The page "Deep-marine+sediments" does not exist. You can create a draft and submit it for review or request that a redirect be created, but consider checking the search results below to see whether the topic is already covered.
View (previous 20 | next 20) (20 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 500) Marine sediment bioturbation have been found in marine sediments from tidal, coastal and deep sea sediments. In addition sand dune, or Eolian, sediments are important for preserving... 109 KB (12,371 words) - 09:42, 22 December 2024
Marine sediment bioturbation have been found in marine sediments from tidal, coastal and deep sea sediments. In addition sand dune, or Eolian, sediments are important for preserving... 109 KB (12,371 words) - 09:42, 22 December 2024Pelagic sediment particles produced in surface waters. In case of marine sediments, ooze does not refer to a sediment's consistency, but to its composition, which directly... 9 KB (919 words) - 16:42, 2 October 2024
 Seabed (redirect from Marine floor) oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. Categorized by where the materials come from or composition, these sediments are classified as either: from... 26 KB (4,423 words) - 06:49, 30 December 2024
Seabed (redirect from Marine floor) oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. Categorized by where the materials come from or composition, these sediments are classified as either: from... 26 KB (4,423 words) - 06:49, 30 December 2024 Sediment till are ice-transported sediments. Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain shape, and composition. Sediment size is measured on a log... 22 KB (2,833 words) - 15:30, 8 January 2025
Sediment till are ice-transported sediments. Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain shape, and composition. Sediment size is measured on a log... 22 KB (2,833 words) - 15:30, 8 January 2025- Omnitrophica These bacteria appear to thrive in anoxic environments, such as deep marine sediments, hypersaline environments, freshwater lakes, aquifers, flooded soils... 2 KB (178 words) - 18:01, 20 October 2024
 Deep biosphere carbon can reach the seafloor and be available to the deep biosphere. Deeper in the marine sediments, the organic content drops further. Phosphorus is taken... 83 KB (9,542 words) - 01:22, 11 December 2024
Deep biosphere carbon can reach the seafloor and be available to the deep biosphere. Deeper in the marine sediments, the organic content drops further. Phosphorus is taken... 83 KB (9,542 words) - 01:22, 11 December 2024 Fauna (redirect from Marine fauna) disturb the sediment. The deepest burrowers are the ghost shrimps (Thalassinidea), which go as deep as 3 metres (10 ft) into the sediment at the bottom... 11 KB (1,204 words) - 18:48, 16 October 2024
Fauna (redirect from Marine fauna) disturb the sediment. The deepest burrowers are the ghost shrimps (Thalassinidea), which go as deep as 3 metres (10 ft) into the sediment at the bottom... 11 KB (1,204 words) - 18:48, 16 October 2024 Orogeny front and early deposited foreland basin sediments become progressively involved in folding and thrusting. Sediments deposited in the foreland basin are mainly... 38 KB (4,243 words) - 15:11, 13 December 2024
Orogeny front and early deposited foreland basin sediments become progressively involved in folding and thrusting. Sediments deposited in the foreland basin are mainly... 38 KB (4,243 words) - 15:11, 13 December 2024Sedimentary rock (redirect from Sediment bed) Compaction takes place as the sediments come under increasing overburden (lithostatic) pressure from overlying sediments. Sediment grains move into more compact... 64 KB (7,833 words) - 13:41, 29 December 2024
 Siliceous ooze (section Export of silica to the deep ocean) type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the deep ocean floor. Siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments, and make up approximately... 25 KB (3,119 words) - 01:30, 29 December 2024
Siliceous ooze (section Export of silica to the deep ocean) type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the deep ocean floor. Siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments, and make up approximately... 25 KB (3,119 words) - 01:30, 29 December 2024 Penninic were formed. They are characteristically ophiolite sequences and deep marine sediments, metamorphosed to phyllites, schists and amphibolites. Middle Penninic... 6 KB (721 words) - 07:40, 9 October 2024
Penninic were formed. They are characteristically ophiolite sequences and deep marine sediments, metamorphosed to phyllites, schists and amphibolites. Middle Penninic... 6 KB (721 words) - 07:40, 9 October 2024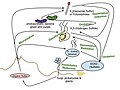 Sulfur cycle (redirect from Marine sulfur cycle) sulfur sink is pyrite burial in shelf sediments or deep seafloor sediments (4×1010 kg/a; δ34S = −20‰). The total marine sulfur output flux is 1.0×1011 kg/a... 61 KB (7,394 words) - 15:01, 9 December 2024
Sulfur cycle (redirect from Marine sulfur cycle) sulfur sink is pyrite burial in shelf sediments or deep seafloor sediments (4×1010 kg/a; δ34S = −20‰). The total marine sulfur output flux is 1.0×1011 kg/a... 61 KB (7,394 words) - 15:01, 9 December 2024 Marine habitat Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and... 70 KB (8,470 words) - 07:22, 5 January 2025
Marine habitat Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and... 70 KB (8,470 words) - 07:22, 5 January 2025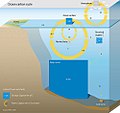 Oceanic carbon cycle (redirect from Marine carbon cycle) as well as the largest loss of carbon from the oceanic system. Deep marine sediments and geologic formations are important since they provide a thorough... 60 KB (6,479 words) - 04:09, 6 January 2025
Oceanic carbon cycle (redirect from Marine carbon cycle) as well as the largest loss of carbon from the oceanic system. Deep marine sediments and geologic formations are important since they provide a thorough... 60 KB (6,479 words) - 04:09, 6 January 2025 Flysch flysch was deposited by rivers. The insight that flysch is actually a deep marine sediment typical for a particular plate tectonic setting came only much later... 5 KB (564 words) - 11:52, 8 November 2023
Flysch flysch was deposited by rivers. The insight that flysch is actually a deep marine sediment typical for a particular plate tectonic setting came only much later... 5 KB (564 words) - 11:52, 8 November 2023- Micromonospora profundi bacterium from the genus Micromonospora which has been isolated from deep marine sediments from the Black Sea. Veyisoglu, A; Carro, L; Cetin, D; Guven, K;... 2 KB (114 words) - 21:31, 24 November 2024
 Gammaproteobacteria Dong H, Ji S, Ye Y, Wu N (2007-09-26). "Microbial Diversity in the Deep Marine Sediments from the Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea". Geomicrobiology... 37 KB (3,702 words) - 18:14, 28 December 2024
Gammaproteobacteria Dong H, Ji S, Ye Y, Wu N (2007-09-26). "Microbial Diversity in the Deep Marine Sediments from the Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea". Geomicrobiology... 37 KB (3,702 words) - 18:14, 28 December 2024 Challenger Deep Ashura, to sample sediments and biologics at the bottom of the Challenger Deep. The principal investigator at the Challenger Deep was Taishi Tsubouchi... 174 KB (19,929 words) - 02:38, 29 December 2024
Challenger Deep Ashura, to sample sediments and biologics at the bottom of the Challenger Deep. The principal investigator at the Challenger Deep was Taishi Tsubouchi... 174 KB (19,929 words) - 02:38, 29 December 2024 Marine biology Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and... 42 KB (4,590 words) - 22:35, 7 January 2025
Marine biology Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and... 42 KB (4,590 words) - 22:35, 7 January 2025 Frederick Colwell August 2002). "Microbial Communities from Methane Hydrate-Bearing Deep Marine Sediments in a Forearc Basin". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 68... 5 KB (567 words) - 06:09, 10 May 2024
Frederick Colwell August 2002). "Microbial Communities from Methane Hydrate-Bearing Deep Marine Sediments in a Forearc Basin". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 68... 5 KB (567 words) - 06:09, 10 May 2024
- Texts from WikisourceCambrian Geology and Paleontology/Volume 2/Abrupt appearance of the Cambrian Fauna on the North American Continent non-marine deposition of the later Algonkian sediments and the period of erosion preceding the deposition of the superjacent Cambrian sediments, is unknownSee all results
- Quotes from WikiquoteSeaweed farming change. Seaweed farms release carbon that may be buried in sediments or exported to the deep sea, therefore acting as a CO2 sink. The crop can also beSee all results
- Textbooks from WikibooksHistorical Geology/Marine sediments This article contains a short general discussion of marine sediments and some important terms and concepts relating to this field. We need not in thisSee all results