This is an old revision of this page, as edited by NeilN (talk | contribs) at 00:29, 27 November 2017 (Configured pending changes settings for Scrotum: Persistent vandalism (expires 00:29, 27 November 2018 (UTC))). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:29, 27 November 2017 by NeilN (talk | contribs) (Configured pending changes settings for Scrotum: Persistent vandalism (expires 00:29, 27 November 2018 (UTC)))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) An accepted version of this page, accepted on 27 November 2017, was based on this revision.For the obsolete dinosaur fossil name, see Megalosaurus § "Scrotum humanum".| Scrotum | |
|---|---|
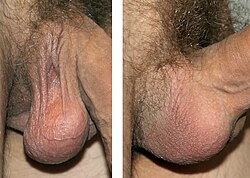 Human scrotum in a relaxed state (left) and a tense state (right) Human scrotum in a relaxed state (left) and a tense state (right) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Labioscrotal folds |
| Artery | Anterior scrotal artery & Posterior scrotal artery |
| Vein | Testicular vein |
| Nerve | Posterior scrotal nerves, Anterior scrotal nerves, genital branch of genitofemoral nerve, perineal branches of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |
| Lymph | Superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Scrotum |
| MeSH | D012611 |
| TA98 | A09.4.03.001 A09.4.03.004 |
| TA2 | 3693 |
| FMA | 18252 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The scrotum is an anatomical male reproductive structure that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sack of skin and smooth muscle that is present in most terrestrial male mammals and located under the penis. One testis is typically lower than the other, which functions to avoid compression in the event of impact. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein and pampiniform plexus. In humans and some other mammals, the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperature.
The scrotum is biologically homologous to the labia majora in females. Although present in most mammals, the external scrotum is absent in streamlined marine mammals, such as whales and seals, as well as in some lineages of land mammals, such as the afrotherians, xenarthrans, and numerous families of bats, rodents, and insectivores.
Structure
Innervation
| Nerve | Surface |
|---|---|
| Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve | anterolateral |
| Anterior scrotal nerves (from ilioinguinal nerve) | anterior |
| Posterior scrotal nerves (from perineal nerve) | posterior |
| perineal branches of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve | inferior |
Blood supply
| Blood vessels | |
|---|---|
| Anterior scrotal artery | |
| Posterior scrotal artery | |
| Testicular artery |
Integument
| Skin associated tissues | |
|---|---|
| Hair | |
| Sebaceous glands | |
| Apocrine glands | |
| Smooth muscle |
The skin on the scrotum is more highly pigmented compared to the rest of the body. The septum is a connective tissue membrane dividing the scrotum into two cavities.
Lymphatic system
The scrotum lymph drains initially into the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, this then drains into the deep inguinal lymph nodes. The deep inguinal lymph nodes drain into the common iliac which ultimately releases lymph into the cisterna chyli.
| Lymphatic vessels | |
|---|---|
| Superficial inguinal lymph nodes | |
| Popliteal lymph nodes | |
| Popliteal lymph nodes |
Development

Genital homology between sexes
Main article: Sexual homologyMale sex hormones are secreted by the testes later in embryonic life to cause the development of secondary sex organs. The scrotum is developmentally homologous to the labia minora and labia majora. The raphe does not exist in females. Reproductive organs and tissues develop in females and males begin during the fifth week after fertilization. The gonadal ridge grows behind the peritoneal membrane. By the sixth week, string-like tissues called primary sex cords form within the enlarging gonadal ridge. Externally, a swelling called the genital tubercule appears over the cloacal membrane.
Up until the eighth week after fertilization, the reproductive organs do not appear to be different between the male and female and are called in-differentiated. Testosterone secretion starts during week eight, reaches peak levels during week 13 and eventually declines to very low levels by the end of the second trimester. The testosterone causes the masculinization of the labioscrotal folds into the scrotum. The scrotal raphe is formed when the embryonic, urethral groove closes by week 12.
Asymmetry
One testis is typically lower than the other, which is believed to function to avoid compression in the event of impact; in humans, the left testis is typically lower than the right. An alternative view is that testis descent asymmetry evolved to enable more effective cooling of the testicles.
Scrotal growth and puberty
Though the testes and scrotum form early in embryonic life, sexual maturation begins upon entering puberty. The increased secretion of testosterone causes the darkening of the skin and development of pubic hair on the scrotum.
Internal structure
Additional tissues and organs reside inside the scrotum and are described in more detail in the following articles:
- Appendix of epididymidis
- Cavity of tunical albuginea
- Cremaster muscle
- Dartos
- Ductus Deferens
- Efferent ductules
- Epididymis
- Leydig cell
- Lobule of testes
- Paradidymis
- Rete testes
- Scrotal septum
- Seminiferous tubule
- Sertoli cell
- Spermatic cord
- Testes
- Tunica albuginea of testis
- Tunica vaginalis parietal layer
- Tunica vaginalis visceral layer
- Tunica vasculosa testis
- Vas deferens
Function

The scrotum regulates the temperature of the testes and maintains it at 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit), i.e. two degrees below the body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit). Higher temperatures affect spermatogenesis Temperature control is accomplished by the smooth muscles of the scrotum moving the testicles either closer to or further away from the abdomen dependent upon the ambient temperature. This is accomplished by the cremaster muscle in the abdomen and the dartos fascia (muscular tissue under the skin).

Having the scrotum and testicles situated outside the abdominal cavity may provide additional advantages. The external scrotum is not affected by abdominal pressure. This may prevent the emptying of the testes before the sperm were matured sufficiently for fertilization. Another advantage is it protects the testes from jolts and compressions associated with an active lifestyle. Animals that have stately movements – such as elephants, whales, and marsupial moles – have internal testes and no scrotum. Unlike placental mammals, male marsupials have a scrotum that is anterior to the penis. In some sex positions, such as doggystyle the scrotum may provide friction for the clitoris, and may subsequently serve as an impetus for sexual pleasure or orgasm in the woman.
Clinical significance
A study has indicated that use of a laptop computer positioned on the lap can negatively affect sperm production.
Diseases and conditions
The scrotum and its contents can develop diseases or incur injuries. These include:
- Candidiasis (yeast infection)
- sebaceous cyst
- epidermal cyst
- hydrocele
- hematocele
- Molluscum contagiosum
- spermatocele
- Paget's disease of the scrotum
- varicocele
- inguinal hernia
- epididymo-orchitis
- testicular torsion
- genital warts
- testicular cancer
- dermatitis
- undescended testes
- Chyloderma
- mumps
- scabies
- herpes
- pubic lice
- Chancroid (Haemophilus ducreyi)
- Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis)
- Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
- Granuloma inguinale or (Klebsiella granulomatis)
- Syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
- scrotum eczema
- scrotal psoriasis disease
- Riboflavin deficiency
See also
This article uses anatomical terminology.- Scrotal infusion, a temporary form of body modification
- Sex organ
- Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection
- Testicular self-examination
Bibliography
- Books
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1237 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1237 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)- Van De Graaff, Kent M.; Fox, Stuart Ira (1989). Concepts of Human Anatomy and Physiology. Dubuque, Iowa: William C. Brown Publishers. ISBN 0697056759.
- Elson, Lawrence; Kapit, Wynn (1977). The Anatomy Coloring. New York, New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0064539148.
- "Gross Anatomy Image". Medical Gross Anatomy Atlas Images. University of Michigan Medical School. 1997. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- Berkow, MD, editor, Robert (1977). The Merck Manual of Medical Information; Home Edition. Whitehouse Station, New Jersey: Merck Research Laboratories. ISBN 0911910875.
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
References
- ^ Anthony F.Bogaert, "Genital asymmetry in men", Human Reproduction vol.12 no.1 pp.68–72, 1997. PMID 9043905.
- "Scrotum". National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 6 January 2011.
- Lovegrove, B.G. 2015. "Cool sperm: why some placental mammals have a scrotum." Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 27(5):801-814. doi: 10.1111/jeb.12373
- Moore, Keith; Anne Agur (2007). Essential Clinical Anatomy, Third Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 132. ISBN 0-7817-6274-X.
- ^ Elson 1977. sfn error: no target: CITEREFElson1977 (help)
- "Scrotum". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- "VIII. The Lymphatic System. 5. The Lymphatics of the Lower Extremity. Gray, Henry. 1918. Anatomy of the Human Body". Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- Van de Graaff 1989, p. 927-931. sfn error: no target: CITEREFVan_de_Graaff1989 (help)
- Gallup, G. G., Jr., Finn, M. M., & Sammis, B. "On the origin of descended scrotal testicles: The activation hypothesis., Evolutionary Psychology, 7, 2009, p. 517-524.
- ^ Van de Graaff 1989, p. 935. sfn error: no target: CITEREFVan_de_Graaff1989 (help)
- ^ Van de Graaff 1989, p. 936. sfn error: no target: CITEREFVan_de_Graaff1989 (help)
- "Science : Bumpy lifestyle led to external testes - 17 August 1996 - New Scientist". New Scientist. Retrieved 2007-11-06.
- Hugh Tyndale-Biscoe; Marilyn Renfree (30 January 1987). Reproductive Physiology of Marsupials. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33792-2.
- Libbie Henrietta Hyman (15 September 1992). Hyman's Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. University of Chicago Press. pp. 583–. ISBN 978-0-226-87013-7.
- Menna Jones; Chris R. Dickman; Michael Archer (2003). Predators with Pouches: The Biology of Carnivorous Marsupials. Csiro Publishing. ISBN 978-0-643-06634-2.
- Jones, Richard (2013). Human Reproductive Biology. Academic Press. p. 74.
The rear-entry position of mating may allow the scrotum to stimulate the clitoris and, in this way, may produce an orgasm ...
- "Laptops may damage male fertility". BBC News. 2004-12-09. Retrieved 2012-01-30.
- Sheynkin, Yefim; et al. (February 2005). "Increase in scrotal temperature in laptop computer users". Hum. Reprod. 20 (2): 452–455. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh616. PMID 15591087.
- "Paget's disease of the scrotum Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes". RightDiagnosis.com. Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- "Common scrotal skin diseases". TCMWell. Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- ^ TCMwell. sfn error: no target: CITEREFTCMwell (help)
| Outline of human sexuality | |
|---|---|
| Physiology and biology | |
| Health and education | |
| Identity and diversity | |
| Law | |
| History | |
| Relationships and society |
|
| By country | |
| Sexual activities |
|
| Sex industry | |
| Religion and sexuality | |