This is an old revision of this page, as edited by ToddC4176 (talk | contribs) at 00:18, 12 July 2006 (→Abolitionism as a cause of the war). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:18, 12 July 2006 by ToddC4176 (talk | contribs) (→Abolitionism as a cause of the war)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| American Civil War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 (counterclockwise from upper right) Confederate prisoners at Gettysburg; Battle of Fort Hindman, Arkansas; Rosecrans at Stones River, Tennessee | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Abraham Lincoln, Ulysses S. Grant |
Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 2,200,000 | 1,064,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Killed in action: 110,000 Total dead: 360,000 Wounded: 275,200 |
Killed in action: 93,000 Total dead: 258,000 Wounded: 137,000+ | ||||||
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a sectional conflict in the United States between the Federal government ("Union") and 11 southern slave states that declared their secession and formed the Confederate States of America, led by President Jefferson Davis. The "Union", led by President Abraham Lincoln and the Republican party which opposed expansion of slavery, rejected any right of secession. Fighting began April 12, 1861 when Confederate forces attacked a Federal fort at the Battle of Fort Sumter.
In the first year the Union asserted control of the border states and established a naval blockade as both sides raised large armies. In 1862 the large, bloody battles began. After the Battle of Antietam in September 1862, Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation made the freeing of the slaves a war goal — one bitterly opposed by Copperheads. Emancipation ensured that Britain and France did not intervene to help the Confederates. In the East, Robert E. Lee rolled up a series of Confederate victories over a series of Union commanders, but his best general, Stonewall Jackson, was killed at the Battle of Chancellorsville in May 1863. Lee's invasion of the North was repulsed at the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863; he barely managed to escape back to Virginia. In the West, the Union Navy captured New Orleans in 1862, and armies under Ulysses Grant seized control of the Mississippi River by capturing Vicksburg in July 1863, thus splitting the Confederacy.
By 1864 long-term Union advantages in geography, manpower, industry, finance, political organization and transportation were overwhelming the Confederacy. Grant fought a bloody series of battles with Lee in Virginia in summer 1864. Lee won in a tactical sense but lost strategically, as he could not replace his casualties and was forced to retreat into trenches around his capital, Richmond, Virginia. Meanwhile William T. Sherman captured Atlanta and marched to the sea, destroying a wide swath of Georgia. In 1865 the Confederacy collapsed as Lee surrendered and all the slaves were freed.
The full restoration of the Union was the work of a highly contentious postwar era known as Reconstruction. The war produced more than 970,000 casualties (3% of the population), including approximately 620,000 soldier deaths — two-thirds by disease. The causes of the war, the reasons for the outcome, and even the name of the war itself, are subjects of lingering controversy, even today. The main results of the war were the restoration and strengthening of the Union, and the end of slavery in the United States.
Causes of the War
- Main articles: Origins of the American Civil War, Timeline of events
The immediate causes of secession and war were the issue of slavery in the territories and the election of Abraham Lincoln, which signaled the end of Southern control over the federal government. If Lincoln was not an immediate threat to slavery, he threatened to put it "in the course of ultimate extinction." And loss of the territories to free states meant the South would be increasingly marginalized.
Southern fears of losing control of the federal government, and northern fears that the slave power already controlled the government, brought the crisis to a head in the late 1850s. Sectional disagreements over the morality of slavery, the scope of democracy and the economic merits of free labor vs. slave plantations caused some parties to collapse (the Whigs and Know Nothings), and new ones to arise (the Free Soil Party in 1848, the Republicans in 1854, Constitutional Union in 1860). In 1860 the last remaining national political party, the Democratic party, also split on sectional lines.
Slavery and Anti-Slavery
The Compromise of 1850 included a new, stronger fugitive slave law that allowed federal agents to capture and return slaves that escaped into northern free states. Northerners, especially those who read abolitionist newspapers like "The Liberator" or the highly influential novel Uncle Tom's Cabin, had moral objections to enforcing fugitive slave laws.
The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 overthrew the Compromise of 1820 that had outlawed slavery so far in the territories north of Missouri, and led to the new anti-slavery Republican party.
The Dred Scott Supreme Court decision of 1857 added to the controversy. Chief Justice Roger Taney's decision said that slaves "have no rights which any white man is bound to respect", and that slaves could be taken to free states and territories. Lincoln warned that "the next Dred Scott decision" could threaten northern states with slavery.
Since only one-fiftieth of one per cent of slaves escaped in 1860, the fugitive slave controversy wasn't a practical reason for secession. The number that escaped was offset by Northern blacks who were kidnapped as slaves. And secession only did away with enforcement of the fugitive slave law altogether. And Kansas had only two slaves in 1860 because the territories had the wrong soil and climate for labor intensive forms of agriculture. So the main Southern fear seems to have been for the future of slavery.
There was a strong correlation between the number of plantations in a region and the degree of support for secession. The states of the deep south had the greatest concentration of plantations and were the first to secede. The upper south slave states of Virginia, North Carolina, Arkansas and Tennessee had fewer plantations and rejected secession until the Fort Sumter crisis forced them to choose sides. Border states had fewer plantations still and sided with the Union.
Failure to Compromise
Until 1860 the political system had always successfully handled interregional crises. All but one crisis involved slavery, starting with debates on the three-fifths clause in the Constitutional Convention of 1787. Congress had solved the crisis over the admission of Missouri as a slave state in 1819-21, the controversy over South Carolina's nullification of the tariff in 1833, the acquisition of Texas in 1845, and the status of slavery in the territory acquired from Mexico in 1850.
However in 1854, the old Second Party System broke down after passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act. The Whig Party disappeared, and the new Republican Party arose in its place. It was the nation's first major party with only sectional appeal and a commitment to stop the expansion of slavery. Open warfare in Kansas Territory, the Dred Scott decision of 1857, John Brown's raid in 1859 and the split in the Democratic party in 1860 polarized the nation North and South. The election of Lincoln in 1860 was the final trigger for secession. During the secession crisis, many sought one final compromise the "Crittenden Compromise," but the attempt failed.
Historians such as James G. Randall in the 1930s argued that the rise of mass democracy, the breakdown of the Second Party System, the hardened Constitutional positions, and the increasingly hostile sectional rhetoric made it impossible to agree on any compromise. Indeed, the Crittenden Compromise was rejected by Republicans. One possible "compromise" was peaceful secession agreed to by the United States, which was seriously discussed in late 1860—and supported by many abolitionists—but was rejected by James Buchanan's conservative Democrats as well as the Republican leadership.
A deeper reason for the failure to compromise was the profound fear across the nation that grand conspiracies were afoot that threatened to destroy the Republic. By the 1850s two loomed most threatening: the sectional antislavery Republican party (the Black Republicans) and the aristocratic slaveholding class.
Abolitionism as a cause of the war
Before the 1830s many people, North and South, considered slavery an undesirable institution. But a new sensibility emerged from a small but outspoken abolitionist movement, led by New Englanders and free blacks, including William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick Douglass, and Lucretia Mott. They condemned slavery not just as a generic evil but as a specific sin that would damn the slaveowner to hell unless he immediately repented and set in motion a plan to end his connection with slavery. The Constitution itself was implicated--Garrison once publicly burned a copy of the U. S. Constitution because of the fugitive slave clause and called it ”a covenant with death and an agreement with hell." Throughout the 20th century many scholars concluded that the extremism of the abolitionists made compromise impossible and war inevitable.
Fear of Abolitionism Motivates Southerners
Historians continue to debate whether slave owners actually felt either guilt or shame But there is no doubt the southerner slave owners were angered by the abolitionist attacks. Starting in the 1830s there was a widespread and growing ideological defense of the "peculiar institution" in the South. By the 1850s Northern teachers suspected of any tinge of abolitionism were expelled from the region, and abolitionist literature was banned there as well. The secessionists rejected the denials of Republicans that they were abolitionists, and pointed to John Brown's attempt in 1859 to start a slave uprising as proof that multiple northern conspiracies were afoot to ignite bloody slave rebellions. No evidence of any Brown-like conspiracy has been discovered by historians.
State Rights
The States' Rights debate cuts across the issues. Southerners argued that the federal government was strictly limited and could not abridge the rights of states as reserved in the Tenth Amendment, and so had no power to prevent slaves from being carried into new territories. States' rights advocates also cited the fugitive slave clause in the Constitution to demand federal jurisdiction over slaves who escaped into the North. Anti-slavery forces took reversed stances on these issues.
Jefferson Davis said that a "disparaging discrimination" and a fight for "liberty" against "the tyranny of an unbridled majority" gave the Confederate states a right to secede.
South Carolina's "Declaration of the Immediate Causes for Secession" started with an argument for states' rights in the South in defense of slavery, followed by a complaint about states' rights in the North, claiming that Northern states weren't fulfilling their federal obligations
Economics
The free-labor and slavery-based labor systems of North and South had different, interdependent economic bases. The Middle Atlantic and New England regions developed a commercial market economy and built the nation's first factories. Tariffs were not a factor — after 1847 tariffs were low and did not protect industry. The Midwest, the free states west of the Appalachians, had an agricultural economy that exported its surplus production to the other U.S. regions and to Europe. The South, in addition to much subsistence agriculture, depended upon large-scale production of export crops, primarily cotton and (to a lesser extent) tobacco, raised by slaves. (Slaves were a key component in Southern wealth, comprising the second most valuable form of property in the region, after real estate.) Some of its cotton was sold to New England textile mills, though much more of it was shipped to Britain. The dominance of this crop led to the expression "King Cotton." However, shipping, brokerage, insurance, and other financial mediation for the trade was centered in the North, particularly in New York City.

16th President (1861–1865)
These contrasting economic interests led to sectional agendas that, at times, competed in Congress. Pennsylvania politicians, for example, pushed for a protective tariff to foster the iron industry. Southerners, tied to an export economy, sought free-trade policies. There was some demand in the West for federally funded "internal improvements" (roads, canals, ports and waterways), but less support in the agricultural South. However, there was no unanimity of support for such programs even within each region. Northern farmers also depended upon exports; early railroad managers desired reduced tariffs on imported iron; many Northern Democrats opposed any federal role in the nation's infrastructure, while Southern Whigs favored it. As a result, the significance of economic conflict has been exaggerated: North and South did not compete but were complementary. Each depended on the other for prosperity. King Cotton's greatest importance may have been in fostering the secessionist belief that it would prove a sufficient support for an independent Southern nation. Many believed that British prosperity depended on cotton, and that surely Britain (and possibly France) would help protect cotton supplies by helping the Confederacy gain independence. This analysis proved a delusion during the war, but it seems to have been influential in 1860-61 during the debates.
Free Labor vs. Pro slavery Arguments
Historian Eric Foner (1970) has argued that a free-labor ideology dominated thinking in the North, which emphasized economic opportunity. By contrast, Southerners described free labor as "greasy mechanics, filthy operators, small-fisted farmers, and moonstruck theorists." They argued that only a slave-owning society allowed the leisure for education and cultural refinement. They depicted slavery as a positive good for the slaves themselves, especially the Christianizing that had rescued them from the paganism of Africa.
Slavery in the Territories
The specific political crisis that led to secession stemmed from a dispute over the expansion of slavery into new territories. The Republicans, while maintaining that Congress had no power over slavery in the states, asserted that it did have power to ban slavery in the territories. The Missouri Compromise of 1820 maintained the balance of power in Congress by adding Maine as a free state and Missouri as a slave state. It prohibited slavery in the remainder of the Louisiana Purchase Territory north of 36°30'N lat. (the southern boundary of Missouri). The acquisition of vast new lands after the Mexican War (1846–1848), however, reopened the debate—now focused on the proposed Wilmot Proviso, which would have banned slavery in territories annexed from Mexico. Though it never passed, the Wilmot Proviso aroused angry debate. Northerners argued that slavery would provide unfair competition for free migrants to the territories; slaveholders claimed Congress had no right to discriminate against them by preventing them from bringing their legal property there. The dispute led to open warfare in the Kansas Territory after it was organized by the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854. This act repealed the prohibition on slavery there under the Missouri Compromise, and put the fate of slavery in the hands of the territory's settlers, a process known as "popular sovereignty." Fighting erupted between proslavery "border ruffians" from neighboring Missouri and antislavery immigrants from the North (including John Brown, among other abolitionists). Tensions between North and South now were violent.
Southern Fears of Republican Control
Southern secession was triggered by the election of Republican Abraham Lincoln because regional leaders feared that he would make good on his promise to stop the expansion of slavery and would thus put it on a course toward extinction. Many Southerners thought that even if Lincoln did not abolish slavery, sooner or later another Yankee would do so, and that it was thus time to quit the Union. The slave states had lost the balance of power in the Electoral College and the Senate, and were facing a future as a perpetual minority against an increasingly powerful North.
Southern Fears of Modernization
In a broader sense, the North was rapidly modernizing in a manner deeply threatening to the South, for the North was not only becoming more economically powerful it was developing new modernizing, urban values while the South was clinging more and more to the old rural traditional values of the Jeffersonian yeoman. As James McPherson argues:
- The ascension to power of the Republican Party, with its ideology of competitive, egalitarian free-labor capitalism, was a signal to the South that the Northern majority had turned irrevocably towards this frightening, revolutionary future.
A House Divided Against Itself
Secession Winter
Before Lincoln took office, seven states declared their secession from the Union, and established a Southern government, the Confederate States of America on February 9, 1861. They took control of federal forts and other properties within their boundaries, with little resistance from President Buchanan, whose term ended on March 3, 1861. Buchanan asserted, "The South has no right to secede, but I have no power to prevent them." One fourth of the U.S. Army — the entire garrison in Texas — was surrendered to state forces by its commanding general David E. Twiggs, who then joined the Confederacy. By seceding, the rebel states would reduce the strength of their claim to the Western territories that were in dispute, cancel any obligation for the North to return fugitive slaves to the Confederacy, and assure easy passage in Congress of many bills and amendments they had long opposed.
The Confederacy
Main article: Confederate States of AmericaSeven Deep South cotton states seceded by February 1861, starting with South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. These seven states formed the Confederate States of America (February 4 1861), with Jefferson Davis as president, and a governmental structure closely modeled on the U.S. Constitution. In April and May 1861 four more slave states seceded and joined the Confederacy: Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina.
The Union States
Main article: Union (American Civil War)There were 23 states which remained loyal to the Union during the war: California, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Wisconsin. During the war, Nevada and West Virginia joined as new states of the Union. Tennessee and Louisiana were returned to Union control early in the war.


The territories of Colorado, Dakota, Nebraska, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Washington fought on the Union side. Several slave-holding Native American tribes supported the Confederacy, giving the Indian territory a small bloody civil war.
Border States
Main article: Border states (Civil War)
The Border States in the Union comprised West Virginia (which broke away from Virginia and became a separate state), and four of the five northernmost slave states (Maryland, Delaware, Missouri, and Kentucky). Once Lincoln called for troops, militia units that had been drilling in the North rushed toward Washington and Baltimore. Before the Confederate government realized what was happening, Lincoln had seized firm control of Maryland and the District of Columbia.
Maryland had numerous pro-Confederate officials who tolerated anti-Union rioting in Baltimore and the burning of bridges. Lincoln responded with martial law, moved in Union troops, and arrested the pro-Confederates.
In Missouri, an elected convention on secession voted decisively to remain within the Union. When pro-Confederate Governor Claiborne F. Jackson called out the state militia, it was attacked by federal forces under General Nathaniel Lyon, who chased the governor and the rest of the State Guard to the southwestern corner of the state. (See also: Missouri secession). In the resulting vacuum the convention on secession reconvened and took power as the Unionist provisional government of Missouri.
Kentucky did not secede; for a time it declared itself neutral. During a brief invasion by Confederate forces, Southern sympathizers organized a secession convention, inaugurated a Confederate Governor, and gained recognition from the Confederacy. However, the military occupation of Columbus by Confederate General Leonidas Polk in September 1861 turned popular opinion in Kentucky against the Confederacy, and the state reaffirmed its loyal status and expelled the Confederate government.
Residents of the northwestern counties of Virginia organized a secession from Virginia and entered the Union in 1863 as West Virginia. Similar secessions appeared in east Tennessee, but were suppressed by the Confederacy. Jefferson Davis arrested over 3,000 men suspected of being loyal to the Union and held them without trial.
Overview
The War Begins
- For more details on this topic, see Battle of Fort Sumter
Lincoln's victory in the presidential election of 1860 triggered South Carolina's declaration of secession from the Union. By February 1861, six more Southern states made similar declarations. On February 7, the seven states adopted a provisional constitution for the Confederate States of America and established their temporary capital at Montgomery, Alabama. A pre-war February peace conference of 1861 met in Washington in a failed attempt at resolving the crisis. The remaining eight slave states rejected pleas to join the Confederacy. Confederate forces seized all but three federal forts within their boundaries (they did not take Fort Sumter); President Buchanan protested but made no military response aside from a failed attempt to resupply Fort Sumter via the ship Star of the West, and no serious military preparations. However, governors in Massachusetts, New York, and Pennsylvania began buying weapons and training militia units to ready them for immediate action.
On March 4, 1861, Abraham Lincoln was sworn in as president. In his inaugural address, he argued that the Constitution was a more perfect union than the earlier Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, that it was a binding contract, and called any secession "legally void". He stated he had no intent to invade southern states, but would use force to maintain possession of federal property. His speech closed with a plea for restoration of the bonds of union.
The South sent delegations to Washington and offered to pay for the federal properties and enter into a peace treaty with the United States. Lincoln rejected any negotiations with Confederate agents on the grounds that the Confederacy was not a legitimate government, and that making any treaty with it would be tantamount to recognition of it as a sovereign government.
Fort Sumter in South Carolina was one of the three remaining Union-held forts in the Confederacy, and Lincoln was determined to hold it. Under orders from Confederate President Jefferson Davis, Confederates under General P. G. T. Beauregard bombarded the fort with artillery on April 12, forcing its surrender. Northerners reacted quickly to this attack on the flag, and rallied behind Lincoln, who called for all of the states to send troops to recapture the forts and to preserve the Union. With the scale of the rebellion apparently small so far, Lincoln called for 74,000 volunteers for 90 days only.
Four states in the upper South (Tennessee, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Virginia) which had repeatedly rejected Confederate overtures, now refused to send forces against their neighbors, declared their secession, and joined the Confederacy. To reward Virginia the Confederate capital was moved to Richmond, Virginia, a highly vulnerable location at the end of the supply line.
Anaconda Plan and Blockade, 1861
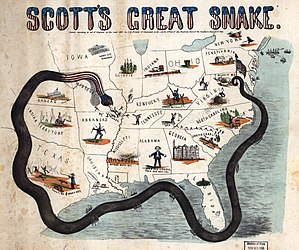
Winfield Scott, the commanding general of the U.S. Army, devised the Anaconda Plan to win the war with as little bloodshed as possible. His idea was that a Union blockade of the main ports would strangle the rebel economy; then the capture of the Mississippi River would split the South. Lincoln adopted the plan but overruled Scott's warnings against an immediate attack on Richmond.
- For more details on this topic, see Naval Battles of the American Civil War, Union blockade and Confederate States Navy
In May 1861 Lincoln proclaimed the Union blockade of all southern ports, which - although in the first two years of the war was only moderately successful - eventually shut down nearly all international traffic and most local port-to-port traffic. Although few naval battles were fought and few men were killed, the blockade shut down King Cotton and ruined the southern economy. British investors built small, very fast "blockade runners" that brought in military supplies (and civilian luxuries) from Cuba and the Bahamas and took out some cotton and tobacco. When the U.S. Navy did capture blockade runners, the ships and cargo were sold and the proceeds given to the Union sailors. The British crews were released. The "ironclad" CSS Virginia's maiden voyage sank the blockade ship USS Cumberland and burned the Congress on her "trial run." The second day the Battle at Hampton Roads took place between the ironclads USS Monitor and the CSS Virginia in March 1862, ending in a draw. Other naval battles included Island No. 10, Memphis, Drewry's Bluff, Arkansas Post, and Mobile Bay. The Second Battle of Fort Fisher virtually ended blockade running.
Eastern Theater 1861–1863
Further information: Eastern Theater of the American Civil WarBecause of the fierce resistance of a few initial Confederate forces at Manassas, Virginia, in July 1861, a march by Union troops under the command of Maj. Gen. Irvin McDowell on the Confederate forces there was halted in the First Battle of Bull Run, or First Manassas, whereupon they were forced back to Washington, D.C., by Confederate troops under the command of Generals Joseph E. Johnston and P.G.T. Beauregard. It was in this battle that Confederate General Thomas Jackson received the name of "Stonewall" because he stood like a stone wall against Union troops. Alarmed at the loss, and in an attempt to prevent more slave states from leaving the Union, the U.S. Congress passed the Crittenden-Johnson Resolution on July 25 of that year, which stated that the war was being fought to preserve the Union and not to end slavery.
Major General George B. McClellan took command of the Union Army of the Potomac on July 26 (he was briefly general-in-chief of all the Union armies, but was subsequently relieved of that post in favor of Maj. Gen. Henry W. Halleck), and the war began in earnest in 1862.
Upon the strong urging of President Lincoln to begin offensive operations, McClellan attacked Virginia in the spring of 1862 by way of the peninsula between the York River and James River, southeast of Richmond. Although McClellan's army reached the gates of Richmond in the Peninsula Campaign, Joseph E. Johnston halted his advance at the Battle of Seven Pines, then Robert E. Lee defeated him in the Seven Days Battles and forced his retreat. McClellan was stripped of many of his troops to reinforce John Pope's Union Army of Virginia. Pope was beaten spectacularly by Lee in the Northern Virginia Campaign and the Second Battle of Bull Run in August.

Emboldened by Second Bull Run, the Confederacy made its first invasion of the North, when General Lee led 45,000 men of the Army of Northern Virginia across the Potomac River into Maryland on September 5. Lincoln then restored Pope's troops to McClellan. McClellan and Lee fought at the Battle of Antietam near Sharpsburg, Maryland, on September 17 1862, the bloodiest single day in American military history. Lee's army, checked at last, returned to Virginia before McClellan could destroy it. Antietam is considered a Union victory because it halted Lee's invasion of the North and provided an opportunity for Lincoln to announce his Emancipation Proclamation.
When the cautious McClellan failed to follow up on Antietam, he was replaced by Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside. Burnside suffered near-immediate defeat at the Battle of Fredericksburg on December 13 1862, when over twelve thousand Union soldiers were killed or wounded. After the battle, Burnside was replaced by Maj. Gen. Joseph "Fighting Joe" Hooker. Hooker, too, proved unable to defeat Lee's army; despite outnumbering the Confederates by more than two to one, he was humiliated in the Battle of Chancellorsville in May 1863. He was replaced by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade during Lee's second invasion of the North, in June. Meade defeated Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1 to July 3, 1863), the bloodiest battle in American history, which is sometimes considered the war's turning point. Lee's army suffered 28,000 casualties (versus Meade's 23,000). Lincoln was angry that Meade failed to intercept Lee's retreat, and after an inclusive fall campaign, decided in early 1864 to turn to the Western Theater for new leadership.
On the use of balloons, see Aerial warfare section on the American Civil War.
Western Theater 1861–1863
Further information: Western Theater of the American Civil WarWhile the Confederate forces had numerous successes in the Eastern theater, they crucially failed in the West. They were driven from Missouri early in the war as a result of the Battle of Pea Ridge. Leonidas Polk's invasion of Kentucky enraged the citizens there who previously had declared neutrality in the war, turning that state against the Confederacy.
Nashville, Tennessee, fell to the Union early in 1862. Most of the Mississippi was opened with the taking of Island No. 10 and New Madrid, Missouri, and then Memphis, Tennessee. The Union Navy captured New Orleans, Louisiana without a major fight in May 1862, allowing the Union forces to begin moving up the Mississippi as well. Only the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, prevented unchallenged Union control of the entire river.
Braxton Bragg's second Confederate invasion of Kentucky was repulsed by Don Carlos Buell at the confused and bloody Battle of Perryville, and he was narrowly defeated by William S. Rosecrans at the Battle of Stones River in Tennessee.
The one clear Confederate victory in the West was the Battle of Chickamauga. Bragg, reinforced by the corps of James Longstreet (from Lee's army in the east), defeated Rosecrans, despite the heroic defensive stand of George Henry Thomas. Rosecrans retreated to Chattanooga, which Bragg then besieged.
The Union's key strategist and tactician in the west was Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, who won victories at: Forts Henry and Donelson, by which the Union seized control of the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers; Shiloh; the Battle of Vicksburg, cementing Union control of the Mississippi River and considered one of the turning points of the war. Grant marched to the relief of Rosecrans and defeated Bragg at the Battle of Chattanooga, Tennessee, driving Confederate forces out of Tennessee and opening a route to Atlanta and the heart of the Confederacy.
Trans-Mississippi Theater 1861–1865
Further information: Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil WarThough geographically isolated from the battles to the east, a few small-scale military actions took place west of the Mississippi River. Confederate incursions into Arizona and New Mexico were repulsed in 1862. Guerilla activity turned much of Missouri and Indian Territory (Oklahoma) into a battleground. Late in the war the Federal Red River Campaign was a failure. Texas remained in Confederate hands throughout the war, but was cut off after the capture of Vicksburg in 1863 gave the Union control of the Mississippi River.
End of the War 1864–1865

At the beginning of 1864, Lincoln made Grant commander of all Union armies. Grant made his headquarters with the Army of the Potomac, and put Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman in command of most of the western armies. Grant understood the concept of total war and believed, along with Lincoln and Sherman, that only the utter defeat of Confederate forces and their economic base would bring an end to the war. Grant devised a coordinated strategy that would strike at the heart of Confederacy from multiple directions: General Meade and Benjamin Butler were ordered to move against Lee near Richmond; General Franz Sigel (and later Philip Sheridan) were to attack the Shenandoah Valley; General Sherman was to capture Atlanta and march to the sea; Generals George Crook and William W. Averell were to operate against railroad supply lines in West Virginia; and General Nathaniel Banks was to capture Mobile, Alabama.
Union forces in the East attempted to maneuver past Lee and fought several battles during that phase ("Grant's Overland Campaign") of the Eastern campaign. Grant's battles of attrition at the Wilderness, Spotsylvania and Cold Harbor resulted in heavy losses, but forced Lee's Confederates to fall back again and again. An attempt to outflank Lee from the south failed under Butler, who was trapped inside the Bermuda Hundred river bend. Grant was tenacious and, despite astonishing losses (over 66,000 casualties in six weeks), kept pressing Lee's Army of Northern Virginia back to Richmond. He pinned down the Confederate army in the Siege of Petersburg, where the two armies engaged in trench warfare for over nine months.
Grant finally found a commander, General Philip Sheridan, aggressive enough to prevail in the Valley Campaigns of 1864. Sheridan proved to be more than a match for Jubal Early, and defeated him in a series of battles, including a final decisive defeat at Cedar Creek. Sheridan then proceeded to destroy the agricultural base of the Valley, a strategy similar to the tactics Sherman later employed in Georgia.
Meanwhile, Sherman marched from Chattanooga to Atlanta, defeating Confederate Generals Joseph E. Johnston and John B. Hood. The fall of Atlanta, on September 2, 1864, was a significant factor in the re-election of Lincoln as president. Hood left the Atlanta area to menace Sherman's supply lines and invade Tennessee in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign. Union general John M. Schofield defeated Hood at Franklin, and George H. Thomas defeated Hood at Nashville, effectively destroying Hood's army.
Leaving Atlanta, and his base of supplies, Sherman's army marched with an unknown destination, laying waste to about 20% of the farms in Georgia in his celebrated "March to the Sea". He reached the Atlantic Ocean at Savannah in December 1864. Sherman's army was followed by thousands of freed slaves; there were no major battles along the March. When Sherman turned north through South Carolina and North Carolina to approach the Virginia lines from the south, it was the end for Lee and his men.
Lee's army, thinned by desertion, was now much smaller than Grant's. The Union won a decisive victory at the Battle of Five Forks on April 1, forcing Lee to evacuate Petersburg and Richmond. The mayor of Richmond surrendered the city to black troops of the 5th Massachusetts Cavalry. The remaining Confederate units fled west and after a defeat at Sayler's Creek, Lee surrendered his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, at Appomattox Court House. In an untraditional gesture and as a sign of Grant's respect and anticipation of folding the Confederacy back into the Union with dignity and peace, Lee was permitted to keep his officer's sabre and his near-legendary horse, Traveller. Johnston surrendered his troops to Sherman shortly thereafter in Durham, North Carolina. All Confederate land forces surrendered by June 1865.
Slavery during the War
Main article: History of slavery in the United StatesLincoln initially declared his official purpose to be the preservation of the Union, not emancipation. He had no wish to alienate the thousands of slaveholders in the Union border states. The long war, however, had a radicalizing effect on federal policies. With the Emancipation Proclamation, announced in September 1862 and put into effect four months later, Lincoln adopted the abolition of the Slave Power as a second mission—that is slaves owned by rebels had to be taken away from them and freed.
The Emancipation Proclamation declared all slaves held in territory then under Confederate control to be "then, thenceforth, and forever free," but did not affect slaves in areas under Union control. In addition, it would only affect the Confederate States if those states did not re-enter the Union by January 1, 1863. It is unclear what Lincoln had in mind if one of the Confederate States had taken him up on his offer. Another effect of the Emancipation Proclamation was to make less likely the intervention of European powers. By changing the public perception abroad as to the causes of the conflict, Lincoln removed any public support for intervention by the European powers on the side of the Confederacy.
The officially neutral border states (Kentucky, Missouri, and Maryland) were unaffected by the Emancipation Proclamation, as was Delaware, which still had slavery. All abolished slavery on their own, except Kentucky. Although the Emancipation Proclamation technically went into effect in January of 1863, its true effects were felt only as areas came under Federal control, as they were no longer obliged to return slaves to their masters. The 13th amendment, ratified December 6, 1865, finally abolished slavery everywhere in the United States.
Threat of International Intervention
The best chance for Confederate victory was entry into the war by Britain and France. The Union, under Lincoln and Secretary of State William Henry Seward worked to block this, and threatened war if any country officially recognized the existence of the Confederate States of America. (None ever did.) In 1861 southerners voluntarily embargoed cotton shipments, hoping to start an economic depression in Europe that would force Britain to enter the war in order to get cotton. Cotton diplomacy proved a failure as Europe had a surplus of cotton, while the 1860-62 crop failures in Europe made the North's grain exports of critical importance. It was said that "King Corn was more powerful than King Cotton", as US grain went from a quarter of the British import trade, to almost half.
When England did face a cotton shortage, it was temporary. And the war created employment for arms makers, iron workers, and British ships to transport weapons.
Lincoln's announcement of a blockade of the Confederacy, a clear act of war, enabled Britain, followed by other European powers, to announce their neutrality in the dispute. This enabled the Confederacy to begin to attempt to gain support and funds in Europe. President Jefferson Davis replaced his first two secretaries of state (Robert Toombs and Robert M. T. Hunter) with Judah P. Benjamin in early 1862. Although Benjamin had more international knowledge and legal experience he failed to create a dynamic foreign policy for the Confederacy.
The first attempts to achieve European recognition of the Confederacy were dispatched on February 25, 1861 and led by William Lowndes Yancey, Pierre A. Rost, and Ambrose Dudley Mann. The British foreign minister Lord John Russell met with them, and the French foreign minister Edouard Thouvenel received the group unofficially. Neither Britain nor France ever promised formal recognition, for that meant war with the United States.
Charles Francis Adams proved particularly adept as minister to Britain for the Union, and Britain was reluctant to boldly challenge the Union's blockade. Independent British maritime interests spent hundreds of millions of pounds to build and operate highly profitable blockade runners — commercial ships flying the British flag and carrying supplies to the Confederacy by slipping through the blockade. The officers and crews were British and when captured they were released. The Confederacy purchased several warships from commercial ship builders in Britain; the most famous, the Alabama, did considerable damage and led to serious postwar disputes. The Confederacy sent journalists Henry Hotze and Edwin De Leon to open propaganda stations to feed news media in Paris and London. However, public opinion against slavery created a political liability for European politicians, especially in Britain. War loomed in late 1861 between the U.S. and Britain over the Trent Affair, involving the Union boarding of a British mail steamer to seize two Confederate diplomats. However, London and Washington were able to smooth over the problem after Lincoln released the two diplomats.
In 1862 the British considered mediation — though even such an offer would have risked war with the U.S. The Union victory in the Battle of Antietam caused them to delay this decision. The Emancipation Proclamation further reinforced the political liability of supporting the Confederacy. As the war continued, the Confederacy's chances with Britain grew hopeless, and they focused increasingly on France. Napoléon III proposed to offer mediation in January 1863, but this was dismissed by Seward. Despite some sympathy for the Confederacy, France's own seizure of Mexico ultimately deterred them from war with the Union. Confederate offers late in the war to end slavery in return for recognition were not seriously considered by London or Paris.
Analysis of the Outcome
Could the South have won? The goals were not symmetric. To win independence the South had to convince the North it could not win, but it did not have to invade the North. To restore the Union the North had to conquer vast stretches of territory. In the short run (a matter of months) the two sides were evenly matched. But in the long run (a matter of years) the North had advantages that increasingly came into play, while it prevented the South from gaining diplomatic recognition in Europe.
Both sides had long-term advantages but the Union had more of them. The Union had to control the entire coastline, defeat all the main Confederate armies, seize Richmond, and control most of the population centers. As the occupying force they had to station hundreds of thousands of soldiers to control railroads, supply lines, and major towns and cities. The long-term advantages widely credited by historians to have contributed to the Union's success include:

- The more industrialized economy of the North aided in the production of arms, munitions and supplies, as well as finances, and transportation. The graph shows the relative advantage of the USA over the CSA at the start of the war. The advantages widened rapidly during the war, as the Northern economy grew, and Confederate territory shrank and its economy weakened.
- The Union population was 22 million and the South 9 million in 1861; the disparity grew as the Union controlled more and more southern territory with garrisons, and cut off the trans-Mississippi part of the Confederacy.
- The Union at the start controlled over 80% of the shipyards, steamships, river boats, and the Navy. It augmented these by a massive shipbuilding program. This enabled the Union to control the river systems and to blockade the entire southern coastline.
- Excellent railroad links between Union cities allowed for the quick and cheap movement of troops and supplies. Transportation was much slower and more difficult in the South which was unable to augment its much smaller system or repair damage, or even perform routine maintenance.
- Strategically the location of the capital Richmond tied Lee to a highly exposed position at the end of supply lines. (Loss of Richmond, everyone realized, meant loss of the war.)
- The failure to win diplomatic or military support from any foreign powers cut the Confederacy from access to markets. Its King Cotton misperception of the world economy led to bad diplomacy, such as the refusal to ship cotton before the blockade started.
Civil War Leaders and Soldiers
- For more details on this topic, see Military leadership in the American Civil War
Most of the important generals on both sides had formerly served in the United States Army—some, including Ulysses S. Grant and Robert E. Lee, during the Mexican-American War between 1846 and 1848. Most were graduates of the United States Military Academy at West Point. Southern military commanders and strategists included Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee, Joseph E. Johnston, Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, James Longstreet, P.G.T. Beauregard, John Mosby, Braxton Bragg, John Bell Hood, James Ewell Brown (JEB) Stuart, William Mahone, Judah P. Benjamin, Jubal Early, and Nathan Bedford Forrest.
Northern military commanders and strategists included Abraham Lincoln, Edwin M. Stanton, Ulysses S. Grant, William Tecumseh Sherman, George H. Thomas, George B. McClellan, Henry W. Halleck, Joseph Hooker, Ambrose Burnside, Irvin McDowell, Winfield Scott, Philip Sheridan, George Crook, George Armstrong Custer, George G. Meade, Winfield Hancock, and Robert Gould Shaw.
After 1980, scholarly attention turned to ordinary soldiers, women, and African Americans involved with the War. As James McPherson observed "The profound irony of the Civil War was that Confederate and Union soldiers ... interpreted the heritage of 1776 in opposite ways. Confederates fought for liberty and independence from what they regarded as a tyrannical government; Unionists fought to preserve the nation created by the founders from dismemberment and destruction."(McPherson 1994 p 24)
Aftermath
Main article: Reconstruction
The fighting ended with the surrender of the conventional Confederate forces. There was no significant guerrilla warfare. Many senior Confederate leaders escaped to Europe or Mexico; Davis was captured and imprisoned for two years, but never brought to trial.
As the war was in its final stages, Lincoln was assassinated in a plot by Confederate sympathizers. Other members of his cabinet were also targets in the plot, and William H. Seward was attacked and left for dead in his home.
Northern leaders agreed that victory would require more than the end of fighting. It had to encompass the two war goals: Confederate nationalism had to be totally repudiated, and all forms of slavery had to be eliminated. They disagreed sharply on the criteria for these goals. They also disagreed on the degree of federal control that should be imposed on the South, and the process by which Southern states should be reintegrated into the Union.
Reconstruction, which began early in the war and ended in 1877, involved a complex and rapidly changing series of federal and state policies. The long-term result came in the three "Civil War" amendments to the Constitution (the XIII, which abolished slavery, the XIV, which extended federal legal protections to citizens regardless of race, and the XV, which abolished racial restrictions on voting). In 1877 federal intervention ended and the "Jim Crow" era began.
Amendments XIV and XV were made inactive through Ku Klux Klan violence, former Confederate "Redeemer" governors and Southern resistance until the Civil Rights movement.
The war had a lasting impact on American politics and culture. For decades after the war, Northern Republicans "waved the bloody shirt," bringing up wartime casualties as an electoral tactic. Memories of the war and Reconstruction held the segregated South together as a Democratic block—the "Solid South"—in national politics for another century. The Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s had its roots in the failure of Reconstruction. A few debates surrounding the legacy of the war continue, especially regarding memorials and celebrations of Confederate heroes and battle flags. Americans with Confederate ancestors cherish the memory of their bravery and determination, yet their cause is also tied to the history of African American slavery.
See also
- List of American Civil War topics
- African Americans in the Civil War
- Canada and the American Civil War
- Casualties of the American Civil War
- List of Medal of Honor recipients
- Military history of the Confederate States
- National Civil War Museum
- Naming the American Civil War
- List of people associated with the American Civil War
- Official Records of the American Civil War
- Opposition to the American Civil War
- Origins of the American Civil War
- Photography and photographers of the American Civil War
- Rail transport in the American Civil War
- U.S. Congress Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War
- Illinois in the Civil War
Notes
- Abraham Lincoln, House Divided Speech, Springfield, Illinois, June 16, 1858
- Abraham Lincoln, Letter to Henry L. Pierce, & Others, April 6. 1859 and Abraham Lincoln's Address at a Sanitary Fair at Baltimore, MD, April 18, 1864 vs. Confederate Vice President Alexander Stephen's Cornerstone Speech, Savannah, GA, March 21, 1861
- Eric Foner. Free Soil, Free Labor, Free Men: The Ideology of the Republican Party Before the Civil War (1970) ch 2
- Dred Scott v. Sandford, U. S. Supreme Court, Roger Taney's decision, 1857
- First Lincoln Douglas Debate at Ottawa, Illinois August 21, 1858
- J. G. Randall, Lincoln the President, 1997, vol 1, pages 237-241
- James M. McPherson, Battle Cry of Freedom 1988 p 242, 255, 282-83. Maps on page 101 (The Southern Economy) and page 236 (The Progress of Secession) are also relevant
- William E. Gienapp, "The Crisis of American Democracy: The Political System and the Coming of the Civil War." in Boritt ed. Why the Civil War Came 79-123
- Gienapp, "Crisis of American Democracy" p. 92
- James Brewer Stewart, Holy Warriors: The Abolitionists and American Slavery (1976); Pressly, 270ff
- Against Slavery: An Abolitionist Reader, 2000, page 26
- Pressly, 97, 123-24, 133, 271ff, 283, 302.
- Beringer 1986 pp 359-60
- David Brion Davis, Inhuman Bondage (2006) pp 186-192.
- David Brion Davis, Inhuman Bondage (2006) p 197, 409; Stanley Harrold, The Abolitionists and the South, 1831-1861 (1995) p. 62
- Resolved, That the union of these States rests on the equality of rights and privileges among its members, and that it is especially the duty of the Senate, which represents the States in their sovereign capacity, to resist all attempts to discriminate either in relation to person or property, so as, in the Territories--which are the common possession of the United States--to give advantages to the citizens of one State which are not equally secured to those of every other State., Jefferson Davis' Resolutions on the Relations of States, Senate Chamber, U.S. Capitol, February 2, 1860, From The Papers of Jefferson Davis, Volume 6, pp. 273-76. Transcribed from the Congressional Globe, 36th Congress, 1st Session, pp. 658-59.
- Jefferson Davis' Second Inaugural Address, Virginia Capitol, Richmond, February 22, 1862 Transcribed from Dunbar Rowland, ed., Jefferson Davis, Constitutionalist, Volume 5, pp. 198-203. Summarized in The Papers of Jefferson Davis, Volume 8, p. 55.
- Declaration of the Immediate Causes Which Induce and Justify the Secession of South Carolina from the Federal Union - Adopted December 24, 1860
- Abraham Lincoln, The Man Behind the Myths, Stephen B. Oates, 1994, page 69
- J. Mills Thornton III, Politics and Power in a Slave Society: Alabama, 1800-1860 (1978)
- James McPherson, "Antebellum Southern Exceptionalism: A New Look at an Old Question," Civil War History 29 (Sept. 1983)
- Mark Neely, Confederate Bastille: Jefferson Davis and Civil Liberties 1993 p. 10-11
- Mark E. Neely Jr.; "Was the Civil War a Total War?" Civil War History, Vol. 50, 2004 pp 434+
- McPherson, Battle Cry 386
- Allen Nevins, War for the Union 1862-1863, pages 263-264
- McPherson 313-16, 392-3
- Heidler, 1591-98
- Heidler, 1643-47
- Heidler, 598-603
References
Overviews
- Beringer, Richard E., Archer Jones, and Herman Hattaway, Why the South Lost the Civil War (1986) influential analysis of factors; The Elements of Confederate Defeat: Nationalism, War Aims, and Religion (1988), abridged version, more readily available
- Catton, Bruce, The Civil War, American Heritage, 1960, ISBN 0-8281-0305-4, illustrated narrative
- Donald, David ed. Why the North Won the Civil War (1977) (ISBN 0020316607), short interpretive essays
- Donald, David et al. The Civil War and Reconstruction (latest edition 2001); 700 page survey
- Eicher, David J., The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War, (2001), ISBN 0-684-84944-5.
- Fellman, Michael et al. This Terrible War: The Civil War and its Aftermath (2003), 400 page survey
- Foote, Shelby. The Civil War: A Narrative (3 volumes), (1974), ISBN 0-394-74913-8. Highly detailed narrative covering all fronts
- McPherson, James M. Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (1988), 900 page survey; Pulitzer prize
- Nevins, Allan. Ordeal of the Union, an 8-volume set (1947-1971). the most detailed political, economic and military narrative; by Pulitzer Prize winner
- 1. Fruits of Manifest Destiny, 1847-1852; 2. A House Dividing, 1852-1857; 3. Douglas, Buchanan, and Party Chaos, 1857-1859; 4. Prologue to Civil War, 1859-1861; 5. The Improvised War, 1861-1862; 6. War Becomes Revolution, 1862-1863; 7. The Organized War, 1863-1864; 8. The Organized War to Victory, 1864-1865
- Rhodes, James Ford. History of the Civil War, 1861-1865 (1918), Pulitzer Prize; a short version of his 5-volume history
- Ward, Geoffrey C. The Civil War (Alfred Knopf, 1990), based on PBS series by Ken Burns; visual emphasis
- Weigley, Russell Frank. A Great Civil War: A Military and Political History, 1861-1865 (2004); primarily military
Reference books and bibliographies
- Blair, Jayne E. The Essential Civil War: A Handbook to the Battles, Armies, Navies And Commanders (2006)
- Carter, Alice E. and Richard Jensen. The Civil War on the Web: A Guide to the Very Best Sites- 2nd ed. (2003)
- Current, Richard N., et al eds. Encyclopedia of the Confederacy (1993) (4 Volume set; also 1 vol abridged version) (ISBN 0132759918)
- Faust, Patricia L. (ed.) Historical Times Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Civil War (1986) (ISBN 0061812617) 2000 short entries
- Esposito, Vincent J. West Point Atlas of American Wars (1959), these maps are online
- Heidler, David Stephen, ed. Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History (2002), 1600 entries in 2700 pages in 5 vol or 1-vol editions
- Resch, John P. et al., Americans at War: Society, Culture and the Homefront vol 2: 1816-1900 (2005)
- Wagner, Margaret E. Gary W. Gallagher, and Paul Finkelman, eds. The Library of Congress Civil War Desk Reference (2002)
- Woodworth, Steven E. ed. American Civil War: A Handbook of Literature and Research (1996) (ISBN 0313290199), 750 pages of historiography and bibliography
Biographies
- Warner, Ezra J., Generals in Blue: Lives of the Union Commanders, Louisiana State University Press, 1964, ISBN 0-8071-0882-7
- Warner, Ezra J., Generals in Gray: Lives of the Confederate Commanders, Louisiana State University Press, 1959, ISBN 0-8071-0823-5
Soldiers
- Frank, Joseph Allan and George A. Reaves. Seeing the Elephant: Raw Recruits at the Battle of Shiloh (1989)
- Hess, Earl J. The Union Soldier in Battle: Enduring the Ordeal of Combat (1997)
- McPherson, James. What They Fought For, 1861-1865 (Louisiana State University Press, 1994)
- McPherson, James. For Cause and Comrades: Why Men Fought in the Civil War (1998)
- Wiley, Bell Irvin. The Life of Johnny Reb: The Common Soldier of the Confederacy (1962) (ISBN 0807104752)
- Wiley, Bell Irvin. Life of Billy Yank: The Common Soldier of the Union (1952) (ISBN 0807104760)
Primary sources
- U.S. War Dept., The War of the Rebellion: a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies, U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901. 70 very large volumes of letters and reports written by both armies. Online at
- Commager, Henry Steele (ed.). The Blue and the Gray. The Story of the Civil War as Told by Participants. (1950), excerpts from primary sources
- Eisenschiml, Otto; Ralph Newman; eds. The American Iliad: The Epic Story of the Civil War as Narrated by Eyewitnesses and Contemporaries (1947), excerpts from primary sources
- Hesseltine, William B. ed.; The Tragic Conflict: The Civil War and Reconstruction (1962), excerpts from primary sources
- Woodword, C. Vann, Ed., Mary Chesnut's Civil War, Yale University Press, 1981, ISBN 0-300-02979-9 Pulitzer Prize
Novels about the war
- Crane, Stephen, The Red Badge of Courage
- Doctorow, E.L., The March
- Frazier, Charles, Cold Mountain
- Jakes, John, The Titans ISBN 0515048275
- Jakes, John, Love and War
- Mitchell, Margaret, Gone with the Wind
- Ripley, Alexandra, Charleston
- Reed, Ishmael, Flight to Canada
- Shaara, Jeffrey, Gods and Generals; The Last Full Measure
- Shaara, Michael, The Killer Angels
- Street, James, By Valour and Arms
- Turtledove, Harry, Fort Pillow
- Verne, Jules, Texar's Revenge, or, North Against South (Nord Contre Sud)
- Vidal, Gore, Lincoln
Cinema & Television
Films about the war
- The Birth of a Nation (1915)
- Gone With the Wind (1939)
- The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966)
- The Blue and the Gray (1982)
- Glory (1989)
- Gettysburg (1993)
- Ride with the Devil (1999)
- Gods and Generals (2003)
- Cold Mountain (2003)
Documentaries about the war
- The Civil War, directed by Ken Burns
- The Great Battles of the Civil War, directed by Jay Wertz
External links
- Civil War Search Directory
- The Civil War Home Page
- updated Guide to Civil War and Reconstruction Online historical and scholarly sources
- George Scott Black Civil War Spy
- links to magazines and documents
- The American Civil War Homepage, from U Tennessee
- The Antislavery Literature Project
- Civil War photos at the National Archives
- Civil War in Virginia
- Civil War Pictures Database
- Online texts of Civil War books at the National Park Service
- Religion and the American Civil War
- University of Tennessee: U.S. Civil War Generals
- Shotgun's Home of the American Civil War
- American Civil War
- American Civil War Detailed Chronology
- The Civil War, a PBS documentary by Ken Burns
- Individual state's contributions to the Civil War: California, Florida, Illinois #1, Illinois #2, Ohio, Pennsylvania
- State declarations of the causes of secession: Mississippi, Georgia, Texas, South Carolina
- Alexander Stephens' Cornerstone Speech
- Civil War Trails — A project to map out sites related to the Civil War in Maryland, Virginia, and North Carolina
- Civil War Audio Resources
- The Handbook of Texas Online: Civil War
- The Brothers War
- Civil War Band Collection: 1st Brigade Band of Brodhead, Wisconsin A digital collection of first person narrative accounts from Wisconsin soldiers and citizens, documenting their wartime experiences.
- Wisconsin Goes to War: Our Civil War Experience
| History of the United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: