This is an old revision of this page, as edited by JZNIOSH (talk | contribs) at 15:46, 18 November 2013 (→Safety: fixed language). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:46, 18 November 2013 by JZNIOSH (talk | contribs) (→Safety: fixed language)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)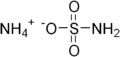
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ammonium sulfamate | |
| Other names Ammonium sulphamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.974 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | H6N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 114.125 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid hygroscopic |
| Density | 1.8 g/cm |
| Melting point | 131 °C (268 °F; 404 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | very soluble |
| Solubility | soluble in glycerol, glycol, formamide insoluble in methanol, ether, n-octanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 2000 mg/kg, oral (rat) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Ammonium sulfamate (British spelling Ammonium sulphamate) is a white crystalline solid, readily soluble in water. It is commonly used as a broad spectrum herbicide, with additional uses as a compost accelerator, flame retardant and in industrial processes.
Manufacture and distribution
It is a salt formed from ammonia and sulfamic acid.
Ammonium sulfamate is distributed under the following tradenames, which are principally herbicidal product names: Amicide, Amidosulfate, Ammate, Amcide, Ammate X-NI, AMS, Fyran 206k, Ikurin, Sulfamate, AMS and Root-Out.
Uses
Herbicide
Ammonium sulfamate is considered to be particularly useful in controlling tough woody weeds, tree stumps and brambles.
Ammonium sulfamate has been successfully used in several major UK projects by organisations like the British Trust for Conservation Volunteers, English Heritage, the National Trust,and various railway, canal and waterways authorities.
Several years ago the Henry Doubleday Research Association (HDRA) (known as Garden Organic), published an article on ammonium sulfamate after a successful set of herbicide trials. Though not approved for use by organic growers it does provide an option when alternatives have failed.
The following problem weeds / plants can be controlled: Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica var japonica), Marestail / Horsetail (Equisetum), Ground-elder, Rhododendron ponticum, Brambles, Brushwood, Ivy (Hedera species), Senecio/Ragwort, Honey fungus (Armillaria), and felled tree stumps and most other tough woody specimens.
| This section contains instructions, advice, or how-to content. Please help rewrite the content so that it is more encyclopedic or move it to Wikiversity, Wikibooks, or Wikivoyage. (March 2010) |
General application
A typical treatment would be as a foliar spray of 1 kilogram in 5 litres of water over 10 square metres (2 lbs in 1 gallon over 100 square feet). The addition of a small amount of washing up liquid to the spray solution acts as a wetting agent to help cut though the natural oils on the foliage. Children and animals need not be excluded from treated areas. Once applied it is slowly (typically 3–4 months in a mild climate) converted in the soil to the useful fertilizer ammonium sulfate (ammonium sulphate). New plants should not be sown until this process is completed.
Rhododendron ponticum
The UK Government's 'Forest Research' recommend the application of a 40% solution to the fresh cut stumps or as a foliar spray.
Japanese knotweed
Japanese knotweed is subject to legal controls in the UK and ammonium sulfamate is one of the few products that will provide effective treatment. It should be cut back to leave 300 mm (12 inch) high canes and have a 400 gram per litre solution injected down the stalk. Placing a pile of Ammonium Sulfamate crystals immediately on top of a freshly cut crown head is also a method often used.
Honey fungus
The HDRA has given advice about Armillaria and the use of ammonium sulfamate, as has the Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). Once honey fungus has been confirmed, first dig up and destroy all dead/dying woody plants, removing the stump and as much of the root system as possible. Then, if removal of a stump is impossible, the stump can ground or chipped up by a contractor. The resulting woodchips should be burned or disposed of outside the garden, not used as a mulch. As a last resort, a stump can be treated with ammonium sulfamate (a stump killer sold as Root Out), which will kill it and hasten its decay.
Compost accelerator
Ammonium sulfamate is used as a compost accelerator. It is especially effective in breaking down the tougher and woodier weeds put onto the compost heap.
Flame retardant
Ammonium sulfamate (like other ammonium salts, e.g. Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, Ammonium sulfate) is a useful flame retardant. These salt based flame retardants offer advantages over other metal/mineral-based flame retardants in that they are water processable. Their relatively low decomposition temperature makes them suitable for flame retarding cellulose based materials (paper/wood). Ammonium sulfamate (like Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate) is sometimes used in conjunction with Magnesium sulfate or Ammonium sulfate (in ratios of approximately 2:1) for enhanced flame retardant properties.
Other uses
Within industry ammonium sulfamate is used as a flame retardant, a plasticiser and in electro-plating. Within the laboratory it is used as a reagent.
Safety
Ammonium sulfamate is considered to be slightly toxic to humans and animals, making it appropriate for amateur home garden, professional and forestry uses. It is generally accepted to be safe for use on plots of land that will be used for growing fruit and vegetables intended for consumption.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has set a permissible exposure limit at 15 mg/m over an eight-hour time-weighted average, while the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommends exposures no greater than 10 mg/m over an eight-hour time-weighted average. These occupational exposure limits are protective values, given the IDLH concentration is set at 1500 mg/m.
It is also considered to be environmentally friendly due to its degradation to non-harmful residues.
European Union licensing
The pesticides review by the European Union led to herbicides containing ammonium sulfamate becoming unlicensed, and therefore effectively banned, from 2008. This situation arose as the Irish Rapporteur refused to review the data supplied unless it contained details of animal testing on dogs. As there was already substantial animal data within the package supplied the data pack holder felt further tests without substantiation would cause unnecessary animal suffering. Its licence was not withdrawn on grounds of safety of efficacy.
Its availability and use as a compost accelerator is unaffected by the EU's pesticide legislation.
References
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09958 Chemical properties from Sigma-Adrich
- http://www.daxproducts.co.uk Dax Products website, makers of Root Out
-
Bidlack, Verne C.; Fasig, Edgar W. (1951) , "10", Paint and Varnish Production Manual, John Wiley & Sons, p. 275
{{citation}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|chapterurl=and|month=(help) - "Pesticide Information Profiles : Ammonium sulfamate". EXTOXNET Extension Toxicology Network. files maintained and archived at Oregon State University. June 1996. Retrieved Mar 21, 2010.
- "Ammonium sulfamate". NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 4, 2011. Retrieved November 18, 2013.
- "Ammonium sulfamate". Documentation for Immediately Dangerous To Life or Health Concentrations (IDLHs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. May 1994. Retrieved November 18, 2013.
- "Amateur products withdrawn from the market containing ammonium sulphamate". Health and Safety Executive. Retrieved Mar 21, 2010.