 650,000 workers in the U.S. and the second-largest, the L-1 visa, has 350,000. Many other United States visas exist for guest workers as well, including the H-2A visa, which allows farmers to bring in an unlimited number of agricultural guest workers. The United States ran a Mexican guest-worker program in the period 1942–1964, known as the Bracero Program.
An article in The New Republic criticized such guest worker programs by equating the visiting workers to second-class citizens, who would never be able to gain citizenship and would have less residential rights than Americans.
Migration of educated and skilled workers is called brain drain. For example, the U.S.welcomes many nurses to come work in the country. The brain drain from Europe to the United States means that some 400,000 European science and technology graduates now live in the U.S. and most have no intention to return to Europe. Nearly 14 million immigrants came to the United States from 2000 to 2010.
Immigrants to the United States and their children founded more than 40 percent of the 2010 Fortune 500 companies. They founded seven of the ten most valuable brands in the world.
Reverse brain drain is the movement of human capital from a more developed country to a less developed country. It is considered a logical outcome of a calculated strategy where migrants accumulate savings and develop skills overseas that can be used in their home country.
Reverse brain drain can occur when scientists, engineers, or other intellectual elites migrate to a less developed country to learn in its universities, perform research, or gain working experience in areas where education and employment opportunities are limited in their home country. These professionals then return to their home country after several years of experience to start a related business, teach in a university, or work for a multi-national in their home country.
A remittance is a transfer of money by a foreign worker to his or her home country. Remittances are playing an increasingly large role in the economies of many countries, contributing to economic growth and to the livelihoods of less prosperous people (though generally not the poorest of the poor). According to World Bank estimates, remittances totaled US$414 billion in 2009, of which US$316 billion went to developing countries that involved 192 million migrant workers. For some individual recipient countries, remittances can be as high as a third of their GDP. As remittance receivers often have a higher propensity to own a bank account, remittances promote access to financial services for the sender and recipient, an essential aspect of leveraging remittances to promote economic development. The top recipients in terms of the share of remittances in GDP included many smaller economies such as Tajikistan (45%), Moldova (38%), and Honduras (25%).
The IOM found more than 200 million migrants around the world in 2008, including illegal immigration. Remittance flows to developing countries reached US$328 billion in 2008 and new projections on remittance flows to developing countries show they are expected to reach US$515 billion in 2015.
A transnational marriage is a marriage between two people from different countries. A variety of special issues arise in marriages between people from different countries, including those related to citizenship and culture, which add complexity and challenges to these kinds of relationships. In an age of increasing globalization, where a growing number of people have ties to networks of people and places across the globe, rather than to a current geographic location, people are increasingly marrying across national boundaries. Transnational marriage is a by-product of the movement and migration of people.
Support and criticism
Reactions to processes contributing to globalization have varied widely with a history as long as extraterritorial contact and trade. Philosophical differences regarding the costs and benefits of such processes give rise to a broad-range of ideologies and social movements. Proponents of economic growth, expansion and development, in general, view globalizing processes as desirable or necessary to the well-being of human society. Antagonists view one or more globalizing processes as detrimental to social well-being on a global or local scale; this includes those who question either the social or natural sustainability of long-term and continuous economic expansion, the social structural inequality caused by these processes, and the colonial, Imperialistic, or hegemonic ethnocentrism, cultural assimilation and cultural appropriation that underlie such processes.
As summarized by Noam Chomsky:
The dominant propaganda systems have appropriated the term "globalization" to refer to the specific version of international economic integration that they favor, which privileges the rights of investors and lenders, those of people being incidental. In accord with this usage, those who favor a different form of international integration, which privileges the rights of human beings, become "anti-globalist." This is simply vulgar propaganda, like the term "anti-Soviet" used by the most disgusting commissars to refer to dissidents. It is not only vulgar, but idiotic. Take the World Social Forum (WSF), called "anti-globalization" in the propaganda system – which happens to include the media, the educated classes, etc., with rare exceptions. The WSF is a paradigm example of globalization. It is a gathering of huge numbers of people from all over the world, from just about every corner of life one can think of, apart from the extremely narrow highly privileged elites who meet at the competing World Economic Forum, and are called "pro-globalization" by the propaganda system.
Proponents
In general, corporate businesses, particularly in the area of finance, see globalization as a positive force in the world. Many economists cite statistics that seem to support such positive impact. For example, per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth among post-1980 globalizing countries accelerated from 1.4 percent a year in the 1960s and 2.9 percent a year in the 1970s to 3.5 percent in the 1980s and 5.0 percent in the 1990s. This acceleration in growth seems even more remarkable given that the rich countries saw steady declines in growth from a high of 4.7 percent in the 1960s to 2.2 percent in the 1990s. Also, the non-globalizing developing countries seem to fare worse than the globalizers, with the former's annual growth rates falling from highs of 3.3 percent during the 1970s to only 1.4 percent during the 1990s. This rapid growth among the globalizers is not simply due to the strong performances of China and India in the 1980s and 1990s—18 out of the 24 globalizers experienced increases in growth, many of them quite substantial.
Economic liberalism and free trade
Main articles: Economic liberalism and Neoliberalism
Economic liberals and neoliberals generally argue that higher degrees of political and economic freedom in the form of free trade in the developed world are ends in themselves, producing higher levels of overall material wealth. Globalization is seen as the beneficial spread of liberty and capitalism. Jagdish Bhagwati, a former adviser to the U.N. on globalization, holds that, although there are obvious problems with overly rapid development, globalization is a very positive force that lifts countries out of poverty by causing a virtuous economic cycle associated with faster economic growth. Economist Paul Krugman is another staunch supporter of globalization and free trade with a record of disagreeing with many critics of globalization. He argues that many of them lack a basic understanding of comparative advantage and its importance in today's world.
The flow of migrants to advanced economic countries has been claimed to provide a means through which global wages converge. An IMF study noted a potential for skills to be transferred back to developing countries as wages in those a countries rise. Lastly, the dissemination of knowledge has been an integral aspect of globalization. Technological innovations (or technological transfer) is conjectured to benefit most the developing and least developing countries (LDCs), as for example in the adoption of mobile phones.
There has been a rapid economic growth in Asia after embracing market orientation-based economic policies that encourage private property rights, free enterprise and competition. In particular, in East Asian developing countries, GDP per head rose at 5.9% a year from 1975 to 2001 (according to 2003 Human Development Report of UNDP). Like this, the British economic journalist Martin Wolf says that incomes of poor developing countries, with more than half the world’s population, grew substantially faster than those of the world’s richest countries that remained relatively stable in its growth, leading to reduced international inequality and the incidence of poverty.
Certain demographic changes in the developing world after active economic liberalization and international integration resulted in rising general welfare and, hence, reduced inequality. According to Wolf, in the developing world as a whole, life expectancy rose by four months each year after 1970 and infant mortality rate declined from 107 per thousand in 1970 to 58 in 2000 due to improvements in standards of living and health conditions. Also, adult literacy in developing countries rose from 53% in 1970 to 74% in 1998 and much lower illiteracy rate among the young guarantees that rates will continue to fall as time passes. Furthermore, the reduction in fertility rate in the developing world as a whole from 4.1 births per woman in 1980 to 2.8 in 2000 indicates improved education level of women on fertility, and control of fewer children with more parental attention and investment. Consequentially, more prosperous and educated parents with fewer children have chosen to withdraw their children from the labor force to give them opportunities to be educated at school improving the issue of child labor. Thus, despite seemingly unequal distribution of income within these developing countries, their economic growth and development have brought about improved standards of living and welfare for the population as a whole.
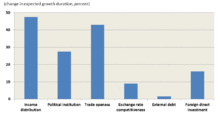
Global democracy
Main article: Democratic globalizationDemocratic globalization is a movement towards an institutional system of global democracy that would give world citizens a say in political organizations. This would, in their view, bypass nation-states, corporate oligopolies, ideological Non-governmental organizations (NGO), political cults and mafias. One of its most prolific proponents is the British political thinker David Held. Advocates of democratic globalization argue that economic expansion and development should be the first phase of democratic globalization, which is to be followed by a phase of building global political institutions. Dr. Francesco Stipo, Director of the United States Association of the Club of Rome, advocates unifying nations under a world government, suggesting that it "should reflect the political and economic balances of world nations. A world confederation would not supersede the authority of the State governments but rather complement it, as both the States and the world authority would have power within their sphere of competence". Former Canadian Senator Douglas Roche, O.C., viewed globalization as inevitable and advocated creating institutions such as a directly elected United Nations Parliamentary Assembly to exercise oversight over unelected international bodies.
International cooperation
Military cooperation – Past examples of international cooperation exist. One example is the security cooperation between the United States and the former Soviet Union after the end of the Cold War, which astonished international society. Arms control and disarmament agreements, including the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (see START I, START II, START III, and New START) and the establishment of NATO’s Partnership for Peace, the Russia NATO Council, and the G8 Global Partnership against the Spread of Weapons and Materials of Mass Destruction, constitute concrete initiatives of arms control and de-nuclearization. The U.S.–Russian cooperation was further strengthened by anti-terrorism agreements enacted in the wake of 9/11.
Environmental cooperation – One of the biggest successes of environmental cooperation has been the agreement to reduce chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) emissions, as specified in the Montreal Protocol, in order to stop ozone depletion. The most recent debate around nuclear energy and the non-alternative coal-burning power plants constitutes one more consensus on what not to do. Thirdly, significant achievements in IC can be observed through development studies.
Global civics

Global civics suggests that civics can be understood, in a global sense, as a social contract between global citizens in the age of interdependence and interaction. The disseminators of the concept define it as the notion that we have certain rights and responsibilities towards each other by the mere fact of being human on Earth. World citizen has a variety of similar meanings, often referring to a person who disapproves of traditional geopolitical divisions derived from national citizenship. An early incarnation of this sentiment can be found in Socrates, who Plutarch quoted as saying: "I am not an Athenian, or a Greek, but a citizen of the world." In an increasingly interdependent world, world citizens need a compass to frame their mindsets and create a shared consciousness and sense of global responsibility in world issues such as environmental problems and nuclear proliferation.
Cosmopolitanism is the proposal that all human ethnic groups belong to a single community based on a share morality. A person who adheres to the idea of cosmopolitanism in any of its forms is called a cosmopolitan or cosmopolite. A cosmopolitan community might be based on an inclusive morality, a shared economic relationship, or a political structure that encompasses different nations. The cosmopolitan community is one in which individuals from different places (e.g. nation-states) form relationships based on mutual respect. For instance, Kwame Anthony Appiah suggests the possibility of a cosmopolitan community in which individuals from varying locations (physical, economic, etc.) enter relationships of mutual respect despite their differing beliefs (religious, political, etc.).
Canadian philosopher Marshall McLuhan popularized the term Global Village beginning in 1962. His view suggested that globalization would lead to a world where people from all countries will become more integrated and aware of common interests and shared humanity.
Critiques
Main article: Criticisms of globalizationCritiques of globalization generally stem from discussions surrounding the impact of such processes on the planet as well as the human costs. They challenge directly traditional metrics, such as GDP, and look to other measures, such as the Gini coefficient or the Happy Planet Index, and point to a "multitude of interconnected fatal consequences–social disintegration, a breakdown of democracy, more rapid and extensive deterioration of the environment, the spread of new diseases, increasing poverty and alienation" which they claim are the unintended consequences of globalization.

Criticisms have arisen from church groups, national liberation factions, unionists, intellectuals, artists, protectionists, anarchists, those in support of relocalization (e.g., consumption of nearby production) and others. Some have been reformist in nature, (arguing for a more moderate form of capitalism) while others are more revolutionary (power shift from private to public control) or reactionary (public to private).
Some critics of globalization argue that it harms the diversity of cultures. As a dominating country’s culture is introduced into a receiving country through globalization, it can become a threat to the diversity of local culture. Some argue that globalization may ultimately lead to Westernization or Americanization of culture, where the dominating cultural concepts of economically and politically powerful Western countries spread and cause harm on local cultures.
Some opponents of globalization see the phenomenon as a promotion of corporatist interests. They also claim that the increasing autonomy and strength of corporate entities shapes the political policy of countries. They advocate global institutions and policies that they believe better address the moral claims of poor and working classes as well as environmental concerns. Economic arguments by fair trade theorists claim that unrestricted free trade benefits those with more financial leverage (i.e. the rich) at the expense of the poor.
Critics argue that globalization results in:
- Poorer countries suffering disadvantages: While it is true that free trade encourages globalization among countries, some countries try to protect their domestic suppliers. The main export of poorer countries is usually agricultural productions. Larger countries often subsidise their farmers (e.g., the EU's Common Agricultural Policy), which lowers the market price for foreign crops.
Joseph Stiglitz argues that countries that have managed globalization on their own have succeeded in reaping benefits from globalization, while countries that were economically managed by international institutions such as the IMF have not gained as much from globalization.
- The shift to outsourcing: Globalization allowed corporations to move manufacturing and service jobs from high cost locations, creating economic opportunities with the most competitive wages and worker benefits.

- Weak labor unions: The surplus in cheap labor coupled with an ever growing number of companies in transition weakened labor unions in high-cost areas. Unions lose their effectiveness and workers their enthusiasm for unions when membership begins to decline.
- An increase in exploitation of child labour: Countries with weak protections for children are vulnerable to infestation by rogue companies and criminal gangs who exploit them. Examples include quarrying, salvage, and farm work as well as trafficking, bondage, forced labor, prostitution and pornography.
Helena Norberg-Hodge, the director and founder of ISEC, criticizes globalization in many ways. In her book Ancient Futures, Norberg-Hodge claims that "centuries of ecological balance and social harmony are under threat from the pressures of development and globalization." She also criticizes the standardization and rationalization of globalization, as it does not always yield the expected growth outcomes. Although globalization takes similar steps in most countries, scholars such as Hodge claim that it might not be effective to certain countries, for globalization has actually moved some countries backward instead of developing them.
Anti-globalization movement
Main article: Anti-globalization movementAnti-globalization, or counter-globalisation, consists of a number of criticisms of globalization but, in general, is critical of the globalization of corporate capitalism. The movement is also commonly referred to as the alter-globalization movement, anti-globalist movement, anti-corporate globalization movement, or movement against neoliberal globalization. It can be explained as encompassing the ideologies present in the following other “movements”, which will be discussed below: opposition to capital market integration, social justice and inequality, anti-consumerism, anti-global governance and environmentalist opposition. Each of these ideologies can be framed around a specific strand of the anti-globalization movement, but in general the movement gears their efforts towards all of these primary principles. It is considered a rather new and modern day social movement, as the issues it is fighting against are relevant in today’s time. However, the events that occurred which fuels the movement can be traced back through the lineage of the movement of a 500-year old history of resistance against European colonialism and U.S. imperialism. This refers to the continent of Africa being colonized and stripped of their resources by the Europeans in the 19th century. It is also related closely with the anti-Vietnam war mobilizations between 1960 and1970, with worldwide protests against the adjustment of structure in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Although British sociologist Paul Q. Hirst and political economist Grahame F. Thompson note the term is vague; "anti-globalization movement" activities may include attempts to demonstrate sovereignty, practice local democratic decision-making, or restrict the international transfer of people, goods and capitalist ideologies, particularly free market deregulation. Canadian author and social activist Naomi Klein argues that the term could denote either a single social movement or encompass multiple social movements such as nationalism and socialism. Bruce Podobnik, a sociologist at Lewis and Clark College, states that "the vast majority of groups that participate in these protests draw on international networks of support, and they generally call for forms of globalization that enhance democratic representation, human rights, and egalitarianism." Economists Joseph Stiglitz and Andrew Charlton write:
The anti-globalization movement developed in opposition to the perceived negative aspects of globalization. The term 'anti-globalization' is in many ways a misnomer, since the group represents a wide range of interests and issues and many of the people involved in the anti-globalization movement do support closer ties between the various peoples and cultures of the world through, for example, aid, assistance for refugees, and global environmental issues.
In general, opponents of globalization in developed countries are disproportionately middle-class and college-educated. This contrasts sharply with the situation in developing countries, where the anti-globalization movement has been more successful in enlisting a broader group, including millions of workers and farmers.
These supporters of the movement are aware of the unequal power and respect in terms of international trade between the developed and underdeveloped countries of the world. The activists that support the AGM, as mentioned previously before, can range in terms of the specific issue(s) that they oppose. Again, there are a few different dimensions of globalization: economic, political, cultural, ecological and ideological. The diverse subgroups that make up this movement include some of the following: trade unionists, environmentalists, anarchists, land rights and indigenous rights activists, organizations promoting human rights and sustainable development, opponents of privatization, and anti-sweatshop campaigners.
Movement tactics
D.A. Snow et al. contend that the anti-globalization movement is an example of a new social movement, which uses tactics that are unique and use different resources than previously used before in other social movements. Actors of the movement participate in things such as disruptive tactics. These include flash mobs for example, which work extremely well in catching the attention of others and spreading awareness about the issue of globalization. There is also the spreading of information about the social movement through social media and word of mouth about NGOs, organizations and movement groups working to help alleviate the effects of globalization. Websites such as Twitter and Facebook have become a useful outlet for people to become aware of what is going on around the globe, any protests or tactics taking place and the progress of non-governmental organizations aiding in these impoverished countries.
One of the most infamous tactics of the movement is the Battle of Seattle in 1999, where there were protests against the World Trade Organization's Third Ministerial Meeting. It can be described as being a massive group of passionate, grass roots people within the anti-globalization movement protesting against the WTO’s corporate rule. All over the world, the movement has held protests outside meetings of institutions such as the WTO, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, the World Economic Forum, and the Group of Eight (G8). Within the Seattle demonstrations the protesters that participated used both creative and violent tactics to gain the attention towards the issue of globalization. It is still one of the most significant and memorable social movement protests in the past 20 years.
Opposition to capital market integration
Main article: Anti-capitalist movements
Capital markets have to do with raising and investing moneys in various human enterprises. Increasing integration of these financial markets between countries leads to the emergence of a global capital marketplace or a single world market. In the long run, increased movement of capital between countries tends to favor owners of capital more than any other group; in the short run, owners and workers in specific sectors in capital-exporting countries bear much of the burden of adjusting to increased movement of capital. It is not surprising that these conditions lead to political divisions about whether or not to encourage or increase international capital market integration.
Those opposed to capital market integration on the basis of human rights issues are especially disturbed by the various abuses which they think are perpetuated by global and international institutions that, they say, promote neoliberalism without regard to ethical standards. This can also be referred to as “corporate capitalism”, as previous mentioned, which are money driven organizations such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund, along with many of the popular and competitive multinational corporations, like Nike and other institutions. Common targets include the World Bank (WB), International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the World Trade Organization (WTO) and free trade treaties like the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA), the Multilateral Agreement on Investment (MAI) and the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS). In light of the economic gap between rich and poor countries, movement adherents claim "free trade" without measures in place to protect the under-capitalized will contribute only to the strengthening the power of industrialized nations (often termed the "North" in opposition to the developing world's "South"). Some of the powerful Northern corporations have implemented policies like privatizing public industry and reducing tariffs. By doing this it has created a growth in sweatshops in the developing world, where wages are minimal and unfair, and conditions are unsafe to the workers’ health and psychological state. The global North can benefit from this by getting goods for a cheaper monetary amount. However, this is at the expense of these impoverished people and the community or country as a whole. Now, fair trade has been introduced in order to attempt to rebuild the economies of third world countries by paying employees, who work to produce goods to be exported, a fair price for their efforts.
Global justice and inequality
Main article: Global justice movement
The global justice movement is the loose collection of individuals and groups—often referred to as a "movement of movements"—who advocate fair trade rules and perceive current institutions of global economic integration as problems. The movement is often labeled an anti-globalization movement by the mainstream media. Those involved, however, frequently deny that they are anti-globalization, insisting that they support the globalization of communication and people and oppose only the global expansion of corporate power. The movement is based in the idea of social justice, desiring the creation of a society or institution based on the principles of equality and solidarity, the values of human rights, and the dignity of every human being. Social inequality within and between nations, including a growing global digital divide, is a focal point of the movement. Many nongovernmental organizations have now arisen to fight these inequalities that many in Latin America, Africa and Asia face. A few very popular and well known Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) include: War Child, Red Cross, Free The Children and CARE International. They often create partnerships where they work towards improving the lives of those who live in third world countries by building schools, fixing infrastructure, cleaning water supplies, purchasing equipment and supplies for hospitals, and other aid efforts.

Inequality
Main articles: Economic inequality and International inequalityIncreasing international commerce with high barriers to entry, corporate consolidation, tax havens and other methods of tax avoidance, and political corruption have all caused increases in income inequality and wealth concentration: the increasingly unequal distribution of economic assets (wealth) and income within or between global populations, countries, and individuals. Economic inequality varies between societies, historical periods, economic structures or systems (for example, capitalism or socialism), ongoing or past wars, between genders, and between differences in individuals' abilities to create wealth. There are various numerical indices for measuring economic inequality. A prominent one is the Gini coefficient, but there are also many other methods.
Economic inequality affects equity, equality of outcome, and equality of opportunity. Although earlier thought considered economic inequality as necessary and beneficial, it has more recently come to be seen as a growing social problem. Early studies suggesting that greater equality inhibits economic growth have been shown to be flawed because they did not account for the many years it can take inequality changes to manifest in growth changes. In fact, one of the most robust and important determinants of sustained economic growth is the level of income inequality.
International inequality is inequality between countries. Economic differences between rich and poor countries are very large. According to the United Nations Human Development Report for 2004, the GDP per capita in countries with high, medium and low human development (a classification based on the UN Human Development Index) was 24,806, 4,269 and 1,184 PPP$, respectively (PPP$ = purchasing power parity measured in United States dollars).
Gender inequality in the global workforce
Main article: Gender inequalityWomen often participate in the workforce as casual labor. Evidence suggests that while globalization has expanded women’s access to employment, the long-term goal of transforming gender inequalities remains unmet and appears unattainable without regulation of capital and a reorientation and expansion of the state’s role in funding public goods and providing a social safety net.
Anti-consumerism
Main article: Anti-consumerismAnti-consumerism is the socio-political movement against equating personal happiness with consumption and the purchase of material possessions. The term "consumerism" was first used in 1915 to refer to "advocacy of the rights and interests of consumers" (Oxford English Dictionary), but here the term "consumerism" refers to the sense first used in 1960, "emphasis on or preoccupation with the acquisition of consumer goods" (Oxford English Dictionary). Concern over the treatment of consumers has spawned substantial activism, and the incorporation of consumer education into school curricula.
Anti-consumerist activism draws parallels with environmental activism, anti-globalization, and animal-rights activism in its condemnation of modern corporations, or organizations that pursue a solely economic interest. One variation on this topic is activism by postconsumers, with the strategic emphasis on moving beyond addictive consumerism.
In recent years, there have been an increasing number of books (Naomi Klein's 2000 No Logo, for example) and films (e.g. The Corporation & Surplus) popularizing an anti-corporate ideology to the public.
Opposition to economic materialism comes primarily from two sources: religion and social activism. Some religions assert materialism interferes with connection between the individual and the divine or that it is inherently an immoral lifestyle. Social activists believe materialism is connected to global retail merchandizing and supplier convergence, war, greed, anomie, crime, environmental degradation, and general social malaise and discontent.
Anti-global governance
Main article: Global governanceBeginning in the 1930s, opposition arose to the idea of a world government, as advocated by organizations such as the World Federalist Movement (WFM). Those who oppose global governance typically do so on objections that the idea is in-feasible, inevitably oppressive, or simply unnecessary. In general, these opponents are wary of the concentration of power or wealth that such governance might represent. Religious reasons are also cited, in which global governance is seen as the Biblical Antichrist or a representation thereof (see New World Order (conspiracy theory)). Such reasoning dates back to the founding of the League of Nations and, later, the United Nations.
Environmentalist opposition

Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology and social movement regarding concerns for environmental conservation and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the concerns of non-human elements. Environmentalism advocates the preservation, restoration and improvement of the natural environment in an attempt to balance relations between humanity and their broader natural environment. The exact nature of this balance is controversial and there are many different ways for environmental concerns to be expressed in practice. Environmentalism and environmental concerns are often represented by the color green, but this association has been appropriated by the marketing industries and is a key tactic in the art of Greenwashing. Environmentalist concerns with globalization include issues such as global warming, climate change, global water supply and water crises, inequity in energy consumption and energy conservation, transnational air pollution and pollution of the world ocean, overpopulation, world habitat sustainability, deforestation, biodiversity and species extinction.
Another concern is labelled "environmental apartheid", which claims that the resources and wealth of society are typically appropriated by a small minority group of a privileged race or class, under much protection. Thus, the excluded majority never gets a chance to access to resources necessary for well-being and survival. In the pre-Rio period, it was the North that contributed most to the destruction of the environment. Globalization is restructuring control over resources in such a way that the natural resources of the poor are systematically taken over by the rich and the pollution promulgated by the rich is systematically dumped on the poor. For example, 90 percent of historic carbon dioxide emissions have been by the industrialized countries. The developed countries produce 90 percent of the hazardous wastes produced around the world every year. Global free trade has globalized this environmental destruction in an asymmetric pattern. Some argue the economy is controlled by Northern corporations and they are increasingly exploiting resources of less wealthy countries for their global activities while it is the South that is disproportionately bearing the environmental burden of the globalized economy. Globalization is thus leading to a type of environmental apartheid.
A related area of concern is the pollution haven hypothesis, which posits that, when large industrialized nations seek to set up factories or offices abroad, they will often look for the cheapest option in terms of resources and labor that offers the land and material access they require (see Race to the bottom). This often comes at the cost of environmentally sound practices. Developing countries with cheap resources and labor tend to have less stringent environmental regulations, and conversely, nations with stricter environmental regulations become more expensive for companies as a result of the costs associated with meeting these standards. Thus, companies that choose to physically invest in foreign countries tend to (re)locate to the countries with the lowest environmental standards or weakest enforcement.
Key journals
Main article: List of globalization-related journalsKey academic journals examining globalization include:
- Antipode
- Development and Change
- Economic Geography
- Globalization and Health
- Journal of World-Systems Research
See also
Library resources aboutGlobalization
- Civilizing mission
- Columbian Exchange
- Deglobalization
- Development criticism
- Global civics
- Global commons
- Global public goods
- Global studies
- Great Transition
- Interdependence
- Jet Age
- Lisbon Strategy
- Middle East and globalization
- Mundialization
- North-South divide
- Outline of globalization
- Technocapitalism
- Transnational cinema
- Transnational citizenship
- Triadization
- Vermeer's Hat
- United Nations Millennium Declaration
- Washington Consensus
- World Englishes
References
- ^ Al-Rodhan, R.F. Nayef and Gérard Stoudmann. (2006). Definitions of Globalization: A Comprehensive Overview and a Proposed Definition.
- ^ Albrow, Martin and Elizabeth King (eds.) (1990). Globalization, Knowledge and Society London: Sage. ISBN 978-0803983243 p. 8. "...all those processes by which the peoples of the world are incorporated into a single world society." Cite error: The named reference "Albrow" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Stever, H. Guyford (1972). "Science, Systems, and Society." Journal of Cybernetics, 2(3):1-3. doi:10.1080/01969727208542909
- ^ Frank, Andre Gunder. (1998). ReOrient: Global economy in the Asian age. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520214743
- "Globalization and Global History (p.127)" (PDF). Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- Google Books Ngram Viewer: Globalization
- ^ International Monetary Fund . (2000). "Globalization: Threats or Opportunity." 12th April 2000: IMF Publications.
- ^ Bridges, G. (2002). "Grounding Globalization: The Prospects and Perils of Linking Economic Processes of Globalization to Environmental Outcomes". Economic Geography. 78 (3): 361–386. doi:10.2307/4140814.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ O'Rourke, Kevin H. and Jeffrey G. Williamson. (2000). "When Did Globalization Begin?" NBER Working Paper No. 7632.
- "Globalization". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- "Globalization". Oxford English Dictionary Online. September 2009. Retrieved 5 November 2010.
- "''The Battle of Armageddon'', October 1897 pages 365–370". Pastor-russell.com. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- Hopkins, A.G. (ed.). (2004). Globalization in World History. London: Norton, pp. 4–8. ISBN 978-0393979428
- Robertson, Roland (1992). Globalization : social theory and global culture (Reprint. ed.). London: Sage. ISBN 0803981872.
- Giddens, Anthony. (1991). The Consequences of Modernity Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 64. ISBN 9780745609232
- Held, David, et al. (1999). Global Transformations Cambridge: Polity Press. ISBN 9780745614984
- Larsson, Thomas. (2001). The Race to the Top: The Real Story of Globalization Washington, D.C.: Cato Institute. p. 9. ISBN 978-1930865150
- Friedman, Thomas L. "The Dell Theory of Conflict Prevention". Emerging: A Reader. Ed. Barclay Barrios. Boston: Bedford, St. Martins, 2008. 49
- Fotopoulos, Takis. (2001). "Globalization, the reformist Left and the Anti-Globalization 'Movement.'" Democracy & Nature: The International Journal of Inclusive Democracy, 7:(2) (July 2001).
- ^ Saggi, Kamal (2002). "Trade, Foreign Direct Investment, and International Technology Transfer: A Survey." World Bank Research Observer, 17 (2): 191-235. doi: 10.1093/wbro/17.2.191
- Steger, Manfred (2009). Globalization: A Very Short Introduction. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-19-955226-9.
- ^ Martell, Luke (2010). The Sociology of Globalization. Policy Press.
- Kochler, Hans (2000). Globality versus Democracy: The Changing Nature of International Relations in the Era of Globalization. Vienna: International Progress Organization. p. 35.
- Hopkins, A.G., ed., 2003. Globalization in World History. New York City, NY: Norton. ISBN 0-393-97942-3 PP. 4-5, 7
- Chaudhuri, K.N. (1965\1999). The English East India Company: The Study of an Early Joint-stock Company 1600-1640 (Vol. 4). London: Routledge/Thoemmes Press.
- Levinson, Marc. "Sample Chapter for Levinson, M.: The Box: How the Shipping Container Made the World Smaller and the World Economy Bigger". The Box: How the Shipping Container Made the World Smaller and the World Economy Bigger. Princeton University Press. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
- Gittins, Ross. "How the invention of a box changed our world - Business - smh.com.au". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
- "World Exports as Percentage of Gross World Product". Global Policy Forum. Archived from the original on 12 July 2008. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- Wolf, Martin (2001). "Will the nation-state survive globalization?" Foreign Affairs, 80(1).
- Ritzer, George (2011). Globalization: The Essentials. NY: John Wiley & Sons.
- Roubini, Nouriel (15 January 2009). "A Global Breakdown Of The Recession In 2009". Forbes.
- Faiola, Anthony. (2009). "A Global Retreat As Economies Dry Up." The Washington Post, 5 March 2009.
- Gjelten, Tom. (2009). "Economic Crisis Poses Threat To Global Stability." NPR, 18 February 2009.
- Lodge, George C. (1995). Managing Globalization in the Age of Interdependence. Golden Books Center: Kuala Lumpur. p.2.
- Sorrells, Kathryn. (2012). Intercultural Communication Globalization and Social Justice. Thousand Oaks: Sage Pubs. ISBN 9781412927444
- Hitt, Michael A.; Hoskisson, Robert E.; Kim, Hicheon (August 1997). "International Diversification: Effects on Innovation and Firm Performance in Product-Diversified Firms". The Academy of Management Journal. 40 (4). New York, NY: Sage Publications: 767–798. ISSN 0001-4273.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Daniels, J., Radebaugh, L., Sullivan, D. (2007). International Business: environment and operations, 11th edition. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-186942-6
- Joshi, Rakesh Mohan, (2009) International Business. Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-568909-7
- Hitt, Michael A. (2006). "International Diversification: Antecedents, Outcomes, and Moderators" (PDF). Journal of Management. 32(6): 831–867.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Graph: Gapminder.org
- dictionary.reference.com
- Ingham, Barbara (2004). International economics: a European focus. Pearson Education. p. 336. ISBN 0-273-65507-8.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Bhagwati, Jagdish N.; Panagariya, Arvind (1996). The economics of preferential trade agreements. AEI Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-0844739694.
- Definition of Free Trade Zone-Source-Britannica
- Economics: Principles in action. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458: Pearson Prentice Hall. 2003. p. 454. ISBN 0-13-063085-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location (link) - Asia-Pacific leads world in integration of trade
- Vogel, Ezra F. 1991. The Four Little Dragons: The Spread of Industrialization in East Asia. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- AFTA & FTAs (ASEAN Secretariat)
- "U.S. Imports of Crude Oil". U.S. Census Bureau.
- Shafik Hebous (2011) "Money at the Docks of Tax Havens: A Guide", CESifo Working Paper Series No. 3587, p. 9
- Dharmapala, Dhammika und Hines Jr., James R. (2006) Which Countries Become Tax Havens?
- Moran Harari, Markus Meinzer and Richard Murphy (October 2012) "Financial Secrecy, Banks and the Big 4 Firms of Accountants" Tax Justice Network
- "The Truth About Tax Havens — retrieved 28 December 2007" (PDF). Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- "International Taxation: Large U.S. Corporations and Federal Contractors with Subsidiaries in Jurisdictions Listed as Tax Havens or Financial Privacy Jurisdictions GAO:GAO-09-157". Government Accountability Office. 18 December 2008. Retrieved 21 January 2009.
- Tax Justice Network (July 22, 2012) "Revealed: Global super-rich has at least $21 trillion hidden in secret tax havens"
- Canadian Broadcasting Co. (July 22, 2012) "Wealthy hiding $21 trillion in tax havens, report says"
- John Whiting, tax policy director at the UK's Chartered Institute of Taxation commented "There clearly are some significant amounts hidden away, but if it really is that size what is being done with it all?" and "If the suggestion is that such amounts are actively hidden and never accessed, that seems odd — not least in terms of what the tax authorities are doing. In fact, the US, UK and German authorities are doing a lot", and noting that if the figures were accurate "you would expect the havens to be more conspicuously wealthy than they are". However, he also admitted that "I cannot disprove the figures at all, but they do seem staggering" "Tax havens: Super-rich 'hiding' at least $21tn". 22 July 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2012.
- "Fighting Anti-Tax Haven Demagoguery on CNN". 30 July 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2012.
- "Idle cash piles up: David Cay Johnston" Reuters, July 16, 2013
- "Repatriating Offshore Funds" U.S. Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations, October 11, 2011
- "Picking Up the Tab" U.S. Public Interest Research Group, April 2012
- "These Islands Aren’t Just a Shelter From Taxes" New York Times, May 5, 2012
- "Super Rich Tax Cheats" American News Project, January 8, 2009
- "'A green light to tax evasion': Super-rich tax dodgers given immunity from prosecution" Daily Mirror, November 3, 2012
- "If you want to know who’s really keeping billions in poverty, then the answer is the partners in the Big 4 firms of accountants" Tax Justice Network, April 5, 2012
- "Tax avoidance: fair or foul?" Accountancy Age Debates, January 14, 2013
- "Google will not oppose clampdown on tax avoidance, chairman says" Guardian, January 28, 2013
- "Tax avoidance isn't a left or right issue, it's a cancer eating our democracy" New Statesman, June 21, 2012
- "Helsinki Boycotts Tax Havens", Inter Press Service, October 6, 2012
- "David Cameron: Tax avoiding foreign firms like Starbucks and Amazon lack 'moral scruples'" The Telegraph, January 4, 2013
- "Germany's Merkel calls for G8 fight against tax havens" Reuters, February 13, 2013
- "Which Fortune 500 Companies Are Sheltering Income in Overseas Tax Havens?" Citizens for Tax Justice, October 17, 2012
- "Speaker Biographies" Networking Seminars, February 2013
- "Britain could end these tax scams by hitting the big four" The Guardian, December 10, 2012
- "Did the Bounds of Cyber War Just Expand to Banks and Neutral States?" The Atlantic, August 17, 2012
- "UNWTO technical manual: Collection of Tourism Expenditure Statistics" (PDF). World Tourism Organization. 1995. p. 14. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- Swine flu prompts EU warning on travel to US. The Guardian. 28 April 2009.
- "International tourism challenged by deteriorating global economy" (PDF). UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. 7 (1). World Tourism Organization. 2009. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "UNWTO World Tourism Barometer Interim Update" (PDF). UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. World Tourism Organization. 2010. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Crossing U.S. Borders. US Department of Homeland Security.
- "UNWTO World Tourism Barometer June 2009" (PDF). UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. 7 (2). World Tourism Organization. 2011. Retrieved 3 August 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "2011 Highlights" (PDF). UNWTO World Tourism Highlights. UNWTO. 2011. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Swaddling, Judith (2000). The Ancient Olympic Games (2 ed.). Austin: University of Texas Press. p. 54. ISBN 0-292-70373-2. OCLC 10759486. Retrieved 6 June 2009.
- Young (2004), p. 12
- Rose, A. K., & Spiegel, M. M. (2011). The Olympic Effect*. The Economic Journal, 121(553), 652–677.
- Tilcsik, A. and Marquis, C. 2013. “Punctuated Generosity: How Mega-events and Natural Disasters Affect Corporate Philanthropy in U.S. Communities.” Administrative Science Quarterly, 58(1): 111–148..
- Glynn, M. A. (2008). "Configuring the field of play: how hosting the Olympic Games impacts civic community." Journal of Management Studies, 45(6), 1117–1146.
- "700 million to watch World Cup Final". The Spy Report. Media Spy. 12 July 2010. Archived from the original on 15 July 2010. Retrieved 12 July 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - The Sports Market (2011). A.T. Kearney.
- "Father and son plead guilty in rhino horn smuggling". Los Angeles Times. September 16, 2012.
- "Black Market Products Index". Havocscope. Retrieved 10 January 2013. (Calculated by adding up the various black market activities that are currently being monitored )
{{cite web}}: External link in|postscript= - "UN.org". United Nations. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- "Drug Trade". BBC News.
- "Will traditional Chinese medicine mean the end of the wild tiger?". San Francisco Chronicle. 11 November 2007.
- "India says Chinese medicine fuels tiger poaching". Reuters. 17 September 2009.
- "Rhino rescue plan decimates Asian antelopes". New Scientist. 12 February 2003.
- "Human trafficking for organs, tissue removal" (PDF). Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- "Human trafficking for organs/tissue removal". Fightslaverynow.org. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- "Human trafficking for ova removal or surrogacy". Councilforresponsiblegenetics.org. 31 March 2004. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- Haken, Jeremy. "Transnational Crime In The Developing World" (PDF). Global Financial Integrity. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- Sorrells, Kathryn (2013). Intercultural Communication: Globalization and Social Justice. Los Angeles: Sage. p. 101. ISBN 978-1-4129-2744-4.
- "Economic Roots of Trafficking in the UNECE Region - Regional Prep. Meeting for Beijing". Unece.org. 15 December 2004. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- "Forced Labor and Human Trafficking: Estimating the Profits". Cornell University ILR School. 1 March 2005. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- "UN-backed container exhibit spotlights plight of sex trafficking victims". Un.org. 6 February 2008. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- "Difference between Smuggling and Trafficking". Anti-trafficking.net. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- "China close to have $1 million millionaires". The Economic Times. 13 April 2011.
- ^ Joshi, Rakesh Mohan, (2009) International Business, Oxford University Press, New Delhi and New York ISBN 0-19-568909-7.
- Riley, T: "Year 12 Economics", page 9. Tim Riley Publications, 2005
- Brandt 2008, p. 13 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBrandt2008 (help)
- "World Port Rankings 2005". American Association of Port Authorities. 2005. Retrieved 15 September 2009.
- "World Port Rankings 2006". American Association of Port Authorities. 2006. Retrieved 15 September 2009.
- http://aapa.files.cms-plus.com/Statistics/WORLD%20PORT%20RANKINGS%2020081.pdf
- China has grown into the world's second largest economy, its resilience apparent in its relative economic stability during the 2008 global financial meltdown. Indeed, this sustained economic growth may be observed in many East Asian and Asia-Pacific economies, indicating that the 21st century's economic growth will be driven by Asian economies.
- Nick Gillespie (2008). "What Slumdog Millionaire can teach Americans about economic stimulus". Reason.
- ^ Kuruvilla (2008). "ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT STRATEGIES AND MACRO- AND MICRO-LEVEL HUMAN RESOURCE POLICIES: THE CASE OF INDIA'S "OUTSOURCING" INDUSTRY". Industrial & Labor Relations Review. 62 (1): 39–72.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "Outsourcing to Africa: The world economy calls | The Economist". 16 April 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- "Aggregate Demand, Instability and Growth" Review of Keynesian Economics, January 2013 (see also this review of the paper)
- Illicit Financial Flows From Developing Countries: 2002-2006, Dev Kar and Devon Cartwright-Smith, 2008
- Hundreds of bosses flee UK over 50% tax, The Times, December 13, 2009
- Greek Euro exit looms closer as banks crumble
- €100 billion in Spanish capital flight and ECB inertia
- "Austerity measure". Financial Times Lexicon. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- Traynor, Ian (11 June 2010). "Austerity Europe: who faces the cuts". London: Guardian News. Retrieved 29 September 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Wesbury, Brian S. (26 July 2010). "Government Austerity: The Good, Bad And Ugly". Forbes. Archived from the original on 29 September 2010. Retrieved 29 September 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Krugman, Paul (15 April 2012). "Europe's Economic Suicide". The New York Times.
- {{cite web , Tales of Fiscal Adjustments, Alberto Alesina & Silvia Ardagna}}
- Luc Eyraud and Anke Weber. (2013) "The Challenge of Debt Reduction during Fiscal Consolidation" IMF Working Paper Series No. WP/13/67 (International Monetary Fund)
- Brad Plumer (October 12, 2012) "IMF: Austerity is much worse for the economy than we thought" Washington Post
- Andrew Berg and Jonathan Ostry. (2011) “Inequality and Unsustainable Growth: Two Sides of the Same Coin” IMF Staff Discussion Note No. SDN/11/08 (International Monetary Fund)
- Paul Krugman (March 10, 2013) "The IMF on the Austerity Trap" New York Times
- Barry Eichengreen and Kevin H O’Rourke (23 October 2012) "Gauging the multiplier: Lessons from history" VoxEU.org
- Paul Krugman (March 9, 2013) "The English Prisoner" New York Times
- Vujakovic, Petra. (2010). "How to Measure Globalization? A New Globalization Index (NGI)." Atlantic Economic Journal, 38(2): 237. doi:10.1007/s11293-010-9217-3
- KOF Detailed country rankings, 2013
- October 16, 2006. Data for the year 2006. No longer published.
- World Economic Forum. "Rankings: Global Enabling Trade Report 2010" (PDF).
- Cowen, Tyler; Barber, Benjamin (May/June 2003). "Globalization and Culture" (PDF). Cato Policy Report. Retrieved November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Nadeem, S (2009) Macaulay's (Cyber) Children: The Cultural Politics of Outsourcing in India. Cultural Sociology
- Hacker, Violaine (2011), "Building Medias Industry while promoting a community of values in the globalization: from quixotic choices to pragmatic boon for EU Citizens", Politické Védy-Journal of Political Science, Slovakia
- McAlister, Elizabeth. 2005. "Globalization and the Religious Production of Space." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, Vol. 44, No 3, September 2005, 249–255.
- Americanization
- http://criticalglobalisation.com/Issue3/36_59_LIMITS_CULTURAL_GLOBALISATION_JCGS3.pdf
- "2010 Form 10-K, McDonald's Corporation". United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- Steger, Manfred.Globalization. New York: Sterling Publishing, 2009.
- Clayton, Thomas. 2004. "Competing Conceptions of Globalization" Revisited: Relocating the Tension between World-Systems Analysis and Globalization Analysis. In: Comparative Education Review, vol. 48, no.3, 274-294.
- Throsby, David. (2002.) "The music industry in the new millennium: Global and Local Perspectives." Paper prepared for The Global Alliance for Cultural Diversity Division of Arts and Cultural Enterprise UNESCO, Paris.
- "Ethnic fusion Music". Allmusic.
- "Worldbeat". Allmusic.
- "World Fusion Music". worldmusic.nationalgeographic.com.
- Wallerstein, Immanuel. 2004. World-Systems Analysis. An Introduction. London: Duke University Press, pp.23-59.
- Beard, David and Keneth Gloag. 2005. Musicology: The Key Concepts. London and New York: Routledge.
- "International Flows of Selected Goods and Services" (PDF). Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- Ghosh, Biswajit (2011). "Cultural Changes and Challenges in the Era of Globalisation." Journal of Developing Societies, SAGE Publications, 27(2): 153-175.
- A Global Perspective on Bilingualism and Bilingual Education (1999), G. Richard Tucker, Carnegie Mellon University
- A Global Perspective on Bilingualism and Bilingual Education (1999), G. Richard Tucker, Carnegie Mellon University
- "The importance of multilingualism". multilingualism.org. Retrieved 16 September 2010.
- Viacheslav A. Chirikba, "The problem of the Caucasian Sprachbund" in Pieter Muysken, ed., From Linguistic Areas to Areal Linguistics, 2008, p. 31. ISBN 90-272-3100-1
- McCrum, Robert (26 November 2011). "From the Bible to the latest Swedish thriller: 2011 is the year of the translator". The Observer. Retrieved November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - "Anthro.palomar.edu". Anthro.palomar.edu. 27 July 2009. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- Swain, Samarak. (2011). Social Issues of India. Nrew Dheli: New Vishal Publications. ISBN 9781257094547.
- ^ Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia (2011). "Introduction". In Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia (eds.). Cambridge Handbook of Endangered Languages. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88215-6.
- "Moseley, Christopher (ed.). 2010. Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger, 3rd edn. Paris, UNESCO Publishing. Online version:". UNESCO.org. 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- Scholte, Jan-Aart (2005). "Chapter 6: Globalization and Governance". Globalization: A Critical Introduction. Palgrave.
- PriceWaterhouseCoopers. "Beyond the BRICs".
- Pawel Zaleski Global Non-governmental Administrative System: Geosociology of the Third Sector, Gawin, Dariusz & Glinski, Piotr : "Civil Society in the Making", IFiS Publishers, Warszawa 2006
- Vaccine delivery strategy overview.
- id=20601086&sid=aRYXnh3Vgh3w&refer=latin_america "Gates Foundation to Promote Savings by World's Poor, WSJ Says". Bloomberg. 31 July 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check|url=value (help); Missing pipe in:|url=(help) - The Index of Global Philanthropy and Remittances 2012. Hudson Institute Center for Global Prosperity.
- "North Korean Refugees NGO". Northkoreanrefugees.com. 20 October 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (2 July 2008). "UNHCR Freedom in the World 2008 - North Korea". Unhcr.org. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ Fiss, Peer and Hirsch, Pal: "The Discourse of Globalization: Framing and Sensemaking of an Emerging Concept. American Sociological Review, February 2005. vol. 70 no 1: 29–52.
- ^ Greg Ip: "The Declining Value Of Your College Degree", Wall Street Journal. 17 July 2008.
- "Africans and Asians Tend to View Globalization Favorably. Europeans and Americans are More Skeptical". World Public Opinion.org. 7 November 2006.
- ^ "Widespread Unease about Economy and Globalization". BBC World Service Poll. http://www.worldpublicopinion.org/pipa/pdf/feb08/BBCEcon_Feb08_rpt.pdf
- Gordon, Philip. 2004. "Globalization: Europe's Wary Embrace". Yale Global, 1 November 2004. http://yaleglobal.yale.edu/content/globalization-europes-wary-embrace
- Gordon, Philip. 2004. "Globalization: Europe's Wary Embrace". Yale Global, 1 November 2004. http://yaleglobal.yale.edu/content/globalization-europes-wary-embrace
- Time Magazine: Why Denmark Loves Globalisation
- Takenaka Heizo and Chida Ryokichi. 1998. "Japan," Domestic Adjustments to Globalization; (ed, Charles E. Morrison and Hadi Soesastro), Tokyo: Japan center for International Exchange, 1998, pp. 76–102.
- ^ Bhagwati, Jagdish (2004). In Defense of Globalization. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Shoa S. Rajgopal. 2002. Reclaiming Democracy, the Anti-globalization Movement in South Asia". Feminist review 70, 2002. http://visuality.org/globalization/wmst250_readings/the_antiglobalization_mvmnt.pdf
- Carol Graham "Winners and Losers: Perspectives on Globalization from the Emerging Market Economies" Brookings. Saturday 1 January 2011 http://www.brookings.edu/articles/2001/fall_globaleconomics_graham.aspx
- John Parker, Burgeoning bourgeoisie, A special report on the new middle classes in emerging markets. The Economist .12 February 2009. http://www.economist.com/node/13063298?story_id=13063298&source=hptextfeature
- "Globalization and the Rural-Urban Divide". IATRC Summer Symposium, 30 June – 2 July 2008.http://aede.osu.edu/programs/anderson/trade/Seoul_Symposium_Report.pdf
- Shoa S. Rajgopal. 2002. Reclaiming Democracy, the Anti-globalization Movement in South Asia". Feminist review 70, 2002. http://visuality.org/globalization/wmst250_readings/the_antiglobalization_mvmnt.pdf
- "Percentage of Individuals using the Internet 2000-2012", International Telecommunications Union (Geneva), June 2013, retrieved 22 June 2013
- Internet users graphs, Market Information and Statistics, International Telecommunications Union
- "Google Earth demonstrates how technology benefits RI`s civil society, govt". Antara News. 26 May 2011. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- "The New Digital Economy: How it will transform business", Oxford Economics, 2 July 2011
- Badger, Emily (6 February 2013). "How the Internet Reinforces Inequality in the Real World". The Atlantic. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- "E-commerce will make the shopping mall a retail wasteland" ZDNet, January 17, 2013
- "‘Free Shipping Day’ Promotion Spurs Late-Season Online Spending Surge, Improving Season-to-Date Growth Rate to 16 Percent vs. Year Ago" Comscore, December 23, 2012
- "The Death of the American Shopping Mall" The Atlantic — Cities, December 26, 2012
- Tuomi, Ilkka "Internet, Innovation and Open Source: Actors in the Network" 2000 First Monday
- Jean-Noël Biraben, 1980, "An Essay Concerning Mankind's Evolution", Population, Selected Papers, Vol. 4, pp. 1–13. Original paper in French: (b) Jean-Noël Biraben, 1979, "Essai sur l'évolution du nombre des hommes", Population, Vol. 34 (no. 1), pp. 13–25.
- UN World Population Prospects, the 2010 Revision: (686 million births from 1985–1990).
- "World Population estimates by the US Census Bureau".
- "World Population Clock — Worldometers". Worldometers.info. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- "International Data Base (IDB) — World Population". Census.gov. 28 June 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- von Braun, "High and Rising Food Prices", 2008, p 5, slide 14
- Kindall, Henery W & Pimentel, David (1994). "Constraints on the Expansion of the Global Food Supply". Ambio. 23 (3).
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "The limits of a Green Revolution?". BBC News. 29 March 2007.
- "Feed the world? We are fighting a losing battle, UN admits". The Guardian. 26 February 2008.
- Jacquet J. L & D. Pauly (2007). "The rise of seafood awareness campaigns in an era of collapsing fisheries". Marine Policy. 31 (3): 308–313. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2006.09.003.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "World faces 'perfect storm' of problems by 2030, chief scientist to warn". The Guardian. 18 March 2009.
- "Global crisis 'to strike by 2030'". BBC News. 19 March 2009.
- "Global food production will have to increase 70% for additional 2.3 billion people by 2050". Finfacts.com. 24 September 2009.
- Tainter, JA 1996. Complexity, Problem Solving, and Sustainable Societies. In Costanza, R, Segura,O & Martinez-Alier, J (eds) Getting Down to Earth: Practical Applications of Ecological Economics. Washington, D.C.: Island Press:61–76.
- Pimentel, D & Pimentel, M 2008. Food, Energy, and Society. 3rd edition. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press:137–159.
- Catton, WR Jr 1980. Overshoot: The Ecological Basis of Revolutionary Change. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
- Helga Vierich "Before farming and after globalization: the future of hunter- gatherers may be brighter than you think", In Before Farming 2008/4 article 4(1). See also discussion at: Waspress.co.uk
- The World Health Organization and the Transition From "International" to "Global" Public Health. Brown et al., AJPH: Jan 2006, Vol 96, No 1. http://www.ajph.org/cgi/reprint/96/1/62
- Global Health Initiative (2008). Why Global Health Matters. Washington, DC: FamiliesUSA.
- Koplan JP, Bond TC, Merson MH, et al; Consortium of Universities for Global Health Executive Board. Towards a common definition of global health. Lancet. 2009;373:1993-1995.
- Macfarlane SB, Jacobs M, Kaaya EE. In the name of global health: trends in academic institutions. J Public Health Policy. 29(4):383-401. 2008
- Patel V, Prince M. Global mental health - a new global health field comes of age. JAMA. 2010;303:1976-1977.
- "Climate change deal reached in Durban". Un.org. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- Dr. Daulaire. Globalization and Health. http://econpapers.repec.org/article/paldevelp/v_3a42_3ay_3a1999_3ai_3a4_3ap_3a22-24.htm
- "The Impact of Globalization on Infectious Disease Emergence and Control: Exploring the Consequences and Opportunities, Workshop Summary – Forum on Microbial Threats". Nap.edu. 1 June 2003. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- "The virus from Africa reached the U.S. by way of Haiti, a genetic study shows". Los Angeles Times. 30 October 2007.
- "Chagas disease", HealthCentral.com.
- "Trends in Tuberculosis Incidence --- United States, 2006". CDC.gov. 23 March 2007 / 56(11);245–250.
- Stéphane Barry and Norbert Gualde, in L'Histoire n° 310, June 2006, pp.45–46, say "between one-third and two-thirds"; Robert Gottfried (1983). "Black Death" in Dictionary of the Middle Ages, volume 2, pp.257–67, says "between 25 and 45 percent".
- Johnson, D. L.; Ambrose, S. H.; Bassett, T. J.; Bowen, M. L.; Crummey, D. E.; Isaacson, J. S.; Johnson, D. N.; Lamb, P.; Saul, M.; Winter-Nelson, A. E. (1997). "Meanings of Environmental Terms". Journal of Environmental Quality. 26 (3): 581–589. doi:10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600030002x.
- Symons, Donald (1979). The Evolution of Human Sexuality. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 31. ISBN 0-19-502535-0.
- Globalization of Water: Sharing the Planet's Freshwater resources|url=http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-1405163356.html
- ^ "Booming nations 'threaten Earth'" BBC News. 12 January 2006.
- "Effects of Over-Consumption and Increasing Populations". 26 September 2001. Retrieved on 19 June 2007
- Revesz, R.L (1997). "Federalism and Environmental Regulation: A Normative Critique. The New Federalism: Can the States Be Trusted?". Stanford, CA: Hoover Institution Press: 97–127.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "Brazil Amazon deforestation soars". BBC News. 24 January 2008.
- "Global Environmental Governance". Discovery Guides. ProQuest. Retrieved 24 December 2012.
- "United Nations Air Pollution and Public Policy". United Nations Technical Co-operation. United Nations. Retrieved 24 December 2012.
- Almqvist, E. (2002). "Ambio". 3: 161–176.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Curtis, Fred (2009). "Peak Globalization: Climate Change, oil depletion, and global trade". Ecological Economics. 69 (2): 427–434.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Oil price 'may hit $200 a barrel', BBC News
- "Running Out of Planet to Exploit". The New York Times. 21 April 2008.
- "International Petroleum (Oil) Consumption Data". U.S. Energy Information Administration. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- "China overtakes US as world's biggest CO2 emitter". Guardian.co.uk. 19 June 2007.
- Rudel,R.L. & Coomes, O.T (2005). "Forest transitions: towards a global understanding of land use change". 15: 23–31.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Meyfroidt, P., Lambin, E.F. 2011. Global Forest Transition: Prospects for an End to Deforestation. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 36: 343-371
- "Japan depletes Borneo's rainforests; China remains largest log importer"
- Earth's natural wealth: an audit. New Scientist. 23 May 2007.
- "'Only 50 years left' for sea fish", BBC News. 2 November 2006.
- Juliet Eilperin (2 November 2006). "Seafood Population Depleted by 2048, Study Finds". The Washington Post.
- FAO. "The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture" (PDF). FAO. Retrieved November 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Held, David (1999). Global Transformations. Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Torres, Raymond (ed.) (2013). World of work report 2013: Repairing the economic and social fabric (PDF). Geneva: International Labour Organisation, International Institute for Labour Studies. ISBN 978-9292510183.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - Marin, Dalia and Theirry Verdier (2012). Globalization and the empowerment of talent. Journal of International Economics 86(2): 209-223.
- Reich, Robert. (1992). The Work of the Nations, Preparing Ourselves for 21st century Capitalism. Toronto: Alfred A. Knopf,
- "Economics focus: Cash machines | The Economist". 16 April 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- "China trade blamed for 2.4 mln lost US jobs-report". Reuters. 23 March 2010.
- "Factory jobs: 3 million lost since 2000". USATODAY.com. 20 April 2007.
- "Asia strips Africa's textile industry". Asia Times Online. 26 April 2005
- Zaw, HayMann. "Unemployment in Europe: get the figures for every country". Student. The Gurdian. Retrieved 1 September 2013.
- Thompson, Derek. "Europe's Record Youth Unemployment: The Scariest Graph in the World Just Got Scarier". The Atlantic.
- Zaw, HayMann. "Young people 'worried about unemployment'". BBC. Retrieved 1 September 2013.
- Zaw, HayMann. "Globalization and Unemployment". The Council On Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 1 September 2013.
- North, David. "Estimating the Size of the H-1B Population in the U.S." Center for Immigration Studies.
- Hira, Ron. "Bridge to Immigration or Cheap Temporary Labor?" (PDF). Economic Policy Institute.
- Hardy, Roger (27 February 2008). "Migrants demand labour rights in Gulf". BBC.
- The New Republic. That's Hospitality April 17, 2006
- Arends-Kuenning, Mary. (2006). The Balance of Care: Trends in the Wages and Employment of Immigrant Nurses in the US between 1990 and 2000. Globalizations 3(3): 333-48. See also: Culture and Globalization: Center for Global Studies at the University of Illinois
- Chu, Jeff (11 January 2004). "How To Plug Europe's Brain Drain". Time magazineTemplate:Inconsistent citations
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - "Immigrant Population at Record 40 Million in 2010". Yahoo! News. 6 October 2011.
- The "New American" Fortune 500. The partnership for a new American economy. June 2011
- Stark, O & Bloom, D.E. (1985). The new economics of labor migration. The American Economic Review. 75(2) p.173-178.
- Cyranoski, David (19 February 2009). "Materials science: China's crystal cache". Nature. 457 (7232): 953–5. doi:10.1038/457953a. PMID 19225494.
High-temperature superconductor specialist Hong Ding had several attractive offers last year. But neither Boston University in Massachusetts, where he had been for a decade, nor any other institution could match the deal he was offered at the Institute of Physics in Beijing. "It is a matter of time before the United States becomes alarmed by this rapid reverse of the brain drain," says Ding. Dessau, who tried and failed to recruit Ding, says that "10 years ago it would have been unheard of . But I wouldn't be surprised if the trend continues."
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ "Payment Systems and Remittances - Remittance Market Outlook". Go.worldbank.org. 30 March 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- Remittance flows to developing countries are estimated to exceed $300 billion in 2008. 18 February 2009.
- "Migration in the Asia-Pacific Region". Stephen Castles, University of Oxford. Mark J. Miller, University of Delaware. July 2009.
- "Guinea: Unstoppable exodus", BBC News, 18 May 2004.
- "Rich world needs more foreign workers: report". FOXNews.com, 2 December 2008
- "Migration and Remittances". The World Bank.
- ^ Sen, Amartya K. (1970). Collective choice and social welfare. San Francisco, CA: Holden-Day.
- Noam Chomsky Interview. Znet 7 May 2002
- Dollar, David, Kraay, Aart. "Trade, Growth, and Poverty". Finance and Development. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sachs, Jeffrey (2005). The End of Poverty. New York, New York: The Penguin Press. ISBN 1-59420-045-9.
- Conversi, Daniele (2009) 'Globalization, ethnic conflict and nationalism', in B. Turner (ed.) Handbook of Globalization Studies. London: Routledge/ Taylor & Francis; Barkawi, Tarak (2005) Globalization and War. Rowman & Littlefield; Smith, Dennis (2006) Gobalization: The Hidden Agenda. Cambridge: Polity Press. See also Barber, Benjamin R., Jihad vs. McWorld. Ballantine Books, 1996
- "Human Development Report 2003" (PDF). UNDP. 2003. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- Martin Wolf (2004). "Why Globalization Works". Yale University Press. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ^ Berg, Andrew G.; Ostry, Jonathan D. (2011). "Equality and Efficiency". Finance and Development. 48 (3). International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- "USACOR.org". USACOR.org. 28 July 2009. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- Roche, Douglas. "The Case for a United Nations Parliamentary Assembly" (PDF). The World Federalist Movement–Institute for Global Policy. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- ^ "International cooperation as a stepping-stone to a world government | Global Policy Journal - Practitioner, Academic, Global Governance, International Law, Economics, Security, Institutions, Comment & Opinion, Media, Events, Journal". Global Policy Journal. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- Altinay, Hakan (2010). "The Case for Global Civics". Global Economy and Development at Brookings.
- WORLD CITIZENS AUSTRALIA
- Altinay, Hakan (June 2010). "A Global Civics: Necessary? Feasible?". Global Policy.
- "Cosmopolitan". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- Kwame Anthony Appiah, "Cosmopolitan Patriots," Critical Inquiry 23, no. 3 (Spring, 1997): 617-639.
- Marshall McLuhan and Bruce R. Powers (17 September 1992) The Global Village: Transformations in World Life and Media in the 21st century . Oxford University Press: 17 September 1992
- Chapman, Roger. Culture wars: an encyclopedia of issues, viewpoints, and voices, Volume 1. 2009: M.E.Sharp
- Measuring Inequality. The World Bank.
- "The Happy Planet Index". Neweconomics.org. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- Capra, Fritjof (2002). The Hidden Connections. New York, New York: Random House. ISBN 0-385-49471-8.
- Lee, Laurence (17 May 2007). "WTO blamed for India grain suicides". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 17 May 2007.
- Bakan, Joel (2004). The Corporation. New York, New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-4744-2.
- Perkins, John (2004). Confessions of an Economic Hit Man. San Francisco, California: Berrett-Koehler. ISBN 1-57675-301-8.
- "Fórum Social Mundial". Forumsocialmundial.org.br. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- NAFTA at 10, Jeff Faux, Economic Policy Institute, D.C.
- ^ Hurst E. Charles. Social Inequality: Forms, Causes, and consequences, 6th ed. P.41
- Lechner, Frank (2011). The Globalization Reader. Wiley-Blackwell; 4th ed. ISBN 978-0470655634.
- Pavcnik, Nina; Pavcnik, Nina (2005). "Child Labor in the Global Economy". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 19 (1): 199–220. doi:10.1257/0895330053147895.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Norberg-Hodge, Helena (1992). Ancient futures : learning from Ladakh (Sierra Club Books pbk. ed.). San Francisco: Sierra Club Books. ISBN 0871566435.
- Jacques Derrida (May 2004) Enlightenment past and to come, speech at the party for 50 years of Le Monde diplomatique
- Morris, Douglas "Globalization and Media Democracy: The Case of Indymedia", Shaping the Network Society, MIT Press 2003. Courtesy link to (pre-publication version) FIS.utoronto.ca
- Juris, Jeffrey S. (2008). Networking Futures: The Movements against Corporate Globalization. Durham: Duke University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-8223-4269-4.
- ^ Engler, M. (2007, May 30). The Anti-Globalization Movement Defined — STWR – Share The World's Resources. Share The World’s Resources — STWR. Retrieved March 14, 2013, from http://www.stwr.org/the-un-people-politics/the-anti-globalization-movement-defined.html
- Thompson, Grahame F. and Paul Q. Hirst. (2002). The Future of Globalisation." In Cooperation and Conflict, 37(3): 247–265. doi:10.1177/0010836702037003671 CAC.sagepub.com
- Klein, Naomi (6 April 2002). No Logo: No Space, No Choice, No Jobs. Picador. ISBN 0-312-42143-5.
- Podobnik, Bruce, Resistance to Globalization: Cycles and Evolutions in the Globalization Protest Movement, p. 2.
- Stiglitz, Joseph & Charlton Fair Trade for All: How Trade Can Promote Development. 2005 p. 54 n. 23
- Marable, Manning. (2006.) "Globalization and Racialization." Synthesis/Regeneration, 39 (Winter).
- Staggenborg, S. (2011). Social movements (Rev. ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
- Snow, D. A., Soule, S. A., & Kriesi, H. (2004). The Blackwell companion to social movements. Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub..
- Frieden, Jeffry A. (1991). "Invested Interests: The Politics of National Economic Policies in a World of Global Finance." International Organization, 45(4): 425-451. Published by: The MIT Press.
- Lemay, J. (2005). Anti-globalization movements and the collective identity of organizations: The tribulations of a fair trade association. Anthropologie Et Societes, 29(3), 39-58. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/60041247?accountid=14701
- Tom Mertes, "A Movement of Movements", New York: Verso, 2004
- della Porta, D. 2005. "The Social Bases of the Global Justice Movement: Some Theoretical Reflections and Empirical Evidence from the First European Social Forum." Civil Society and Social Movements Programme Paper No. 21.Geneva: UNRISD (United Nations Research Institute for Social Development).
- Education and Social Justice By J. Zajda, S. Majhanovich, V. Rust, 2006, ISBN 1-4020-4721-5
- Nursing ethics: across the curriculum and into practice By Janie B. Butts, Karen Rich, Jones and Bartlett Publishers 2005, ISBN 978-0-7637-4735-0
- http://www.legislature.mi.gov/documents/mcl/pdf/mcl-act-135-of-2004.pdf
- Wojciech Kopczuk, Emmanuel Saez, and Jae Song find that “most of the increase in the variance of (log) annual earnings is due to increases in the variance of (log) permanent earnings with modest increases in the variance of transitory (log) earnings.” Thus, in fact, the increase in earnings inequality is in lifetime income. Furthermore, they find that it remains difficult for someone to move up the earnings distribution (though they do find upward mobility for women in their lifetime). See their “Earnings Inequality and Mobility in the United States: Evidence from Social Security Data since 1937,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 125, no. 1 (2010): 91– 128.
- U.S. Income Inequality: It’s Not So Bad By Thomas A. Garrett| Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis| Spring 2010
- Wilkinson, Richard (2009). The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better. Allen Lane. p. 352. ISBN 978-1-84614-039-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Banerjee, Abhijit V.; Duflo, Esther (2003). "Inequality And Growth: What Can The Data Say?". Journal of Economic Growth. 8 (3): 267–99. doi:10.1023/A:1026205114860. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- Cultural Liberty in Today’s Diverse World. UN Human Development Report, 2004.
- Seguino, Stephanie and Caren Gron (2006). Gender equality and globalization: Macroeconomic policy for developing countries. Journal of International Development (18): 1081–1104. DOI: 10.1002/jid.1295 http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTGENDER/Resources/Seguino_GrownGenderEquityandGlobalizationJID.pdf
- About us. World Federalist Movement - Institute for Global Policy.
- Kennedy, Paul. (2006.) The Parliament of Man: The Past, Present, and Future of the United Nations. New York: Harper Collins. ISBN 978-0375501654
- "Ideology and Sustainability". Formal.stanford.edu. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- Ronald Bailey from the February 2002 issue. "Debunking Green Myths". Reason.com. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Donald Gibson. Environmentalism: Ideology and Power. Nova Science Pub Inc. 2003
- Cat Lincoln (2009). "Light, Dark and Bright Green Environmentalism". Green Daily. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Bigs, Shannon. (2011). "Is the UN Promoting Environmental Apartheid? News from the Durban Climate Talks and Why You Should Care." People-to-People Blog.
- Low, Nicholas. (2002). Global Ethics and Environment. Routledge Science. ISBN 978-0415197359.
- Lechner, Frank J., and John Boli. 2012. The Globalization Reader, 4th ed. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0470655634.
- Levinson, Arik (2008). "Unmasking the Pollution Haven Effect". International Economic Review. 49 (1): 223–54. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2354.2008.00478.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- Acocella, Nicola (2005). Economic policy in the age of globalisation. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-54038-0.
- Barbara, Christopher (2008). International legal personality: Panacea or pandemonium? Theorizing about the individual and the state in the era of globalization. Saarbrücken: Verlag Dr. Müller. ISBN 3-639-11514-7.
- von Braun, Joachim (2007). Globalization of Food and Agriculture and the Poor. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-569528-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Carpenter, John. "Puritan Missions as Globalization," Fides et Historia. 31:2, 1999 pp. 103–123.
- Chanda, Nayan (2007). Bound Together: How Traders, Preachers, Warriors and Adventurers Shaped Globalization. Yale University Press, New Haven. ISBN 978-0-300-11201-6.
- Chomsky, Noam and Robert W. McChesney (2011). Profit Over People: Neoliberalism & Global Order. Seven Stories Press. ISBN 978-1888363821.
- Fernando, Salvetti (ed.) (2010). "Glocal" Working. Living and Working across the World with Cultural Intelligence. Milan: Franco Angeli. ISBN 978-88-568-2733-0.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - Glyn, Andrew (2006). Capitalism Unleashed: Finance, Globalization, and Welfare. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-922679-2.
- Jones, Andrew (2010) Globalization. Key Thinkers. Cambridge: Polity Press, John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0745643221
- Kitching, Gavin (2001). Seeking Social Justice through Globalization. Escaping a Nationalist Perspective. Penn State Press. ISBN 0-271-02162-4.
- Klein, Naomi (2008). The Shock Doctrine: The Rise of Disaster Capitalism. Picador. ISBN 978-0312427993.
- Kohler, Gernot (2003). Globalization: Critical Perspectives. Hauppauge, New York: Nova Science Publishers. ISBN 1-59033-346-2..
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) With contributions by Samir Amin, Christopher Chase-Dunn, Andre Gunder Frank, Immanuel Wallerstein - Mander, Jerry (1996). The case against the global economy: and for a turn toward the local. San Francisco: Sierra Club Books. ISBN 0-87156-865-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Moore, Karl (2009). Origins of Globalization. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-80598-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Murray, Warwick E. (2006). Geographies of Globalization. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-31799-1.
- Neumann, Iver B. (2010). Governing the Global Polity: Practice, Mentality, Rationality. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07093-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Osterhammel, Jürgen (2005). Globalization: A Short History. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-12165-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Panitch, Leo and Sam Gindin (2012). The Making of Global Capitalism: the Political Economy of American Empire. London: Verso. ISBN 978-1-84467-742-9
- Pfister, Ulrich (2012). Globalization. Mainz: Institute of European History,.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Reinsdorf, Marshall and Matthew J. Slaughter (2009). International Trade in Services and Intangibles in the Era of Globalization. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-70959-8.
- Samimi, Parisa, Guan Choo Lim and Abdul Aziz Buang (2011). "Globalization Measurement: Notes on Common Globalization Indexes". Knowledge Management, Economics and Information Technology. 1 (7).
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sen, Amartya (1999). Development as Freedom. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0375406190.
- Sirkin, Harold L (2008). Globality: Competing with Everyone from Everywhere for Everything. New York: Business Plus. p. 292. ISBN 0-446-17829-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Smith, Charles (2007). International Trade and Globalisation, 3rd edition. Stocksfield: Anforme. ISBN 1-905504-10-1.
- Steger, Manfred (2002). Globalism: the new market ideology. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. ISBN 0-7425-0072-1.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2002). Globalization and Its Discontents. New York: W.W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-32439-7.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2006). Making Globalization Work. New York: W.W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-06122-1.
- Tausch, Arno (2008). Multicultural Europe: Effects of the Global Lisbon Process. Hauppauge, New York: Nova Science Publishers. ISBN 978-1-60456-806-6.
- Osle, Rafael Domingo (2010). The New Global Law. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521193870.
- Wolf, Martin (2004). Why Globalization Works. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10252-9.
External links
- Globalization Website (Emory University) Links, Debates, Glossary etc.
- BBC News Special Report – "Globalisation"
- Globalization collected news and commentary at The Guardian
- "Resilience, Panarchy, and World-Systems Analysis", from the Ecology and Society Journal
- "Globalization" Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Analysis of the idea and its history.
- Mapping Globaliztion, Pinceton University
- OECD Globalization statistics
- "Globalization", from The Canadian Encyclopedia
- YaleGlobal Online
- Global 3000 Globalization Program by Deutsche Welle-TV
| International trade | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terminology |
| ||||||||||
| Organizations and policies | |||||||||||
| Political economy | |||||||||||
| Regional organizations |
| ||||||||||
| Exports by product |
| ||||||||||
| Capitalism | |
|---|---|
| Aspects and perspectives | |
| General |
|
| Ideology |
|
| Cultural aspects |
|
| Social aspects |
|
| Criticism |
|
| Antithesis |
|
Template:Link FA Template:Link GA
Categories: