| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "1-Nonyl-4-phenol" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2023) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
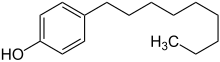
| Preferred IUPAC name 4-Nonylphenol | |
| Other names Phenol, nonyl-; 4-Nonylphenol; p-Nonylphenol; para-Nonylphenol; p-n-Nonylphenol; 4-n-Nonylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.909 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H24O |
| Molar mass | 220.356 g·mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Density | 0.94 |
| Melting point | 43 to 45 °C (109 to 113 °F; 316 to 318 K) |
| Boiling point | 180 to 181 °C (356 to 358 °F; 453 to 454 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
1-Nonyl-4-phenol is an organic compound consisting of an n-nonyl group attached to the 4-position of phenol. The related nonylphenols with branched nonyl groups are commercially important detergents. It is used with mixed-metals stabilizers for heat stabilization of plastic and is a starting material for producing phenol resins. It's insoluble in water, but soluble in organic compounds like benzene and heptane.
References
- "4-Nonylphenol". Retrieved 14 May 2024.