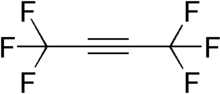
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,1,1,4,4,4-Hexafluorobut-2-yne | |
| Other names HFB | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.667 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4F6 |
| Molar mass | 162.034 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Density | 1.602 g/cm |
| Melting point | −117 °C (−179 °F; 156 K) |
| Boiling point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Structure | |
| Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Toxic gas |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H331 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P311, P410+P403 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate Hexachlorobutadiene Acetylene |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Hexafluoro-2-butyne (HFB) is a fluorocarbon with the chemical structure CF3C≡CCF3. HFB is a particularly electrophilic acetylene derivative, and hence a potent dienophile for Diels–Alder reactions.
Synthesis and reactions
HFB is prepared by the action of sulfur tetrafluoride on acetylenedicarboxylic acid or by the reaction of potassium fluoride (KF) with hexachlorobutadiene.
It reacts with sulfur to give 3,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete.
Cycloaddition of HFB and dithionitronium (NS2) gives the 1,2,5-dithiazolium cation. This derivative can be reduced to the 7 electron neutral radical. This particular 1,3,5-dithiazole is also rare example of a radical that can be obtained as solid, liquid, and gaseous states. As a gas, it is blue.
References
- "Hexafluoro-2-butyne 99%". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Essers, Michael; Haufe, Günter (2006). "Hexafluoro-2-butyne". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00669. ISBN 0471936235.
- E S Turbanova, A A Petrov (1991). "Perfluoroalkyl(aryl)acetylenes". Russian Chemical Reviews. 60 (5): 501–523. Bibcode:1991RuCRv..60..501T. doi:10.1070/RC1991v060n05ABEH001092.
- Brownridge, Scott; Du, Hongbin; Fairhurst, Shirley A.; Haddon, Robert C.; Oberhammer, Heinz; Parsons, Simon; Passmore, Jack; Schriver, Melbourne J.; Sutcliffe, Leslie H.; Westwood, Nicholas P. C. (2000). "The Isolation, Characterisation, Gas Phase Electron Diffraction and Crystal Structure of the Thermally Stable Radical CF3CSNSCCF3". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (19): 3365–3382. doi:10.1039/B001489N.