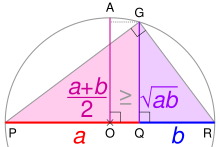
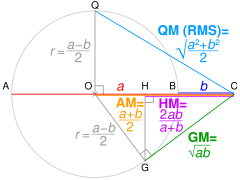
PR is the diameter of a circle centered on O; its radius AO is the arithmetic mean of a and b. Using the geometric mean theorem, triangle PGR's altitude GQ is the geometric mean. For any ratio a:b, AO ≥ GQ.
In mathematics, the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, or more briefly the AM–GM inequality, states that the arithmetic mean of a list of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list; and further, that the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same (in which case they are both that number).
The simplest non-trivial case is for two non-negative numbers x and y, that is,
with equality if and only if x = y. This follows from the fact that the square of a real number is always non-negative (greater than or equal to zero) and from the identity (a ± b) = a ± 2ab + b:
Hence (x + y) ≥ 4xy, with equality when (x − y) = 0, i.e. x = y. The AM–GM inequality then follows from taking the positive square root of both sides and then dividing both sides by 2.
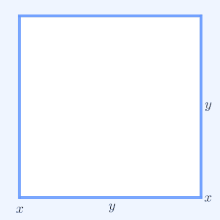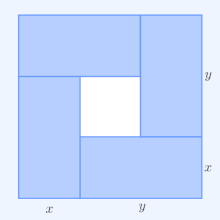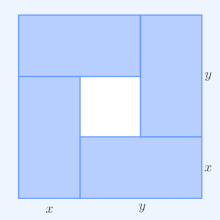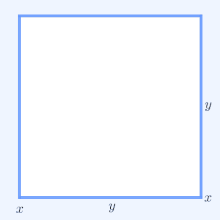
For a geometrical interpretation, consider a rectangle with sides of length x and y; it has perimeter 2x + 2y and area xy. Similarly, a square with all sides of length √xy has the perimeter 4√xy and the same area as the rectangle. The simplest non-trivial case of the AM–GM inequality implies for the perimeters that 2x + 2y ≥ 4√xy and that only the square has the smallest perimeter amongst all rectangles of equal area.
The simplest case is implicit in Euclid's Elements, Book 5, Proposition 25.
Extensions of the AM–GM inequality treat weighted means and generalized means.
Background
The arithmetic mean, or less precisely the average, of a list of n numbers x1, x2, . . . , xn is the sum of the numbers divided by n:
The geometric mean is similar, except that it is only defined for a list of nonnegative real numbers, and uses multiplication and a root in place of addition and division:
If x1, x2, . . . , xn > 0, this is equal to the exponential of the arithmetic mean of the natural logarithms of the numbers:
The inequality
Restating the inequality using mathematical notation, we have that for any list of n nonnegative real numbers x1, x2, . . . , xn,
and that equality holds if and only if x1 = x2 = · · · = xn.
Geometric interpretation
In two dimensions, 2x1 + 2x2 is the perimeter of a rectangle with sides of length x1 and x2. Similarly, 4√x1x2 is the perimeter of a square with the same area, x1x2, as that rectangle. Thus for n = 2 the AM–GM inequality states that a rectangle of a given area has the smallest perimeter if that rectangle is also a square.
The full inequality is an extension of this idea to n dimensions. Consider an n-dimensional box with edge lengths x1, x2, . . . , xn. Every vertex of the box is connected to n edges of different directions, so the average length of edges incident to the vertex is (x1 + x2 + · · · + xn)/n. On the other hand, is the edge length of an n-dimensional cube of equal volume, which therefore is also the average length of edges incident to a vertex of the cube.
Thus the AM–GM inequality states that only the n-cube has the smallest average length of edges connected to each vertex amongst all n-dimensional boxes with the same volume.
Examples
Example 1
If , then the AM-GM inequality tells us that
Example 2
A simple upper bound for can be found. AM-GM tells us
and so
with equality at .
Equivalently,
Example 3
Consider the function
for all positive real numbers x, y and z. Suppose we wish to find the minimal value of this function. It can be rewritten as:
with
Applying the AM–GM inequality for n = 6, we get
Further, we know that the two sides are equal exactly when all the terms of the mean are equal:
All the points (x, y, z) satisfying these conditions lie on a half-line starting at the origin and are given by
Applications
Cauchy-Schwarz inequality
The AM-GM equality can be used to prove the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality.
Annualized returns
In financial mathematics, the AM-GM inequality shows that the annualized return, the geometric mean, is less than the average annual return, the arithmetic mean.
Nonnegative polynomials
The Motzkin polynomial is a nonnegative polynomial which is not a sum of square polynomials. It can be proven nonnegative using the AM-GM inequality with , , and , that is, Simplifying and multiplying both sides by 3 gives so
Proofs of the AM–GM inequality
The AM–GM inequality can be proven in many ways.
Proof using Jensen's inequality
Jensen's inequality states that the value of a concave function of an arithmetic mean is greater than or equal to the arithmetic mean of the function's values. Since the logarithm function is concave, we have
Taking antilogs of the far left and far right sides, we have the AM–GM inequality.
Proof by successive replacement of elements
We have to show that
with equality only when all numbers are equal.
If not all numbers are equal, then there exist such that . Replacing xi by and xj by will leave the arithmetic mean of the numbers unchanged, but will increase the geometric mean because
If the numbers are still not equal, we continue replacing numbers as above. After at most such replacement steps all the numbers will have been replaced with while the geometric mean strictly increases at each step. After the last step, the geometric mean will be , proving the inequality.
It may be noted that the replacement strategy works just as well from the right hand side. If any of the numbers is 0 then so will the geometric mean thus proving the inequality trivially. Therefore we may suppose that all the numbers are positive. If they are not all equal, then there exist such that . Replacing by and by leaves the geometric mean unchanged but strictly decreases the arithmetic mean since
- . The proof then follows along similar lines as in the earlier replacement.
Induction proofs
Proof by induction #1
Of the non-negative real numbers x1, . . . , xn, the AM–GM statement is equivalent to
with equality if and only if α = xi for all i ∈ {1, . . . , n}.
For the following proof we apply mathematical induction and only well-known rules of arithmetic.
Induction basis: For n = 1 the statement is true with equality.
Induction hypothesis: Suppose that the AM–GM statement holds for all choices of n non-negative real numbers.
Induction step: Consider n + 1 non-negative real numbers x1, . . . , xn+1, . Their arithmetic mean α satisfies
If all the xi are equal to α, then we have equality in the AM–GM statement and we are done. In the case where some are not equal to α, there must exist one number that is greater than the arithmetic mean α, and one that is smaller than α. Without loss of generality, we can reorder our xi in order to place these two particular elements at the end: xn > α and xn+1 < α. Then
Now define y with
and consider the n numbers x1, . . . , xn–1, y which are all non-negative. Since
Thus, α is also the arithmetic mean of n numbers x1, . . . , xn–1, y and the induction hypothesis implies
Due to (*) we know that
hence
in particular α > 0. Therefore, if at least one of the numbers x1, . . . , xn–1 is zero, then we already have strict inequality in (**). Otherwise the right-hand side of (**) is positive and strict inequality is obtained by using the estimate (***) to get a lower bound of the right-hand side of (**). Thus, in both cases we can substitute (***) into (**) to get
which completes the proof.
Proof by induction #2
First of all we shall prove that for real numbers x1 < 1 and x2 > 1 there follows
Indeed, multiplying both sides of the inequality x2 > 1 by 1 – x1, gives
whence the required inequality is obtained immediately.
Now, we are going to prove that for positive real numbers x1, . . . , xn satisfying x1 . . . xn = 1, there holds
The equality holds only if x1 = ... = xn = 1.
Induction basis: For n = 2 the statement is true because of the above property.
Induction hypothesis: Suppose that the statement is true for all natural numbers up to n – 1.
Induction step: Consider natural number n, i.e. for positive real numbers x1, . . . , xn, there holds x1 . . . xn = 1. There exists at least one xk < 1, so there must be at least one xj > 1. Without loss of generality, we let k =n – 1 and j = n.
Further, the equality x1 . . . xn = 1 we shall write in the form of (x1 . . . xn–2) (xn–1 xn) = 1. Then, the induction hypothesis implies
However, taking into account the induction basis, we have
which completes the proof.
For positive real numbers a1, . . . , an, let's denote
The numbers x1, . . . , xn satisfy the condition x1 . . . xn = 1. So we have
whence we obtain
with the equality holding only for a1 = ... = an.
Proof by Cauchy using forward–backward induction
The following proof by cases relies directly on well-known rules of arithmetic but employs the rarely used technique of forward-backward-induction. It is essentially from Augustin Louis Cauchy and can be found in his Cours d'analyse.
The case where all the terms are equal
If all the terms are equal:
then their sum is nx1, so their arithmetic mean is x1; and their product is x1, so their geometric mean is x1; therefore, the arithmetic mean and geometric mean are equal, as desired.
The case where not all the terms are equal
It remains to show that if not all the terms are equal, then the arithmetic mean is greater than the geometric mean. Clearly, this is only possible when n > 1.
This case is significantly more complex, and we divide it into subcases.
The subcase where n = 2
If n = 2, then we have two terms, x1 and x2, and since (by our assumption) not all terms are equal, we have:
hence
as desired.
The subcase where n = 2
Consider the case where n = 2, where k is a positive integer. We proceed by mathematical induction.
In the base case, k = 1, so n = 2. We have already shown that the inequality holds when n = 2, so we are done.
Now, suppose that for a given k > 1, we have already shown that the inequality holds for n = 2, and we wish to show that it holds for n = 2. To do so, we apply the inequality twice for 2 numbers and once for 2 numbers to obtain:
where in the first inequality, the two sides are equal only if
and
(in which case the first arithmetic mean and first geometric mean are both equal to x1, and similarly with the second arithmetic mean and second geometric mean); and in the second inequality, the two sides are only equal if the two geometric means are equal. Since not all 2 numbers are equal, it is not possible for both inequalities to be equalities, so we know that:
as desired.
The subcase where n < 2
If n is not a natural power of 2, then it is certainly less than some natural power of 2, since the sequence 2, 4, 8, . . . , 2, . . . is unbounded above. Therefore, without loss of generality, let m be some natural power of 2 that is greater than n.
So, if we have n terms, then let us denote their arithmetic mean by α, and expand our list of terms thus:
We then have:
so
and
as desired.
Proof by induction using basic calculus
The following proof uses mathematical induction and some basic differential calculus.
Induction basis: For n = 1 the statement is true with equality.
Induction hypothesis: Suppose that the AM–GM statement holds for all choices of n non-negative real numbers.
Induction step: In order to prove the statement for n + 1 non-negative real numbers x1, . . . , xn, xn+1, we need to prove that
with equality only if all the n + 1 numbers are equal.
If all numbers are zero, the inequality holds with equality. If some but not all numbers are zero, we have strict inequality. Therefore, we may assume in the following, that all n + 1 numbers are positive.
We consider the last number xn+1 as a variable and define the function
Proving the induction step is equivalent to showing that f(t) ≥ 0 for all t > 0, with f(t) = 0 only if x1, . . . , xn and t are all equal. This can be done by analyzing the critical points of f using some basic calculus.
The first derivative of f is given by
A critical point t0 has to satisfy f′(t0) = 0, which means
After a small rearrangement we get
and finally
which is the geometric mean of x1, . . . , xn. This is the only critical point of f. Since f′′(t) > 0 for all t > 0, the function f is strictly convex and has a strict global minimum at t0. Next we compute the value of the function at this global minimum:
where the final inequality holds due to the induction hypothesis. The hypothesis also says that we can have equality only when x1, . . . , xn are all equal. In this case, their geometric mean t0 has the same value, Hence, unless x1, . . . , xn, xn+1 are all equal, we have f(xn+1) > 0. This completes the proof.
This technique can be used in the same manner to prove the generalized AM–GM inequality and Cauchy–Schwarz inequality in Euclidean space R.
Proof by Pólya using the exponential function
George Pólya provided a proof similar to what follows. Let f(x) = e – x for all real x, with first derivative f′(x) = e – 1 and second derivative f′′(x) = e. Observe that f(1) = 0, f′(1) = 0 and f′′(x) > 0 for all real x, hence f is strictly convex with the absolute minimum at x = 1. Hence x ≤ e for all real x with equality only for x = 1.
Consider a list of non-negative real numbers x1, x2, . . . , xn. If they are all zero, then the AM–GM inequality holds with equality. Hence we may assume in the following for their arithmetic mean α > 0. By n-fold application of the above inequality, we obtain that
with equality if and only if xi = α for every i ∈ {1, . . . , n}. The argument of the exponential function can be simplified:
Returning to (*),
which produces x1 x2 · · · xn ≤ α, hence the result
Proof by Lagrangian multipliers
If any of the are , then there is nothing to prove. So we may assume all the are strictly positive.
Because the arithmetic and geometric means are homogeneous of degree 1, without loss of generality assume that . Set , and . The inequality will be proved (together with the equality case) if we can show that the minimum of subject to the constraint is equal to , and the minimum is only achieved when . Let us first show that the constrained minimization problem has a global minimum.
Set . Since the intersection is compact, the extreme value theorem guarantees that the minimum of subject to the constraints and is attained at some point inside . On the other hand, observe that if any of the , then , while , and . This means that the minimum inside is in fact a global minimum, since the value of at any point inside is certainly no smaller than the minimum, and the value of at any point not inside is strictly bigger than the value at , which is no smaller than the minimum.
The method of Lagrange multipliers says that the global minimum is attained at a point where the gradient of is times the gradient of , for some . We will show that the only point at which this happens is when and
Compute and
along the constraint. Setting the gradients proportional to one another therefore gives for each that and so Since the left-hand side does not depend on , it follows that , and since , it follows that and , as desired.
Generalizations
Weighted AM–GM inequality
There is a similar inequality for the weighted arithmetic mean and weighted geometric mean. Specifically, let the nonnegative numbers x1, x2, . . . , xn and the nonnegative weights w1, w2, . . . , wn be given. Set w = w1 + w2 + · · · + wn. If w > 0, then the inequality
holds with equality if and only if all the xk with wk > 0 are equal. Here the convention 0 = 1 is used.
If all wk = 1, this reduces to the above inequality of arithmetic and geometric means.
One stronger version of this, which also gives strengthened version of the unweighted version, is due to Aldaz. Specifically, let the nonnegative numbers x1, x2, . . . , xn and the nonnegative weights w1, w2, . . . , wn be given. Assume further that the sum of the weights is 1. Then
- .
Proof using Jensen's inequality
Using the finite form of Jensen's inequality for the natural logarithm, we can prove the inequality between the weighted arithmetic mean and the weighted geometric mean stated above.
Since an xk with weight wk = 0 has no influence on the inequality, we may assume in the following that all weights are positive. If all xk are equal, then equality holds. Therefore, it remains to prove strict inequality if they are not all equal, which we will assume in the following, too. If at least one xk is zero (but not all), then the weighted geometric mean is zero, while the weighted arithmetic mean is positive, hence strict inequality holds. Therefore, we may assume also that all xk are positive.
Since the natural logarithm is strictly concave, the finite form of Jensen's inequality and the functional equations of the natural logarithm imply
Since the natural logarithm is strictly increasing,
Matrix arithmetic–geometric mean inequality
Most matrix generalizations of the arithmetic geometric mean inequality apply on the level of unitarily invariant norms, since, even if the matrices and are positive semi-definite, the matrix may not be positive semi-definite and hence may not have a canonical square root. In Bhatia and Kittaneh proved that for any unitarily invariant norm and positive semi-definite matrices and it is the case that
Later, in the same authors proved the stronger inequality that
Finally, it is known for dimension that the following strongest possible matrix generalization of the arithmetic-geometric mean inequality holds, and it is conjectured to hold for all
This conjectured inequality was shown by Stephen Drury in 2012. Indeed, he proved
Finance: Link to geometric asset returns
In finance much research is concerned with accurately estimating the rate of return of an asset over multiple periods in the future. In the case of lognormal asset returns, there is an exact formula to compute the arithmetic asset return from the geometric asset return.
For simplicity, assume we are looking at yearly geometric returns r1, r2, ... , rN over a time horizon of N years, i.e.
where:
- = value of the asset at time ,
- = value of the asset at time .
The geometric and arithmetic returns are respectively defined as
When the yearly geometric asset returns are lognormally distributed, then the following formula can be used to convert the geometric average return to the arithemtic average return:
where is the variance of the observed asset returns This implicit equation for aN can be solved exactly as follows. First, notice that by setting
we obtain a polynomial equation of degree 2:
Solving this equation for z and using the definition of z, we obtain 4 possible solutions for aN:
However, notice that
This implies that the only 2 possible solutions are (as asset returns are real numbers):
Finally, we expect the derivative of aN with respect to gN to be non-negative as an increase in the geometric return should never cause a decrease in the arithmetic return. Indeed, both measure the average growth of an asset's value and therefore should move in similar directions. This leaves us with one solution to the implicit equation for aN, namely
Therefore, under the assumption of lognormally distributed asset returns, the arithmetic asset return is fully determined by the geometric asset return.
Other generalizations
Other generalizations of the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means include:
- Muirhead's inequality,
- Maclaurin's inequality,
- QM-AM-GM-HM inequalities,
- Generalized mean inequality,
- Means of complex numbers.
See also
Notes
- If AC = a and BC = b. OC = AM of a and b, and radius r = QO = OG.
Using Pythagoras' theorem, QC² = QO² + OC² ∴ QC = √QO² + OC² = QM.
Using Pythagoras' theorem, OC² = OG² + GC² ∴ GC = √OC² − OG² = GM.
Using similar triangles, HC/GC = GC/OC ∴ HC = GC²/OC = HM.
References
- Hoffman, D. G. (1981), "Packing problems and inequalities", in Klarner, David A. (ed.), The Mathematical Gardner, Springer, pp. 212–225, doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-6686-7_19, ISBN 978-1-4684-6688-1
- "Euclid's Elements, Book V, Proposition 25".
- Steele, J. Michael (2004). The Cauchy-Schwarz Master Class: An Introduction to the Art of Mathematical Inequalities. MAA Problem Books Series. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-54677-5. OCLC 54079548.
- Motzkin, T. S. (1967). "The arithmetic-geometric inequality". Inequalities (Proc. Sympos. Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, 1965). New york: Academic Press. pp. 205–224. MR 0223521.
- Aaron Potechin, Sum of Squares seminar, University of Chicago, "Lecture 5: SOS Proofs and the Motzkin Polynomial", slide 25
- Cauchy, Augustin-Louis (1821). Cours d'analyse de l'École Royale Polytechnique, première partie, Analyse algébrique, Paris. The proof of the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means can be found on pages 457ff.
- Arnold, Denise; Arnold, Graham (1993). Four unit mathematics. Hodder Arnold H&S. p. 242. ISBN 978-0-340-54335-1. OCLC 38328013.
- Aldaz, J.M. (2009). "Self-Improvement of the Inequality Between Arithmetic and Geometric Means". Journal of Mathematical Inequalities. 3 (2): 213–216. doi:10.7153/jmi-03-21. Retrieved 11 January 2023.
- Bhatia, Rajendra; Kittaneh, Fuad (1990). "On the singular values of a product of operators". SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications. 11 (2): 272–277. doi:10.1137/0611018.
- Bhatia, Rajendra; Kittaneh, Fuad (2000). "Notes on matrix arithmetic-geometric mean inequalities". Linear Algebra and Its Applications. 308 (1–3): 203–211. doi:10.1016/S0024-3795(00)00048-3.
- S.W. Drury, On a question of Bhatia and Kittaneh, Linear Algebra Appl. 437 (2012) 1955–1960.
- Mindlin, Dimitry (2011). "On the Relationship between Arithmetic and Geometric Returns". SSRN Electronic Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2083915. ISSN 1556-5068.
- cf. Iordanescu, R.; Nichita, F.F.; Pasarescu, O. Unification Theories: Means and Generalized Euler Formulas. Axioms 2020, 9, 144.
External links
- Arthur Lohwater (1982). "Introduction to Inequalities". Online e-book in PDF format.






 is the edge length of an n-dimensional cube of equal volume, which therefore is also the average length of edges incident to a vertex of the cube.
is the edge length of an n-dimensional cube of equal volume, which therefore is also the average length of edges incident to a vertex of the cube.
 , then the AM-GM inequality tells us that
, then the AM-GM inequality tells us that

 can be found. AM-GM tells us
can be found. AM-GM tells us



 .
.







 is a
is a  ,
,  , and
, and  , that is,
, that is,  Simplifying and multiplying both sides by 3 gives
Simplifying and multiplying both sides by 3 gives  so
so 


 such that
such that  . Replacing xi by
. Replacing xi by  and xj by
and xj by  will leave the arithmetic mean of the numbers unchanged, but will increase the geometric mean because
will leave the arithmetic mean of the numbers unchanged, but will increase the geometric mean because

 such replacement steps all the numbers will have been replaced with
such replacement steps all the numbers will have been replaced with  , proving the inequality.
, proving the inequality.
 . Replacing
. Replacing  by
by  and
and  by
by  leaves the geometric mean unchanged but strictly decreases the arithmetic mean since
leaves the geometric mean unchanged but strictly decreases the arithmetic mean since
 . The proof then follows along similar lines as in the earlier replacement.
. The proof then follows along similar lines as in the earlier replacement.








































 , then there is nothing to prove. So we may assume all the
, then there is nothing to prove. So we may assume all the  . Set
. Set  , and
, and  . The inequality will be proved (together with the equality case) if we can show that the minimum of
. The inequality will be proved (together with the equality case) if we can show that the minimum of  subject to the constraint
subject to the constraint  is equal to
is equal to  , and the minimum is only achieved when
, and the minimum is only achieved when  . Let us first show that the constrained minimization problem has a global minimum.
. Let us first show that the constrained minimization problem has a global minimum.
 . Since the intersection
. Since the intersection  is compact, the
is compact, the  subject to the constraints
subject to the constraints  and
and  is attained at some point inside
is attained at some point inside  . On the other hand, observe that if any of the
. On the other hand, observe that if any of the  , then
, then  , while
, while  , and
, and  . This means that the minimum inside
. This means that the minimum inside  at any point inside
at any point inside  not inside
not inside  , which is no smaller than the minimum.
, which is no smaller than the minimum.
 where the gradient of
where the gradient of  is
is  times the gradient of
times the gradient of  , for some
, for some 
 and
and

 that
that  and so
and so  Since the left-hand side does not depend on
Since the left-hand side does not depend on  , and since
, and since  , as desired.
, as desired.

 .
.

 and
and  are positive semi-definite, the matrix
are positive semi-definite, the matrix  may not be positive semi-definite and hence may not have a canonical square root. In Bhatia and Kittaneh proved that for any unitarily invariant norm
may not be positive semi-definite and hence may not have a canonical square root. In Bhatia and Kittaneh proved that for any unitarily invariant norm  and positive semi-definite matrices
and positive semi-definite matrices 

 that the following strongest possible matrix generalization of the arithmetic-geometric mean inequality holds, and it is conjectured to hold for all
that the following strongest possible matrix generalization of the arithmetic-geometric mean inequality holds, and it is conjectured to hold for all 



 = value of the asset at time
= value of the asset at time  = value of the asset at time
= value of the asset at time  .
.


 is the
is the 




