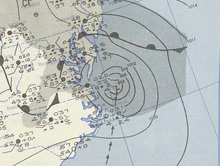
 Surface weather analysis of the system as a non-frontal low on February 3 while crossing the Florida Peninsula Surface weather analysis of the system as a non-frontal low on February 3 while crossing the Florida Peninsula | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | February 3, 1952 |
| Extratropical | February 4, 1952 |
| Dissipated | February 5, 1952 |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 70 mph (110 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 990 mbar (hPa); 29.23 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None reported |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | Yucatan Peninsula, Cuba, Florida, The Bahamas, East Coast of the United States |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1952 Atlantic hurricane season | |
The 1952 Groundhog Day Storm is one of two Atlantic tropical cyclones on record in February. First observed in the western Caribbean Sea on February 2 as a non-frontal low, it moved rapidly throughout its duration and struck southwestern Florida early the next day as a gale-force storm. In the state, the winds damaged some crops and power lines, but no serious damage was reported. The system became a tropical storm after emerging over the Atlantic Ocean before quickly transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on February 4. Strong winds and waves washed a freighter ashore, but no injuries were related to the event. Subsequently, the storm brushed eastern New England, causing minor power outages, before it moved inland near Maine. There were no reported fatalities related to the storm.
Meteorological history
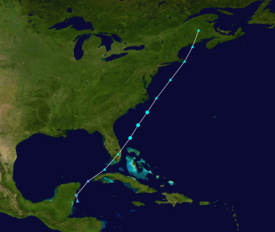
Map key Saffir–Simpson scale Tropical depression (≤38 mph, ≤62 km/h)
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown Storm type
 Tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone  Subtropical cyclone
Subtropical cyclone  Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression
Extratropical cyclone, remnant low, tropical disturbance, or monsoon depression On February 2, Groundhog Day, a disturbance was first observed in the western Caribbean Sea. Winds were estimated at 35 mph (56 km/h), and it tracked rapidly northward, initially to the north-northwest. After passing near Cancún along the Yucatan Peninsula, it turned northeastward and brushed the northwest coast of Cuba. Early on February 3, the storm approached Key West, and shortly thereafter moved ashore near Cape Sable, Florida. It quickly crossed the state, passing near Miami before emerging into the western Atlantic Ocean. The Miami National Weather Service office recorded a wind gust of 84 mph (135 km/h), as well as sustained tropical storm force winds for about four hours; the station also recorded a barometric pressure of 1004 mbar (29.66 inHg).
After leaving Florida, the storm continued rapidly northeastward and transitioned into a tropical cyclone. Late on February 3, it reached its peak strength with maximum sustained winds of 70 mph (110 km/h). On February 4, it completed the transition into an extratropical cyclone off the coast of North Carolina. Around that time, gale-force winds extended 100 miles (160 km) to the east of the center. Later that day, it passed over Cape Cod, and early on February 5, it moved into eastern Maine. The Hurricane Research Division assessed the storm as losing its identity shortly thereafter, over New Brunswick. However, a map produced by the U.S. Weather Bureau indicated that the storm continued northward into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and later crossed eastern Quebec and Labrador. By February 6, it reached the ocean again, deepening to a minimum pressure of 988 millibars (29.2 inHg). At that point, the Weather Bureau track ended, and as such the ultimate fate of the storm is unknown.
Impact and records
Residents and tourists in southern Florida were unprepared for the unusual off-season storm. Winds of up to 65 mph (105 km/h) spread across the area, causing damage to windows and power lines. The storm dropped 2–4 inches (51–102 millimetres) of precipitation along its path; the combination of unseasonable rainfall and winds resulted in crop damage in Miami-Dade County.
After the storm moved into the western Atlantic, the Miami U.S. Weather Bureau issued storm warnings for the North Carolina coastline from Wilmington to Cape Hatteras; the region was warned to prepare for strong winds. The agency also issued a small craft advisory southward through Charleston, South Carolina. Offshore, the storm produced winds of up to 85 mph (137 km/h), as well as waves up to 35 feet (11 m) in height. The combination of the winds and rough waves drove a freighter ashore along Portsmouth Island in the Outer Banks, after the engine was damaged when water entered the fuel line. The 26 person crew initially planned to evacuate, but they later decided to stay on the freighter as the U.S. Coast Guard were deployed to assist. The seas damaged a portion of the ship, but the entire crew was rescued without any injuries. The storm later brushed New England, bringing rain, fog, warmer temperatures, and gusty winds. The combination resulted in downed power poles and tree limbs, leaving 10,000 houses without electricity.
The storm was described as a "freak", forming about three months after the end of the hurricane season. The chief forecaster at Miami U.S. Weather Bureau, Grady Norton, remarked that he was unsure how the cyclone developed. It is the only tropical or subtropical storm on record during February, and was the earliest tropical cyclone to strike the United States. Its structure initially was uncertain, and the storm was not included in the 1952 Atlantic hurricane season summary published by the Miami Weather Bureau office. Ultimately it was included in the tropical cyclone database. Had it been operationally treated as a tropical cyclone, it would have been named Tropical Storm Able.
See also
- List of off-season Atlantic hurricanes
- List of Florida hurricanes (1950–1974)
- Tropical Storm Ana (2015) – The earliest tropical cyclone on record to make landfall on the United States, in any given year
- Tropical Storm Alex (2022) - A storm with a similar track.
References
- ^ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved December 19, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Landsea, Chris (April 2022). "The revised Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT2) - Chris Landsea – April 2022" (PDF). Hurricane Research Division – NOAA/AOML. Miami: Hurricane Research Division – via Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory.
- ^ USAToday.com (2008). "Only February tropical storm hit Florida in 1952". USA Today. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ^ Staff Writer (1952-02-04). "Ship With 26 Is Wrecked Off Carolina As Gale From Atlantic Sweeps Up Coast". United Press. Archived from the original on 2001-08-13. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- Jay S. Winston (1952). "Weather and Circulation of February 1952" (PDF). Washington, D.C. Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ^ Staff Writer (1952-02-05). "Johnny Come Lately Winds High". United Press. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- Staff Writer (1952-02-04). "Cyclone Whirls Near Carolinas". United Press. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- Staff Writer (1952-02-05). "Hulk Wallows". Associated Press. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- Grady Norton (1953-01-12). "Hurricanes of 1952" (PDF). U.S. Weather Bureau Office in Miami. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
| Atlantic tropical cyclones in the off-season | |
|---|---|
| Pre-1850 | |
| 1850–99 | |
| 1900–49 | |
| 1950–74 | |
| 1975–99 | |
| 2000s | |
| 2010s | |
| 2020s | |
| Tropical cyclones of the 1952 Atlantic hurricane season | ||
|---|---|---|
 | TSOne 2Able 3Baker 3Charlie 1Dog 3Easy 4Fox | |