This is an old revision of this page, as edited by EvergreenFir (talk | contribs) at 17:13, 7 March 2017 (Reverted 1 edit by 2601:190:4200:DF2E:0:0:0:F162 (talk): No... . (TW)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:13, 7 March 2017 by EvergreenFir (talk | contribs) (Reverted 1 edit by 2601:190:4200:DF2E:0:0:0:F162 (talk): No... . (TW))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)Gender differences in suicide rates have been shown to be significant; there are highly asymmetric rates of attempted and completed suicides between males and females.
The gap, also called the "gender paradox of suicidal behavior", can vary significantly among different countries. Globally as of 2012, death by suicide occurs about 1.8 times more often among males than among females. In the western world, males die three to four times more often by means of suicide than do females. This difference is even more pronounced in those over the age of 65, with tenfold more males than females dying by suicide. Suicide attempts are between two and four times more frequent among females. Researchers have attributed the difference between attempted and completed suicides among the sexes to males using more lethal means to end their lives. However, separating intentional suicide attempts, from non-suicidal self-harm, is not currently done in the United States, when gathering statistics at the national level. The extent of suicidal thoughts is not clear, but research suggests that suicidal thoughts are more common among females than among males.
Overview
| Rank | Country | Males | Females | Total | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52.5 | 7.9 | 28.6 | 2009 | |
| 2 | 35.6 | 18.5 | 26.3 | 2009 | |
| 3 | 43.0 | 7.7 | 24.0 | 2009 | |
| 4 | 40.4 | 8.4 | 23.5 | 2009 | |
| 5 | 41.3 | 6.9 | 22.8 | 2009 | |
| 6 | 28.3 | 10.1 | 19.1 | 2009 | |
| 7 | 32.1 | 7.6 | 19.0 | 2009 | |
| 8 | 33.5 | 5.7 | 18.6 | 2009 | |
| 9 | 32.2 | 5.2 | 17.6 | 2009 | |
| 10 | 25.4 | 8.9 | 17.1 | 2009 |
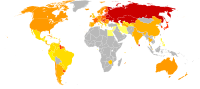
 Suicide rate per 100,000 males (left) and per 100,000 females (right) (data from 1978–2008)
No data
<1.0
1.0–5.0
5.0–5.8
5.8–8.5
8.5–12.0
12.0–19.0
19.0–22.5
22.5–26.0
26.0–29.5
29.5–33.0
33.0–36.5
>36.5
Suicide rate per 100,000 males (left) and per 100,000 females (right) (data from 1978–2008)
No data
<1.0
1.0–5.0
5.0–5.8
5.8–8.5
8.5–12.0
12.0–19.0
19.0–22.5
22.5–26.0
26.0–29.5
29.5–33.0
33.0–36.5
>36.5
The role that gender plays as a risk factor for suicide has been studied extensively. While females, according to one study, may show higher rates of reported nonfatal suicidal behavior and suicide ideation, males have a much higher rate of completed suicides. However, a 2009 study tends to show little to no difference in suicidal ideation between men and women. A 2008 study of suicide attempts by gender found that females have a higher rate of attempted suicide than males earlier in life, and that this rate decreases with age. For males, the rate of attempted suicide remains fairly constant when controlled for age. Males and females also tend to differ in their methods of suicide and responses to suicidal feelings.
Factors
Many researchers have attempted to find explanations for why gender is such a significant indicator for suicide. In 1981, suicide of men was 1.9 times higher than in women in the UK. In 2012, the male suicide rate increased to over three times higher than the female suicide rate. A common explanation relies on the social constructions of hegemonic masculinity and femininity. According to literature on gender and suicide, male suicide rates are explained in terms of traditional gender roles. Male gender roles tend to emphasize greater levels of strength, independence, and risk-taking behavior. Reinforcement of this gender role often prevents males from seeking help for suicidal feelings and depression.
Numerous other factors have been put forward as the cause of the gender paradox. Part of the gap may be explained by heightened levels of stress that result from traditional gender roles. For example, the death of a spouse and divorce are risk factors for suicide in both genders, but the effect is somewhat mitigated for females. In the Western world, females are more likely to maintain social and familial connections that they can turn to for support after losing their spouse. Another factor closely tied to gender roles is employment status. Males' vulnerability may be heightened during times of unemployment because of societal expectations that males should provide for themselves and their families.
It has been noted that the gender gap is less stark in developing nations. One theory put forward for the smaller gap is the increased burden of motherhood due to cultural norms. In regions where the identity of females is constructed around the family, having young children may correlate with lower risks for suicide. At the same time, stigma attached to infertility or having children outside of marriage can contribute to higher rates of suicide among women.
In 2003, a group of sociologists examined the gender and suicide gap by considering how cultural factors impacted suicide rates. The four cultural factors; power-difference, individualism, uncertainty avoidance, and masculinity, were measured for 66 countries using data from the World Health Organization. Cultural beliefs regarding individualism were most closely tied to the gender gap; countries that placed a higher value on individualism showed higher rates of male suicide. Power-difference, defined as the social separation of people based on finances or status, was negatively correlated with suicide. However, countries with high levels of power-difference had higher rates of female suicide. The study ultimately found that stabilizing cultural factors had a stronger effect on suicide rates for women than men.
Differing methods by gender
Main article: Suicide methodsThe reported difference in suicide rates for males and females is partially a result of the methods used by each gender. Although females attempt suicide at a higher rate, they are more likely to use methods that are less immediately lethal. Males frequently complete suicide via high mortality actions such as hanging, carbon-monoxide poisoning, and firearms. This is in contrast to females, who tend to rely on drug overdosing. While overdosing can be deadly, it is less immediate and therefore more likely to be caught before death occurs. In Europe, where the gender discrepancy is the greatest, a study found that the most frequent method of suicide among both genders was hanging; however, the use of hanging was significantly higher in males (54.3%) than in females (35.6%). The same study found that the second most common methods were firearms (9.7%) for men and poisoning by drugs (24.7%) for women.
Preventative strategies
In the United States, both the Department of Health and Human Services and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention address different methods of reducing suicide, but do not recognize the separate needs of males and females. In 2002, the English Department of Health launched a suicide prevention campaign that was aimed at high-risk groups including young men, prisoners, and those with mental health disorders. The Campaign Against Living Miserably is a charity in the UK that attempts to highlight this issue for public discussion. Researchers have also recommended more aggressive and long-term treatments and follow up for males that show indications of suicidal thoughts. Shifting cultural attitudes about gender roles and norms, and especially ideas about masculinity, may also contribute to closing the gender gap. Some studies have found that because young females are at a higher risk of attempting suicide, policies tailored towards this demographic are most effective at reducing overall rates.
Statistics
The incidence of completed suicide is vastly higher among males than females among all age groups in most of the world.
United States
In the United States, the male-to-female teenage suicide death ratio is estimated at 3:1. Typically males die from suicide three to five times more often than females. Use of mental health resources may be a significant contributor to the gender difference in suicide rates in the US. Studies have shown that females are 13–21% more likely than males to receive a psychiatric affective diagnosis. While 72–89% of females who committed suicide had contact with a mental health professional at some point in their life, only 41–58% of males who committed suicide had made use of this resource.
Within the United States, there are variances in gendered rates of suicide by ethnic group. According to the CDC, as of 2013 the suicide rates of Whites and American Indians are more than twice the rates of African Americans and Hispanics. A 2008 study showed that the rate of self-reported attempted suicide is highest among American Indian and Alaskan Native males, and lowest among African American females. Rates of self-reported attempted suicide are highest among American Indian and Alaskan Native females and lowest among African American and white males. This reflects the general trend described by the gender paradox. Explanations for why rates of attempted and completed suicide vary by ethnicity are often based on cultural differences. Among African American suicides, it has been suggested that females usually have better access to communal and familial relations that may mitigate other risk factors for suicide. Among Hispanic populations, the same study showed that cultural values of marianismo, which emphasizes female docility and deference to males, may help explain the higher rate of suicide of Latinas relative to Latinos. The authors of this study did not extrapolate their conclusions on ethnicity to populations outside the United States.
Europe
The gender-suicide gap is generally highest in Western countries. Among the nations of Europe, the gender gap is particularly large in Eastern European countries such as Lithuania, Belarus, and Hungary. Some researchers attribute the higher rates in former Soviet countries to be a remnant of recent political instability. An increased focus on family, under Soviet control, led to females becoming more highly valued. Rapid economic fluctuations prevented males from providing fully for their families, which prevented them from fulfilling their traditional gender role. Combined, these factors could account for the gender gap. Other research indicates that higher instances of alcoholism among males in these nations may be to blame. In 2014, suicides rates amongst under-45 men in UK reached a 15-year high of 78% of the total 5,140.
Non-Western nations
A higher male mortality from suicide is also evident from data from non-Western countries. In 1979–81, out of 74 countries with a non-zero suicide rate, 69 countries had male suicide rates greater than females, two reported equal rates for the sexes (Seychelles and Kenya), while three reported female rates exceeding male rates (Papua New Guinea, Macau, and French Guiana). The contrast is even greater today, with WHO statistics showing China as the only country where the suicide rate of females matches or exceeds that of males. Barraclough found that the female rates of those aged 5–14 equaled or exceeded the male rates only in 14 countries, mainly in South America and Asia.
China
In most countries, the majority of committed suicides are made by men but, in China, women are 40% more likely to commit suicide. Traditional gender roles in China hold women responsible for keeping the family happy and intact. Suicide for women in China is shown in literature to be an acceptable way to avoid disgrace that may be brought to themselves or their families. China and other non-Western countries have been affected less by the loss of manufacturing jobs, changing patterns of social relationships, and modification of family structure. This is one explanation of why suicide rates in China tend to be closer to the much lower suicide rate difference between men and women found in previous decades, in Western countries. Another explanation for increased suicide in women in China is that pesticides are easily accessible and tend to be used in many suicide attempts made by women. Another explanation is that women are seen as subservient to men due to Chinese gender roles. Thirdly, difficult living conditions and strict views on marriage and family values cause women high stress which is a risk factor for suicidal behavior. The rate of nonlethal suicidal behavior is 40 to 60 percent higher in women than it is in men. This is due to the fact that more women are diagnosed as depressed than men, and also that depression is correlated with suicide attempts.
See also
- List of suicides (antiquity-present)
- List of suicides in the 21st century
References
- Udry, J. Richard (November 1994). "The Nature of Gender" (PDF). Demography. 31 (4): 561–573. doi:10.2307/2061790. JSTOR 2061790. PMID 7890091.
- ^ Canetto, Silvia. "The Gender Paradox in Suicide". Suicide and Life Threatening Behavior. 28 (1): 5. doi:10.1111/j.1943-278X.1998.tb00622.x.
- ^ Värnik, P (March 2012). "Suicide in the world". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 9 (3): 760–71. doi:10.3390/ijerph9030760. PMC 3367275. PMID 22690161.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - "Estimates for 2000–2012". WHO. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ Understanding abnormal behavior (Tenth ed., ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Cengage Learning. 2012-01-01. p. 255. ISBN 978-1-111-83459-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - Chang, B; Gitlin, D; Patel, R (September 2011). "The depressed patient and suicidal patient in the emergency department: evidence-based management and treatment strategies". Emergency medicine practice. 13 (9): 1–23, quiz 23–4. PMID 22164363.
- Stern, Theodore A.; Fava, Maurizio; Wilens, Timothy E.; Rosenbaum, Jerrold F. (2015). Massachusetts General Hospital Comprehensive Clinical Psychiatry (2 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 589. ISBN 9780323328999.
- ^ Krug, Etienne G. (2002). World Report on Violence and Health. World Health Organization. p. 191. ISBN 9789241545617.
- Suicidal Behaviour: Assessment of People-At-Risk. Sage Publications India. 2010. p. 139. ISBN 8132104994. Retrieved March 4, 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - Sex Differences: Summarizing More than a Century of Scientific Research. Psychology Press. 2013. p. 387. ISBN 1136874933. Retrieved March 4, 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - "Suicide Statistics — AFSP". American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ^ Crosby AE, Han B, Ortega LAG, Parks SE, Gfoerer J. "Suicidal thoughts and behaviors among adults aged ≥18 years-United States, 2008-2009." MMWR Surveillance Summaries 2011;60(no. SS-13).
- WHO on Suicide Prevention, World Health Organization. Retrieved May 16, 2014.
- Data from WHO online databank using "intentional self harm" causes of death
- ^ Orszag, Peter R. "Why Do More Men Commit Suicide?". Bloomberg. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- Thompson, Martie; Laney S. Light (2011). "Examining Gender Differences in Risk Factors for Suicide Attempts Made 1 and 7 Years Later in a Nationally Representative Sample". Journal of Adolescent Health. 48: 391–397. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.07.018.
- "Suicides in the United Kingdom, 2012 Registrations – ONS". ons.gov.uk.
- ^ Payne, Sarah; et al. "The social construction of gender and its influence on suicide: a review of the literature". Journal of Men's Health. 5 (1): 23–35. doi:10.1016/j.jomh.2007.11.002.
- ^ Möller-Leimkühler, Anne Maria (Feb 2003). "The gender gap in suicide and premature death or: why are men so vulnerable?". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 253 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1007/s00406-003-0397-6. PMID 12664306.
- ^ Stack, Steven. "New Micro-Level Data on the Impact of Divorce on Suicide, 1959–1980: A Test of Two Theories". Journal of Marriage and the Family. 52 (1): 119–127. doi:10.2307/352844. JSTOR 10.2307/352844.
- Girard, Chris. "Age, Gender, and Suicide: A Cross-National Analysis". American Sociological Review. 58 (4): 553–574. doi:10.2307/2096076. JSTOR 10.2307/2096076.
- ^ Rudmin, Lloyd Webster. "Questions of Culture, Age, and Gender in the Epidemiology of Suicide". Scandinavian Journal of Psychology. 44: 373–381. doi:10.1111/1467-9450.00357.
- Schrijvers, Didier. "The gender paradox in suicidal behavior and its impact on the suicidal process". Journal of Affective Disorders. 138 (2): 19–26. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2011.03.050.
- ^ Varnik, A; et al. "Suicide methods in Europe: a gender-specific analysis of countries participating in the European Alliance Against Depression". Journal of Epidemiology and Public Health. 62 (6): 545–551. doi:10.1136/jech.2007.065391.
- Thompson, Martie; et al. "Examining Gender Differences in Risk Factors for Suicide Attempts Made 1 and 7 Years Later in a Nationally Representative Sample". Journal of Adolescent Health. 48: 391–397. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.07.018.
- "Teen Suicide Statistics". Adolescent Teenage Suicide Prevention. FamilyFirstAid.org. 2001. Retrieved 2006-04-11.
- Murphy, George E. "Why Women are Less Likely Than Men to Commit Suicide". Comprehensive Psychiatry. 39 (4): 165–175. doi:10.1016/S0010-440X(98)90057-8.
- ^ Kung, Hsiang-Ching; et al. "Risk factors for male and female suicide decedents ages 15–64 in the United States". Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 38 (8): 419–426. doi:10.1007/s00127-003-0656-x.
- ^ Goldston, David B.; Sherry Davis Molock; Leslie B. Whitbeck; Jessica L. Murakami; Luis H. Zayas; Gordon C. Nagayama Hall. "Cultural Considerations in Adolescent Suicide Prevention and Psychosocial Treatment". American Psychologist. 63 (1): 14–31. doi:10.1037/0003-066x.63.1.14. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- "Suicide Statistics". AFSP.
- Landburg, Jonas. "Alcohol and Suicide in eastern Europe". Centre for Social Research on Alcohol and Drugs. 27: 361–373. doi:10.1080/09595230802093778.
- "'A crisis of masculinity': men are struggling to cope with life". The Daily Telegraph. 19 Nov 2014. Retrieved 2014-11-20.
- Lester, Patterns, Table 3.3, pp. 31-33
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on January 22, 2012. Retrieved November 16, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Barraclough BM (1987). "Sex ratio of juvenile suicide". J Am Acad Child Adolescent Psychiatry. 26 (3): 434–5. doi:10.1097/00004583-198705000-00027. PMID 3496328.
- ^ Barlow, D. H., and V. M. Durand. Abnormal psychology, an integrative approach. Wadsworth Pub Co, 2011. Print.
- Zhang, J., Jiang, Chao., Jia, S., Wieckorek, W.F., Arch Suicide Res. 2002; 6(2): 167–184.
| Sex differences in humans | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biology |  | |
| Medicine and Health | ||
| Neuroscience and Psychology | ||
| Sociology | ||