| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "2-Bromo-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2019) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
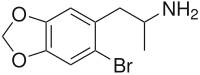
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-(6-Bromo-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)propan-2-amine | |
| Other names
2-Bromo-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine 2-(2-Bromo-4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl)ethan-1-methyl-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H17BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 275.166 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
2-Bromo-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine (6-Bromo-MDA) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dose is listed as 350 mg and the duration unknown. It produces stimulant effects but with no psychedelic or empathogenic action. Very little data exists about its pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity.
See also
References
This psychoactive drug-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |