| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid | |||
| Other names 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 2220661 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.278 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 5309 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C7H4N2O7 | ||
| Molar mass | 228.116 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | Yellow needles or plates | ||
| Melting point | 182 °C (360 °F; 455 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Soluble | ||
| Solubility in organic solvents | Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H318, H319, H335 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS or DNSA, IUPAC name 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid) is an aromatic compound that reacts with reducing sugars and other reducing molecules to form 3-amino-5-nitrosalicylic acid, which strongly absorbs light at 540 nm. It was first introduced as a method to detect reducing substances in urine by James B. Sumner and has since been widely used, for example, for quantifying carbohydrate levels in blood. It is mainly used in assay of alpha-amylase. However, enzymatic methods are usually preferred due to DNS's lack of specificity.
Synthesis
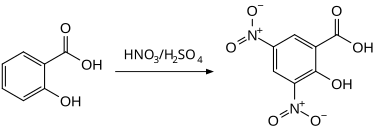
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid can be prepared by the nitration of salicylic acid.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 3–318. ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8.
- Sumner, J.B. Dinitrosalicylic acid: a reagent for the estimation of sugar in normal and diabetic urine. Journal of Biological Chemistry 47, 5, 1921.
- "Description of lab use from the Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maryland". Archived from the original on 2007-08-17. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- Miller, Gail Lorenz (1959). "Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar". Anal. Chem. 31 (3): 426–428. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030.
- Thiel, W.; Mayer, R.; Jauer, E.-A.; Modrow, H.; Dost, H.: Synthesis and Spectral Characterization of Blue Dyes of the Benzene Series in J. Prakt. Chem. (Leipzig) 328 (1986) 497-514, doi:10.1002/prac.19863280406.
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |