| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
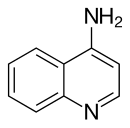
| Preferred IUPAC name Quinolin-4-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.771 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H8N2 |
| Molar mass | 144.177 g·mol |
| Appearance | Powder to crystalline, White/Yellow/Orange |
| Melting point | 151.0 to 155.0 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Causes skin and serious eye irritation |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
4-Aminoquinoline is a form of aminoquinoline with the amino group at the 4-position of the quinoline. The compound has been used as a precursor for the synthesis of its derivatives.
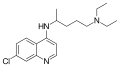
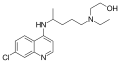
A variety of derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline are antimalarial agents useful in treating erythrocytic plasmodial infections. Examples include amodiaquine, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine. Other uses for the derivatives are: anti-asthmatic, antibacterial, anti-fungal, anti-malarial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory agents.
A patent application for 4-aminoquinoline compounds was filed in 2002 and published in 2005.
See also
References
- ^ Al-Ahmary KM, Alenezi MS, Habeeb MM (2016-08-01). "Synthesis, spectroscopic and DFT theoretical studies on the hydrogen bonded charge transfer complex of 4-aminoquinoline with chloranilic acid". Journal of Molecular Liquids. 220: 166–182. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.074. ISSN 0167-7322.
- Bosak A, Opsenica DM, Šinko G, Zlatar M, Kovarik Z (2019-08-01). "Structural aspects of 4-aminoquinolines as reversible inhibitors of human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase". Chemico-Biological Interactions. 308: 101–109. Bibcode:2019CBI...308..101B. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2019.05.024. ISSN 0009-2797. PMID 31100281. S2CID 157067252.
- Bray PG, Hawley SR, Ward SA (1996). "4-Aminoquinoline resistance of Plasmodium falciparum: insights from the study of amodiaquine uptake". Mol. Pharmacol. 50 (6): 1551–8. PMID 8967977.
- DeVita R, Chang L (13 January 2005). "4-Aminoquinoline Compounds" (PDF). United States Patent Application Publication.
External links
- Bourne SA, De Villiers K, Egan TJ (2006). "Three 4-aminoquinolines of antimalarial interest". Acta Crystallogr C. 62 (Pt 2): o53–7. Bibcode:2006AcCrC..62O..53B. doi:10.1107/S0108270105041235. PMID 16456284.
- "4-Aminoquinoline 578-68-7 | TCI America". www.tcichemicals.com. Retrieved 2020-03-06.
| Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – Chromalveolata antiparasitics (P01) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alveo- late |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stramen- opile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article about a heterocyclic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |