This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Kage Acheron (talk | contribs) at 16:36, 5 June 2015 (→Australia: Removed section irrelevant to the E-meter). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:36, 5 June 2015 by Kage Acheron (talk | contribs) (→Australia: Removed section irrelevant to the E-meter)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
The E-meter is a device for displaying and/or recording the electrodermal activity (EDA) of a human being. The word is a common abbreviation for Electropsychometer. It is also known in various applications as an electroencephaloneuromentimograph, electrodermal activity meter, electrodermal response meter, electropsychogalvanometer, electrogalvonometer, electrogalvometer, skin galvanometer, or psychogalvanometer.
The E-meter has been used for more than a century by counselors of psychology and psychoanalysis, as an auditing tool in Scientology and divergent groups, as a research tool in many human studies, and as one component of the Keeler polygraph (lie detector) system.
History
Main article: Electrodermal activity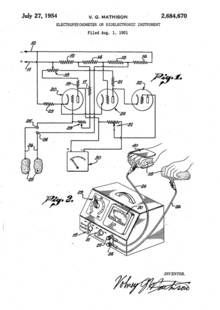
In 1849, Dubois-Reymond in Germany first observed that human skin was electrically active, a phenomenon that is now generally known as electrodermal activity (EDA). The elements of EDA include moment to moment variation in skin conductance, resistance, and internally generated potential, measured between the palms or the soles of the feet, or between two positions on the same palm or sole. Other more complex activity in response to alternating current has been studied.
In 1878 in Switzerland, Hermann and Luchsinger demonstrated a connection between EDA and sweat glands. Vigouroux (France, 1879) was the first researcher to relate these phenomena to psychological activity. In 1888, the French neurologist Féré demonstrated that skin resistance activity could be changed by emotional stimulation and that activity could be inhibited by drugs.
The first EDA meter was developed in Russia 1889 by Ivane Tarkhnishvili. It was popularized for psychotherapy by Carl Gustav Jung in a series of papers published in German in 1906 and in English in 1919. Jung and his colleagues used meters to evaluate the emotional sensitivities of patients during word association. Jung was so impressed with the instrument, he allegedly cried, "Aha, a looking glass into the unconscious!" Jung described his use of the device in counseling in his book, Studies in Word Association, and such use has continued with various practitioners.
Volney Mathison (chiropractor, radio engineer, psychologist, and hypnotist) built an EDA meter based on a Wheatstone bridge, a vacuum tube amplifier, and a large moving-coil meter that projected an image of the needle on the wall. He patented his device in 1954 as an electropsychometer or E-meter, and it came to be known as the "Mathison Electropsychometer." In Mathison's words, the E-meter "has a needle that swings back and forth across a scale when a patient holds on to two electrical contacts." Mathison recorded in his book, Electropsychometry, that the idea of the E-meter came to him in 1950 while listening to a lecture by L. Ron Hubbard:
In 1950 ... I next attended a series of lectures being given by a very controversial figure, who several times emphasized that perhaps the major problem of psychotherapy was the difficulty of maintaining the communication of accurate or valid data from the patient to the therapist. ... it appeared to me that the psychogalvanometer showed most promise.
Mathison began working with Hubbard in 1951 and that year filed application for his first E-meter patent, U.S. Patent 2,684,670. After the partnership broke up in 1954, Mathison continued improving his E-meters with additional patents (U.S. patent 2,736,313, U.S. patent 2,810,383), marketing them through his own company and publications, retaining many of the concepts and terms from his time with Hubbard.
In a separate line of development, EDA monitors were incorporated in polygraph machines by Leonarde Keeler. Rigorous testing of the polygraph has yielded mixed results (see Polygraph main page), and some critics classify polygraph operation as a pseudoscience.
Scientology E-Meter

The E-meter was adopted for use in Dianetics and Scientology when Mathison collaborated with L. Ron Hubbard in 1951. Some sources say the E-meter was "developed by Volney Mathison following Hubbard's designs," or that Hubbard invented it.
In the book, L. Ron Hubbard, Messiah or Madman?, Bent Corydon wrote:
In late 1954 the use of the E-meter was discontinued by Hubbard. Wrote Hubbard: "Yesterday, we used an instrument called an E-Meter to register whether or not the process was still getting results so that the auditor would know how long to continue it. While the E-Meter is an interesting investigation instrument and has played its part in research, it is not today used by the auditor... As we long ago suspected, the intervention of a mechanical gadget between the auditor and the preclear had a tendency to depersonalize the session..."
Though it seemed for a while that Scientology's more advanced techniques would serve without an E-meter, a few months later in May 1955, Hubbard wrote:
And here come E-Meters back into the picture. The HASI is, at this moment, building a new and better E-Meter than has ever been built before, under the trademarked name of Physio-galvanometer, or O-Meter. It has very little in common with the old type E-Meter. Nevertheless, an old type E-Meter can be utilized.
The Scientology meter was smaller, based on transistors rather than vacuum tubes, and powered by a low-voltage, rechargeable battery rather than line voltage.
From then on, the E-meter was a required tool for Scientology ministers. The "Hubbard Mark II" E-meter was christened in 1960, and the Hubbard Mark III shortly after. On December 6, 1966, Hubbard won a patent on the Mark V version under the name "Hubbard Electropsychometer." Corydon wrote that the Hubbard E-meter was actually developed by Scientologists Don Breeding and Joe Wallis, though the patent (U.S. patent 3,290,589) does not list other developers.
Corydon's account was said to be based on the memoirs of Hubbard's son, Ronald DeWolf, but in 1987, DeWolf sued the publisher to prevent publication and swore an affidavit repudiating everything in the book.
The Scientology E-meter has been redesigned and re-patented several times since it's first introduction to Dianetics (e.g.: U.S. patent 4,459,995, U.S. patent 4,578,635, U.S. patent 4,702,259).
Modern applications

EDA meters are used in both therapist-patient and bio-feedback settings. EDA is one of the factors recorded by polygraphs, and EDA meters are often used in human studies to gauge psychological responses. EDA monitoring is on the increase in clinical applications. Hugo D. Critchley, Chair in Psychiatry at the Brighton and Sussex Medical School states, "EDA is a sensitive psychophysiological index of changes in autonomic sympathetic arousal that are integrated with emotional and cognitive states."
Use in Scientology
E-meters are used in Scientology and Dianetics by Scientology ministers known as "auditors." Scientology materials traditionally refer to the subject as the "preclear," although auditors continue to use the meter on subjects who are well beyond the "clear" level. The auditor gives the preclear a series of commands or questions while the preclear holds a pair of cylindrical electrodes ("cans") connected to the meter, and the auditor notes both the verbal response and the activity of the meter. Auditor training includes familiarization with a number of characteristic needle movements, each with a specific significance.
Some critics of Dianetics and Scientology assert that the Scientology concepts associated with the E-meter and its use are regarded by the scientific and medical communities as pseudoscience, and that the E-meter has never been subjected to clinical trials as a therapeutic tool. Nevertheless, by 1972, more than 1500 articles on electrodermal activity (EDA) had been published in professional publications, and today EDA is regarded as the most popular method for investigating human psychophysiological phenomena. Even apart from Scientology,
Scientologists claim that in the hands of a trained operator, the meter can indicate whether a person has been relieved from the spiritual impediment of past experiences. In accordance with a 1974 federal court order, the Church of Scientology asserts that the E-meter is intended for use only in church-sanctioned auditing sessions; it is not a curative or medical device. The E-meters used by the Church were previously manufactured by Scientologists at their Gold Base facility, but now are manufactured in Hong Kong and Taiwan.
According to Hubbard, the E-meter is used by the operator for three vital functions:
- To determine what process to run and what to run it on.
- To observe how well the process is running.
- To know when the process should be stopped.
The E-meter is used to assess the emotion charge of single words, of whole sentences, and of questions. It can also indicate the general state of the subject when the operator is not speaking. Few users of the E-meter claim that it does anything to the subject. To most, it does no more than suggest to the operator a change of mental, emotional, or parasympathetic nervous state or activity.
Functional description
One of E-meter's primary components is a Wheatstone bridge, an electrical circuit configuration invented in 1833 that enables the detection of very small differences between two electrical impedances (in this case, resistance). The E-meter is constructed so that one resistance is the subject's body and the other is a rheostat controlled by the operator. A small voltage from the battery is applied to electrodes held in the subjects hands. As the electrical properties (electrodermal activity) of the subject's body changes during the counseling, the resulting changes in the small electrical current are displayed in needle movements on a large analog panel meter. The dial face is without numbers because the absolute resistance in ohms is relatively unimportant, while the operator watches primarily for characteristic needle motions. The voltage applied to the electrodes is less than 1.5V, and the electric current through the subject's body is less than a half a milliampere.
In the Scientology E-meter, the large control, known as the "tone arm," adjusts the meter bias, while a smaller controls the gain. The operator manipulates the tone arm to keep the needle near the center of the dial so its motion is easily observed. A simple E-meter powered by direct current, such as that used by the Scientologists and the like, displays several kinds of electrodermal activity (EDA) on the one dial without distinction, including changes in conductance, resistance, and bioelectric potential. Researchers in psychophysiology are also exploring admittance and impedance aspects of EDA that can be observed only with alternating current.
The E-Meter is similar in mechanism to a polygraph or lie detector, measuring variations in galvanic skin response that can be highly sensitive to emotions. Fear, anger, startled response, orienting response and sexual feelings are among the reactions which may produce similar skin conductance responses, and these responses account for the changes picked up by E-Meter measuring. According to Scientology doctrine, the resistance corresponds to the "mental mass and energy" of the subject's mind, which are claimed to change when the subject thinks of particular mental images (engrams). One account tells about L. Ron Hubbard using the E-meter to determine whether or not fruits can experience pain, as in his 1968 assertion that tomatoes "scream when sliced."
The standard medical explanation for the movement of the needle is the operation of the sympathetic nervous system on the sweat glands. Because sweat contains dielectrics (salt, etc.), conductivity is increased when the sweat glands are activated. But some advocates argue that the meter responds more quickly than would be possible by the exudation and drying of sweat, They propose an additional mechanism termed the "Tarchanoff Response" through which the cerebral cortex of the brain affects the current directly. Still others researchers confess that the phenomenon is not completely understood, despite more than 150 years of research.
E-meter and the law
United States
Main article: History of DianeticsThe medical establishment had been watching Hubbard's enterprises since 1951 when the New Jersey State Board of Medical Examiners prosecuted the Hubbard Dianetic Research Foundation (Elizabeth, NJ) for teaching medicine without a licence. In 1958, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) seized and destroyed 21,000 Dianazene tablets from Hubbard's Distribution Center, Inc., charging that they were falsely labeled as a treatment for radiation sickness.
On January 4, 1963, in service of an FDA complaint, more than 100 US marshals and deputized longshoremen with drawn guns raided the Founding Church of Scientology in Washington, D.C. and confiscated more than three tons of property including 5,000 books, 2,900 booklets, and several hundred E-meters. The FDA accused the Church of making false medical claims that the E-meters could treat physical and mental illnesses. The FDA also charged that the meters did not bear adequate directions for treating the conditions for which they were recommended.
The Church sued to get the property back, and years of litigation ensued. In the first trial beginning on April 3, 1967, the jury found that the Church misrepresented the E-meter and the judge ordered the confiscated materials destroyed. But in 1969, the US Court of Appeals reversed the verdict; the Church, it said, had made substantial showing that Scientology is a religion and the government had done nothing to rebut the claim. The US Court of Appeals wrote:
made no attempt to contradict the expert testimony introduced by the Government. They have conceded that the E-meter is of no use in the diagnosis or treatment of disease as such, and have argued that it was never put forward as having such use. Auditing or processing, in their view, treats the spirit of man, not his body, though through the healing of the spirit the body can be affected. They have culled from their literature numerous statements disclaiming any intent to treat disease and recommending that Scientology practitioners send those under their care to doctors when organic defects may be found. They have introduced through testimony a document which they assert all those who undergo auditing or processing must sign which states that Scientology is "a spiritual and religious guide intended to make persons more aware of themselves as spiritual beings, and not treating or diagnosing human ailments of body or mind, and not engaged in the teaching of medical arts or sciences * * *."
Finally, with respect to their claim to be a religion and hence within the protection of the First Amendment, they have shown that the Founding Church of Scientology is incorporated as a church in the District of Columbia, and that its ministers are qualified to perform marriages and burials. They have introduced their Creed into evidence. The Government has made no claim that the Founding Church is not a bona fide religion, that auditing is not part of the exercise of that religion, or that the theory of auditing is not a doctrine of that religion.
Having conceded that Scientology is a religion, wrote the Court, the government was forbidden by the First Amendment of the Constitution to rule on the truth or falsity of the Church's doctrines and interfere with its practices, provided the claims are not manifestly insincere and the practices are reasonably harmless. The Court ordered a new trial with the mandate that the trial court could not forbid auditing, use of the E-meter, or purveyance of the literature within a religious context. The FDA appealed the decision, but in 1969, the US Supreme Court declined to review the case, commenting only that "Scientology meets the prima facie test of religion." In his 1973 judgment, District Court Judge Gerhardt A. Gesell (presiding over the trial) expressed his own opinion of Scientology in strong words:
Hubbard and his fellow Scientologists developed the notion of using an E-Meter to aid auditing. Substantial fees were charged for the meter and for auditing sessions using the meter. They repeatedly and explicitly represented that such auditing effectuated cures of many physical and mental illnesses. An individual processed with the aid of the E-Meter was said to reach the intended goal of 'clear' and was led to believe that there was reliable scientific proof that once cleared many, indeed most, illnesses would successfully be cured. Auditing was guaranteed to be successful.
Unable to do more under the mandate from the Court of Appeals, Judge Gesell ordered all the property to be returned to the Church, and thereafter, the E-meter may be used only in "bona fide religious counseling." All meters and referring literature must include a label disclaiming any medical benefits, thus:
The E-Meter is not medically or scientifically useful for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of any disease. It is not medically or scientifically capable of improving the health or bodily functions of anyone.
The church adopted a modified version of that statement, which it still invokes in connection with the E-meter. The current statement reads:
The Hubbard Electrometer is a religious artifact. By itself, this meter does nothing. It is for religious use by students and Ministers of the church in Confessionals and pastoral counseling only.
Since the FDA's legal objective was to outlaw and condemn the E-meters and literature (as had been ordered in the first trial), this was a substantial and embarrassing defeat for the FDA. For the Church of Scientology, it was not a significant change. The Church had not stated in any publication that the E-meter could or would heal anything.
Judge Gesell also ordered the Church to pay all the government's legal fees and warehousing costs for the confiscated property for the nine years of litigation. He also required the church to pay the salaries and travel expenses of FDA agents who might, from time to time, inspect for compliance with the court's order. The raid had been ruled illegal, but the government retained copies of the documents.
Europe
In 1979 in Sweden, a court forbade calling the E-meter an invaluable aid to measuring man's mental state and changes in it in an advertisement. The prohibition was upheld by the European Commission of Human Rights in case X. and Church of Scientology v. Sweden.
In October 2009, a three-judge panel at the Correctional Court in Paris, France convicted the church and six of its members of organized fraud. The Court's decision followed a three-week trial, where two plaintiffs alleged they were defrauded by the organization. One plaintiff's complaint involved the use of an E-Meter by Scientologists with medical implications. This plaintiff claimed that, after being audited with the device, she was encouraged to pay tens of thousands of euros for vitamins, books, and courses to improve her condition. She argued that amounted to fraud. The Court agreed, and the ruling was upheld on appeal in 2013. See Scientology in France#Conviction for fraud.
Australia
In 1964, the government of Victoria, Australia held a Board of Inquiry into Scientology which returned its findings in a document colloquially known as the Anderson Report. Psychiatrist Dr. Ian Holland Martin, honorary federal secretary of the Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, gave evidence that the E-Meter 'used for Scientology' was a 'psycho-galvano-meter' and was 'dangerous in unqualified hands'. He said that if the E-meter 'was suggested to possess mysterious powers' to someone who did not understand that it had 'been thoroughly discredited as a lie detector' then 'that person would be suggestible to ideas foisted on him by the operator'. The final report of the inquiry stated that the E-meter enabled Scientology:
"...to assume, intensify and retain control over the minds and wills of preclears. Fears of its abilities keep them in constant subjection. Its use can be so manipulated by cunningly phrased questions that almost any desired result can be obtained, and it is used unscrupulously to dominate students and staff alike. All the evil features of scientology are intensified where the E-meter is involved. When used in conjunction with hypnotic techniques, its evil impact is greatly increased. This simple electrical device is not, of course, the sole basis for the condemnation of scientology, but without the E-meter scientology would be partly disarmed."
Other states echoed the ban. But then in 1969, the High Court of Western Australia ruled the ban illegal, and South Australia repealed its law in 1973. Victoria repealed its law in 1982. And in 1983, the High Court of Australia granted Scientology full rights as a religion in all respects.
Present status
| This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2015) |

As of January 2005, the cost of the Mark V was $900 and the Mark VII Super Quantum E-meter was US $4,650 (up from US $3,850 in 1995). Scientologists of the Free Zone have developed their own E-meter models which are available at much lower prices. They also offer circuit diagrams and instructions for building a meter.
Scientology beliefs and theories
L. Ron Hubbard sets out his theory of how the E-meter works in his book Understanding the E-Meter:
For the meter to be read, the tiny flow of electrical energy through the preclear (person) has to remain steady. When this tiny flow is changed the needle of the E-Meter moves. This will happen if the preclear pulls in or releases mental mass. This mental mass (condensed energy), acts as an additional resistance or lack of resistance to the flow of electrical energy from the E-Meter.
Hubbard claimed that this "mental mass" has the same physical characteristics, including weight, as mass as commonly understood by lay persons:
In Scientology it has been discovered that mental energy is simply a finer, higher level of physical energy. The test of this is conclusive in that a thetan "mocking up" (creating) mental image pictures and thrusting them into the body can increase the body mass and by casting them away again can decrease the body mass. This test has actually been made and an increase of as much as thirty pounds, actually measured on scales, has been added to, and subtracted from, a body by creating "mental energy." Energy is energy. Matter is condensed energy.
This text in Understanding the E-Meter is accompanied by three drawings. The first shows a man standing on a weighing scale, which reflects a weight of "150" (the units are not given). The next shows the man on the same scale, weighed down under a burden of "Mental Image Pictures", and the scale indicates a weight of "180". The last picture shows the man standing upright on the scale, now unburdened by "Mental Image Pictures" and with a smile on his face, while the scale again indicates a weight of "148".
Bob Thomas, senior executive of the church in the early 1970s, gave a prosaic description.
The immediate goal of the E-meter is to enhance communication. In other words, just to take a parallel: if an analyst were allowing his patient to free-associate, and the patient were connected in some way with a galvanometer which showed the analyst what things the patient mentioned were emotionally charged and what things were not emotionally charged, a lot of time would be saved. So it's simply an assist for the practitioner to direct the individual to areas which he himself may not realize are troubled or charged with emotion or are repressed; and to better direct his attention into those areas ...
The E-meter is a simple psycho-galvanometer. It's got some increased sensitivity built into it and the myological reactions that you sometimes get in the galvanometer have been damped out by the circuitry, so that the mental reactions, the reactions of the spirit, on the body are emphasized and can be read more clearly. But that's simply the design of the circuitry; it doesn't basically affect the kind of device. It registers what is called, commonly, the psychogalvanomic reflex, which is a reflex that is a poorly understood mechanism of the psyche. The body resistance seems to vary when the individual thinks of a painful or pain-associated or traumatic-associated concept, or word or idea. ... Some very early work was done on this by Jung ..."
See also
References
- America's Alternative Religions, by Timothy Miller, 1995, ISBN 0-7914-2398-0;page 386
- "About Us". Observation Mountain Academy. Observation Mountain Academy. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- "e-meter". Ron's Org Grenchen. Ron's Org Grenchen. 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ Boucsein, Wolfram (2012). Electrodermal Activity. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 3–4. ISBN 9781461411260. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Daniels, Victor. "Notes on Carl Gustav Jung". Sonoma State University. Sonoma State University. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
By 1906 was using GSR and breath measurement to note changes in respiration and skin resistance to emotionally charged worlds. Found that indicators cluster around stimulus words which indicate the nature of the subject's complexes...Much later L. Ron Hubbard used this approach in Scientology's "auditing," using the "e-meter" (a galvanic skin response indicator) to discern the presence of complexes.
- Binswanger, L. (1919). "XII". In Jung, Carl (ed.). Studies in Word-Association. New York, NY: Moffat, Yard & company. pp. 446 et seq. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- Anderson, Kevin. "Report of the Board of Enquiry into Scientology" (PDF). ApologeticsIndex. Apologetics Index (TM). p. 128. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
The E-meter is not a new type of instrument. It is one which is well known to science and has been in use in one form or another for many years. As early as the 1920's, experiments were conducted in psychological research with what was then called an electro-galvanometer or psychogalvanometer.
- Atack, Jon. "Possible origins for Dianetics and Scientology". Scientology 101. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
Some form of 'E-meter' has actually been in use since before WWI
- "You can learn control of how your skin talks". San Bernardino, California: The San Bernardino County Sun. The San Bernardino County Sun. October 11, 1977. p. 12. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
Current research using the skin's electrical activity as a communications medium between patient and therapist looks promising in such stress problems as drug abuse, alcoholism, neuroses and other tension states.
- ^ Brown, Barbara (November 9, 1977). "Skin Talks -- And It May Not Be Saying What You Want To". Pocatello, Idaho: Field Enterprises, Inc. Idaho State Journal. p. 32. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
Carl Jung, possibly the most creative psychologist who ever lived, experimented with skin talk in 1900. Using a primitive instrument to record changes in skin electrical activity, he conducted psychological interviews with patients and found that the skin responded to hidden emotions. It is said he was so astounded by this phenomenon that he exclaimed, 'Aha, a looking glass into the unconscious!'
- Mitchell, Gregory. "Carl Jung & Jungian Analytical Psychology". Mind Development Courses. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- "Technically it is a specially developed 'Wheatstone Bridge' well known to electrically minded people as a device to measure the amount of resistance to a flow of electricity", L. R. Hubbard, in: "The Book Introducing the E-Meter", page 1. Quoted in: Kotzé report, The Report of the Commission of Enquiry into Scientology, 1972, Republic of South Africa. Section III, Chapter 8
- ^ Singh, Simon; Edzard Ernst (2008). Trick or Treatment: The Undeniable Facts about Alternative Medicine. W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 163–65. ISBN 0-393-06661-4.
- Freeman, John (1987). Suppressed and Incredible Inventions. Health Research. p. 41. ISBN 0-7873-1091-3.
- Garrison, Omar V. (1974). The Hidden Story of Scientology. Secaucus, NJ: The Citadel Press. p. 64. ISBN 0-8065-0440-4.
- Mathison, Volney (1952). Electropsychometry (PDF) (1 ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Mathison Electropsychometers. p. 101. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- Mathison, Volney G. (1954). Electropsychometry (PDF) (4 ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Mathison Psychometers. pp. 101–104.
- ^ "Remember Venus?". TIME. 1952-12-22. Retrieved 2008-01-28.
- Mathison, Volney (1952). Electropsychometry (4 ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Mathison Electropsychometers. p. 1. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- Melton, J. Gordon (2000). Studies in Contemporary Religion: The Church of Scientology. United States of America: Signature Books, Inc. p. 10. ISBN 1-56085-139-2.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Barrett, Stephen; Wallace, Janssen, eds. (1993). "The Gadgeteers". The Health Robbers. A Close Look at Quackery in America. Prometheus Books, Buffalo NY. pp. 321–335. ISBN 0-87975-855-4.
- ^ Corydon, Bent (1987). Messiah or Madman. Lyle Stuart. p. 313.
- Hubbard, L. Ron (13 May 1955). Professional Auditor's Bulletin No. 52. London, UK: Hubbard Communication Office. p. 1. ISBN 87-87347-82-2.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Grant, Boyd (2014). What is Scientology? History, Beliefs, Rules, Secrets, and Facts (1 ed.). Newark, DE: Speedy Publishing. p. 5.
- Affidavit submitted by DeWolf to a notary in Nevada
- Shapiro, David A.; Shapiro, Diana (November 1982). "Meta-analysis of comparative therapy outcome studies: A replication and refinement". Psychological Bulletin (Vol 92(3)). American Psychological Association: 581–604. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
{{cite journal}}:|issue=has extra text (help) - Nagai, Yoko; Goldstein, Laura H.; Fenwick, Peter B.C.; Trimblea, Michael R. (April 2004). "Clinical efficacy of galvanic skin response biofeedback training in reducing seizures in adult epilepsy: a preliminary randomized controlled study". Epilepsy & Behavior. 5 (2). Elsevier: 216–223. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2003.12.003. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
Biofeedback training significantly reduced seizure frequency in the active biofeedback group
- "Biofeedback, Galvanic skin response (GSH) or Electrodermal Response, Types of Biofeedback Machines or Biofeedback Techniques<". Holisticonline.com. ICBS, Inc. 1 January 2004. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Caprara, H. John; Eleazer, Paul D.; Barfield, Robert D.; Chavers, Scott (16 December 2005). "Objective Measurement of Patient's Dental Anxiety by Galvanic Skin Reaction". Journal of Endodontics. 29 (8). Elsevier Inc.: 493–496. doi:10.1097/00004770-200308000-00001. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
A statistically significant correlation was found between skin conductance and dental anxiety in all cases.
- Vanderark, Sherman D.; Ely, Daniel (1992). "Biochemical and Galvanic Skin Responses to Music Stimuli by College Students in Biology and Music". Perceptual and Motor Skills. 74. Ammons Scientific: 1079–1090. doi:10.2466/pms.1992.74.3c.1079. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Rankin, Robert E.; Campbell, Donald T., Donald T. (July 1955). "Galvanic skin response to Negro and white experimenters". The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology. 51 (1). American Psychological Association: 30–33. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Ogorevc, Jaka; Geršak, Gregor; Novak, Domen; Drnovšek, Janko (November 2013). "Metrological evaluation of skin conductance measurements". Measurement. 46 (9): 2993–3001. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2013.06.024. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- Critchley, Hugo D. (April 2002). "Book Review: Electrodermal Responses: What Happens in the Brain". Neuroscientist. 8 (2): 132–142. doi:10.1177/107385840200800209. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ "How the E-Meter works, Church of Scientology International". Scientology.org. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- "Inside Scientology Reaching for the Stars". Nightline. 23 October 2009. ABC.
- ^ Boucsein, Wolfram (2012). Electrodermal Activity. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 7. ISBN 9781461411260. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Yearbook of the European Convention on Human Rights by the European Court of Human Rights, ISBN 90-247-2383-3
- Religionsfreiheit und Konformismus: Über Minderheiten und die Macht der Mehrheit, Gerhard Besier, 2004. ISBN 3-8258-7654-3
- ^ "A Place called Gold, St. Petersburg Times, 1998". Sptimes.com. 1998-10-25. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- Hubbard, L Ron. "Unreading Questions and Items". HCO Bulletin 27 May 1970.
- Hubbard, L Ron. "SOP Goals". HCO Bulletin 18 February 1961.
- Hubbard, L Ron. "Floating Needles and End Phenomena". HCO Bulletin 20 February 1970.
- Lebron, Robyn (13 Jan 2012). Searching for Spiritual Unity... Can There Be Common Ground?. CrossBooks. p. 549. ISBN 9781462719525. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- Cavanaugh, Jeanne (April 27, 2004). Scientology and the FDA: A Look Back, A Modern Analysis, And A New Approach. Boston, MA: Harvard University. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
As described, Scientology does not assert that the E-meter can directly cure or mitigate disease; rather, the E-meter plays a vital role in the allegedly illness-alleviating process of auditing by identifying the presence and location of the cause of psychosomatic illnesses. Other systems work to actually accomplish the discharge of illness-causing agents.
- "The Genesis of the Wheatstone Bridge" by Stig Ekelof discusses Christie's and Wheatstone's contributions, and why the bridge carries Wheatstone's name. Published in "Engineering Science and Education Journal", volume 10, no 1, February 2001, pages 37-40.
- HCO WW Staff: Essential Information Every Scientologist Should Know, HCO Information Letter of 24 November 1963. Hubbard Communications Office, East Grinstead, Sussex, England. Quoted in: Kotzé report, The Report of the Commission of Enquiry into Scientology, 1972, Republic of South Africa. Section III, Chapter 8
- Hubbard, L. Ron (1982). Understanding the E-Meter. Bridge Publications. ISBN 0-88404-078-X.
- Brown, Barbara (November 9, 1977). "Skin Talks -- And It May Not Be Saying What You Want To". Pocatello, Idaho: Field Enterprises, Inc. Idaho State Journal. p. 32. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Hubbard, Lafayette (1982). "Understanding the E-Meter" (PDF). The Starlight Meter. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "How the E-Meter Works". Church of Scientology International. Church of Scientology International. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Shepherd, Peter (2001). "The GSR Meter Course" (PDF). Tools for Transformation. Trans4Mind Ltd. p. 23. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- "How the E-Meter Works". Scientology. Church of Scientology International. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- Shepherd, Peter (2001). "The GSR Meter Course" (PDF). Tools for Transformation. Trans4Mind Ltd. p. 10. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Hubbard, Lafayette. The Book of E-meter Drills (PDF). p. 11. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
- Boucsein, Wolfram (2012). Electrodermal Activity. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 2. ISBN 9781461411260.
- "Official Scientology page on the E-meter". Scientology.org. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- "30 Dumb Inventions". Life. 1968-01-01. Retrieved 2009-10-28.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - "Scientology Mythbusting with Jon Atack: The Tomato Photo!". tonyortega.org. 2013-02-02. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- Skin conductance main page: "Lastly, galvanic skin responses are delayed 1-3 seconds."
- Hubbard, Lafayette. The Book of E-meter Drills (PDF). p. 27. Retrieved 8 April 2015.
An Instant Read. An instant read is defined as that reaction of the needle which occurs at the precise end of any major thought voiced by the auditor. (quoting HCO B May 25, 1962)
{{cite book}}: line feed character in|quote=at position 91 (help) - ^ Shepherd, Peter (18 July 2001). "The GSR Meter Course" (PDF). Tools for Transformation. Trans4Mind Ltd. p. 20. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
The GSR Meter helps the Practitioner to discover these key items, since when one's attention is drawn to an item, the charge on the item will cause an increase in brain arousal, which is visible on the GSR Meter as a sudden fall in body resistance, i.e. an instantaneous fall of the needle.
Cite error: The named reference "trans4mind" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Bulletin of the Hubbard Dianetic Research Foundation, Elizabeth, NJ. January 1951
- Atack, Jon (1990). A Piece of Blue Sky. New York, NY: Carol Publishing Group. ISBN 0-8184-0499-X.
- Wallis, Roy. Sectarianism: Analyses of Religious and Non-Religious Sects, Page 92, 1975, ISBN 0-470-91910-8
- Miller, Russell (1987). Bare-faced Messiah, The True Story of L. Ron Hubbard (First American Edition ed.). New York: Henry Holt & Co. pp. 227–228. ISBN 0-8050-0654-0.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ Lewis, James R. (2009). Scientology. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. pp. Introduction: 5. ISBN 9780199887118.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
robberswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Wright, Skelley (February 5, 1969). "Opinion". Washington, DC: United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia. p. 1151. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- "The Battle Mounts - Those Who Oppose Scientology". Those Who Oppose Scientology. Church of Scientology International. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Christopher Riche Evans (1974). Cults of Unreason. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 0-374-13324-7. Chapter 6.
- Russell Miller (1987). "15. Visits To Heaven". Bare-Faced Messiah: The true story of L. Ron Hubbard. Key Porter Books. ISBN 1-55013-027-7.
- ^ Heins, Marjorie (1982). "Other People's Faiths: The Scientology Litigation and the Justiciability of Religious Fraud" (PDF). Hastings Constitutional Law Quarterly. 9 (1): 170. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- ^ Garrison, Omar V. (1974). The Hidden Story of Scientology (1 ed.). Secaucus, NJ: Citadel Press. p. 136. ISBN 0-8065-0440-4. Cite error: The named reference "Garrison" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Wright, Skelley (February 5, 1969). "Opinion". Washington, DC: United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia. p. 1154. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Heins, Marjorie (1982). ""Other People's Faiths": The Scientology Litigation and the Justiciability of Religious Fraud" (PDF). Hastings Constitutional Law Quarterly. 9 (1): 171. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- Malko, George (1970). Scientology: The Now Religion. New York: Dell/Delacorte Press. pp. Chapter 4. ISBN 978-1112963735.
... the U.S. Court of Appeals ... reversed the decision of the federal jury and stated that until the government can offer proof that Scientology is not a religion, the E-Meters and the literature seized are protected by our rights of freedom of worship.
- Heins, Marjorie (1982). "Other People's Faiths: The Scientology Litigation and the Justiciability of Religious Fraud" (PDF). Hastings Constitutional Law Quarterly. 9 (1): 175, fn. 116. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- "Court Order - FDA - Scientology Dianetics Hubbard E-meter". Scribd.com. 2008-08-25. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- Dianetics: self-improvement home study course, Bridge Publications, 2002.
- Evans, Christopher Riche (1973). Cults of Unreason. United States: Harrap, Farrar, Straus and Giroux, Delacorte Press. ISBN 978-0-374-13324-5.
They are not - as the Food and Drug Administration found to its embarrassment in the case of the E-meter - sold or promoted as therapeutic devices.
- "Appeals: Victory for the Scientologists". Time Magazine. Time, Inc. 14 February 1969. Retrieved 15 April 2015.
- http://www.cnn.com/2009/WORLD/europe/10/27/france.scientology.fraud/index.html?eref=igoogle_cnn
- AFP (17 October 2013). "Scientology's fraud conviction upheld in France". The Telegraph. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ "SCIENTOLOGY VENUS TRIP 'A DELUSION'". The Canberra Times (ACT : 1926 - 1995). ACT: National Library of Australia. 2 June 1964. p. 27. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- State of Victoria (1965) Report of the Board of Inquiry into Scientology p.96 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~dst/Cowen/audit/ar14.html
- Lewis, James R. (2009). Scientology. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. pp. Introduction: 5, 6. ISBN 9780199887118. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- Garrison, Omar V. (1974). The Hidden Story of Scientology. Secaucus, NJ: The Citadel Press, Lyle Stuart, Inc. pp. 62–4. ISBN 0-8065-0440-4.
External links
| This section's use of external links may not follow Misplaced Pages's policies or guidelines. Please improve this article by removing excessive or inappropriate external links, and converting useful links where appropriate into footnote references. (June 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Scientology Today: What is the E-Meter and how does it work?
- The E-Meter Papers
- Secrets of Scientology: The E-Meter, David S. Touretzky
- E-Meter Patent