This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) at 13:24, 3 June 2020 (Added FDA UNII). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 13:24, 3 June 2020 by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) (Added FDA UNII)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)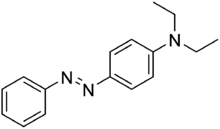
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Solvent yellow 56 C.I. 11021 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.834 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H19N3 |
| Molar mass | 253.349 g·mol |
| Melting point | 168 °C (334 °F; 441 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Solvent Yellow 56 is the organic compound N,N-diethyl-p-(phenylazo)aniline. It is an azo dye, which has the appearance of a reddish yellow powder. Its EINECS number is 219-616-8. Its structure is similar to Solvent Yellow 124, which used as a fuel dye in European Union, and to Aniline Yellow.
Uses
It is used to dye hydrocarbon solvents, oils, fats, waxes (candles), notably petrol, mineral oil and shoe polishes, and polystyrene resins. In pyrotechnics, it is used in some yellow colored smokes, reflecting its tendency to sublime.
References
- ^ Hunger, Klaus; Mischke, Peter; Rieper, Wolfgang; Raue, Roderich; Kunde, Klaus; Engel, Aloys (2005). "Azo Dyes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_245. ISBN 978-3527306732.