This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Op47 (talk | contribs) at 23:07, 18 December 2013 (Remove split tag, no rationale, discussion or obvious reason to split. CW paragraphs on relations with other countries.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:07, 18 December 2013 by Op47 (talk | contribs) (Remove split tag, no rationale, discussion or obvious reason to split. CW paragraphs on relations with other countries.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) For other uses, see Eritrea (disambiguation). "Erythrea" redirects here. For the sea, see Erythrean Sea.
State of Eritrea
| |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Emblem
Emblem
| |
| Anthem: Ertra, Ertra, Ertra Eritrea, Eritrea, Eritrea | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Asmara |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2012) | |
| Demonym(s) | Eritrean |
| Government | Single-party presidential republic |
| • President | Isaias Afewerki |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence from Ethiopia | |
| • End of Italian Eritrea | November 1941 |
| • End of United Kingdom mandate | 1951 |
| • De facto Ethiopian independence | 24 May 1991 |
| • De jure Ethiopian independence | 24 May 1993 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 117,600 km (45,400 sq mi) (101st) |
| • Water (%) | 0.14% |
| Population | |
| • 2012 estimate | 6,233,682 (107th) |
| • 2008 census | 5,291,370 |
| • Density | 51.8/km (134.2/sq mi) (154th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2012 estimate |
| • Total | $4.396 billion |
| • Per capita | $776 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate |
| • Total | $3.092 billion |
| • Per capita | $546 |
| HDI (2011) | low (181st) |
| Currency | Nakfa (ERN) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (not observed) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +291 |
| ISO 3166 code | ER |
| Internet TLD | .er |
Eritrea (/ˌɛrˈtreɪ.ə/ or /ˌɛrˈtriːə/; Ge'ez: Template:Lang-ti ʾErtrā ; Template:Lang-ar Iritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea is the Italian form of the Greek name Ἐρυθραία (Erythraía ), meaning "red ". With its capital at Asmara, it is bordered by Sudan to the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the east. The northeastern and eastern parts of Eritrea have an extensive coastline along the Red Sea, across from Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The nation has a total area of approximately 117,600 km (45,406 sq mi), and includes the Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands.
Eritrea is a multi-ethnic country, with nine recognized ethnic groups. It has a population of around six million inhabitants. Most residents speak Afro-Asiatic languages, either of the Semitic or Cushitic branches. Among these communities, the Tigrinya make up about 55% of the population, with the Tigre constituting around 30% of inhabitants. In addition, there are a number of Nilo-Saharan-speaking Nilotic ethnic minorities. Most people in the territory adhere to Christianity or Islam.
The Kingdom of Aksum, covering much of modern-day Eritrea and northern Ethiopia, rose somewhere around the first or second centuries and adopted Christianity shortly after its formation. In medieval times much of Eritrea fell under the Medri Bahri Kingdom, with a smaller region being part of the Hamasien Republic. The creation of modern day Eritrea is a result of the incorporation of independent Kingdoms and various vassal states of the Ethiopian empire and the Ottoman Empire, eventually resulting in the formation of Italian Eritrea. In 1947 Eritrea became part of a federation with Ethiopia, the Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Subsequent annexation by Ethiopia led to the Eritrean War of Independence, ending with Eritrean independence in 1991.
Eritrea is a member of the African Union, the United Nations and IGAD, and is an observer in the Arab League.
History
Main article: History of EritreaTogether with northern Somalia, Ethiopia, Djibouti, and the Red Sea coast of Sudan, Eritrea is considered the most likely location of the land known to the ancient Egyptians as Punt (or "Ta Netjeru", meaning "God's Land"), whose first mention dates to the 25th century BC. The ancient Puntites were a nation of people that had close relations with Pharaonic Egypt during the times of Sahure and Hatshepsut.
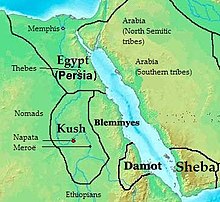
D'mt was a kingdom located in southern Eritrea and northern Ethiopia that existed during the 8th and 7th centuries BC. With its capital at Yeha, the realm developed irrigation schemes, used plows, grew millet, and made iron tools and weapons. After the fall of Dʿmt in the 5th century BC, the plateau came to be dominated by smaller successor kingdoms, until the rise of one of these polities, the Aksumite Kingdom during the first century, which was able to reunite the area.
The history of Eritrea is tied to its strategic position on the Red Sea littoral, with a coastline that extends more than 1,000 km. Many scientists believe that it is from this area that anatomically modern humans first expanded out of Africa. From across the seas came various invaders and colonizers, such as the South Arabians hailing from the present-day Yemen area, as well as the Ottoman Turks, the Portuguese from Goa (India), the Egyptians, the British and, in the 19th century, the Italians. Over the centuries, invaders also came from the neighboring countries in Africa, like Egypt and Sudan to the west and north, as well as Ethiopia to the south. However, present-day Eritrea was largely affected by the Italian colonisers of the 19th century.
In the period following the opening of the Suez canal in 1869, when European powers scrambled for territory in Africa and tried to establish coaling stations for their ships, Italy invaded Ethiopia and occupied Eritrea. On 1 January 1890, Eritrea officially became a colony of Italy. In 1936, it became a province of Italian East Africa (Africa Orientale Italiana), along with Ethiopia and Italian Somaliland. By 1941, Eritrea had about 760,000 inhabitants, including 70,000 Italians.
Through the 1941 Battle of Keren, the British expelled the Italians and took over the administration of the country. The British continued to administer the territory under a UN Mandate until 1951, when Eritrea was federated with Ethiopia per UN Resolution 390A(V) under the prompting of the United States adopted in December 1950.

Template:Contains Ethiopic text The strategic importance of Eritrea, due to its Red Sea coastline and mineral resources, along with their shared history, was the main cause for the federation with Ethiopia, which in turn led to Eritrea's annexation as Ethiopia's 14th province in 1962. This was the culmination of a gradual process of takeover by the Ethiopian authorities, a process which included a 1959 edict establishing the compulsory teaching of Amharic, the main language of Ethiopia, in all Eritrean schools. The lack of regard for the Eritrean population led to the formation of an independence movement in the early 1960s (1961), which erupted into a 30-year war against successive Ethiopian governments that ended in 1991. Following a UN-supervised referendum in Eritrea (dubbed UNOVER) in which the Eritrean people overwhelmingly voted for independence, Eritrea declared its independence and gained international recognition in 1993.
The de facto predominant languages are Tigrinya and Arabic, both of which belong to the Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. English is used in the government's international communication and is the language of instruction in all formal education beyond the fifth grade.
Eritrea is a single-party state. Though its constitution, adopted in 1997, stipulates that the state is a presidential republic with a unicameral parliamentary democracy, it has yet to be implemented. In 1998 a border dispute with Ethiopia led to the two-year Eritrean–Ethiopian War. The war resulted in the death of as many as 100,000 Ethiopian and Eritrean soldiers, although specific casualty estimates are varied.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of EritreaThe People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ) is the ruling party in Eritrea. Other political groups are not allowed to organize, although the unimplemented Constitution of 1997 provides for the existence of multi-party politics. The National Assembly has 150 seats, of which 75 are occupied by the PFDJ. National elections have been periodically scheduled and cancelled; none has ever been held in the country. The president, Isaias Afewerki, has been in office since independence in 1993.
Independent local sources of political information on Eritrean domestic politics are scarce; in September 2001 the government closed down all of the nation's privately owned print media, and outspoken critics of the government have been arrested and held without trial, according to various international observers, including Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International. In 2004 the U.S. State Department declared Eritrea a Country of Particular Concern (CPC) for its record of religious persecution.
National elections

Eritrean National elections were set for 2001 but was then decided that because 20% of Eritrea's land was under occupation, elections would be postponed until the resolution of the conflict with Ethiopia. However, local elections have continued in Eritrea. The most recent round of local government elections were held in 2010 and 2011. On further elections, the President's Chief of Staff, Yemane Gebremeskel said,
The electoral commission is handling these elections this time round so that may be the new element in this process. The national assembly has also mandated the electoral commission to set the date for national elections, so whenever the electoral commission sets the date there will be national elections. It's not dependent on regional elections.
As yet, no national elections have been held since independence.
Regions and districts

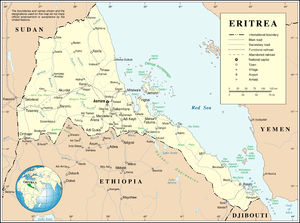
Eritrea is divided into six regions (zobas) and subdivided into districts (sub-zobas). The geographical extent of the regions is based on their respective hydrological properties. This is a dual intent on the part of the Eritrean government: to provide each administration with sufficient control over its agricultural capacity, and to eliminate historical intra-regional conflicts.
The regions, followed by the sub-region, are:
Military
The Eritrean Defence Forces are the official armed forces of the State of Eritrea.
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in EritreaThe human rights record of Eritrea is considered poor. Since Eritrea's conflict with Ethiopia in 1998–2001, Eritrea's human rights record has worsened. Several human rights violations are committed by the government or on behalf of the government. Freedom of speech, press, assembly, and association are limited. Those that practise "unregistered" religions, try to flee the nation, or escape military duty are arrested and put into prison. Domestic and international human rights organizations are not allowed to function in Eritrea.
The registered, census-based religions are the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church (a miaphysite Oriental Orthodox denomination), the Roman Catholic Church, Eritrean Lutheran Church, and Sunnite Islam. All other religions are persecuted, including other denominations of Islam, such as Shi'ism, and other denominations of Christianity, such as any of the myriad Protestant denominations. All denominations of Christianity enjoyed freedom of worship until 2002 when the government outlawed worship and assembly outside the 'registered' denominations. All groups who worship secretly in a house or any other unregistered place of assembly are arrested and imprisoned without charge or trial. Religious prisoners are often tortured in Eritrea. Freedom of worship is one of the top reasons thousands of Eritreans flee the country. There are thousands of Eritrean refugees in Ethiopia and the Sudan seeking asylum in Europe or another region of the West. Eritrea is a one-party state in which national legislative elections have been repeatedly postponed.
Media freedom
In its 2010 Press Freedom Index, Reporters Without Borders classified the media environment in Eritrea at 178 out of 178, the lowest possible rating and below that of totalitarian North Korea at 177. According to the BBC, "Eritrea is the only African country to have no privately owned news media", and Reporters Without Borders said of the public media, " do nothing but relay the regime's belligerent and ultra-nationalist discourse. ... Not a single now lives in Asmara." The state-owned news agency censors news about external events. Independent media have been banned since 2001.
Foreign relations

Eritrea is a full member of the African Union (AU), the successor of the Organization of African Unity (OAU). However, it had withdrawn its representative to the AU in protest at the AU's alleged lack of leadership in facilitating the implementation of a binding border decision demarcating the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia. The Eritrean government has since January 2011 appointed an envoy, Tesfa-Alem Tekle, to the AU.
Relations with the United States
Eritrea's relationship with the United States has a short yet complex history. The United States Army operated Kagnew Station in Eritrea (which at the time was under British, then Ethiopian rule) from 1943 to 1977 as part of an agreement with Ethiopia's Emperor Haile Selassie I. When the United Nations was debating the future of the territory of Eritrea in the beginning of the 1950s (while it was under British trusteeship as a result of the end of World War II and Italian colonialism), the United States was instrumental in promoting Eritrea's linkage with Imperial Ethiopia, opposing the idea of an independent Eritrea. This was succinctly put by then US ambassador to the UN (later to become US Secretary of State) John Foster Dulles: "From the point of view of justice, the opinions of the Eritrean people must receive consideration. Nevertheless the strategic interest of the United States in the Red Sea basin and the considerations of security and world peace make it necessary that the country has to be linked with our ally Ethiopia."
In spite of all this, independent Eritrea enjoyed cordial relations with the United States which extended considerable amounts of development aid to Eritrea. In the late 1990s, prior to the renewed conflict with Ethiopia, the United States cooperated extensively with Eritrea in an effort to contain and isolate the Islamist regime of Sudan. The US under the Bill Clinton administration was one of the main mediating parties during the border war between Eritrea and Ethiopia 1998–2001, although the Eritrean government continuously expressed its reservations against what it saw as a pro-Ethiopia bias from the US and thus began the gradual deterioration of relations with the US.
During the beginning of the George W. Bush administration and the US War on Terrorism of the early 2000s, the US still considered Eritrea a friendly state and US Secretary of Defense, Donald Rumsfeld paid Eritrea's president a visit in Eritrea. Relations ultimately worsened in October 2008 when U.S. Assistant Secretary of State Jendayi Frazer called the nation a 'state sponsor of terrorism' and stated that the U.S. government might add Eritrea to its list of rogue states, along with Iran and Sudan. The stated reason for this was the presence of Sheikh Hassan Dahir Aweys, an exiled Somali Islamist leader, whom the U.S. suspects of having links to Al Qaeda, at a Somali opposition conference in Asmara.
During the week of 2 August 2009, U.S. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton claimed that Eritrea was supplying weapons to the Somali militant group al-Shabab. Although Eritrea denied this accusation in a public statement the following day, the United Nations, with the backing of the African Union, imposed sanctions and an arms embargo on Eritrea under Resolution 1907 for its alleged role in Somalia and refusal to withdraw troops from the border with Djibouti.
Relations with the European Union
Eritrea's relationship with the Italian Republic and the European Union are still both reasonably strong and do not seem to be as strained as is the country's relationship with the United States. On 27 January 2009, the Dutch Ambassador, Yoka Brandt, Director General of International Development Cooperation, paid an official visit to the country for bilateral talks with President Isaias' government, which were held in Massawa.
Relations with Israel
Main article: Eritrea–Israel relationsEritrea and Israel have ambassadors in each other's capitals. Israel maintains an embassy in Asmara and Eritrea has a presence in Ramat Gan. Avi Granot, head of the Africa division in the Israeli foreign ministry, has described Eritrea as a strategic ally, the one friendly port on the Red Sea. There are approximately 60,000 African refugees in Israel, mostly from Sudan and Eritrea.
Relations with neighbouring countries
Eritrea's relations with its neighbours have been strained due to a series of wars and disputes. These include a break of diplomatic relations with Sudan when Eritrea accused Sudan of hosting a network of terrorists in 1994, a war with Yemen over the Hanish Islands in 1996, and a border conflict with Ethiopia from 1998–2001. An international border commission, the Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission had delimited and virtually demarcated the border, but Ethiopia has refused to implement it.
Eritrea's relations with the Sudan have normalised. Meanwhile, Eritrea has been recognised as a broker for peace between the separate factions of the Sudanese civil war: "It is known that Eritrea played a role in bringing about the peace agreement ." In addition, the Sudanese government and Eastern Front rebels requested Eritrea to mediate peace talks in 2006.
The dispute with Yemen over the Hanish Islands in 1996 resulted in a brief war. As part of an agreement to cease hostilities the two nations agreed to refer the issue to the Permanent Court of Arbitration at the Hague in 1998. Yemen was granted full ownership of the larger islands while Eritrea was awarded the peripheral islands to the southwest of the larger islands. At the conclusion of the proceedings, both nations acquiesced to the decision. Since 1996, both governments have remained wary of one another but relations are relatively normal.
Relations with Ethiopia
See also: Eritrean–Ethiopian War
The undemarcated border with Ethiopia is the primary external issue currently facing Eritrea. Eritrea's relations with Ethiopia turned from that of cautious mutual tolerance, following the 30-year war for Eritrean independence, to a deadly rivalry that led to the outbreak of hostilities from May 1998 to June 2000 which claimed approximately 70,000 casualties from both sides. The border conflict cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
Disagreements following the war have resulted in stalemate punctuated by periods of elevated tension and renewed threats of war. The stalemate led the President of Eritrea to urge the UN to take action on Ethiopia with the Eleven Letters penned by the President to the United Nations Security Council. The situation has been further escalated by the continued efforts of the Eritrean and Ethiopian leaders in supporting opposition in one another's countries. In 2011, Ethiopia accused Eritrea of planting bombs at an African Union summit in Addis Ababa, which was later supported by a UN report. Eritrea has denied the claims.
Amid fears of an emerging Islamic and nationalist Somalia, Ethiopia invaded Somalia with U.S. assistance, putting in place the initially weak and locally unpopular UN/AU-backed Transitional Federal Government which, without Ethiopian support, had been unable to exercise any control beyond its base in Baidoa and along the Ethio-Somali border. The Transitional Federal Government as of 2011 took full control of the capital and made significant gains on the territory of the now-defunct Islamic Courts Union. The United States Central Intelligence Agency also conducted a covert program of funding and assisting a coalition of Somali warlords to replace the Islamic Courts Union government in southern Somalia.
For its part, Eritrea once hosted members of the ousted Union of Islamic Courts and the Somali Free Parliament, including the current President of the Transitional Federal Government of Somalia, who was also the leader of the Union of Islamic Courts ousted by Ethiopia in 2007. The Eritrean government has been accused of sponsoring, arming and hosting numerous militant leaderships and separatist rebels in the Horn of Africa.
Geography
Main article: Geography of EritreaEritrea is located in the Horn of Africa. It is and is bordered to the northeast and east by the Red Sea, Sudan to the west, Ethiopia to the south, and Djibouti to the east. Eritrea lies between latitudes 12° and 18°N, and longitudes 36° and 44°E.

The country is virtually bisected by a branch of the East African Rift. It has fertile lands to the west, descending to desert in the east. Eritrea, at the southern end of the Red Sea, is the home of the fork in the rift. The Dahlak Archipelago and its fishing grounds are situated off the sandy and arid coastline. The land to the south, in the highlands, is slightly drier and cooler.
The strategically important Bab-el-Mandeb strait connects the coasts of Eritrea and Yemen. The Afar Triangle or Danakil Depression of Eritrea is the probable location of a triple junction where three tectonic plates are pulling away from one another: the Arabian Plate, and the two parts of the African Plate (the Nubian and the Somali plate) splitting along the East African Rift Zone (USGS). The highest point of the country, Emba Soira, is located in the center of Eritrea, at 3,018 meters (9,902 ft) above sea level.
The main cities of the country are the capital city of Asmara and the port town of Asseb in the southeast, as well as the towns of Massawa to the east, the northern town of Keren, and the central town Mendefera.
Eritrea formerly supported a large population of elephants. The Ptolemaic kings of Egypt used the country as a source of war elephants in the third century BC. Between 1955 and 2001 there were no reported sightings of elephant herds, and they are thought to have fallen victim to the war of independence. In December 2001 a herd of about 30, including 10 juveniles, was observed in the vicinity of the Gash River. The elephants seemed to have formed a symbiotic relationship with olive baboons—The baboons use the water holes dug by the elephants, while the elephants use the tree-top baboons as an early warning system. It is estimated that there are around 100 elephants left in Eritrea, the most northerly of East Africa's elephants. The endangered Painted Hunting Dog (Lycaon pictus) was previously found in Eritrea, but is now deemed extirpated from the entire country.
In 2006, Eritrea announced it would become the first country in the world to turn its entire coast into an environmentally protected zone. The 1,347 km (837 mi) coastline, along with another 1,946 km (1,209 mi) of coast around its more than 350 islands, will come under governmental protection.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Eritrea See also: List of companies based in Eritrea
The Economy of Eritrea has experienced considerable growth in recent years, indicated by an improvement in gross domestic product (GDP) in October 2012 of 7.5 percent over 2011. A big reason for the recent growth of Eritrean Economy is owing to the commencement of full operations in the gold and silver Bishop mine and to the production of cement from the cement factory in Massawa.
The Real GDP (2009 est.): $4.4 billion, and the annual growth rate (2011 est.):14%.
However, worker remittances from abroad are estimated to account for 32 percent of gross domestic product. Eritrea has an extensive amount of resources such as copper, gold, granite, marble, and potash. The Eritrean economy has undergone extreme changes due to the War of Independence. In 2011, Eritrea's GDP grew by 8.7 percent making it one of the fastest growing economies in the world. The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) expects it to maintain a high growth rate of 8.5 percent in 2013.
The Eritrean-Ethiopian War severely hurt Eritrea's economy. GDP growth in 1999 fell to less than 1%, and GDP decreased by 8.2% in 2000. In May 2000, the war resulted in some $600 million in property damage and loss, including losses of $225 million in livestock and 55,000 homes.
Even during the war, Eritrea developed its transportation infrastructure by asphalting new roads, improving its ports, and repairing war-damaged roads and bridges as a part of the Warsay Yika'alo Program. The most significant of these projects was the building of a coastal highway of more than 500 km connecting Massawa with Asseb as well as the rehabilitation of the Eritrean Railway. The rail line has been restored between the port of Massawa and the capital Asmara, although services are sporadic. Steam locomotives are sometimes used for groups of enthusiasts.
In theory, the country has a national carrier, Eritrean Airlines, but services are intermittent.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Eritrea
There are nine recognized ethnic groups according to the government of Eritrea. Eritrean society is ethnically heterogeneous. An independent census has yet to be conducted, but the Tigrinya people make up about 55% and Tigre people make up about 30% of the population. These form the bulk of the country's predominantly Semitic-speaking population. Most of the rest of the population belong to other Afro-Asiatic-speaking communities of the Cushitic branch, such as the Saho, Hedareb, Afar and Bilen.
Other Afro-Asiatic groups include the Rashaida, who represent about 2% of Eritrea's population. They reside in the northern coastal lowlands of Eritrea as well as the eastern coasts of Sudan. The Rashaida first came to Eritrea in the 19th century from the Hejaz region. More recently, Hadhrami migrants have also settled in the country.
There are also a number of Nilotic ethnic minorities, who are represented in Eritrea by the Kunama and Nara. Each ethnicity speaks a different native tongue but, typically, many of the minorities speak more than one language.
In addition, there exist Italian Eritrean (concentrated in Asmara) and Ethiopian Tigrayan communities. Neither is generally given citizenship unless through marriage or, more rarely, by having it conferred upon them by the State.
Languages
Main article: Languages of Eritrea
Eritrea is a multilingual country. The nation has no official language, as the Constitution establishes the "equality of all Eritrean languages". However, Tigrinya and Modern Standard Arabic serve as de facto national languages. With 2,540,000 total speakers as of 2006, Tigrinya is the most widely spoken language; particularly in the southern and central parts of Eritrea. English also serves as a de facto national working language, and Italian is widely understood.
Most of the languages spoken in Eritrea stem from the Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. Among these are Tigre, Tigrinya, the newly recognized Dahlik, and Arabic (the Hejazi and Hadhrami dialects spoken by the Rashaida and Hadhrami, respectively). Other Afro-Asiatic languages belonging to the Cushitic branch are also widely spoken in the country. The latter include Afar, Beja, Blin and Saho.
In addition, Nilo-Saharan languages (Kunama and Nara) are also spoken as a mother tongue by the Nilotic Kunama and Nara ethnic minority groups that live in the north and northwestern part of the country.
Italian and English are also spoken as working languages, and are used in secondary and university education.
Health
Main article: Health in EritreaEritrea has achieved significant improvements in health care and is one of the few countries to be on target to meet its Millennium Development Goal (MDG) targets in health, in particular child health. Life expectancy at birth has increased from 39.1 in 1960 to 59.5 years in 2008, maternal and child mortality rates have dropped dramatically and the health infrastructure has been expanded. Due to Eritrea's relative isolation, information and resources are extremely limited and according the World Health Organisation (WHO) found in 2008 average life expectancy to be slightly less than 63 years. Immunisation and child nutrition has been tackled by working closely with schools in a multi-sectoral approach; the number of children vaccinated against measles almost doubled in seven years, from 40.7% to 78.5% and the underweight prevalence among children decreased by 12% in 1995–2002 (severe underweight prevalence by 28%). The National Malaria Protection Unit of the Ministry of Health has registered tremendous improvements in reducing malarial mortality by as much as 85% and the number of cases by 92% between 1998 and 2006. The Eritrean government has banned female genital mutilation (FGM), saying the practice was painful and put women at risk of life-threatening health problems.
However, Eritrea still faces many challenges. Despite number of physicians increasing from only 0.2 in 1993 to 0.5 in 2004 per 1000 population, this is still very low. Malaria and Tuberculosis both are common in Eritrea. HIV prevalence among the 15–49 group exceeds 2%. The fertility rate is at about 5 births per woman. Maternal mortality dropped by more than half from 1995 to 2002, although the figure is still high. Similarly, between 1995 and 2002, the number of births attended by skilled health personnel has doubled but still is only 28.3%. A major cause of deaths of neonates is by severe infection. Per capita expenditure on health is low in Eritrea.
Largest towns
This is a list of cities in Eritrea by population:
| Cities in Eritrea | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City | Population | Region | ||
| 1984 Census | 2010 estimate | ||||
| 1 | Asmara | 475,385 | 649,707 | Maekel | |
| 2 | Keren | 126,149 | 146,483 | Anseba | |
| 3 | Teseney | 52,531 | 64,889 | Gash-Barka | |
| 4 | Mendefera | 22,184 | 63,492 | Debub | |
| 5 | Agordat | 15,948 | 47,482 | Gash-Barka | |
| 6 | Assab | 31,037 | 39,656 | Southern Red Sea | |
| 7 | Massawa | 15,441 | 36,700 | Northern Red Sea | |
| 8 | Adi Quala | 14,465 | 34,589 | Debub | |
| 9 | Senafe | 14,019 | 31,831 | Debub | |
| 10 | Dekemhare | 17,290 | 31,000 | Debub | |
| 11 | Segeneiti | 13,328 | 27,656 | Debub | |
| 12 | Nakfa | N/A | 20,222 | Northern Red Sea | |
| 13 | Adi Keyh | 8,691 | 19,304 | Debub | |
| 14 | Barentu | 2,541 | 15,467 | Gash-Barka | |
| 15 | Beilul | N/A | 14,055 | Southern Red Sea | |
| 16 | Edd | N/A | 12,855 | Southern Red Sea | |
| 17 | Ghinda | 7,702 | 10,523 | Northern Red Sea | |
| 18 | Mersa Fatuma | N/A | 9,542 | Southern Red Sea | |
| 19 | Himbirti | N/A | 8,822 | Maekel | |
| 20 | Nefasit | N/A | 8,727 | Debub | |
Education
Main article: Education in EritreaThere are five levels of education in Eritrea: pre-primary, primary, middle, secondary, and post-secondary. There are nearly 238,000 students in the primary, middle, and secondary levels of education. There are approximately 824 schools in Eritrea and two universities (the University of Asmara and the Institute of Science and Technology) as well as several smaller colleges and technical schools.
Education in Eritrea is officially compulsory between seven and 13 years of age. However, the education infrastructure is inadequate to meet current needs. Statistics vary at the elementary level, suggesting that between 65 and 70% of school-aged children attend primary school; Approximately 61% attend secondary school. Student-teacher ratios are high: 45 to 1 at the elementary level and 54 to 1 at the secondary level. There are an average 63 students per classroom at the elementary level and 97 per classroom at the secondary level. Learning hours at school are often less than six hours per day. Skill shortages are present at all levels of the education system, and funding for and access to education vary significantly by gender and location. Illiteracy estimates for Eritrea range from around 40% to as high as 70%.
Barriers to education in Eritrea include traditional taboos, school fees (for registration and materials), and the opportunity costs of low-income households.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Eritrea| Eritrea religious groups, U.S Department of State 2011/ Pew Research 2012 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Christianity (USDOS) | 50% | |||
| Islam (USDOS) | 48% | |||
| Others (USDOS) | 2% | |||
| Christianity (Pew) | 62.9% | |||
| Islam (Pew) | 36.2% | |||
| Others (Pew) | 0.9% | |||
According to recent estimates, 50% of the population adheres to Christian, Islam 48%, while 2% of the population follows other Religions including Traditional African religion and Animism. According to a study made by Pew Research Center, 62.9% adheres to Christianity and 36.2% adheres to Islam.

Since May 2002, the government of Eritrea has officially recognized the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, Sunni Islam, Catholicism, and the Evangelical Lutheran church. All other faiths and denominations are required to undergo a registration process. Among other things, the government's registration system requires religious groups to submit personal information on their membership to be allowed to worship.

The Eritrean government is against reformed or radical versions of its established religions. Therefore, radical forms of Islam and Christianity (viz, Salafism), Jehovah's Witnesses, the Bahá'í Faith, the Seventh-day Adventist Church, and numerous other non-Protestant Evangelical denominations are not registered and cannot worship freely. Three named Jehovah's Witnesses are known to have been imprisoned since 1994. Additionally, on 28 June 2009, police raided a private home where Jehovah's Witnesses were meeting. 23 were arrested including children as young as two years old. Some of the women and children were later released. None have been charged officially or given access to the judicial process. By 29 July 2010, 52 Jehovah's Witnesses had been imprisoned in Eritrea for conducting secret religious gatherings, engaging in religious activity, and for refusing to undertake national service.
As of 2006, there was only one native adherent of Judaism, Sami Cohen, remaining in Eritrea.
In its 2006 religious freedom report, the U.S. State Department named Eritrea a "Country of Particular Concern" (CPC) for the third year in a row.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Eritrea See also: Cuisine of Eritrea and Music of Eritrea
The culture of Eritrea has been largely shaped by the country's location on the Red Sea coast. One of the most recognizable parts of Eritrean culture is the coffee ceremony. Coffee (Ge'ez ቡን būn) is offered when visiting friends, during festivities, or as a daily staple of life. If it is politely declined, then most likely tea ("shai" ሻሂ shahee) will instead be served.
A typical Eritrean dish consists of injera accompanied by a spicy stew, which frequently includes beef, kid, lamb or fish. People in Eritrea also tend to drink coffee and a bitter fermented barley called sowa. Mies is another popular local alcoholic beverage, made out of honey. Overall, Eritrean cuisine strongly resembles those of neighboring Ethiopia and Somalia, except for the fact that Eritrean and Somali cooking tend to feature more seafood than Ethiopian cuisine on account of their coastal locations. Eritrean dishes are also frequently "lighter" in texture than Ethiopian meals. They likewise tend to employ less seasoned butter and spices and more tomatoes, as in the tsebhi dorho delicacy. Additionally, owing to its colonial history, cuisine in Eritrea features more Ottoman and Italian influences than are present in Ethiopian cooking, including more pasta specials and greater use of curry powders and cumin. Alongside sowa, people in Eritrea also tend to drink coffee, whereas sweetened tea is preferred in Somalia.
Besides convergent culinary tastes, Eritreans share an appreciation for similar music and lyrics, jewelry and fragrances, and tapestry and fabrics as other populations in the Horn region. Traditional Eritrean attire is quite varied. Most of the women in the lowlands traditionally dress in brightly colored clothes, while the Tigrinya-speaking highlanders wear bright white gowns called zurias. Men in the lowlands likewise often wear long white shirts accompanied by white pants. In the larger cities, most males dress more casually. Of the Muslim communities, only Rashaida women maintain a tradition of covering their faces.
Football and cycling are the most popular sports in Eritrea. In recent years, Eritrean athletes have also seen increasing success in the international arena. Zersenay Tadese, an Eritrean athlete, currently holds the world record in half marathon distance running. Additionally, the Tour of Eritrea, a multi-stage international cycling event, is held annually throughout the country.
Eritrea's various ethnic groups each have their own different styles of music and accompanying dances. Amongst the Tigrinya, the best known traditional musical genre is the guaila.
See also
Portals:References
- ^ Hailemariam, Chefena (1999). "Multilingualism and Nation Building: Language and Education in Eritrea" (PDF). Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development. 20 (6): 474–493. doi:10.1080/01434639908666385. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Eritrea". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 28 February 2013. (Archived 2013 edition.)
- ^ CIA – Eritrea – Ethnic groups. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 25 June 2012.
- ^ "Eritrea". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ^ "Merriam-Webster Online". Merriam-webster.com. 25 April 2007. Retrieved 2 May 2010. Cite error: The named reference ":0" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ISO 3166-1 Newsletter VI-13 International Organization for Standardization
- Munro-Hay, Stuart (1991) Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity. Edinburgh: University Press, p. 57 ISBN 0-7486-0106-6.
- Henze, Paul B. (2005) Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia, ISBN 1-85065-522-7.
- Aksumite Ethiopia. Workmall.com (24 March 2007). Retrieved on 3 March 2012.
- Najovits, Simson (2004) Egypt, trunk of the tree, Volume 2, Algora Publishing, p. 258, ISBN 087586256X.
- Pankhurst, Richard K.P. (17 January 2003) "Let's Look Across the Red Sea I", Addis Tribune
- Walter RC, Buffler RT, Bruggemann JH; et al. (2000). "Early human occupation of the Red Sea coast of Eritrea during the last interglacial". Nature. 405 (6782): 65–9. doi:10.1038/35011048. PMID 10811218.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Tesfagiorgis, Gebre Hiwet (1993). Emergent Eritrea: challenges of economic development. The Red Sea Press. p. 111. ISBN 0-932415-91-1.
- Law, Gwillim. "Regions of Eritrea". Administrative Divisions of Countries ('Statoids'). Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- United Nations General Assembly. "Eritrea: Report of the United Nations Commission for Eritrea; Report of the Interim Committee of the General Assembly on the Report of the United Nations Commission for Eritrea" (PDF). Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- "Eritrea – The spreading revolution". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Eritrea orders Westerners in UN mission out in 10 days. International Herald Tribune. 7 December 2005
- "Country profile: Eritrea". BBC News. 17 June 2008. Retrieved 1 July 2008.
- "2005 Executive Summary". International Religious Freedom Report. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor. 8 November 2005. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- Interview of Mr. Brandon Edmonds, Director of the Office of the President of Eritrea, PFDJ (1 April 2004)
- ^ Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. US State Department http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2011humanrightsreport/index.htm?dynamic_load_id=186194#wrapper.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Eritrea Human Rights Overview Human Rights Watch
- ^ Associated Press (25 October 2013). "Eritrea's human rights record comes under fire at United Nations". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 October 2013.
- CSW-USA on Eritrea CSW
- Eritrea. Grassroots International
- "Press Freedom Index 2009 – Reporters Without Borders". En.rsf.org. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- "Country profile: Eritrea". BBC News. 30 November 2010.
- "World Report – Eritrea – Reporters Without Borders". En.rsf.org. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ Keita, Mohamed (18 February 2011). "Sub-Saharan Africa censors Mideast protests". Committee to Protect Journalists.
- Tekle, Tesfa-Alem (20 January 2011). "Eritrea appoints AU envoy in Ethiopia – Sudan Tribune: Plural news and views on Sudan". Sudan Tribune. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- "Embargoed Countries". US Department of State. 6 October 2008.
- Martell, Peter (11 September 2007). "How Eritrea fell out with the west". BBC. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- "Clinton vows new U.S. support for Somalia". USA Today. 6 August 2009. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- "Eritrea: 'We Are Not Arming Somali Insurgents' – Government". Stratfor. 7 August 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- Greenwood, Phoebe (17 July 2012) Eritrean regime cashes in on arms and human trafficking, says UN report. The Guardian.
- "Israel to jail illegal migrants for up to 3 years". Reuters. 3 June 2012.
- "Turabi terms USA "world's ignoramuses", fears Sudan's partition". Sudan Tribune. 4 November 2005. Archived from the original on 18 July 2006. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "Sudan demands Eritrean mediation with eastern Sudan rebels". Sudan Tribune. 18 April 2006. Archived from the original on 19 May 2006. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "PCA – Documents: Eritrea-Yemen Award – CHAPTER I". Library2.lawschool.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "International Maritime Boundary". Archived from the original on 18 February 2006. Retrieved 17 July 2006.
- "Flights back on between Yemen and Eritrea". BBC. 13 December 1998. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "Ethiopian raid on Eritrean bases raises fears of renewed conflict". The Guardian. 16 March 2012.
- Will arms ban slow war? BBC. 18 May 2000
- "Horn tensions trigger UN warning". BBC. 4 February 2004. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "Army build-up near Horn frontier". BBC. 2 November 2005. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "Horn border tense before deadline". BBC. 23 December 2005. Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- Rice, Xan (28 July 2011). "Eritrea planned massive bomb attack on African Union summit, UN says". The Guardian. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
- "U.N.: Eritrea giving arms to Somalis tied to al Qaeda". CNN. 26 July 2007. Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- Mazzetti, Mark (27 December 2006). "U.S. Signals Backing for Ethiopian Incursion Into Somalia". New York Times.
- "Africa's rebels take to tranquil Eritrea capital". Investing.reuters.co.uk. 17 September 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "The rediscovery of Eritrea's elephants". BBC Wildlife Magazine. 2003. Retrieved 28 July 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Hogan, C. Michael (31 January 2009) Painted Hunting Dog: Lycaon pictus, GlobalTwitcher.com.
- Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: Eritrea. Imf.org (14 September 2006). Retrieved on 20 September 2013.
- http://www.afdb.org/en/countries/east-africa/eritrea/eritrea-economic-outlook/
- Eritrea Overview. Worldbank.org (19 October 2012). Retrieved on 20 September 2013.
- "Eritrea". State.gov. 9 March 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- Kirkby, Daniela. Eritrea: Africa’s Economic Success Story. iNewp.com. Retrieved on 20 September 2013.
- http://www.eritrean-embassy.se/about-eritrea/culture/
- https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/er.html
- Alders, Anne. "the Rashaida". Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- "Constitution of the State of Eritrea". Shaebia.org. Archived from the original on 3 May 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Eritrea - Languages". Ethnologue. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- ^ Minahan, James (1998). Miniature empires: a historical dictionary of the newly independent states. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 76. ISBN 0-313-30610-9.
The majority of the Eritreans speak Semitic or Cushitic languages of the Afro-Asiatic language group. The Kunama, Baria, and other smaller groups in the north and northwest speak Nilotic languages.
- ^ Rodríguez Pose, Romina and Samuels, Fiona (2010) Progress in health in Eritrea: Cost-effective inter-sectoral interventions and a long-term perspective. London: Overseas Development Institute
- "IRIN Africa | ERITREA: Government outlaws female genital mutilation | Eritrea | Gender Issues | Human Rights". Irinnews.org. 5 April 2007. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ Health profile at Eritrea WHO Country Office. afro.who.int
- Baseline Study on Livelihood Systems in Eritrea (PDF). National Food Information System of Eritrea. January 2005.
- Eritrea country profile. Library of Congress Federal Research Division (September 2005). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Kifle, Temesgen (2002). Educational Gender Gap in Eritrea. PDF copy
- ^ http://www.webcitation.org/5ywEZKW1R
- http://www.pewforum.org/files/2009/10/Muslimpopulation.pdf
- ^ Fisher, Jonah (17 September 2004). "Religious persecution in Eritrea". BBC News. Retrieved 11 December 2009.
- "Jehovah's Witnesses — Eritrea Country Profile – October 2008". Retrieved 25 September 2009.
- "Je hovah's Witnesses Official Media Web Site". Jw-media.org. 29 July 2010. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Harris, Ed (30 April 2006). "Asmara's last Jew recalls 'good old days'". BBC News. Retrieved 25 May 2007.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - "Eritrea. International Religious Freedom Report 2008". U.S. Department of State. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- It’s coffee time Network Africa Online, April 2008 interview.
- ^ Pamela Goyan Kittler, Kathryn P. Sucher, Marcia Nahikian-Nelms (2011). Food and Culture, 6th ed. Cengage Learning. p. 202. ISBN 0538734973.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Eritrea: Travel Trade Manual. Ministry of Tourism of Eritrea. 2000. p. 4.
- Tekle, Amare (1994). Eritrea and Ethiopia: From Conflict to Cooperation. The Red Sea Press. p. 142. ISBN 0932415970.
- Carman, Tim (9 January 2009). "Mild Frontier: the differences between Eritrean and Ethiopian cuisines come down to more than spice". Washington City Paper. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- Tekle, Amare (1994). Eritrea and Ethiopia: From Conflict to Cooperation. The Red Sea Press. p. 197. ISBN 0932415970.
- World records ratified. Iaaf.org (8 May 2010). Retrieved on 20 September 2013.
Further reading
- Beretekeab R. (2000); Eritrean making of a Nation 1890–1991, Uppsala University, Uppsala.
- Cliffe, Lionel; Connell, Dan; Davidson, Basil (2005), Taking on the Superpowers: Collected Articles on the Eritrean Revolution (1976–1982). Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-188-0
- Cliffe, Lionel & Davidson, Basil (1988), The Long Struggle of Eritrea for Independence and Constructive Peace. Spokesman Press, ISBN 0-85124-463-7
- Connell, Dan (1997), Against All Odds: A Chronicle of the Eritrean Revolution With a New Afterword on the Postwar Transition. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-046-9
- Connell, Dan (2001), Rethinking Revolution: New Strategies for Democracy & Social Justice : The Experiences of Eritrea, South Africa, Palestine & Nicaragua. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-145-7
- Connell, Dan (2004), Conversations with Eritrean Political Prisoners. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-235-6
- Connell, Dan (2005), Building a New Nation: Collected Articles on the Eritrean Revolution (1983–2002). Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-198-8
- Firebrace, James & Holand, Stuart (1985), Never Kneel Down: Drought, Development and Liberation in Eritrea. Red Sea Press, ISBN 0-932415-00-8
- Gebre-Medhin, Jordan (1989), Peasants and Nationalism in Eritrea. Red Sea Press, ISBN 0-932415-38-5
- Hatem Elliesie: Decentralisation of Higher Education in Eritrea, Afrika Spectrum, Vol. 43 (2008) No. 1, p. 115–120.
- Hill, Justin (2002), Ciao Asmara, A classic account of contemporary Africa. Little, Brown, ISBN 978-0-349-11526-9
- Iyob, Ruth (1997), The Eritrean Struggle for Independence : Domination, Resistance, Nationalism, 1941–1993. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-59591-6
- Jacquin-Berdal, Dominique; Plaut, Martin (2004), Unfinished Business: Ethiopia and Eritrea at War. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-217-8
- Johns, Michael (1992), "Does Democracy Have a Chance", Congressional Record, 6 May 1992
- Keneally, Thomas (1990), "To Asmara" ISBN 0-446-39171-9
- Kendie, Daniel (2005), The Five Dimensions Of The Eritrean Conflict 1941–2004: Deciphering the Geo-Political Puzzle. Signature Book Printing, ISBN 1-932433-47-3
- Killion, Tom (1998), Historical Dictionary of Eritrea. Scarecrow Press, ISBN 0-8108-3437-5
- Mauri, Arnaldo (2004), "Eritrea's Early Stages in Monetary and Banking Development", International Review of Economics, Vol. LI, n. 4,
- Mauri, Arnaldo (1998), "The First Monetary and Banking Experiences in Eritrea", African Review of Money, Finance and Banking, n. 1–2.
- Miran, Jonathan (2009), Red Sea Citizens: Cosmopolitan Society and Cultural Change in Massawa. Indiana University Press, ISBN 978-0-253-22079-0
- Müller, Tanja R.: Bare life and the developmental State: the Militarization of Higher Education in Eritrea, Journal of Modern African Studies, Vol. 46 (2008), No. 1, p. 1–21.
- Negash T. (1987); Italian Colonisation in Eritrea: Policies, Praxis and Impact, Uppsala Univwersity, Uppsala.
- Ogbaselassie, G (10 January 2006). "Response to remarks by Mr. David Triesman, Britain's parliamentary under-secretary of state with responsibility for Africa". Retrieved 7 June 2006.
- Pateman, Roy (1998), Eritrea: Even the Stones Are Burning. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-057-4
- Phillipson, David W. (1998), Ancient Ethiopia.
- Reid, Richard. (2011) Frontiers of violence in north-east Africa: genealogies of conflict since c.1800. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0199211883
- Wrong, Michela (2005), I Didn't Do It For You: how the world betrayed a small African Nation. Harper Collins, ISBN 0-06-078092-4
External links
- Government
- Ministry of Information of Eritrea (official government website).
- EriTV News, Music, Movie and Comedy from Eritrea Television
- "Eritrea". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Eritrea web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Template:Dmoz
- Eritrea profile from BBC News.
 Wikimedia Atlas of Eritrea
Wikimedia Atlas of Eritrea
- Other
- HRCE – Human Rights Concern – Eritrea
- Documentary on Women's liberation in Eritrea
- Tigrinya online learning with numbers, alphabet and history (Eritrea and north Ethiopia (Tigray-Province)).
- Template:It icon Ferrovia eritrea Eritrean Railway
- Atlas of Eritrea
- Template:It icon About Eritrea
- Key Development Forecasts for Eritrea from International Futures.
- Magazine
- Template:It icon Special section about Eritrea from Espresso online magazine
- History of Eritrea: First recordings – Munzinger – exploitation by colonialism and fight against colonialism (Italy, England, Ethiopia, Soviet Union, USA, Israel) – independence
| Geographic locale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link GA
Categories:- Use dmy dates from September 2013
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Eritrea
- Arabic-speaking countries and territories
- Countries in Africa
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Former Italian colonies
- Horn of Africa
- Least developed countries
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the United Nations
- Single-party states
- States and territories established in 1993
- World Digital Library related

