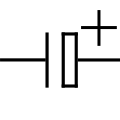This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Sbmeirow (talk | contribs) at 04:19, 22 December 2019 (→Further reading: fix). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 04:19, 22 December 2019 by Sbmeirow (talk | contribs) (→Further reading: fix)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices or functions, such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors, in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols are largely standardized internationally today, but may vary from country to country, or engineering discipline, based on traditional conventions.
Standards for symbols
The graphic symbols used for electrical components in circuit diagrams are covered by national and international standards, in particular:
- IEC 60617 (also known as British Standard BS 3939).
- There is also IEC 61131-3 - for ladder-logic symbols.
- JIC JIC (Joint Industrial Council) symbols as approved and adopted by the NMTBA (National Machine Tool Builders Association). They have been extracted from the Appendix of the NMTBA Specification EGPl-1967
- ANSI Y32.2-1975 (also known as IEEE Std 315-1975 or CSA Z99-1975)
- IEEE Std 91/91a: graphic symbols for logic functions (used in digital electronics). It is referenced in ANSI Y32.2/IEEE Std 315.
- Australian Standard AS 1102. (Based on a slightly modified version of IEC 60617, Withdrawn without replacement with a recommendation to use IEC 60617)
The number of standards leads to confusion and errors. Symbols usage is sometimes unique to engineering disciplines and national or local variations to international standards exist. For example, lighting and power symbols used as part of architectural drawings may be different from symbols for devices used in electronics.
Gallery of common electronic symbols
Symbols shown are typical examples, not a complete list.
Traces
-
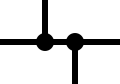 IEC-style trace junction
IEC-style trace junction
-
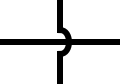 Trace crossing
Trace crossing
Grounds
Sources
-
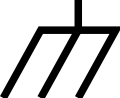
 Battery, single cell and multi-cell
Battery, single cell and multi-cell
-
 Battery, multi-cell
Battery, multi-cell
-
 Voltage source
Voltage source
-
 Controlled voltage source
Controlled voltage source
-
 Current source
Current source
-
 Controlled current source
Controlled current source
-
 AC voltage source
AC voltage source
Resistors
-
 (a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are American style symbols)
(a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are American style symbols)
-
 (a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are IEC style symbols)
(a) resistor, (b) rheostat (variable resistor), and (c) potentiometer (All of them are IEC style symbols)
-
 Thermistor or Varistor
Thermistor or Varistor
Capacitors
-
 IEC-style capacitor, general symbol
IEC-style capacitor, general symbol
-
 Capacitor, polarized (American)
Capacitor, polarized (American)
-
 Capacitor, variable
Capacitor, variable
-
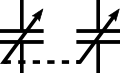 IEC-style ganged (co-moving) variable capacitors
IEC-style ganged (co-moving) variable capacitors
-
 Trimmer capacitor
Trimmer capacitor
Diodes
-
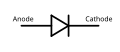 Diode
Diode
-
 Zener diode
Zener diode
-
 Tunnel diode
Tunnel diode
-
 Schottky diode
Schottky diode
-
 Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
-
 Photodiode
Photodiode
-
 Varicap
Varicap
-
 Shockley diode
Shockley diode
-
 Silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR)
Silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR)
-
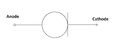 Constant-current diode
Constant-current diode
Inductors
Transformers
-
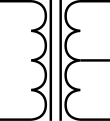 Transformer with center tap
Transformer with center tap
-
 Transformer with two secondary windings
Transformer with two secondary windings
-
 Current Transformer
Current Transformer
-
 Zero-Sequence Current Transformer (ZSCT) (also known as a window-type current transformer)
Zero-Sequence Current Transformer (ZSCT) (also known as a window-type current transformer)
-
 Bushing-Type Current Transformer
Bushing-Type Current Transformer
-
 Voltage Transformer
Voltage Transformer
Transistors
Unipolar
-
 N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
-
 P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
-
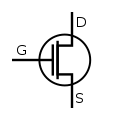 Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
-
 Enhancement mode, N-channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, N-channel MOSFET
-
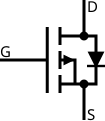 Enhancement mode, P-channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, P-channel MOSFET
Bipolar
-
 NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
-
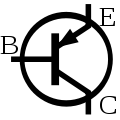 PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
-
 NPN darlington
NPN darlington
-
 PNP darlington
PNP darlington
Vacuum tubes
-
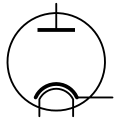 Vacuum tube diode
Vacuum tube diode
-
 Vacuum tube triode
Vacuum tube triode
-
 Vacuum tube tetrode
Vacuum tube tetrode
-
 Vacuum tube pentode
Vacuum tube pentode
Switches
-
 Switch, Single Pole/Single Throw (SPST)
Switch, Single Pole/Single Throw (SPST)
-
 Switch, Single Pole/Double Throw (SPDT)
Switch, Single Pole/Double Throw (SPDT)
-
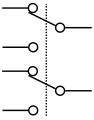 Switch, Double Pole/Double Throw (DPDT)
Switch, Double Pole/Double Throw (DPDT)
-
 Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, make (IEEE Std 315)
Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, make (IEEE Std 315)
-
 Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, break (IEEE Std 315)
Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, break (IEEE Std 315)
-
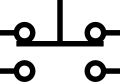 Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, two circuit (IEEE Std 315)
Pushbutton, Momentary or Spring-Return, two circuit (IEEE Std 315)
Relays
-
 American-style relays, SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT
American-style relays, SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT
-
 IEC relay symbol, SPDT
IEC relay symbol, SPDT
Lamps
-
 Indicating lamp (IEEE Std 315-1975)
Indicating lamp (IEEE Std 315-1975)
-
 Incandescent lamp
Incandescent lamp
-
 Incandescent light bulb (as an indicator)
Incandescent light bulb (as an indicator)
-
 Neon lamp
Neon lamp
-
 Light bulb
Light bulb
Current limiters
-
 IEC Fuse (b), equivalent symbols (a,c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
IEC Fuse (b), equivalent symbols (a,c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
-
 Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
-
 Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Electro-acoustic devices
-
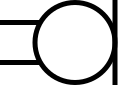 IEC-style microphone
IEC-style microphone
-
 Microphone (IEEE Std 315)
Microphone (IEEE Std 315)
-
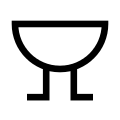 Buzzer
Buzzer
-
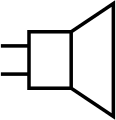 Loudspeaker (IEEE Std 315)
Loudspeaker (IEEE Std 315)
Antennas
Miscellaneous devices
-
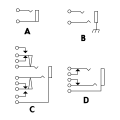 Phone jacks
Phone jacks
-
 Operational amplifier
Operational amplifier
-
 Ferrite bead ring (IEEE Std 315)
Ferrite bead ring (IEEE Std 315)
-
 Crystal oscillator
Crystal oscillator
-
 Hall effect sensor
Hall effect sensor
Gallery of historical electronic symbols
The shape of electronic symbols have changed over time. Some symbols were more prevalent in some countries. The following are historic electronic symbols that might be found in old electronic books and schematics.
Capacitors (historical)
See also
References
- Guidelines for Drawing Schematics
- Circuit Symbols for all Electronic Components. Talking Electronics, 2013. Retrieved 01 Apr 2015.
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic Symbols. RapidTables, 2012. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
Further reading
- How to Read Electronic Circuit Diagrams; 2nd Ed; Brown, Lawrence, Whitson; Tab Books; 214 pages; 1988; ISBN 978-0830628803.
- How to Read Schematic Diagrams; 4th Ed; Donald Herrington; Sams Publishing; 160 pages; 1986; ISBN 978-0672224577. (2nd Ed in 1973)
External links
- IEEE Standard American National Standard Canadian Standard Graphic Symbols for Electrical and Electronics Diagrams (Including Reference Designation Letters)
- International standard IEC 60617 DB Graphical symbols for diagrams
- Electrical Schematic Symbols
- Collection of Open Source Electrical, Pneumatic, Hydraulic and Electronic Symbols
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic Components
- Electrical & Electronic Drawing Symbols
- Collection of Electrical and Electronic Symbols
- Circuit Schematic Symbols
- Collection of Electrical and Electronic Schematic Symbols