This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Entropyandvodka (talk | contribs) at 08:28, 11 March 2015 (→Biblical narrative: Expanded on origin section of Moabites and Ammonites.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 08:28, 11 March 2015 by Entropyandvodka (talk | contribs) (→Biblical narrative: Expanded on origin section of Moabites and Ammonites.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about a location in Jordan. For other uses, see Moab (disambiguation).| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Moab" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Jordan |
 |
| Prehistory |
| Ancient history |
| Classical period |
| Islamic era |
| Emirate and mandate |
| Post-independence |
|
|
Moab (/ˈmoʊæb/; Moabite: 𐤌𐤀𐤁 Mʾb; Arabic مؤاب Mu'āb; Hebrew: מוֹאָב, Modern: Mo'av, Tiberian: Môʼāḇ, "seed of father"; Greek Μωάβ Mōav; Assyrian Mu'aba, Ma'ba, Ma'ab; Egyptian Mu'ab) is the historical name for a mountainous strip of land in Jordan. The land lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel. The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west.
Origins
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The Moabites likely settled in the Transjordanian highlands. Whether they were among the nations referred to in the Ancient Egyptian language as Shutu or Shasu is a matter of some debate among scholars.
Despite a scarcity of archaeological evidence, the existence of Moab prior to the rise of the Israelite state has been deduced from a colossal statue erected at Luxor by Pharaoh Ramesses II, in the 13th century BCE, which lists Mu'ab among a series of nations conquered during a campaign.
| ||||||
| The name which was translated into "Moab" in hieroglyphs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Era: New Kingdom (1550–1069 BC) | ||||||
Biblical narrative
According to the biblical account, Moab and Ammon were born to Lot and Lot's elder and younger daughters, respectively, in the aftermath of the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah. The Bible refers to both the Moabites and Ammonites as Lot's sons, born of incest with his daughters Genesis 19:37–38.
The Moabites first inhabited the rich highlands at the eastern side of the chasm of the Dead Sea, extending as far north as the mountain of Gilead, from which country they expelled the Emim, the original inhabitants, but they themselves were afterward driven southward by warlike tribes of Amorites, who had crossed the river Jordan. These Amorites, described in the Bible as being ruled by King Sihon, confined the Moabites to the country south of the river Arnon, which formed their northern boundary.
The Israelites, in entering the "promised land", did not pass through the land of the Moabites (Judges 11:18), but conquered Sihon's kingdom and his capital at Heshbon. After the conquest of Canaan the relations of Moab with Israel were of a mixed character, sometimes warlike and sometimes peaceable. With the tribe of Benjamin they had at least one severe struggle, in union with their kindred the Ammonites and the Amalekites. The Benjaminite shofet Ehud ben Gera assassinated the Moabite king Eglon and led an Israelite army against the Moabites at a ford of the Jordan river, killing many of them.
The Book of Ruth, on the other hand, testifies to the existence of a friendly intercourse between Moab and Bethlehem, one of the towns of the tribe of Judah. By his descent from Ruth, David may be said to have had Moabite blood in his veins. He committed his parents to the protection of the king of Moab (who may have been his kinsman), when hard pressed by King Saul. (1 Samuel 22:3,4) But here all friendly relations stop forever. The next time the name is mentioned is in the account of David's war, who made the Moabites tributary. Moab may have been under the rule of an Israelite governor during this period; among the exiles who returned to Judea from Babylonia were a clan descended from Pahath-Moab, whose name means "ruler of Moab".
After the destruction of the First Temple, the knowledge of which people belonged to which nation was lost and the Moabites were treated the same as other gentiles. As a result, all members of the nations could convert to Judaism without restriction. The problem in Ezra and Nehemiah occurred because Jewish men married women from the various nations without their first converting to Judaism.
At the disruption of the kingdom under the reign of Rehoboam, Moab seems to have been absorbed into the northern realm. It continued in vassalage to the Kingdom of Israel until the death of Ahab which according to E. R. Thiele's reckoning was in about 853 BCE, when the Moabites refused to pay tribute and asserted their independence, making war upon the kingdom of Judah.
After the death of Ahab in about 853 BCE, the Moabites under Mesha rebelled against Jehoram, who allied himself with Jehoshaphat, King of the Kingdom of Judah, and with the King of Edom. According to the Bible, the prophet Elisha directed the Israelites to dig a series of ditches between themselves and the enemy, and during the night these channels were miraculously filled with water which was as red as blood. Deceived by the crimson color into the belief that their opponents had attacked one another, the Moabites became overconfident and were entrapped and utterly defeated at Ziz, near En Gedi, which states that the Moabites and their allies, the Ammonites and the inhabitants of Mount Seir, mistook one another for the enemy, and so destroyed one another). According to Mesha's inscription on the Mesha Stele, however, he was completely victorious and regained all the territory of which Israel had deprived him. The battle of Ziz is the last important date in the history of the Moabites as recorded in the Bible. In the year of Elisha's death they invaded Israel. and later aided Nebuchadnezzar in his expedition against Jehoiakim.
Although allusions to Moab are frequent in the prophetical books and although two chapters of Isaiah (xv.-xvi.) and one of Jeremiah (xlviii.) are devoted to the "burden of Moab," they give little information about the land. Its prosperity and pride, which the Israelites believed incurred the wrath of God, are frequently mentioned; and their contempt for Israel is once expressly noted.

In the Nimrud clay inscription of Tiglath-pileser III the Moabite king Salmanu (perhaps the Shalman who sacked Beth-arbel in Hosea x. 14) is mentioned as tributary to Assyria. Sargon II mentions on a clay prism a revolt against him by Moab together with Philistia, Judah, and Edom; but on the Taylor prism, which recounts the expedition against Hezekiah, Kammusu-Nadbi (Chemosh-nadab), King of Moab, brings tribute to Sargon as his suzerain. Another Moabite king, Mutzuri ("the Egyptian" ?), is mentioned as one of the subject princes at the courts of Esarhaddon and Assurbanipal, while Kaasḥalta, possibly his successor, is named on cylinder B of Assurbanipal.
Decline and fall
Sometime during the Persian period Moab disappears from the extant historical record. Its territory was subsequently overrun by waves of tribes from northern Arabia, including the Kedarites and (later) the Nabataeans. In Nehemiah 4:1 the Arabs are mentioned instead of the Moabites as the allies of the Ammonites. Their region, however, continued to be known by its biblical name for some time. For example, when the Crusaders occupied the area, the castle they built to defend the eastern part of the Kingdom of Jerusalem was called Krak des Moabites.
Geography
Moab occupied a plateau about 3,000 feet (910 m) above the level of the Mediterranean, or 4,300 feet (1,300 m) above the Dead Sea, and rising gradually from north to south.
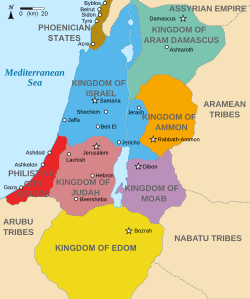
It was bounded on the west by the Dead Sea and the southern section of the Jordan River; on the east by Ammon and the Arabian desert, from which it was separated by low, rolling hills; and on the south by Edom. The northern boundary varied, but generally is represented by a line drawn some miles above the northern extremity of the Dead Sea.
In Ezekiel 25:9 the boundaries are given as being marked by Beth-jeshimoth (north), Baal-meon (east), and Kiriathaim (south).
That these limits were not fixed, however, is plain from the lists of cities given in Isaiah 15–16 and Jeremiah xlviii., where Heshbon, Elealeh, and Jazer are mentioned to the north of Beth-jeshimoth; Madaba, Beth-gamul, and Mephaath to the east of Baalmeon; and Dibon, Aroer, Bezer, Jahaz, and Kirhareseth to the south of Kiriathaim. The principal rivers of Moab mentioned in the Bible are the Arnon, the Dimon or Dibon, and the Nimrim.
The limestone hills which form the almost treeless plateau are generally steep but fertile. In the spring they are covered with grass and the table-land itself produces grain.
In the north are a number of long, deep ravines, and Mount Nebo, famous as the scene of the death of Moses. The rainfall is fairly plentiful and the climate, despite the hot summer, is cooler than the area west of the Jordan river, snow falling frequently in winter and in spring.
The plateau is dotted with hundreds of dolmens, menhirs, and stone circles, and contains many ruined villages, mostly of the Roman and Byzantine periods. The land is now occupied chiefly by Bedouin, though it contains such towns as al-Karak.
The territory occupied by Moab at the period of its greatest extent, before the invasion of the Amorites, divided itself naturally into three distinct and independent portions: The enclosed corner or canton south of the Arnon (referred to as "field of Moab"); the more open rolling country north of the Arnon, opposite Jericho and up to the hills of Gilead (called the "land of Moab"); and the district below sea level in the tropical depths of the Jordan valley.
Economy
The country of Moab was the source of numerous natural resources, including limestone, salt and balsam from the Dead Sea region. The Moabites occupied a vital place along the King's Highway, the ancient trade route connecting Egypt with Mesopotamia, Syria, and Anatolia. Like the Edomites and Ammonites, trade along this route gave them considerable revenue.
Religion
References to the religion of Moab are scant. Most of the Moabites were polytheists like other early Semites, and the Book of Numbers says that they induced the Israelites to join in their sacrifices. Their chief god was Chemosh, and the Israelites sometimes referred to them as the "people of Chemosh."
According to II Kings, at times, especially in dire peril, human sacrifices were offered to Chemosh, as by Mesha, who gave up his son and heir to him. Nevertheless, King Solomon built a "high place" for Chemosh on the hill before Jerusalem, which the Bible describes as "this detestation of Moab". The altar was not destroyed until the reign of Josiah. The Moabite Stone also mentions (line 17) a female counterpart of Chemosh, Ashtar-Chemosh, and a god Nebo (line 14), probably the well-known Babylonian divinity Nabu. The cult of Baal-peor or Peor seems to have been marked by sexual rites, though this may be exaggeration.
Language
| Moabite | |
|---|---|
| Region | Formerly spoken in northwestern Jordan |
| Era | early half of 1st millennium BCE |
| Language family | Afro-Asiatic |
| Writing system | Phoenician alphabet |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | obm |
| Linguist List | obm |
| Glottolog | (insufficiently attested or not a distinct language)moab1234 |
The Moabite language is an extinct Hebrewic dialect, spoken in Moab (modern day central-western Jordan) in the early first millennium BC. It was written using a variant of the Phoenician alphabet.
Most of our knowledge about Moabite comes from the Mesha Stele, which is the only known extensive text in this language. In addition there are the three line El-Kerak Inscription and a few seals. The main features distinguishing Moabite from fellow Canaanite languages such as Hebrew are: a plural in -în rather than -îm (e.g. mlkn "kings" for Biblical Hebrew məlākîm), like Aramaic and Arabic; retention of the feminine ending -at which Biblical Hebrew reduces to -āh (e.g. qryt "town", Biblical Hebrew qiryāh) but retains in the construct state nominal form (e.g.qiryát yisrael "town of Israel"); and retention of a verb form with infixed -t-, also found in Arabic and Akkadian (w-’ltḥm "I began to fight", from the root lḥm.)
According to Glottolog, referencing Huehnergard & Rubin (2011), Moabite was not a distinct language from Hebrew.
In Jewish tradition
According to the Bible, the Moabites opposed the Israelite invasion of Canaan, as did the Ammonites. As a consequence, they were excluded from the congregation for ten generations. The term "tenth generation" is considered an idiom used for an unlimited time as opposed to the third generation which allows an Egyptian convert to marry into the community. The Talmud expresses the view that the prohibition only applied to male Moabite, who were not allowed to marry born Jews or legitimate converts. Female Moabites, when converted to Judaism, were permitted to marry with only the normal prohibition of a convert marrying a kohen (priest) applying. However, the prohibition was not followed during the Exile; and Ezra and Nehemiah sought to compel a return to the law because men had been marrying women who had not been converted at all. The heir of King Solomon was Rehoboam, the son of an Ammonite woman, Naamah.
On the other hand, the marriages of the Bethlehem Ephrathites (of the tribe of Judah) Chilion and Mahlon to the Moabite women Orpah and Ruth, and the marriage of the latter, after her husband's death, to Boaz who by her was the great-grandfather of David, are mentioned with no shade of reproach. The Talmudic explanation, however, is that the language of the law only applies to Moabite and Ammonite men (Hebrew, like all Semitic languages, is gendered). The Talmud also states that Prophet Samuel wrote the book of Ruth in order to settle the dispute as the rule had been forgotten since the time of Boaz. Another interpretation is that the Book of Ruth is simply reporting the events in an impartial fashion, leaving any praise or condemnation to be done by the reader.
The Babylonian Talmud in Yevamot 76B explains that one of the reasons was the Ammonites did not greet the Children of Israel with friendship and the Moabites hired Balaam to curse them. The difference in the responses of the two people led to God allowing the Jewish People to harass the Moabites (though not go to war) but forbade them to even harass the Ammonites. (Compare/contrast with the basic message of Deuteronomy 23:4-5).
It should be noted that Ruth adopted the God of Naomi, her Israelite mother-in-law, and chose to go back to her (Naomi's) people after her husband, his brother and his father, Naomi's husband, died.
Ruth said to Naomi, "Whither thou goest, I will go; whither thou lodgest, I will lodge; thy people shall be my people and thy God my God". The Talmud uses this as the basis for what a convert must do to be converted. There are arguments as to exactly when she was converted and if she had to repeat this statement in front of the court in Bethlehem when they arrived there.
According to the Book of Jeremiah, Moab was exiled to Babylon for his arrogance and idolatry. According to Rashi, it was also due to their gross ingratitude even though Abraham, Israel's ancestor, had saved Lot, Moab's ancestor from Sodom. Jeremiah prophesies that Moab's captivity will be returned in the end of days.
Etymology
| Moab in hieroglyphs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mib / Mab Mjb | |||||||
The etymology of the word Moab is uncertain. The earliest gloss is found in the Septuagint which explains the name, in obvious allusion to the account of Moab's parentage, as ἐκ τοῦ πατρός μου. Other etymologies which have been proposed regard it as a corruption of "seed of a father", or as a participial form from "to desire", thus connoting "the desirable (land)". Rashi explains the word Mo'ab to mean "from the father", since ab in Hebrew and Arabic and the rest of the Semitic languages means "father". He writes that as a result of the immodesty of Moab's name, God didn't command the Jews to refrain from inflicting pain upon the Moabites in the manner in which he did with regards to the Ammonites. Fritz Hommel regards Moab as an abbreviation of Immo-ab = "his mother is his father".
According to Genesis 19:30–38, the ancestor of the Moabites was Lot by incest with his eldest daughter. She and her sister, having lost their fiancés and their mother in the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, decided to continue their father's line through intercourse with their father. The elder got him drunk to facilitate the deed and conceived Moab. The younger daughter did the same and conceived a son named Ben-Ammi, who became ancestor to the Ammonites. According to the Book of Jasher (24,24), Moab had four sons—Ed, Mayon, Tarsus and Kanvil—and his wife, whose name is not given, is apparently from Canaan.
References
- see 2 Kings 3
- Deuteronomy 2:11
- Numbers 21:13; Judges 11:18
- Judges 3:12-30
- 2 Samuel 8:2; 1 Chronicles 18:2
- Edwin Thistle, The Mysterious Numbers of the Hebrew Kings, (1st ed.; New York: Macmillan, 1951; 2d ed.; Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1965; 3rd ed.; Grand Rapids: Zondervan/Kregel, 1983). ISBN 0-8254-3825-X, 9780825438257.
- 2 Chronicles 22:1
- 2 Kings 3; 2 Chronicles 20
- 2 Kings 13:20
- 2 Kings 24:2
- e.g., Isa 25:10; Ezek 25:8–11; Amos 2:1–3; Zephaniah 2:8–11
- Isa 16:6; Jer 48:11–29; Zephaniah 2:10
- Jer. xlviii. 27
- comp. 1 Macc 9:32–42; Josephus, Jewish Antiquities xiii. 13, § 5; xiv. 1, § 4.
- Deuteronomy xxxiv. 1-8
- Ruth 1:1,2,6
- Deuteronomy 1:5; 32:49
- Numbers 22:1
- Num 25:2; Judges 10:6
- Jer 48:7, 48:13
- Num 21:29; Jer 48:46
- 2 Kings 3:27
- 1 Kings 11:7
- 2 Kings 23:13
- Num 25:5; Ps. cvi. 28
- Num 31:16; Josh 22:17
- Moabite at MultiTree on the Linguist List
- ^ Geoffrey W. Bromiley, The International Standard Bible Encyclopedia, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2007, p. 395 under 'Moab'
- Cite error: The named reference
Glottolog2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Deuteronomy 23:4; comp. Nehemiah 8:1–3
- Ezra 9:1–2, 12; Nehemiah 13:23–25
- 1 Kings 14:21
- Ruth 1:2–4
- Ruth 4:10–13
- Deuteronomy 23:3–4
- Jeremiah 48, Tanach. Brooklyn, New York: ArtScroll. p. 1187.
- ^ Rainer Hannig: Großes Handwörterbuch Ägyptisch-Deutsch: (2800-950 v. Chr.). von Zabern, Mainz 2006, ISBN 3-8053-1771-9, S. 1147.
- Genesis 19:37
- Leyden (1904). Verhandlungen des Zwölften Internationalen Orientalisten-Congresses. p. 261.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Singer, Isidore; et al., eds. (1901–1906). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Singer, Isidore; et al., eds. (1901–1906). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
Further reading
- Many comparisons of Biblical Hebrew with the language of the Mêša˓ inscription appear in Wilhelm Gesenius' Hebrew grammar, e.g. §2d, §5d, §7b, §7f, §49a, §54l, §87e, §88c, §117b, etc.
- Routledge, Bruce. Moab in the Iron Age: Hegemony, Polity, Archaeology. 2004. The most comprehensive treatment of Moab to date.
- Bienkowski, Piotr (ed.) Early Edom and Moab: The Beginning of the Iron Age in Southern Jordan (1992).
- Dearman, Andrew (ed.) Studies in the Mesha inscription and Moab (1989).
- Jacobs, Joseph and Louis H. Gray. "Moab". Jewish Encyclopedia. Funk and Wagnalls, 1901–1906, which cites to the following bibliography:
- Tristram, The Land of Moab, London, 1874;
- George Adam Smith, Historical Geography of the Holy Land, ib. 1897;
- Clermont-Ganneau, Recueil d'Archéologie Orientale, ii. 185–234, Paris, 1889;
- Baethgen, Beiträge zur Semitischen Religionsgeschichte, Berlin, 1888;
- Smith, Rel. of Sem. Edinburgh, 1894. J. L. H. G.
- Hertz, J.H., The Pentateuch and Haftoras: Deuteronomy, Oxford, 1936, Oxford University Press.
External links
- Gutenberg E-text of Patriarchal Palestine by Archibald Henry Sayce (1895)
- Moab entry in Smith's Bible Dictionary
- Moab on Nabataea.net
31°54′00″N 35°45′00″E / 31.90000°N 35.75000°E / 31.90000; 35.75000
Categories: