| Mullan wattle | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. maconochieana |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia maconochieana Pedley | |
| |
Acacia maconochieana, also known as Mullan wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an arid area of central Australia.
Description
The shrub or tree typically grows to a height of 2.5 to 12 metres (8 to 39 ft) and has longitudinally fissured, grey coloured bark and densely haired branchlets. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The hairy, evergreen phyllodes have a linear shape with a length of 8 to 18 cm (3.1 to 7.1 in) and a width of 2 to 5 mm (0.079 to 0.197 in) with many fine and closely parallel nerves. It blooms in October and produces yellow flowers.
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist Leslie Pedley in 1986 as a part of the work Acacia maconochieana (Mimosaceae), a new species from semi-arid Australia as described in the journal Austrobaileya. It was reclassified by Pedley as Racosperma maconochieanum in 2003 then returned to genus Acacia in 2006.
Distribution
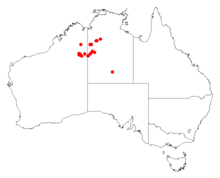
It is native to an area in the Northern Territory and the Kimberley and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia and is commonly situated along the margins of lakes that are periodically flooded growing in sandy or loamy soils. The range of the plant extends from around Gregory Salt Lake in the west through to around Nongra Lake in the Tanami Desert in the east where it is usually a part of low open forest or woodland or open scrubland communities.
Aboriginal names
The Walmajarri people of the Paruku IPA in the Kimberley call this wattle Wirimangurru. Other Aboriginal names are:Jaru: gunanduru, wirrimangurru and Ngarinyman: Gunadurr.
See also
References
- ^ "Acacia maconochieana". World Wide Wattle. Western Australian Herbarium. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- ^ "Acacia maconochieana". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions.
- "Acacia maconochieana Pedley". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- Bessie Doonday; Charmia Samuels; Evelyn (Martha) Clancy; et al. (2013). "Walmajarri plants and animals". Northern Territory Botanical Bulletin. 42: 1–242. Wikidata Q106088428.
- "NT Flora: Acacia Maconochieana". eflora.nt.gov.au. Retrieved 5 November 2021.