
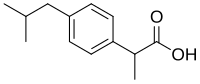
 Left: general chemical structure of profens (Ar = aryl group). Right: chemical structure of ibuprofen
Left: general chemical structure of profens (Ar = aryl group). Right: chemical structure of ibuprofen
The profens are a class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Profens are also known as 2-arylpropionic acids to reflect their chemical structure. The most common example of a profen is ibuprofen, which has been sold under the brand name Profen among others.
Other drugs in the class include:
- Alminoprofen
- Benoxaprofen
- Carprofen
- Dexibuprofen
- Dexketoprofen
- Fenoprofen
- Flunoxaprofen
- Flurbiprofen
- Indoprofen
- Ketoprofen
- Loxoprofen
- Miroprofen
- Naproxen
- Pelubiprofen
- Pirprofen
- Pranoprofen
- Suprofen
- Tarenflurbil
- Tiaprofenic acid
- Vedaprofen
- Zaltoprofen
References
- Evans, A. M. (1996). "Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the profens: Enantioselectivity, clinical implications, and special reference to S(+)-ibuprofen". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 36 (12 Suppl): 7S – 15S. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1996.tb00003.x. PMID 9013378. S2CID 26944804.
- Landoni, M.; Soraci, A. (2001). "Pharmacology of Chiral Compounds 2-Arylpropionic Acid Derivatives". Current Drug Metabolism. 2: 37–51. doi:10.2174/1389200013338810. PMID 11465150.
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (primarily M01A and M02A, also N02BA) | |
|---|---|
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams | |
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other | |
| NSAID combinations | |
| Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; WHO-Essential Medicines; withdrawn drugs; veterinary use. | |
This analgesic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |